Genital herpes belongs to the group of sexually transmitted diseases, but is considered relatively safe because it does not cause disruption to the internal organs and systems of the human body and does not lead to death. Herpes infection, caused by simple herpesviruses types 1 and 2, is transmitted when the partner has an active disease on the lips or genitals.
Genital herpes belongs to the group of sexually transmitted diseases, but is considered relatively safe because it does not cause disruption to the internal organs and systems of the human body and does not lead to death.
What STDs are transmitted orally?
CMV is easily transmitted through any type of sexual contact.
Regardless of the mode of transmission, the virus causes the same symptoms, which are similar to mononucleosis.
When CMV is transmitted orally, specific signs of inflammation of the mouth or pharynx are usually not detected.
Less common, but possible, is transmission through oral sex of sexually transmitted diseases such as:
- Mycoplasma and ureaplasma infections.
- Thrush caused by yeast.
- Gardnerellosis (bacterial vaginosis).
- HIV infection and viral hepatitis.
They can be transmitted orally in cases where there are microtraumas, cracks, wounds in the mouth, i.e. when the virus can enter the blood of a healthy partner.
If one of the sexual partners is infected, then oral sex with him without using a condom will most likely lead to infection of the second partner.
The risk of infection increases significantly if there are wounds, cracks, or microtraumas in the oral mucosa, through which pathogenic microbes penetrate into the tissues even faster.
In addition, the risk of developing the disease in a healthy partner increases significantly if his immunity is weakened.
In this case, the mucous membranes do not perform their barrier function well and “let” STI pathogens into the body almost unhindered.
With high resistance, the body can suppress the development of pathogenic microflora even at the stage of its contact with the mucous membranes.
Despite the fact that the vast majority of sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted orally, this route of infection is still less likely than through sexual intercourse.
There are different types of oral sex, so it is important to understand what type of sex can lead to oral STDs.
The risk of infection with the above options is equally high.
However, the presence of microdamages in the mucous membrane, small wounds or ulcers in the oral cavity is of key importance. The highest risk of infection is for a healthy partner whose oral cavity receives biological fluids.
As for ordinary lip-to-lip kisses, in this case it is almost impossible to get infected. Since saliva contains a small number of microorganisms.
The risks of contracting sexually transmitted diseases and other infections exist only if the healthy and infected partners have wound surfaces. Either in the mouth or on the lips. In other words, only when infected blood penetrates the damaged mucous membrane of the mouth does infection occur.
There are negative factors that increase the percentage of infection:
- present chronic or cold diseases
- decrease in the body's protective properties
- frequent change of sexual partners
- lack of barrier contraception
- violation of the integrity of the skin of the lips and oral mucosa
Among the STDs transmitted through oral sex are:
- HIV infection
- HPV leading to the development of condylomas
- Gonococcal infection (gonorrhoea)
- Herpetic infection
- Fungal disease candidiasis
- Chlamydia
- Hepatitis B virus
- Syphilis
HIV infection is one of the most dangerous viral diseases, for which there is currently no treatment. The body's vital functions are maintained through antiretroviral therapy, which is carried out for life.
Can HIV be transmitted orally, what is the probability of infection?
Infection with the human immunodeficiency virus during oral sex practically does not occur. However, under certain conditions (for example, if there are bites that damage the integrity of the oral mucosa), HIV infection is quite possible.
HIV infection affects the entire body. Therefore, in any biological fluids of the patient there is a certain concentration of the pathogen. So, the percentage of virus in saliva is the lowest, so infection does not occur with simple kisses.
If oral sex occurs with an infected partner, the probability of the virus entering a healthy body is no more than 5-10%, but they are still present. Therefore, it is impossible to say with certainty that oral sexual intercourse does not allow the transmission of infection.
Prevention of oral STDs primarily includes avoiding sexual contact with unfamiliar partners whose sexual health is not certain.
Other equally important preventive measures include:
- Use of barrier methods of contraception
- Having a regular sexual partner
- Preventive visits to a urologist for men and a gynecologist for women
- Timely seeking qualified medical help, especially with the development of pathological symptoms in the oral cavity
- Vaccination against HPV and viral hepatitis B
Emergency preventative measures include rinsing the mouth with miramistin (an antiseptic) during the first two hours after oral sex.
You should also consult a doctor who will prescribe medication prophylaxis - antibacterial or antiviral drugs. After casual oral sex, you need to take swabs from the oral mucosa. As well as blood to determine sexually transmitted diseases and some other infections.
If infectious processes are localized in the oral cavity during the period of therapy, it is not recommended to continue to practice sexual-oral relations.
The reason for this is the high probability of infection spreading to the genitourinary tract.
Is it possible to have sex while treating oral STDs?
In this case, classical sexual intercourse is quite safe.
But if a patient has a virus as the causative agent of the infection, there is a high probability of infecting a sexual partner through a kiss. In this case, we mean HPV and herpes infection.
Sexually transmitted diseases are dangerous to human health and life, since in the absence of timely treatment they lead to serious complications in all organs and systems. Many STIs affect not only the genitals, but also the organs of vision, respiratory and vascular systems, and the central nervous system.
The source of pathogenic microorganisms is the infected genitals of the sexual partner. Upon penetration, sexually transmitted infections can directly affect the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, tonsils, and pharynx.
If there are wounds in the mouth, the risk of contracting an STD increases, since the partner becomes more susceptible to the effects of infectious agents that penetrate the blood and are carried throughout the body through the bloodstream, and the risk of sepsis increases.
What sexually transmitted diseases are transmitted through oral sex? Here are some of them:
- Syphilis is a disease caused by Treponema pallidum, which lives in male ejaculate and vaginal secretions in women. When penetrated into the oral cavity, it leads to the formation of chancre, which is a painful ulcer on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, tongue, tonsils, lips and face. It is possible to develop pharyngitis, sore throat, laryngitis, and enlarged cervical lymph nodes. Syphilis can also be asymptomatic for a long time. When the genitals are affected, it leads to the formation of ulcers and purulent discharge from the genitals.
- Gonorrhea is a disease caused by gonococci, which are transmitted through oral, vaginal sex, and also hematogenously. When the genitals are affected, it is accompanied by the separation of pus from the urethra or vagina. Penetrating into the oral cavity, gonococci cause pharyngitis, which occurs with pain in the oropharynx.
- Chlamydia is an STD caused by parasitic microorganisms that are transmitted through oral and vaginal sexual contact. They cause inflammatory pathologies of the genitourinary system, which are accompanied by copious discharge and pain in the lower abdomen. Upon penetration into the oral cavity, they lead to inflammatory pathologies of the oropharynx. Chlamydia is also dangerous for the eyes.
- Herpes is a viral disease transmitted during traditional and non-traditional sexual contact, as well as through the mouth when kissing. It is characterized by the appearance of blisters on the mucous membranes of the genitals, mouth, and lips, which, when overflowing, form ulcers. Accompanied by burning and itching of the affected areas. During the acute period, herpes is dangerous for a sexual partner.
- Mycoplasmosis and ureaplasmosis are transmitted orally and lead to pharyngitis, laryngitis and other inflammatory pathologies of the respiratory system, which are accompanied by hyperthermia, sore throat, and hoarseness. Affecting the organs of the genitourinary system, mycoplasmas and ureaplasmas lead to yellow discharge from the urethra or vagina, which is accompanied by pain, itching and burning of the genitals.
- Hepatitis A, B, C are also transmitted orally. The infection is found in saliva, vaginal secretions, and ejaculate. At the initial stage, symptoms characteristic of colds appear; as the viral infection multiplies, pain in the right hypochondrium, nausea, joint and muscle pain occur. A characteristic feature of hepatitis is yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin.
- HIV and AIDS are sexually transmitted diseases, which can also be transmitted through oral sex. The infection is found in all body fluids: blood, ejaculate, salivary and vaginal secretions. Infection occurs when one fluid comes into contact with another. This is possible if the sexual partner has wounds in the mucous membranes of the oropharynx and gums.
- Candidiasis is a disease caused by yeast fungi transmitted through traditional and non-traditional sexual contact. Most often it is the result of a violation of the natural microflora of the genital organs due to decreased immunity or long-term treatment with antibiotics. It is accompanied by a cheesy discharge from the genitals; a white coating with an unpleasant odor forms on the mucous membranes of the mouth, which itches and hurts.
- HPV – human papillomavirus is accompanied by the formation of warts and condylomas on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, lips, genitals, anus, and epidermis. If left untreated, HPV becomes the cause of cancer.
HPV types 16 and 18: transmission routes
It is worth mentioning these two types separately as the most dangerous. The appearance of genital warts on a woman’s genitals should be a signal to consult a doctor.
These are the symptoms that are characteristic of a precancerous condition caused by human papilloma viruses types 16 and 18.
When they get on the mucous membranes or skin, they provoke a malignant cellular mutation, which increases the likelihood of cervical cancer by 50 times.
Women and men can become infected with papillomaviruses of any type in one of the following ways:
- Sexually: during genital, anal, oral sex.
- In everyday life: through touch.
- Self-infection is possible when shaving or epilating.
Highly oncogenic viruses are found not only in women - types 16 and 18 of papillomavirus can provoke the development of bladder and (or) penile cancer in men.
When diagnosing the papilloma virus in a person, it can be said with 85-90% probability that the disease was transmitted through household contact to all members of his family. How does infection occur at home?
- in the presence of damage to the skin, pathology occurs when sharing towels, bed linen, cosmetics, soap, and washcloths;
- You can become infected through saliva by sharing the same dishes or toothbrush with a carrier of the disease;
- Wearing clothes of someone who is sick increases the risk of transmitting the virus. If you wear the underwear of an infected person, the possibility of infection increases dramatically;
- self-infection often occurs when shaving or epilating the bikini area. Having accidentally damaged a genital wart or a wart, a person provokes the development of several epithelial neoplasms in the adjacent area.
How you can become infected with the virus in public places:
- When visiting a bathhouse, sauna, or swimming pool, it is quite difficult to become infected with the virus, because need physical contact. But this option cannot be ruled out;
- Frequent handshakes provoke the transmission of viruses in cases where there are microcracks in the upper layer of the epithelium.
What other routes of transmission of the virus exist:
- The medical literature describes cases of infection with the human papillomavirus through donor blood transfusion.
- When performing an operation to remove genital warts, doctors and junior medical staff may inhale viral particles, which begin to actively multiply on the nasal mucosa.
- Poor sterilization of manicure instruments in beauty salons can cause infection among clients.
In order to prevent the papilloma virus from entering the body, it is necessary to take precautions when visiting public places, remain faithful to one partner and lead a healthy lifestyle.
Clinical picture of oral STDs
Symptoms of oral STDs depend on the specific disease and the patient's immune system. Quite often, infections have a latent course, which does not mean the absence of infection. Especially if before this there was oral sex with an unfamiliar partner without using a condom.
The incubation period for oral STDs also differs, making diagnosis much more difficult. Therefore, even if there are no signs of infection, you must consult a doctor and undergo the necessary tests.
Timely diagnosis will allow you to prescribe effective treatment and get rid of the pathology without harm to the body.
After infection, the clinic begins to develop after 5-8 days; the first symptoms are often confused with purulent tonsillitis. Grip develops rapidly, accompanied by pronounced symptoms.
The main signs of oral gonorrhea are:
- unpleasant sensations occur in the oral cavity - severe itching, burning
- there is a sore feeling in the throat
- discomfort and pain in the mouth interfere with normal conversational speech, a person is unable to eat properly and drink fluids, since any irritating factors cause pain
- hoarseness occurs
- redness of the mucous membrane
- a day after the first symptoms, a purulent whitish coating with a foul odor appears in the mouth
- Initially, plaque appears on the tonsils; after some time, purulent contents form in the lacunae
- then the purulent plaque spreads to the palate, tongue, cheeks, palatine arches
- the acute process is accompanied by an increase in body temperature (37.3 - 39 degrees), headache, weakness develops, and an increase in the size of regional lymph nodes occurs
Syphilis is an extremely serious disease, the lack of treatment of which leads to deformities of various parts of the body. The incubation period lasts from 3 to 4 weeks.
The primary symptom of oral syphilis is the formation of a painless, round ulcer (chancre) on the oral mucosa. As a rule, a single syphiloma develops; in rare cases, multiple ulcers form. Since primary syphiloma does not bring pain or other discomfort to the patient, it remains without any attention for a long time.
After two months, the chancre disappears, and healthy tissue forms in its place. One week after the appearance of chancre, there is an increase in the size of nearby lymph nodes, the palpation of which does not cause pain.
The period of primary syphilis is accompanied by a fever, deterioration in general health, headaches, and myalgia. If the symptoms were ignored and there was no treatment, the disease progresses to the next stage.
This is secondary syphilis, the symptoms of which are as follows:
- A papular or roseolous rash forms in all parts of the body, regardless of the primary localization of the infection
- after a couple of months, the rashes disappear regardless of therapy, after which the latent period of the disease begins to develop, which lasts from 2-3 weeks to 2 months
- then secondary syphilomas are formed, present up to 2-3 months
- secondary syphilis is also characterized by the formation of condylomas on the affected mucous membranes, the occurrence of alopecia and a disorder of pigmentation of the skin
- very often, when the infection spreads, damage to hepatocytes, membranes of the brain and spinal cord, kidneys, bone tissue and joints is possible
- in severe cases, damage to the central nervous system occurs (disorders of consciousness, neurological syndromes, epileptic seizures)
The most severe stage is considered tertiary syphilis. This is a condition when the infectious process spreads through the bloodstream, affecting all organs and systems.
Thrush is a fungal disease that is just as easily transmitted through oral sex as during classic sex.
Oral candidiasis manifests itself as follows:
- A white coating appears on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity (on the tongue, palate, tonsils, gums, cheeks) - initially the plaque covers the mucous membrane in patches, often in the form of dots
- after a few days, the plaque spreads to the entire oral cavity
- fungal infection leads to the formation of ulcerative areas that cause discomfort and pain
- painful sensations develop when consuming food and liquids, in particular when swallowing
- I feel increased dryness in the oral cavity, and there are pockets in the corners of the lips
The duration of the asymptomatic period from the moment of infection varies from 2 days to 2-3 weeks.
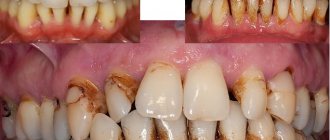
Symptoms of oral genital herpes are:
- swelling
- redness
- sensation of pain and burning, especially when eating food that irritates the mucous membrane (sour, salty)
- deterioration in general health
- sometimes increased body temperature
- headache
- unpleasant, painful sensations in the muscles
After the appearance of primary symptoms, characteristic small, blistering rashes form in the oral cavity, containing transparent exudate. When they are damaged, ulcers and erosions develop in the mouth, causing discomfort and pain to the patient.
In the oral cavity, the development of condylomas after sex is observed in extremely rare cases.
But ignoring this symptom can cause cancer in the throat. Oral condylomas are convex, pointed or smooth growths that can increase in size up to 2-3 centimeters.
The pathology is accompanied by burning and itching.
More often, the disease occurs against the background of serious chronic diseases, with a significant decrease in the immune system.
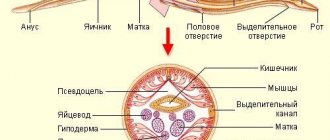
Genital herpes virus
The disease is manifested by the appearance of rashes in the form of bubbles with clear liquid on the mucous membranes and skin.
The blisters tend to burst, forming ulcers.
Rashes in the mouth and lips with herpes type 2 are very painful.
Genital herpes is highly contagious and is often transmitted through the oral route.
A characteristic feature of the disease is its cyclical course.
Periods of remission are followed by exacerbations at a time when immunity is reduced.
Sometimes you can observe the absence of clear symptoms.
At the same time, the virus continues to remain on the mucous membranes and can lead to infection through kissing and oral sex.
The main targets for genital herpes are people with low levels of immunity.
Is it possible to become infected with HIV through oral sex?
To prevent sexually transmitted diseases orally you need to:
- avoid promiscuous sexual relations, especially with strangers;
- use condoms, which reduce the risk of infection by more than 90%;
- exclude any sexual intercourse and kissing during the acute course of an STD.
As an emergency preventive measure, within 2 hours after unconventional contact, you should rinse your mouth and throat with a solution of Chlorhexidine or Miramistin and be sure to spit. Emergency prevention should be supplemented with antibacterial drugs with complex effects: Oletetrin, Safocid, which are active against the most common and dangerous sexually transmitted pathologies.
Sexual tract
For transmission of a dangerous virus to occur, one sexual contact is often enough: vaginal, oral, anal.
With a 70-80% probability, the source of infection is a man, but a woman can also become a spreader of the disease, especially if genital warts have formed on her genitals, oral mucosa or lips.
If this epithelial formation is damaged during sexual contact or through a kiss, the probability of transmitting the virus is 90%.
For those who practice unprotected anal sex, benign or malignant formations form in the anal area. This route of spread of papillomavirus is very common: damaged mucous membranes and minor skin injuries serve as easy routes for infection. Moreover, if one of the partners has formed anogenital warts, then even a condom does not guarantee protection.
Predisposing factors for the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the body are:
- Starting sexual relations too early.
- Frequent change of sexual partners, promiscuity.
- The presence of obvious signs of the disease in the partner: condylomas and warts.
The virus can be transmitted through oral sex through various deformations of the skin of women and men. Moreover, the risk of infection with oncogenic types 16 and 18 is most likely in this way. After the proliferation of microorganisms in the mucous membranes of the mouth, it can cause throat cancer in women and men.
To reduce the risk of infection, it is recommended to use a regular condom in case of blowjob and a femdom (female condom) in case of cunnilingus.
Unlike most sexually transmitted infections, using a condom does not always protect against infection with papillomavirus. For the simple reason that the virus can be transmitted through contact with a partner’s skin if there are microtraumas on it.
The danger lies in the area of localization of condylomas and warts - they often form throughout the groin, where the condom is not used. This is not to mention foreplay.
Despite too little protection against this disease, men cannot refuse to use a condom: anal, genital or oral sex with a condom reduces the risk of spreading papilloma pathogens by 70-80%.
And, of course, the virus is extremely small, but it cannot penetrate through a condom, this is a myth.
If partners do not have external signs of pathology, the likelihood of infection orally or vaginally is low. Even if one of them is a latent carrier of the disease.
What to do if symptoms appear?
When the first signs of an STI appear after oral sex, you should seek advice from:
- ENT, if complications arise from the respiratory system and hearing;
- dentist if the clinical picture affects the gums, teeth and oral cavity.
These specialists refer the patient to examine a smear from the throat to identify the causative agent of the symptoms. The study of biological material is carried out by ELISA, PCR, and bacteriological examination. To obtain more detailed information about which STDs caused the development of such a clinical picture, a biochemical study, ELISA and blood PCR are prescribed.
Danger and consequences of STDs
You can become infected with sexually transmitted diseases orally; they lead to the development of respiratory diseases: acute respiratory diseases, sore throat, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever. Oral thrush often develops.
On the part of the urinary system, venereal pathologies lead to urethritis, pyelonephritis, and inflammation of the ureters. Affecting the organs of the reproductive system, they cause inflammation of the vagina, uterus, ovaries in women, and inflammation of the spermatic cords, testicles, and prostate in men. Some STIs can also cause infertility.
With unconventional sexual contact, the risk of damage to the digestive tract increases, which leads to the development of diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting. A similar clinical picture also develops against the background of dysbiosis during long-term treatment with antibacterial drugs.
Orally and sexually transmitted STDs such as syphilis and gonorrhea can damage the spinal cord and brain, resulting in a risk of disability and death.
HPV is one of the causes of cancer. Through oral contact, human papillomavirus leads to throat cancer.
Does female prostatitis exist?
Doctors have repeatedly said that prostatitis is a purely male disease. This is because it affects the prostate gland. But it does not exist in the female body. However, instead of a prostate, they have a Skene gland. It can be found on the back wall of the urethra. The secretion secreted by this part of the body is very similar in composition to the fluid produced by the prostate.
Experts who have studied the structure of the female genitourinary system confidently claim that the secretion of the Skene gland is not important. And it itself, if unnecessary, can completely disappear in the course of evolution. But as long as the iron is present in the body, it is at risk of contracting infectious diseases. Most often, doctors in such cases diagnose patients with Skinitis, which is an analogue of prostatitis.
Based on all of the above, we can say that female prostatitis exists. It just has a slightly different shape than men's.
Danger and consequences of STDs
Venereal disease is treated according to the cause of its development:
- for gonorrhea, Cefixime and Ofloxacin are prescribed;
- chlamydia can be treated by taking Azithromycin and Doxycycline;
- for herpes, antiviral drugs (Famciclovir, Acyclovir) are prescribed for oral and local use;
- for candidiasis of the oral cavity and genitals, it is recommended to take Fluconazole, Diflucan, Pimafucin, both for oral administration and for local treatment of the affected areas;
- ureaplasma and mycoplasma are destroyed by a course of Azithromycin or Doxycycline;
- hepatitis virus, human papillomas and immunodeficiency require specific antiviral therapy.
In case of HPV, condylomas and papillomas are subject to surgical removal by electrocoagulation, exposure to a laser beam or nitrogen.
Oral therapy for STDs is supplemented by taking immunomodulators, vitamin-mineral complexes, and probiotics.
After treatment, additional diagnostics are prescribed to assess the effectiveness of the selected drugs and the need to replace them.
Testing for STDs during oral sex is performed no earlier than 2-3 weeks after the suspected infection. Mouth swab tests for STDs are performed using a microscopic examination.
Private laboratories use the polymerase chain reaction technique.
PCR is by far the most informative test that allows identifying a pathogenic microorganism during the incubation period. If the taken smear contains minimal traces of an infectious pathogen, it is replicated (copied) using PCR. After diagnosis, the patient is given a form in which a positive or negative result will be noted.
Blood tests for oral STDs are also performed to diagnose infection. The biomaterial is examined by PCR or ELISA - identifying antibodies that are produced by the body in response to the causative agent of the disease.
Control tests for oral STDs are carried out in several stages. After completing antibacterial, antifungal or antiviral therapy, a swab from the mouth or venous blood is examined two weeks later.
For this purpose, the polymerase chain reaction method and microscopic examination are used. If the test results are negative, smears are taken again after another two weeks.
In the absence of a pathogen, a person is considered completely healthy.
Scheme of treatment measures for oral STDs
Treatment of infectious processes depends entirely on the disease itself.
Antibiotics for oral STDs are used only in cases where the causative agent of the disease is bacteria. If the pathology is of viral origin, antibacterial drugs are useless. Since viruses are not sensitive to this group of drugs.
Among the antibiotics used are:
- azithromycin (from 250 mg once a day for 3 days or 500 g once)
- erythromycin (daily dosage 1 g)
- ofloxacin (200 mg once or 200-400 mg per day)
- nystatin (500,000 units up to 8 times a day)
Antiviral medications for oral STDs are used for viral etiologies of the disease.
The doctor selects medications depending on the severity of symptomatic signs and the characteristics of the patient’s body.
Treatment of oral STDs in HIV infection involves the use of immunomodulatory agents that increase the body's protective properties.
Timely treatment can prevent the development of serious complications. Such as penetration of the pathogen into the bloodstream and damage to internal organs and meninges.