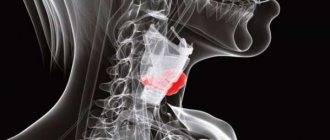
Parathyroid adenoma is a tumor that negatively affects directly all these hormonal processes. Elderly people over forty-five years of age are at increased risk; thyroid tumors are more often diagnosed in women than in men, which may be due to hormonal disorders during pregnancy, lactation, and menopause.
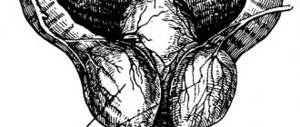
Paired formations of glandular tissue, which are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland, are called parathyroid glands. Typically, most people have a couple of these glands in their bodies, but sometimes people may have five or more parathyroid glands. Their purpose is to produce parathyroid hormone, which is necessary for the proper functioning of metabolic processes between calcium and phosphorus.
Causes of development of parathyroid adenoma
The etiopathogenesis of a disease such as parathyroid adenoma is based on mutations of genes that are responsible for encoding protein structures that transport calcium to the parathyroid glands. Those cells that contain the mutated gene tend to divide uncontrollably, and, consequently, increase the size of the organ. An excessively large number of dividing cells produces large amounts of thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Sometimes you can notice uncontrolled division of cellular structures, provoked by a lack of calcium. In this case, cell division is compensatory in nature, the purpose of which is to replenish the element in the body.
Provoking factors for the development of the disease
Parathyroid adenoma can develop under the intense influence of provoking factors on the body that are not the immediate causes. Factors contributing to the development of benign tumor formations on the parathyroid glands include:
- traumatic neck injury. In this case, the parathyroid gland may not be involved in the pathological process, but damage to nearby tissues occurs;
- complicated heredity - when the parents have a history of parathyroid adenoma;
- nutritional calcium deficiency – when the body does not get enough of this element from food;
- radioactive irradiation of the neck area in the treatment of cancer localized in the head or neck. Radiation therapy may affect regional cervical, sub- and supraclavicular, and axillary lymph nodes.
Life forecast
Timely surgery for parathyroid adenoma guarantees a positive prognosis for the patient’s life.
Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, which is quite short, the attending physician monitors the work of the heart muscle and the level of calcium in the patient’s body.
As a rule, normalization of this indicator in the blood plasma occurs by the end of the second day after surgery. Failure to seek medical help in a timely manner is fraught with malignancy of the adenoma and a worsening life prognosis.
The risk of postoperative relapse occurs in one case out of twenty.
Video about parathyroid adenoma:
Category: Endocrine system
Parathyroid adenoma - main symptoms:
- Weakness
- Nausea
- Cardiopalmus
- Loss of appetite
- Convulsions
- Vomit
- Diarrhea
- Sweating
- Drowsiness
- Constipation
- Nervousness
- Fatigue
- Osteoporosis
- Anxiety
- Urinary disorders
- Loose teeth
- Tooth loss
- Frequent fractures
- Appearance of goiter
A parathyroid adenoma is a small benign formation ranging in size from 1 to 5 cm, which can independently synthesize parathyroid hormone, causing symptoms of hypercalcemia in a person. The parathyroid glands are located on the posterior surface of the thyroid gland, and their main purpose is to produce parathyroid hormone, which takes part in calcium-phosphorus metabolism in the body. An adenoma leads to the production of more parathyroid hormone than necessary, which causes the symptoms of this disease.
More often, the pathology occurs in the fairer sex, and at the age of 20–40 years, and such a tumor is benign, but in 2% of cases it tends to become malignant, so the treatment of such a disease is usually surgical. Diagnosing a pathology such as parathyroid adenoma is a difficult task, because the symptoms that the disease causes are similar to the symptoms of other diseases in the body, which is why the doctor cannot always make a diagnosis in a timely manner. With timely treatment, the prognosis of the disease is favorable, but if the tumor has degenerated into cancer, the prognosis worsens significantly (as with any other cancer pathology).
Clinical symptoms of parathyroid adenoma
A tumor such as a parathyroid adenoma does not have specific symptoms. It is extremely difficult to suspect pathology in the early stages of its formation and development. Most often, this may be an incidental finding during a routine examination. The affected parathyroid glands produce large amounts of calcium; hypercalcemia is observed in the blood, which causes the development of the following symptoms:
- general nonspecific: hyperhidrosis (increased sweating);
- unreasonable weakness;
- drowsiness and excessive fatigue in the absence of strong physical and mental stress;
- decreased appetite;
- change in stool (prevalence of constipation);
- attacks of dizziness, nausea and vomiting, decreased memory and attention, anxiety;
- decreased muscle tone, myalgia and arthralgia (muscle and joint pain), diffuse bone pain, a state of convulsive readiness and seizures;
- psycho-emotional disorders;
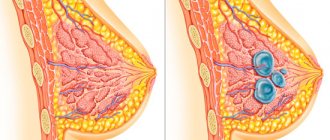
- an increase in the size of the thyroid gland (photo above, does not appear in the early stages of the disease);
- dry skin;
Symptoms of the disease in women during menopause can be varied, but most often the fragility of bones and the occurrence of fractures even with minimal mechanical impact come to the fore.
Symptoms
In the early stages of development of the pathological process, there are no obvious signs. Disturbances in the condition and functioning of the gland with a small benign formation can only be detected during a laboratory blood test.
As the tumor develops and increases in size, the first symptoms of the disease begin to appear, which (due to their nonspecific and vague nature) remain unattended for a long time. General signs of a benign formation of the parathyroid gland:
- constant fatigue, despite proper sleep and rest;
- drowsiness;
- weakness;
- cardiopalmus;
- mood swings;
- increased sweating, regardless of the presence or absence of physical activity or ambient temperature;
- sudden outbursts of aggression and causeless irritability;
- nausea, rarely – vomiting;
- lack of appetite;
- frequent attacks of sore throat in the absence of sore throat and other diseases of the upper respiratory system.
The symptomatic picture of disturbances in the condition and functioning of the kidneys is a sign of adenoma when it enlarges.
As the adenoma develops and increases in size, changes occur in the functioning of the parathyroid gland, which is responsible for regulating calcium levels necessary for the normal interaction of the central nervous system and the musculoskeletal system. Signs of an adenoma when it enlarges are:
- symptomatic picture of disorders of the condition and functioning of the kidneys;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, constant constipation;
- pain and aches in joints and bones that occur suddenly;
- change in voice, in which hoarseness appears.
In the later stages of development of the pathological process, when the tumor is greatly enlarged, the neck changes in volume, and swelling appears on the side of the tumor.
Classification of adenoma
Conventionally, parathyroid adenoma is divided into several types. Among them:
- bone – it is characterized by the development of osteoporosis in bone tissue, increased fragility of tubular bones, loosening and loss of teeth;
- gastrointestinal – chronic diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, ulcers) are exacerbated, characterized by the development of pancreatitis, cholecystitis with severe pain;
- kidney disease - the most common manifestation of this form is urolithiasis. At more advanced stages, the renal form of adenoma provokes the development of nephrocalcinosis - this condition is caused by the deposition of calcium salts in the kidney tissues;
- cardiovascular - increasing heart failure, increased thrombus formation, arterial hypertension (a characteristic feature is a significant increase in systolic blood pressure). Echocardiography can show the deposition of calcifications on the surface of the heart valves.
Adenomas can be classified depending on which cells they originate from. Thus, it is customary to distinguish:
- watery cell adenoma - grows from light stem cells of the gland;
- adenoma originating from the main dark cells;
- lipoadenoma;
- an adenoma that grows from acidophilic cells of an organ.
Etiology of the disease
The main reasons for the development of this disease are:
- Genetic mutation.
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Neck injuries and radiation.
- Radiation exposure.
- Insufficient intake of vitamin D and calcium from food.
Most often, adenoma is caused by changes in genes during mitotic division or during the production of parathyroid hormone. The mutation affects transport proteins that deliver calcium to the tissues of the parathyroid glands. As a result, cells (parathyroid cells) begin to rapidly divide, a tumor-like formation is formed, which gradually increases in size.
According to medical statistics, this pathology mainly occurs in young women.
Diagnostics
In order to make a correct diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo not only certain laboratory and instrumental research methods, but also consult some specialized specialists. Thus, treatment for an adenoma can be prescribed only after the patient has been examined by an oncologist-endocrinologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist, neurologist, cardiologist, nephrologist.
The diagnostic search for the disease is based on the following examination methods:
- laboratory: determination of the level of parathyroid hormone in the blood;
- urine analysis, which determines the daily quantitative excretion of calcium from the body by the kidneys;
- biochemical blood test with mandatory assessment of phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase and calcium levels. The normal calcium level is 2.15-2.55 mmol/l (or 8.6-10.2 mg/dl) . In this case it will be increased. And the level of phosphates should normally be within the range of 0.65-1.3 mmol/l (or 2.01-4.02 mg/dl) , and decreases with adenoma. Normal alkaline phosphatase levels range from 0.9-2.29 µkat/l in men and 0.74-2.1 µkat/l in women ;
- a blood test for the quantitative content of vitamin D - with a disease such as follicular adenoma, its level drops significantly;
- determination of the marker that the parathyroid gland produces in a state of hyperplasia;
- ultrasound examination of the parathyroid and thyroid glands - determines the size, structure, presence of capsules and cavities;
Diagnostic methods
When diagnosing a parathyroid adenoma, in addition to examining the patient, studying the clinical picture and the results obtained during anamnesis, patients are prescribed the following types of research procedures:
- ultrasonic;
- radiographic;
- scintigraphy;
- taking a biopsy of the cervical lymph nodes;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- blood test to detect calcium levels;
- laboratory urine analysis.
Important! Doctors include computer or magnetic resonance imaging as the most accurate and informative methods for diagnosing parathyroid adenoma.
After such a comprehensive diagnosis, a specialist can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the stage of the pathological process and develop optimal treatment tactics for the patient.
Treatment of parathyroid adenoma
Removal of a parathyroid adenoma or the entire gland is the only method of complete treatment. Only the attending physician, who is familiar with the results of the patient’s examination, can thoroughly explain to the patient what kind of disease this is and what treatment tactics he needs.
Conservative drug therapy
Conservative drug treatment is mandatory before surgical intervention on the gland. This is due to the need to reduce the level of calcium in the patient’s blood. The classic scheme of pharmacotherapy for adenoma includes taking drugs such as:
- diphosphonate solution or saline solution - intravenously;
- diuretics - prescribed to force diuresis to accelerate the excretion of calcium in the urine;
- cardiac glycosides – with the development of hypercalcemic crisis;
- solutions of glucose and sodium bicarbonate.
Surgery
Surgery on the thyroid gland for adenoma is performed under general anesthesia. Its duration and volume are determined by the size of the tumor formation. Depending on the size of the capsule and its spread deep into the tissues of the organ, the surgeon decides whether to remove the parathyroid adenoma without affecting the surrounding tissues or to remove the entire organ completely. In some particularly advanced cases, removal of the thyroid gland is indicated.
Removal of the entire parathyroid gland or the local area where the formation is located can be performed using different surgical approaches:
- endoscopic – the most gentle. This technique allows you to reduce the duration of the operation to 10-30 minutes;
- mini-access;
- classical open access is the most aggressive and traumatic. The doctor performs a bilateral examination of the neck, identifying all four parathyroid glands.
Calcium levels return to normal after surgery on average within an hour, but hormones may reach even higher levels for some time.
As a rule, operations are successful, the rehabilitation period does not take much time, and the consequences are not severe. But sometimes there is a development of postoperative complications, among which the greatest attention is paid to:
- hypocalcemia;
- ligament paralysis (duration may vary);
- hoarseness of voice.
Diet
For diseases of the parathyroid glands, accompanied by increased production of calcium in the body, it is recommended to adhere to a certain diet, including:
- limited consumption of foods rich in calcium: milk, cottage cheese, legumes, nuts;
- enriching the diet with phosphorus-containing products: fish, seaweed, shrimp, etc.;
- introduction into the daily diet of diuretic drinks made from natural raw materials: teas and infusions from bear ears, parsley, black currant, birch leaves, etc.
In general, nutrition should be varied and balanced, and also rich in vitamins, macro-, and microelements. The diet for this disease does not have strict restrictions.
Traditional methods of influence (traditional medicine recipes)
Traditional methods of influencing the body for parathyroid adenoma are rarely used, and, as a rule, as an additional treatment to the main therapy (conservative or surgical). Medicinal herbs have a much gentler effect on the body's systems, but treatment with folk remedies cannot be used as monotherapy.
Having decided to try traditional methods of treating a disease such as parathyroid hyperplasia, you should pay attention to the following recipes:
- tincture prepared from 100 grams of lilac flowers and 1 gram of horse chestnut. Place the ingredients in a glass container and pour in 500 ml of vodka. Infuse for 14-15 days in a dark place. Shake the container with tincture daily. Use the product as a compress on the neck with insulation. The course of treatment is a week. Treatment can be repeated after a seven-day break;
- compress of flax seeds boiled in milk. To prepare, you need to mix 1 teaspoon of flaxseeds in 50 ml of cow's milk, let it cool and separate the resulting grounds, which should be applied to the neck in the area of the projection of the affected parathyroid glands;
- tincture of hemlock herb . Pour 1 tbsp into a dark glass container. spoon of finely chopped herbs and pour 500 ml of vodka. Leave for 2 weeks, shaking the bottle daily. Wipe your neck with the prepared product once a day, every day;
- tincture of walnut partitions . Infuse 300 grams of partitions for a week and a half with 500 ml of vodka in a place inaccessible to direct sunlight. Strain the infusion and take 1.5 teaspoons twice a day before meals;
- infusion of yarrow . Pour 100 grams of chopped herbs into 400 ml of water and bring to a boil, turn off the heat and let it brew. Strain thoroughly and drink 50-70 ml three times a day before main meals.
When choosing a particular recipe, you need to pay attention to the individual tolerance of each component in order to avoid unwanted effects. In addition, it is recommended to discuss treatment with folk remedies with a specialist who supervises the patient on an ongoing basis.
Operation
Surgery to remove a benign tumor of the gland is the only method to cure the patient by stopping the development of the pathological process. This method of surgical treatment is complex, the duration of the operation is from 3 to 6 hours. General anesthesia is used.
Depending on the severity of the pathological process, surgery to remove a benign tumor is performed using an open or laparoscopic method, and the cost of surgery depends on this.
Advantage is given to laparoscopy, since this technique is less traumatic, but this method of operation is not suitable for large tumors. The following surgical methods for removing adenoma are used:
- thyroidectomy is a radical treatment method for widespread adenoma and total damage to the organ, which requires complete removal of the gland;
- hemithyroidectomy – one lobe of the organ is removed;
- subtotal removal method - most of the gland is subject to resection, leaving 2-4 g of the organ;
- removal of the isthmus.
After surgical removal of an adenoma, the patient must follow the doctor’s instructions during the rehabilitation period so that the body recovers faster.
After surgical removal of an adenoma, the patient must follow the doctor’s instructions during the rehabilitation period so that the body recovers faster.
Consequences
After surgery, depending on the severity of the clinical case and the success of the surgical intervention, the following complications may occur:
- hoarseness in the voice;
- ligament paralysis;
- hypocalcemia – calcium deficiency.
These changes, depending on the initial severity of the clinical case, can be temporary and go away on their own after a few months or remain with the person for life.
Life after surgery
The standard of living for most patients does not change after surgery.
Although there is often a need to adjust your diet. In severe cases with extensive adenoma, the entire thyroid gland must be removed, which is why the person will subsequently be forced to constantly take hormonal medications and adhere to a strict diet.
After removal of the adenoma, the patient must adhere to a strict diet.
Patient life prognosis
A disease such as follicular adenoma or another form of hyperplasia is benign, and therefore does not pose an immediate threat to the health and life of the patient. But when hormones in the blood increase, and calcium levels increase accordingly, conditions progress that can lead to quite serious complications.
Conditions such as kidney disease caused by calcification of parenchyma and tubules, heart disease that increases the risk of myocardial infarction, and the appearance of malignant tumors in other organs and tissues shorten the life prognosis of patients with adenoma.