755
0
The prevalence of BPH among the male population over 40 years of age is quite high. Statistics say that by the age of 80, about 80% of men suffer from this disease. The disease begins with the formation of nodules in the periurethral zone of the prostate, after which the glandular tissue gradually grows, causing discomfort to the patient.
Today, the treatment of prostatic hyperplasia is carried out using different methods, which will be discussed further.
Causes
Considering the statistics (about 90-95% of the male population have this disease), doctors are inclined to believe that this condition is a natural stage in the development of the gland.
Causes:
- Age-related changes in the body;
- Normal androgen levels;
- Increase in estrogen levels (may be an age-related change).
Benign hyperplasia is diagnosed in 60% of men over 50 years of age. By the age of 80, 90% of the male population consults doctors with urinary disorders and prostate enlargement.
This condition is characterized by excessive division of prostate cells and an increase in the volume of the organ. There is an excess of normal, unchanged prostate cells.
There are several options for the development of this condition:
- Diffuse proliferation of the gland - uniform increase in all parts;
- Nodular - the appearance of one node that grows, or many nodules in different parts of the prostate.
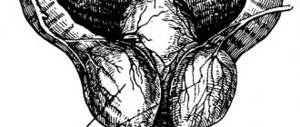
Prevalence of prostate adenoma
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
is the most common disease in elderly and senile men in the Russian Federation.
According to epidemiological studies, 25
percent!
Men over 50
years of age experience distressing symptoms associated with prostate adenoma.
And in the age group of 70 years and more,
every second person suffers from them.
The prostate gland is a very important organ of the male reproductive system; normally it is the size of a walnut and is located between the bladder and the penis. The localization of the prostate allows it to be palpated through the rectum. The secretory function of the pancreas is to produce a special secretion, which after ejaculation ensures the liquefaction of sperm and preserves the viability of sperm due to the presence of nutrients such as fructose and zinc citrate.
The secretion of the prostate makes up 20-30 percent of the volume of seminal fluid (sperm). Another special function of the pancreas is the metabolism of male sex hormones, in particular testosterone, which, under the influence of the enzyme 5α-reductase, is converted into the active form - Dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Clinical manifestations
The main symptoms of BPH are:
- Difficulty urinating;
- Thin stream of urine;
- The need to make an effort to go to the toilet;
- Feelings of insufficient bladder emptying;
- Increased urination;
- The appearance of frequent urination at night;
- False urges that do not end with the release of urine;
- Inability to hold urine when urge.
Clinical manifestations occur regardless of the form of the pathology.
Degrees of prostate enlargement
The degree of enlargement of the gland can be assessed by clinical manifestations:
- The appearance of a weak stream of urine and the need to make an effort to urinate. Increased number of urinations during the day (up to 10-15) and the appearance of urges at night. Symptoms arise due to compression of the enlarged gland on the part of the urethra.
- The stream of urine becomes thin. The man has a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. The development of acute urinary retention, the appearance of cystitis, and urolithiasis is possible. At this stage, the enlarged prostate gland blocks the lumen of the urethra by 50%, increasing intravesical pressure and contributing to the appearance of residual urine - the constant presence of up to 50 ml of urine in the bladder.
- Paradoxical ischuria - the bladder is filled with urine, it stretches its walls and does not allow it to contract. With a full bladder, a man has a constant urge to urinate, urine is released drop by drop. The gland completely blocks the lumen of the urethra.
Causes of development of prostate adenoma (prostate adenoma)
Causes of prostate adenoma
to this day it is not completely clear. The most common theories indicate that development is a consequence of age-related hormonal imbalance.
According to one theory, as men age, the level of Dihydrotestosterone in the blood increases, which stimulates the growth of glandular tissue of the prostate.
Another theory suggests that the balance of the hormones testosterone and estrogen plays a major role in the development of the disease. In young men, testosterone levels are higher than estrogen levels, and with age this ratio shifts in the other direction. Relatively high levels of estrogen can stimulate the proliferation of pancreatic tissue.
It is important to note that adenoma, prostatitis and prostate cancer are completely different diseases (having different causes and mechanisms of development). Therefore, an adenoma cannot “transition” into cancer, just as prostatitis cannot turn into BPH.
Variants of benign hyperplasia
Adenomatous prostatic hyperplasia is a variant of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
This condition is called adenomatous due to the enlargement of the prostate in the form of a single node, which increases in size. It is possible to identify a diffuse or nodular form of gland enlargement using magnetic resonance therapy.
To accurately establish the diagnosis and confirm benign prostatic hyperplasia, perform an organ biopsy.
According to the biopsy results:
- Glandular hyperplasia;
- Glandular-stromal hyperplasia;
- Hyperplasia of transition zones.
Glandular-stromal hyperplasia
The tissue of the gland contains muscle cells, secretory or glandular cells, and stromal cells, which form cords of connective tissue and separate the sections of the gland. Glandular-stromal hyperplasia is indicated by an increase in secretory cells and stromal elements. Hyperplasia has a diffuse (widespread) nature.
Glandular hyperplasia
It is diagnosed when the number of secretory cells increases. An important marker of such hyperplasia is an increase in the level of PSA - specific prostatic antigens. When the level of this substance in the blood increases to more than 2.5 ng/ml, we can talk about an increase in glandular cells.
Hyperplasia of transition zones
The prostate consists of:
- Central zone;
- Periphery;
- Transition zones (from the central part to the periphery).
If adenomatous nodules appear in the transition zone, doctors make a diagnosis of “hyperplasia of the transition zones of the prostate.” Developing in the transition zone, the nodules begin to increase in size and compress the remaining parts of the gland.
Nodal form
The formation of multiple foci of hyperplasia, between which there is unchanged tissue, is called a nodular form of hyperplasia. First, small areas of hyperplasia form in different parts of the prostate. Over time, they grow and become denser. On rectal examination, such a gland is felt as a lumpy compaction with uneven edges.
The nodules can compress healthy prostate tissue and compress the urethra.
Treatment
There are only 3 treatment options.
The main ones include:
- Drug therapy;
- Minimally invasive interventions;
- Surgical operations.
Treatment of hyperplasia with drugs is carried out in the first stages of the disease. The main drugs are alpha-1 adrenergic blockers. These substances do not reduce the volume of the gland, but are used for symptomatic treatment.
The use of such drugs allows you to get rid of:
- Urgency (uncontrollable urge with inability to hold urine);
- Reduced frequency of the urge to urinate;
- Frequent urge to urinate at night.
5a-reductase inhibitors inhibit the action of the enzyme in glandular cells. The absolute indication for the use of drugs in this group is glandular or glandular-stromal hyperplasia of the prostate.
These drugs reduce the intensity of the development of the disease.
Their effect on the adenomatous form of hyperplasia has been proven - when 5a-reductase inhibitors are used, the node slows down its growth and regresses.
Herbal medicines contain extracts from a variety of plant substances. The drugs improve the patient’s quality of life and help improve urination. Their action is to inhibit 5a-reductase, which leads to a decrease in the growth rate of the gland.
Herbs and Supplements
As a rule, special permission from regulatory authorities is not required for the sale of herbal medicines and dietary supplements. Just like medications, herbs and supplements can affect the body's biochemical processes and therefore there is a huge risk of developing side effects. Thus, a sufficient number of cases with serious consequences and even deaths due to the use of such drugs have been recorded. Patients should consult their physician before using any herbal remedies or dietary supplements.
Popular herbal and nutritional supplements for treating BPH include:
Saw Palmetto is one of the most popular herbal remedies for the treatment of BPH. It is made from the berries of the Serenoa palm. However, most clinical trials have shown modest results at best. Thorough research testing the effectiveness of this plant has not yielded any positive results.
Other popular herbal remedies include African plum extract (Pygeum Africanum), rye (Secale cereale), nettle root (Urtica dioica), South African herb root (Hypoxis rooperi) and pumpkin seed oil (Cucurbita peponis).
The plant sterol beta-sitosterol is found in some of these herbs marketed as a dietary supplement for prostate health. However, there is no scientific evidence that these medications are effective in treating BPH. Patients should be aware that high doses of zinc may increase the risk and progression of BPH.
Surgery
All surgical treatment can be divided into minimally invasive interventions and open surgical methods.
Indications for surgical treatment:
- Ineffectiveness of drug therapy;
- Rapid increase in PSA titers;
- Detection of foci of malignant hyperplasia.
Surgical treatment is used only after drug therapy and biopsy. This is due to the fact that most men suffering from hyperplasia are elderly people who have difficulty undergoing surgical interventions.
An alternative to open surgery is minimally invasive surgery. Minimally invasive methods include transurethral resection of the prostate gland. A device is inserted into the urethra, which cuts out a section or the entire gland and brings it out.
Another option for minimally invasive intervention (the gold standard for the treatment of benign hyperplasia) is laser transurethral removal of the affected part of the prostate.
Minimally invasive interventions are not always effective. The main risk of transurethral resection is residual cells. In case of diffuse hyperplasia or when it is combined with a tumor of the urethra, open operations are used, the gland itself or its altered part is removed.
How is it diagnosed?
Urologists, when a patient comes to them, adhere to a clear work scheme; they adhere to a differential diagnosis scheme. At the first appointment:
- collection of medical history and patient complaints;
- examination, including a rectal examination of the prostate.
During the interview, it is necessary to talk in as much detail as possible about the painful symptoms, past diseases (especially viral and infectious ones), allergies and medications taken. It is also worth finding out in advance whether other men in your family had urological ailments (including: prostatitis, adenoma, cancer).
After the examination, the doctor prescribes laboratory tests:
- Determination of urine composition. If blood is found in the urine, this indicates an advanced disease. Detected leukocytes are characteristic of infections of the urinary system, and the urine itself will be cloudy.
- Bacterial culture of urine, prostate secretions, discharge from the urethra. It is prescribed to exclude or confirm the infectious nature of the disease.
- Prostate cancer antigen test. Normally, this figure does not exceed 4.0 ng/ml. If the indicator is elevated, then suspicion of a malignant tumor arises.
- Biochemistry of blood. Prescribed to determine kidney function. If their functions are insufficient, the levels of creatinine, urea, potassium and other electrolytes change. The indicators need to be deciphered as a whole.
Instrumental research methods are required:
- Ultrasound of the prostate;
- uroflowmetry;
- radiography of the pelvic organs without the introduction of a contrast agent;
- urography using a contrast solution;
- biopsy, CT and MRI if a malignant tumor is suspected.
When preparing a patient for surgery, cystoscopy, ECG and other studies may be prescribed. They allow you to exclude other diseases that lead to complications. In this case, the ECHO CG must be immediately deciphered.
Ultrasound is more informative. In the images, the doctor will detect echo signs of the disease in the form of tissue compactions.
Additionally, an ultrasound echographic examination helps to establish the true dimensions of the organ (in the protocol they are indicated in millimeters, since centimeters are too large a measurement for the gland). A photo taken during diagnosis allows you to determine the location of the tumor.
Help from folk remedies
To treat adenoma disease, folk remedies based on celandine, parsley, St. John's wort, chamomile, horsetail, plantain, and nettle are used.
- The composition of the herbal decoction includes: horsetail, buckthorn bark, St. John's wort, chamomile, wormwood, plantain, nettle, rose hips. Boil a spoonful of horsetail in 1 liter of water for 10 minutes, then add a spoonful of buckthorn bark. After 5 minutes, chamomile and St. John's wort are added to the decoction in the same quantity. After another 5 minutes. The broth should be removed from the heat and add wormwood, plantain and nettle. The cooled product must be filtered and combined with a pharmacy rosehip tincture. The finished medicine should be poured into a dark glass container and placed in a cool place. The drug should be taken before meals, 2 tablespoons three times a day.
- To prepare celandine tincture, combine freshly prepared celandine juice and vodka in equal proportions. You need to drink the product the day before meals, one drop. The dose of the drug must be increased to 30 drops. Then reduce in the same order.
- The remedy, which consists of 3 parts of celandine, 7 parts of St. John's wort and chamomile, and 3 parts of linden blossom, has healing properties. 2 tablespoons of herbal mixture should be poured into 500 ml of boiling water. The decoction must be left to steep for at least an hour, then honey can be added. You need to drink the medicine 0.5 cups before eating 2 times a day.
- As a preventive measure, you can drink 2 teaspoons of parsley juice three times a day before meals.
- To prepare a tincture of nettle, horsetail and lingonberry, you need to pour 2 tablespoons of the raw material into 0.5 liters of boiled water. The medicine must be infused for an hour. Use the product half an hour before meals, half a glass three times a day.
Pelvic floor muscle training
Pelvic floor exercises were first developed to help women preparing for childbirth. These exercises can also help men prevent urinary incontinence, especially after surgical procedures. These exercises help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, support the bladder, and close the sphincter. Doing exercises. Because the perineal muscles are sometimes difficult to identify, doctors often recommend using urination time for exercises:
Tighten your muscles until the flow of urine slows or stops. Hold this position for 20 seconds. Relax. In general, you need to perform 5 to 15 contractions, 4:57 times a day.
Nutrition and diet
One of the methods of treating and preventing adenoma disease is following the rules of a balanced diet. When preparing your daily diet, you need to follow the following recommendations:
- Avoid eating foods that may cause complications or allergies;
- Food should be easily digestible;
- Food products should not cause gastrointestinal dysfunction;
- Include foods rich in vitamins and microelements in your daily diet.
The daily menu should consist of products with a high concentration of nutrients and elements that are easily processed and absorbed by the body. Compliance with this rule will help normalize the functioning of internal organs and strengthen the immune system.
If you have prostate adenoma, you need to eat the following foods:
- Vegetables and fruits;
- Dairy products;
- Bread with bran or rye flour;
- All cereals, with the exception of semolina;
- Chicken eggs;
- Beekeeping products;
- Pumpkin, watermelon, melon, berries;
- Dried fruits;
- Seafood and fish;
- Dietary types of meat;
- Vegetable oils;
- Hard cheese with a low fat content;
- Green tea.
If you have prostate adenoma dysfunction, you should avoid eating fatty and fried foods, legumes, offal, canned food, sweets, soda, fatty meat soups and broths, baked goods, and strong coffee.
If you have prostate disease, you need to eat small portions throughout the day. Between the main meals, it is allowed to eat berries, fruits, drink fruit drinks, compotes, freshly prepared juices, and fermented milk products.
The volume of liquid that needs to be consumed per day should be within 2.5 liters. Otherwise, additional stress is created on the kidneys and genitourinary system. To prepare food, you need to use the techniques of stewing, steaming, simmering, and baking in the oven.
Consequences and complications
When the first symptoms of the disease appear, you should consult a specialist.
Untimely treatment leads to the development of complications and consequences.
- Hyperplasia is characterized by a narrowing of the lumen of the urethra. As a result, difficulty urinating develops, and anuresis may develop.
- In the case of disease development due to exposure to pathogenic microorganisms and bacteria, inflammatory processes are considered a common occurrence.
- With prostate dysfunction, urinary stagnation occurs. It forms a sediment, which accumulates over time, thickens, and stones form in the bladder.
- Weakening of the bladder wall leads to the development of diverticulosis. Stagnant processes lead to stretching of connective tissue. Bacteria begin to accumulate in these areas - a source of infection.
- The development of diverticulosis leads to damage and rupture of the bladder. Over time, the muscle tissue of an overcrowded genitourinary system begins to stretch, loses its elasticity and ability to contract. Which leads to its damage during stress or physical activity.
- Urine that is not cleared from the bladder puts additional pressure on the kidneys. These lead to the development of renal failure.
- With further development of the disease, acute urinary retention occurs, that is, complications and pain occur when urinating. The main cause of the pathology is hypothermia, chronic fatigue, and sedentary work.
- With pathology, varicose changes in the veins of the bladder neck may be observed, as evidenced by the color of the urine.
Sonographic signs of BPH
Signs of BPH that can be seen on an ultrasound machine include:
- Increased prostate volume. It becomes larger in comparison with the age norm.
- The appearance of small cysts (1-10 mm) in the prostate.
- Stone formation. When the gland grows, compression of the ducts occurs, stagnation of prostatic secretions and, as a result, the formation of stones.
- Changes in the walls of the bladder. Violation of the correct outflow of urine first leads to a thickening of the wall, and over time to its weakening. The walls of the bladder become flabby and thin, and hernial protrusions appear on them.
Attention! Typically, adenomatous nodes develop symmetrically. In case of asymmetry, additional examination should be performed to exclude malignancy.
Prevention
Prevention of the disease consists of following the rules of a healthy lifestyle.
- Proper nutrition. The diet should include vegetables, fruits, seafood and dairy products. Avoid eating fatty foods, fast foods, sweets, and soda.
- Monitoring fluid intake. The volume of liquid consumed should be within 2.5 liters. Otherwise, there is additional stress on the kidneys. You don't need to drink a lot of water at night.
- Physical activity. Sports activities have a general strengthening effect. Hiking, running, cycling, swimming, and Nordic walking have a beneficial effect on men's health.
- Sexual activity. Regular sex life helps the normal functioning of the genital organs.
- Psychological calm. Unstable psycho-emotional health leads to a weakening of the body's protective functions and the development of various diseases. Avoid stress, depression, and emotional stress. Properly combine physical activity and rest.
- Prostate massage. Promotes the removal from the prostate of substances that have accumulated in it, bacteria and pathogenic microorganisms. The quality and duration of sexual intercourse improves, and a man’s sexual activity increases.
Doctor: Olga Shishkina ✓ Article checked by doctor