What do we know about latex
The material is made from the milky sap of rubber trees (Brazilian Hevea) and is distinguished by its elasticity, wear resistance, and resilience. Pure latex is destroyed by exposure to fat and ultraviolet radiation, so other stabilizing substances are added to prepare industrial mixtures.
Rubber is used to make mattresses, bath mats, toys, pacifiers, protective gloves, glue on postage stamps, tires, IVs, condoms and other items.
Natural latex contains a specific protein that causes allergies in some people.
Synthetic rubber is less likely to cause such a negative reaction in the body.
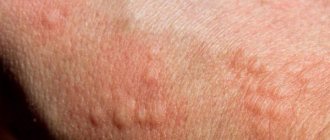
Rash, blisters and other signs
Symptoms of the disease are expressed differently for everyone. Some feel it instantly and acutely, others only after a couple of hours or days. Signs of sensitivity to latex items:
- burning of the epidermis and change in its color from flesh to red;
- lacrimation, pain and inflammation of the outer membranes of the eyes;
- blistering-hyperemic manifestations;
- clear, copious discharge and itching in the nose;
- cough, heaviness when exhaling, bronchial spasm;
- swelling of the mucous membranes of the nose.
An acute latex allergy manifests itself as:
- arrhythmia;
- hypotension, accompanied by blue lips and faintness;
- indifference to everything or excessive emotionality, as well as other manifestations of the nervous system;
- feeling of suffocation;
- swelling;
- hoarseness of voice.
Anaphylactic shock is another symptom of intolerance to latex products. In this case, emergency medical care is required.
This is interesting! A negative immune response is possible regardless of gender and age. An allergic reaction to pacifiers in babies can manifest as a red rash around the mouth. Adults experience irritation with condoms and intimate paraphernalia.
Be healthy!
A latex allergy is a reaction to certain proteins found in natural latex. Natural latex is the milky sap of rubber trees. If you have a latex allergy, your body mistakes latex for a harmful substance.
Latex allergies can occur in a variety of ways, from skin irritation to anaphylaxis, which is a potentially life-threatening condition. Your doctor can determine if you have a latex allergy or if you are at risk of developing an allergy.
If you understand allergies and know which items contain latex, you can prevent an allergic reaction from developing.
Symptoms
If you have a latex allergy, symptoms usually develop after wearing latex gloves or inhaling airborne latex particles that are released when someone removes latex gloves. Symptoms of a latex allergy range from mild to severe, depending on your sensitivity and the extent of your exposure to the allergen. Your reaction may worsen with repeated exposure to latex.
Mild symptoms
Mild latex allergy symptoms include:
- Itching
- Skin redness
- Skin rash, including hives
More severe latex allergy symptoms:
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Itching in the eye area, watery eyes
- Sore throat
- Labored breathing
- Dyspnea
- Cough
Symptoms of anaphylactic shock
The most serious form of allergic reaction to latex is anaphylactic shock, which can be fatal. Anaphylactic reactions develop immediately after exposure to latex in sensitive people, but anaphylaxis rarely develops upon first contact with the allergen.
Signs of anaphylaxis include:
- Labored breathing
- Urticaria-type rash or swelling
- Nausea and vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- drop in blood pressure
- Dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion
- Frequent and/or weak pulse.
When to see a doctor
If you have symptoms of an anaphylactic reaction, you should seek emergency medical attention.
If you have less severe symptoms of a reaction to latex, talk to your doctor. If possible, see a doctor during an allergic reaction to help make a diagnosis.
Causes
An allergy develops when your immune system identifies latex as a harmful substance and produces certain antibodies to fight the allergen. When exposed to an allergen again, the antibodies signal your immune system to release histamine and other chemicals into the blood that cause allergy symptoms. The more intense the exposure to the allergen, the stronger your immune system may react (sensitization).
Allergy to latex develops when:
- Direct contact. The most common cause of latex allergies is contact with objects made of latex such as gloves, condoms and balloons.
- Inhalation of an allergen. You can inhale latex particles in the air. For example, removing latex gloves releases large amounts of particles into the air. However, it may vary depending on the brand of gloves.
There are other types of reactions to latex that are different from an allergic reaction. These include:
- Allergic contact dermatitis. This is a reaction to chemical additives used in the manufacturing process of latex products. It usually results in a skin rash that develops 24 to 48 hours after exposure to latex, similar to the rash caused by poison ivy.
- Irritant contact dermatitis. This is not an allergic reaction, but a form of dermatitis, an irritation caused by wearing rubber gloves or exposure to the powder inside them. At the same time, areas of irritation and dry skin accompanied by itching appear on the skin of the hands.
Not all latex products are made from natural materials. Products containing artificial (synthetic) latex, such as latex paint, are unlikely to cause a reaction.
Risk factors
Some people are at greater risk of developing a latex allergy:
- Patients with spina bifida (spina bifida). The risk of latex allergy is highest in people with spina bifida, a birth defect that affects the development of the spine. People with this disorder are often exposed to latex because they require medical attention from birth.
- People who frequently undergo surgery or medical procedures . Frequent contact with latex gloves increases the risk of developing a latex allergy.
- Healthcare workers. If you work in the healthcare industry, you are at increased risk of developing allergies.
- Workers engaged in rubber production. Repeated exposure to latex may increase sensitivity.
- People suffering from allergic reactions or with a family history of allergies. You are at increased risk of latex allergy if you have other allergies - such as hay fever or food allergies - or if allergic diseases are common in your blood relatives.
The Link Between Food Allergies and Latex Allergies Latex allergies have also been linked to certain foods such as avocados, bananas, chestnuts, kiwi and passion fruit. These products contain some allergens found in latex. If you are allergic to latex, you are more likely to be allergic to these products.
Treatment
There is no cure for latex allergy, although there are many medications that can relieve symptoms. The only way to prevent an allergic reaction from developing is to avoid products containing latex.
However, despite all efforts, exposure to the allergen may still occur. If you have had severe allergic reactions to latex, you may need to carry an epinephrine auto-injector with you at all times. If anaphylactic shock develops, you will need:
- Emergency administration of adrenaline (epinephrine)
- Hospitalization
- Oxygen
- Corticosteroids
For less severe reactions, your doctor may prescribe antihistamines. You can take them after exposure to latex to control symptoms and reduce discomfort.
Prevention
Many products contain latex, but there are alternatives for most of them. You can prevent the development of an allergic reaction to latex by avoiding contact with these products:
- Dishwashing gloves
- Some types of carpets
- Garment belts
- Air balloons
- Rubber toys
- Warmers
- Baby bottles with nipples
- Some disposable diapers
- Rubber bands
- Erasers
- Condoms
- Female condoms
- Goggles
- Racket handles
- Motorcycle and bicycle handlebars
- Blood pressure cuffs
- Stethoscopes
- Intravenous catheters
- Syringes
- Respirators
- Disposable electrodes
- Surgical masks
- Dental Protective Gaskets
Many medical facilities use latex-free gloves. However, because other medications may contain latex or rubber, be sure to tell your doctors, nurses, dentists, and other health care providers about your allergy before performing any diagnostic or treatment procedure. Wearing a medical bracelet can inform others about your latex allergy.
Genital latex allergy
If barrier methods of contraception made from rubber are intolerant, women note the appearance of uncomfortable sensations in the vaginal area, its swelling and redness. This type of allergy occurs in only 5% of sexually active people.
By the way, representatives of the fair half of humanity are more susceptible to this pathology than the stronger sex. An allergy to latex in men is accompanied by hives, swelling of the penis and its redness, and difficulty urinating.
The same reaction is possible to gel lubricants, flavors and spermicides. If there is a true allergy to contraceptives, the patient should also be irritated to other products, such as rubber gloves, patches or pool caps.
Causes of latex allergies
Latex is a natural rubber and is obtained from the sap of the Brazil tree.
This rubber contains many chemical elements, including a large group of latex proteins.
It is the last components of rubber that can trigger a specific reaction of the immune system when they enter the body.
Latex proteins can enter the body of any person in several ways:
- By air. Latex gloves and some other products have powder inside, which contains a certain concentration of proteins foreign to the body. When inhaled, these proteins enter the respiratory tract and cause respiratory latex allergies.
- By contact. That is, allergens can penetrate the skin upon contact with gloves and other rubber products.
- Through the mucous membranes. That is, through the bladder, rectum, nose, oral cavity.
- Through the blood. Penetration of the allergen through the blood is possible when using products containing rubber for medical procedures.
Allergy to latex is most often observed in people who have been or are constantly exposed to contact with products containing natural rubber.
This group of patients includes:
- People who have undergone surgery;
- Patients with installed urinary and intravenous catheters, colostomy bags;
- People with developmental abnormalities of the urinary organs. Since childhood, such people are forced to endure many medical procedures using various soft instruments with the addition of rubber, and perhaps this affects the appearance of an allergic reaction to latex;
- People involved in the production of rubber products;
- Health workers. Allergy to latex among health workers is detected in 10-15% of cases; the longer the work experience, the higher the risk of developing an allergic reaction.
Allergy to latex in women's hands is most often observed with the constant use of gloves when cleaning premises.
According to statistics, about 10% of housewives have various allergic reactions to latex.
When examining patients with intolerance to natural rubber, it was found that the risk of the disease is increased in those who suffer from asthma and eczema, bone marrow pathologies, and other types of allergic reactions.
POPULAR WITH READERS: Allergies in babies, what to do, how to treat
Often noted with allergies to latex and intolerance to avocado, kiwi, chestnuts, bananas.
This is due to the fact that these foods and latex have proteins identical in structure, which are the main reason for the specific reaction of the immune system.
Recognizing intolerance to latex objects
In order not to confuse the body’s reaction to rubber with rashes to other “irritants,” answer a few questions:
- Does itching appear on areas of the skin after contact with elastic bands of bras, swimming trunks, tights or elastic bandages?
- Do you experience unreasonable lacrimation or a burning sensation in the nose after chewing gum, using cocktail straws or cutlery with rubber inserts?
- Do blisters and hives form on the hands after doing housework while wearing protective gloves?
- Is the reaction visible on the skin after medical procedures - examination with gloves, performing cleansing enemas, tightening a rubber band, etc.?
If the answer to all questions is negative, then the cause of the rash and runny nose must be sought elsewhere. Perhaps this is immunity to household chemicals or the reaction of sensitive skin to friction and other manipulations.
If genital allergies have been excluded in this way, it is important to continue to use hypoallergenic contraceptives without adding mucosal irritants.
Diagnostics
Initially, the doctor conducts an external examination of the patient and also examines the medical history. Upon examination, the doctor determines the severity of skin lesions and extent. To confirm the diagnosis, additional tests are performed. These are skin tests or immunological tests.
A doctor may inject a latex-based drug into a patient's blood to confirm the body's response to it. If after such an injection an allergic reaction occurs in the body, this may indicate that the person is allergic to latex.
Who is at risk
People who, due to their occupation or necessity, constantly come into contact with latex products are prone to allergies. These include:
- health workers with extensive work experience;
- patients with diseases of the urinary organs;
- women who constantly use protective gloves for washing and cleaning (the allergy in this case manifests itself on the hands);
- employees of enterprises producing rubber products;
- persons with multiple surgical interventions;
- people suffering from asthma or eczema.
Symptoms of intolerance characteristic of latex allergies
Latex allergy is considered a difficult disease to detect when symptoms first appear.
A small part of rubber is found in many household items and even in clothing, and therefore it is not always possible to immediately determine the true cause of the allergen and the path of its effect on the immune system.
Difficulties in diagnosis are added by the varied clinical picture of an allergic reaction to latex.
It is customary to distinguish three main types of allergies to latex components.
Contact dermatitis.
This type of reaction usually occurs during prolonged and almost constant contact with latex products, for example, when wearing medical gloves.
Dermatitis initially manifests itself as dryness, flaking, then irritation, itching, and cracks in the skin.
The area affected by contact dermatitis corresponds to those places on the body that were in direct contact with latex.
Allergic dermatitis.
Occurs as a delayed reaction to latex proteins. This type of reaction manifests itself in the same way as the previous one, but its manifestations are more pronounced, and dermatitis can cover a larger area of the body.
Immediate allergy reaction.
Considered the most severe reaction to latex proteins. It manifests itself as respiratory signs of allergies, conjunctivitis, skin rash, severe itching, and conjunctivitis.
Tachycardia, convulsions, drop in blood pressure and anaphylactic shock occur less frequently.
What kind of doctor do you need?
If any irritation appears on the skin, you must make an appointment with an allergist-immunologist, who deals specifically with allergic pathologies, clarifies the symptoms and treatment of the disease in a particular case.
If the local clinic does not have such a highly specialized doctor, then you can contact private clinics, as well as a therapist or dermatologist who will conduct a preliminary examination.
Important! If parents suspect signs of an allergy in their baby, they should consult a pediatrician. If necessary, he refers to a dermatologist, allergist or infectious disease specialist to rule out the bacterial nature of the disease.
In addition, there are specialized allergology institutes where immunity can be examined professionally and promptly.
Methods for diagnosing rubber allergies
The specialist examines areas of skin with rashes, listens to the patient and prescribes special laboratory tests. Basic methods for identifying provoking factors and the type of allergy:
- Antibodies of the IgE class. The result of a blood test shows increased sensitivity to potential “provocateurs” of the disease.
- Skin tests. A small amount of different allergens is injected under the skin using a syringe, after which a reaction to each substance is observed. In this way, the cause of the reactions is determined.
- Provocation tests. It is not given to children during the period of exacerbation of the disease. Important for final confirmation of the type of allergy.
- Elimination test. Combines diagnosis and simultaneous therapy. It is necessary when previous methods failed to find out the root cause of the disease. The doctor excludes allergens that can cause a reaction.
Drugs for drug treatment
Before starting therapy, you should exclude all “irritants” - latex gloves, rubber toys, bathroom rugs, etc. The following pharmaceutical products are used to relieve allergy symptoms:
- oral antihistamines (L-Cet, Cetrin);
- drops in the nose or eyes, vasoconstrictors, as well as neutralizing histamine (Naphthyzin, Farmazolin, Visin);
- hormone-containing medications (Hydrocartisone);
- drugs that relieve bronchospasm;
- ointments for the treatment of allergic dermatitis.
Full therapy should be comprehensive, that is, just one cream or eye drops that reduce redness is not enough; antihistamine tablets are also included.
Negative aspects of self-medication
As a rule, allergy medications are sold in pharmacies without a prescription, which opens up free access to medications. Experts warn against treating yourself, because a reaction to latex can be confused with other, more serious diseases, such as acute infections. Eliminating symptoms with ointments and drops can only aggravate the problem without finding out the cause.
It is important to take special care for pregnant women and children. Uncontrolled use of drugs by expectant mothers can cause abnormalities in the development of the embryo.
If any alarming signals appear - rash, swelling, redness - it is necessary to obtain competent advice from an allergist, who will prescribe treatment and determine the duration of the course.
Treatment
Since some people may have a severe allergy to latex, based on the clinical picture, the doctor prescribes the use of certain medications.
Simple dermatitis, which is accompanied by a small rash on the skin, can be eliminated with Zyrtec ointment. If symptoms are severe, the doctor prescribes hormonal drugs, for example, Cloveit. They differ from each other in the activity that they can have on the body, and therefore the doctor must carefully select them.
It is also worth noting that substances that act quickly can also have some side effects on the body. Therefore, you do not need to increase their dose on your own and you must follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
If the symptoms of latex are general, then you cannot do without the use of antihistamines. These include Claritin or Telfast.
Diet is also important. Doctors say that some products contain the same allergens as latex. The diet should include cereals, lean meat and plenty of liquid.
In the case when allergic reactions are severe and cause complications in the patient (swelling, suffocation, loss of consciousness, etc.), it is important to hospitalize such a patient and inject adrenaline into his vein. Further treatment is carried out comprehensively.
Precautions for allergy sufferers
Persons who are aware of their illness should protect themselves from possible reactions, and if they occur, receive prompt help and treatment.
Allergy to latex in women is similar in symptoms to candidiasis and adnexitis, so the gynecologist should be informed about the use of barrier methods of contraception - condoms or a cap. This will allow you to make a timely and accurate diagnosis.
Carefully study the packaging of the products you buy. The ingredients will indicate whether the item contains latex. Choose things with the safe latex symbol, that is, with a minimum content of natural rubber.
Important! During the period of exacerbation of allergies, you should not try new foods or cosmetics, so as not to aggravate the condition.
It is important to exclude all latex products from your household - toys, pens, hair combs, toothbrushes with stakes, rubber mattresses, shower mats, rubber boots and much more. You should not wear underwear with elastic bands or elastic inserts. It is better to give preference to products made from synthetic materials.
Prognosis and prevention
Prevention of latex allergy attacks involves avoiding contact with objects that contain latex. It must be remembered that the label “hypoallergenic” does not reflect the absence of latex in the composition of the item.
It must be said that not only household or medical gloves, but also a lot of other items can cause the development of latex allergies. Here is a partial list of items that may pose a danger to people suffering from latex allergies:
- Balloons;
- Tires;
- ATM buttons (they may have a latex coating).
- Turnstiles;
- Cuffs of medical devices - tonometers, ECG equipment, etc.
- Some types of support bandages.
- Baskets or trolleys used in supermarkets with latex handles.
You can face the danger of developing allergies even in a cafe or restaurant if workers use latex gloves during food preparation.
In the cards of patients suffering from latex allergies, appropriate notes must be made. When visiting specialized specialists practicing in private clinics or offices, you must inform the specialist about your condition at least one day before the scheduled visit. If hospitalization is necessary, patients with latex allergies are placed in special boxes, since otherwise it is extremely difficult to prevent contact with latex products.
In everyday life, it is necessary to replace latex products with analogues that do not contain this substance. For example, use polyurethane gloves instead of latex gloves.
In addition, patients with latex allergies are advised to avoid eating fruits that contain proteins similar to latex proteins.
dermalatlas.ru
Precautions when traveling and at work
Family and friends know how a latex allergy manifests in their loved one and are able to respond quickly. But the disease can show itself anywhere - on the way to kindergarten or on a long-awaited vacation. It is important to be prepared for different turns of events. Wear a special bracelet at all times that indicates that the person is allergic to latex. This will help doctors provide the right emergency care in case of a crisis, accident or other hospitalization.
This is interesting! Silicone medical bracelets are worn not only by allergy sufferers, but also by asthmatics, diabetics, epileptics, pacemaker carriers, and autists. In the USA, the “organ donor” medallion is popular, which confirms a person’s willingness to donate their organs in case of injuries incompatible with life.
You need to have medications with you that will relieve an attack - antihistamine ampoules or tablets. If you have an acute reaction, you should carry Epinephrine (an injection of adrenaline) with you for emergency treatment.
Latex allergy occurs rarely, so the patient sometimes does not realize the cause of the disease for a long time, attributing this reaction to food or household chemicals. An experienced allergist will be able to correctly diagnose, conduct the necessary tests and prescribe treatment. Products made from natural rubber surround us everywhere, and it is important for people with latex allergies to follow medical prescriptions, adhere to a diet and take measures to prevent recurrent or acute manifestations.
Items that contain latex
Hundreds of items are known to contain latex, including most products that can be stretched. Try to avoid the following points:
- medical supplies such as gloves, IV tubing, catheters, and blood pressure cuffs
- dental devices, including orthodontic rubber bands and dental dams
- contraceptives such as condoms and diaphragms
- clothing containing elastic such as pants or underwear, sneakers and raincoats
- some household items such as zippered storage bags, rugs, some mats and rubber gloves
- products for babies and children, including pacifiers, bottle nipples, disposable diapers, teethers or other toys
- some school or office supplies such as rubber bands, erasers, duct tape and paints
- elastic bandages
- rubber balls
Latex cross-reaction with certain products
About 50 percent of people with latex allergies also have other allergies. Some people with latex allergies may also be allergic to certain foods that contain proteins similar to those found in latex. This is known as cross-reaction.
The following products may cause a cross-reaction in some people. Different foods have varying degrees of cross-reaction association.
Products with high association:
- avocado
- bananas
- kiwi
Products with moderate association:
- apples
- carrot
- celery
- papaya
- melons
- tomatoes
- potato
It is also important to be careful with these other potentially cross-reactive products:
- nuts and legumes, including almonds, cashews, chestnuts, hazelnuts, peanuts, pecans and walnuts
- grains, including wheat and rye
- shellfish, including crab, lobster and shrimp
If you have a reaction to any of the products mentioned above, discuss this with your doctor.