Skin tone is an individual characteristic of the body, determined genetically. Skin color is determined by the ratio of carotenoids, melanin, oxygenated and non-oxygenated forms of hemoglobin in the body.
The main factor determining skin color is melanin contained in melanocytes. There are two types of this substance: pheomelanin and eumelanin. The first type is responsible for a light shade (light brown pigment), the second – for a dark shade (dark brown pigment). Depending on the ratio of melanin types, individual skin color is determined. However, in some cases, pathological pigmentation occurs.
Pigmentation disorders and their causes
Changes in skin pigmentation in most individuals are temporary and reversible; such processes are benign in nature. Hypo- or hyperpigmentation of the skin in inflammatory dermatoses does not pose a threat to human health; within 2-3 months the changes self-limit. However, in some cases, pathological pigmentation can be irreversible, and doctors recommend surgical treatment.
What is vitiligo
The disease refers to a serious pathology of the skin. The main symptom is the appearance of white spots with clearly defined boundaries.
The disease needs to be controlled, because if everything is left to chance, vitiligo can affect the condition of the hair. And then they will lose their pigmentation.
Most often, vitiligo is located on the hands, face, neck, elbows, and knees. The development of the disease is accompanied by the destruction of specialized skin cells that produce the pigment melanin. Doctors cannot fully explain why this process occurs. There are several versions:
- genetic predisposition;
- incorrect functioning of the immune system.
The mechanism of the disease is that destruction occurs at the cellular level, the pigment is not preserved. As a result, white patches of skin appear.
Main types of pathology
There are 3 main types of pathological pigmentation:
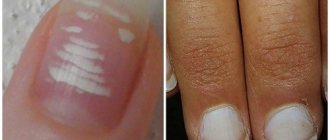
- leukoderma - manifests itself as areas of light skin with a reduced concentration of melanin or its absence (hypopigmentation),
- melasma – characterized by a high content of melanin in the affected areas of the skin (hyperpigmentation),
- Blue-gray dispigmentation is characterized by the formation of blue-gray spots.
Leucoderma
The reasons for the development of leukoderma can be different, as a result of which several types of this pathology are distinguished.
Infectious
There are different forms of infectious leukoderma:
- Leprosy leukoderma. This skin lesion occurs due to infection with Mycobacterium leprosy. The disease is characterized by damage to the skin and central nervous system. White spots on the skin have clearly defined boundaries; there may be a red rim along the contour. The affected areas of the skin are characterized by a lack of sensitivity, compaction of the subcutaneous tissue is determined under them, and the presence of folds is possible.
- Syphilitic leucoderma. Violation of skin pigmentation is observed in the presence of a syphilitic infection in the body. Most often, white spots are identified in the neck area (necklace of Venus); sometimes areas of hypopigmentation are localized on the torso or arms. Patients do not experience discomfort, but signs of the disease can be observed for years. There are several types of skin lesions in this pathology: marbled - areas of white skin are surrounded by pale pigment spots, mesh (or lace) - light spots merge with each other, forming a lace pattern, spotted - areas of hyperpigmentation are identified around white spots of a round shape (approximately the same diameter) .
- Leukoderma in lichen versicolor. The pathology develops due to infection with the fungi Pityriasis orbicularis or Malassezia furfur. Skin lesions are often observed in the scalp and upper half of the body, as well as throughout the body. Microorganisms produce substances that block the formation of melanin. Areas of hypopigmentation form in the affected skin area.
- Leukoderma with lichen alba. The causes of the pathology are unknown. White spots of a round shape are observed more often in boys 3-16 years old in the area of the shoulders, cheeks or lateral thighs. Areas of skin damage are slightly flaky and rise above the surrounding tissues, and may periodically be accompanied by a slight burning or itching. Over the course of a year, these spots disappear. Sometimes changes can persist into adulthood.
- Leucoderma with lichen planus. There are hypotheses that such skin changes occur due to exposure to toxins, viral infection or stress. Ringworm appears in adulthood. Blue-red nodules with a sharply defined border along the contour form on the surface of the skin. These elements can merge, forming plaques with a characteristic mesh pattern. Sometimes there is an indentation in the center of the nodules. The pathology is characterized not only by disorders of skin pigmentation, but also by atrophic changes and itching. The favorite place for localization of rashes is the inner surface of the wrist and elbow joints, thighs, popliteal fossae and groin area, and the oral mucosa. Pathological elements usually disappear on their own after 3-12 months, but periodically reappear over the course of many years.
Medicinal leucoderma
It is characterized by the appearance of white spots on the skin due to exposure of the body to excessive amounts of certain medications. The cause of this phenomenon may be excessive use of furatsilin or steroids.
Professional leucoderma
The cause of such damage is regular exposure to toxic substances on the surface of the skin or the body as a whole during a work shift.
Congenital leukoderma
The causes of these disorders are considered to be hereditary predisposition. The presence of areas of skin hypopigmentation is characteristic of Wulff, Ziprovsky-Margolis, and Waardenburg syndromes.
Albinism
This disorder of the pigment-melanin system is hereditary. The disease manifests itself due to a significant lack of melanocytes and a decrease in the level of pigment concentration in them. There are about 10 types of albinism, which are not amenable to drug treatment and retain their manifestations throughout the patient’s life. Lack of pigment manifests itself in the skin, eyes and hair. The main manifestations of pathology include:
- significant hypopigmentation of the skin, eyes and hair,
- myopia and nystagmus (horizontal twitching of the pupils),
- increased sensitivity of the eyes to light and skin to direct sunlight.
Tuberous sclerosis
The pathology is characterized by autosomal dominant heredity, the formation of tumor-like and plaque-like elements on the skin and in internal organs. From the moment of birth or during the first few years of life, light spots appear in the area of the trunk and buttocks, their number and size increase as the body grows.
From early childhood, the patient may develop tufts of bleached hair, eyelashes, and eyebrows. With age, fibrous tumors can form on the skin, blood vessels, cysts or nodes in the kidneys, liver, myocardial rhabdomyomas, and tumor neoplasms of the retina can be detected. It is also possible that the patient has epilepsy and mental retardation syndrome.
Immune leucoderma
These changes are caused by autoimmune reactions in the human body, as a result of which antibodies are formed that actively destroy pigment-forming cells - melanocytes.
Vitiligo
Pigmentation disorders of this nature are observed in people of different ages. Whitish or light pink spots form on the skin of the face, hands or knees. These elements do not cause unpleasant symptoms; over time they merge and increase in diameter. The hair in the affected area is also discolored.
Halo nevus
A nevus is represented by a brown or pink spot surrounded by a white border. These formations rise slightly above the level of healthy skin. The size of the nevus is about 5 mm; the depigmented border can exceed its diameter by 2-3 times. These skin elements are observed mainly in childhood and are localized on the torso or arms. Often these formations go away on their own, without requiring therapeutic measures.
Post-inflammatory leucoderma
Areas of skin depigmentation can be observed after suffering from inflammatory skin diseases (eczema, lupus, psoriasis, burns). As a result of inflammatory processes, melanocytes in the affected area produce significantly less pigment than in healthy tissues.
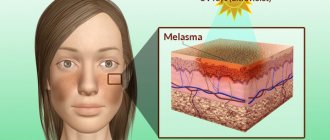
Melasma
The pathology is represented by a disorder of skin pigmentation with excessive accumulation of melanin in the epidermis. Features of manifestations depend on the cause of its development.
Melasma in diseases of internal organs
Skin pigmentation disorders can occur in case of exacerbation of chronic diseases of internal organs. Depending on the cause of melanocyte dysfunction, several types of melasma are distinguished:
- hepatic – manifests itself in severe liver damage (cirrhotic degeneration of organ tissue, liver failure),
- uremic – manifests itself against the background of the development of chronic renal failure,
- endocrine – manifests itself in cases of dysfunction of the adrenal glands, pituitary gland or other glands,
- cachectic - manifests itself against the background of severe tuberculosis.
Toxic reticular melanosis
The disease manifests itself in case of regular contact with industrial oils, petroleum, coal dust, resins, and lubricants. Regular exposure to these substances on the body causes chronic poisoning, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- areas of skin hyperpigmentation of a mesh pattern of blue or red color with clear boundaries are formed,
- redness of the skin in the areas of the face, neck and forearms accompanied by a feeling of heat and itching,
- pigmentation becomes brighter and more extensive over time, accompanied by signs of hyperkeratosis, the formation of small folds, peeling and the formation of telangiectasia.
In addition, patients often complain of decreased appetite, headache, weakness and weight loss.
Dubreuil's precancerous melanosis
This type of melanosis appears after the age of 50, more often in women. Pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- an irregularly shaped hyperpigmented spot forms in the area of the chest, face or hands,
- the affected area has an uneven color of gray, blue, brown, black,
- the spot measures from 2 to 6 cm and is characterized by a rougher surface than healthy tissue.
Becker's melanosis
The pathology is typical for men between 20 and 30 years old. It manifests itself in the formation of a hyperpigmented spot ranging in size from 10 to 50 cm. Most often it is located in the torso area, but other localizations also occur. There may be more pronounced hair growth in the affected area. Damaged skin becomes rougher.
Papillary pigmentary dystrophy (acanthosis nigricans)
The affected areas are represented by brown spots with a velvety surface. These skin changes can form during malignant processes or represent congenital, benign neoplasms. The risk of these elements increases with diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland.
Mastocytosis (urticaria pigmentosa)
It manifests itself as hyperpigmentation in the form of a large number of spots and papules of yellow or red-brown color with a diameter of 3-8 mm. These elements can merge, in some cases accompanied by itching. The pathology is benign in nature and is often detected in childhood. Several years after the first manifestation, signs of the disease may disappear forever.
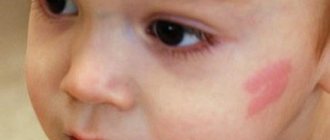
Coffee stain
Areas of pigmentation disturbance are represented by uniformly colored brown spots with clear boundaries. The spot appears on the skin even before birth or in the first years of life, gradually increasing as it grows. Does not cause any unpleasant symptoms.
Chloasma
They are areas of skin hyperpigmentation in the form of a cluster of small yellow-brown spots on the face. These changes are typical for women; they arise as a result of changes in hormonal levels due to menopause, pregnancy, or pathological disruptions of the endocrine system. In the cold season, these elements may be less pronounced.
Lentigo
Skin changes are represented by small flat hyperpigmented spots. As a rule, they occur against the background of certain hereditary diseases.
Moynahan syndrome (LEOPARD)
Seen in young people. It is characterized by the sudden formation of a large number of lentigine-like spots throughout the body.
Freckles
Typical for fair-haired people. Most often appear in adolescence. Freckles are represented by symmetrically located, small spots of yellow-brown color. The intensity of their color, as a rule, increases in the summer.
Causes and features of blue-gray dispigmentation
There are several reasons for the formation of pathology. Increase in the number of active melanocytes. This type of pigmentation disorder includes:
- Nevus of Ota - localized on the face, represented by a dark brown or blue-black spot.
- Nevus of Ita - visually resembles nevus of Ota, but is located in the shoulder and neck area.
- Mongolian spot - appears from birth as a blue-gray spot in the lumbosacral area, disappears by the age of 5.
Non-melanin dyspigmentation due to metabolic disorders. Ochronosis is a hereditary pathology characterized by the accumulation of homogentisic acid oxidase in cells. It is represented by a blue-gray or brown spot in the area of the nails, ears, sclera, nose, and back of the hands. Often accompanied by joint damage.
Exposure to heat. Heat erythema - manifested by the presence of a blue-gray spot with frequent use of heating devices (blankets, rugs, heated mattresses), accompanied by burning, peeling, and possibly erythema.
Taking certain medications. Fixed drug spots - manifested by the formation of blue-gray spots in the same places when taking a specific medication. Often this reaction occurs during treatment with tetracyclines, salicylates, phenophthalein, and barbiturates. Discontinuation of the drug ensures complete recovery.
Deposition of heavy metals. Spots arise as a result of the accumulation of arsenic, gold, bismuth, silver, and mercury in the body. It is possible that such a reaction may develop as a result of treatment with certain medications: bleomycin, chloroquine, zidovudine, clofazimine.
At-risk groups
Best materials of the month
- Why you can't go on a diet on your own
- 21 tips on how to avoid buying stale food
- How to keep vegetables and fruits fresh: simple tricks
- How to curb your sweet cravings: 7 unexpected products
- Scientists say youth can be extended
Depigmentation is very often treated with medications. After eliminating the main cause of the spots, they disappear or become less visible on the skin. The exceptions are albinism and vitiligo. The spots do not cause pain or discomfort to a person. The only disadvantage of the pathology is aesthetic unattractiveness and the appearance of complexes.
Uneven skin coloring most often appears in people before the age of twenty. People aged 30-40 years very rarely seek medical help. A person's race does not play a special role in skin diseases. According to statistical reports, dermatological diseases develop several times less often in men than in women.
Risk groups include people: with a genetic predisposition to skin diseases; have experienced a severe stressful situation; with second and third degree burns; with severe sunburn; with autoimmune diseases. With constant visits to solariums, the risk of depigmentation of the dermis increases by 2-3 times.
The pathology is not accompanied by pain or itching. The only problem with vitiligo and albinism is the psychological factor associated with the aesthetic appearance of the spots.
How to eliminate pigment spots?
Not all age spots can be treated, but it is quite possible to cope with some of them. Undoubtedly, the treatment of age spots on the face and body should be determined by competent specialists and only after the cause of these changes has been established. Properly prescribed therapy will help cope with the problem not only of the skin, but also of the entire body.
Pigmentation on the face is often an unpleasant cosmetic defect for a woman. Various methods can be used to eliminate or lighten them. Cosmetologists often recommend taking vitamin A and C for healthy skin. Hydroquinone or hydrogen peroxide can be used to lighten dark spots. In case of dysfunction of the endocrine glands, the endocrinologist may prescribe corticosteroids that suppress melanin synthesis. However, all these activities are possible only after competent consultation with specialists.
Vitiligo ICD
Classification of skin depigmentation according to this code:
- The lesions are located only on one side. This is a rare form of the disease;
- The pigment is absent on the mucous membrane of the lips, and the genitals are subject to depigmentation;
- Light areas of the skin occupy a certain place and do not grow. The appearance is typical for children;
- In the acrofacial form, vitiligo spreads to the hands, feet, ankles, and face;
- The mixed type is characterized by the presence of several types of spots;
- In the common form, white spots gradually increase in size, connect with nearby areas, and can occupy up to 80% of the skin. The hair also undergoes depigmentation.
There is a significant difference between albinism and vitiligo. After all, albinism is the complete absence of melanin, and vitiligo is its partial destruction.
Cosmetological methods for eliminating age spots
Pigmented spots on the body are not always associated with disorders of the function of internal organs. Skin pigmentation often occurs due to improper skin care, use of low-quality cosmetics, squeezing out pimples and blackheads, and exposure to external factors. In such cases, you can use the services of beauty salons. Let's consider popular cosmetological methods for eliminating pigmentation.
- Chemical peeling. There are deep and superficial chemical peels. This method is characterized by the use of fruit or glycolic acid in the skin cleansing procedure. These substances damage the upper layer of the epidermis, as a result of which the regenerative mechanisms of the skin are launched. After the procedure, the skin restores its natural color.
- Laser therapy. This method of getting rid of darkening of the skin is quite effective and painless. To obtain a lasting result, 2-3 procedures may be required. The laser beam destroys melanin without damaging the skin.
- Mesotherapy. Local injection of glauric acid into the area of dark spots to lighten them.
- Dermabrasion. It is a procedure for mechanical removal of the damaged layer of skin. As a result of this, the darkening is erased with a special device. However, this cosmetic procedure is painful, so it is carried out under anesthesia.
Prevention
Preventive measures help slow the spread of the disease or prevent its occurrence altogether. These include the following recommendations:
- Chronic diseases need to be treated promptly;
- Excessive sunbathing (ultraviolet radiation) should be avoided;
- you must try to avoid injuries and burns;
- You should undergo regular medical examinations and register for pregnancy on time.
Young couples planning a child should visit a geneticist and get tested for a hereditary predisposition to depigmentation.
Depigmented spots on the surface of the skin are a manifestation of various genetic faults or a consequence of exposure to external physical factors. They negatively affect the quality of life, the emotional component, and are difficult to treat. But they do not pose a direct threat to health, and have a good prognosis. If you treat your condition adequately, you can live with the disease for many years.
Vitiligo is a disorder of pigment production. It is expressed in the fact that certain areas of the skin become lighter than others due to the fact that they lack melanin.
The nature of the disease is still being studied by doctors. Skin depigmentation most often affects exposed areas of the body that are exposed to sunlight. Over time, white spots can change their shape and become larger.
Nutritional features for beautiful skin
Spots on the face often indicate insufficient intake of vitamins C, PP, A, E. To compensate for the deficiency of these substances, dietary correction is recommended. Vitamin A is found in large quantities in liver, carrots, parsley, apricots, and fatty fish. Cabbage, oranges, peppers, apples, rowan berries, onions, and kiwi are rich in vitamin C. Its maximum concentration is in rose hips, especially dried ones. Vitamin E is found in large quantities in oils (cottonseed, soybean, flaxseed, wheat germ), and cereals. Eggs, cheese, liver, and milk are rich in vitamin PP. It is not recommended to get carried away with the consumption of salty and sweet foods.
Treatment of vitiligo
In order to correctly develop treatment tactics for a disease, you must find its cause. Some patients are helped by a set of proposed measures, and the hypopigmentation goes away.
But albinism and vitiligo are not diseases that can be treated with medications. This is more like a genetic malfunction in the body, which doctors cannot influence in any way.
But, of course, there is a treatment method. Experts give injections with the following means:
- steroid hormones;
- extracts from the placenta;
- vitamin A analogues (retinoids).
It may be advisable to treat spots with depigmentation with an iodine solution, which is applied in the form of a mesh. And then these areas of the skin are irradiated with ultraviolet light. In some cases, a laser is used.
In any case, no matter how the disease manifests itself, you need to monitor your diet, intake of macro and microelements, take iron-containing products, and also monitor the condition of your skin with the help of a cosmetologist.