Signs and symptoms of breast cyst
The cysts are small in size and very rarely bother the patient. They are most often detected by chance, after undergoing a mammogram. Enlarged cystic formations cause pain, the mammary glands can be felt, and this manifests itself a few days before menstruation.
Large cysts filled with secretion are manifested by constant pain, pulling sensations, burning, and uneven compactions.
Breast cyst clinically manifests itself regardless of the menstrual cycle. Huge, giant cysts are defined by visible deformation of the mammary gland, redness and even bluishness of the skin.
Any inflammation in the cyst is characterized by fever, redness of the skin, and slight or even large enlargement of the axillary lymph nodes.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Palpable pain in the chest area.
- Burning and pulling sensations.
- Change in skin color.
- Breast deformation.
- Fever.
Breast cyst surgery
Removal of a breast cyst is performed by sectoral resection. During the operation, not only the cyst is removed, but also a section of the surrounding tissue (sector) is excised. Essentially, a small part of the mammary gland with the cyst located in it is removed. To prevent rough postoperative scars from deforming the breast and disturbing its aesthetics, the wound is sutured with cosmetic sutures.
For several days after removal of the cyst, a drainage is left in the postoperative wound - a special tube through which fluid drains from the wound. Drainage prevents fluid from accumulating inside the wound cavity and causing complications.
While the patient is still on the operating table, the tissue removed by resection is sent for urgent histological examination. Half an hour later, when the answer from the laboratory is received, the further outcome of the operation is decided. If no “bad” cells are found in the material, the volume of surgical intervention performed is considered sufficient, and the wound is sutured. In a negative scenario, unilateral removal of the mammary gland and adjacent axillary lymph nodes is performed.
Breast resection is not a complex operation. As a rule, it passes without negative consequences. But, like any surgical intervention, they can be accompanied by complications.
After surgery, wound infection may occur, followed by suppuration. This happens infrequently, as the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics. The wound has to be opened, the cavity cleared of pus and treated with antibiotics.
If bleeding is not stopped correctly during surgery, blood may accumulate in the wound cavity and form a hematoma. It will definitely be opened.
Causes of breast cysts
Hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body is not uncommon. At such a moment, the ovaries secrete a higher than normal amount of estrogens, the main female sex hormones. This is what leads to tissue proliferation under the influence of estrogens, the epithelium of the mammary gland ducts, and swelling of its tissues. Such processes clog some ducts and form cysts.
In practice, a cyst is the main element of fibrocystic mastopathy. If the disease is diffuse in nature, i.e. equally distributed in the mammary glands, many small cysts appear. Nodular mastopathy is characterized by large nodes.
The female hormonal system is neurohumoral and controlled by the central nervous system. Any impact may cause the system to malfunction. The neurohumoral system is most sensitive to all kinds of psycho-emotional stress. First of all, the development of cysts is influenced by:
- Long-term intellectual loads.
- Constant emotional stress.
- Frequent worries and stress.
- Sensitivity to problems.
Abortion deals the biggest blow to the endocrine system. They are the ones who can cause problems in a woman’s body. Frequent abortions disrupt the functioning of the ovaries, provoke the release of large amounts of estrogens, and the maturation of cysts.
An increase in estrogen can cause excess weight, especially obesity. Since adipose tissue cells promote the production of estrogen, in obese women, the chances of developing hormone-dependent diseases increase.
Poor nutrition is another main cause of hormonal imbalance. Poor nutrition causes metabolic disorders, which sooner or later will affect the neuroendocrine system. Other endocrine glands and their work also affect the condition and activity of the mammary gland.
Any thermal procedures and ultraviolet rays stimulate the production of estrogen.
The formation of a cyst in the mammary glands can be caused by any injury. The risk of neoplasms also increases after surgery. Since breast tissue is very thin, it reacts to any physical impact. The use of oral contraceptives is a predisposing and common factor in the development of cysts.
Treatment of breast cysts without surgery with tablets
Considering the reasons for the appearance of the pathology, before doing anything directly with the cyst, you need to find out if the patient has hormonal disorders. Often, first you need to cure gynecological diseases that provoke the growth of new cysts. Hormonal pills for breast cysts are prescribed based on the type of disorder:
- Combined oral contraceptives inhibit the production of hormones responsible for ovulation, and therefore for changes in the mammary gland. COCs affect the functioning of the pituitary gland.
- Artificial analogues of progesterone. Such drugs do not have side effects such as body hair growth.
- Dopamine receptor stimulants reduce prolactin production.
- Phytoestrogens are extracts from medicinal plants that normalize the amount of estrogen in the body.
- Medicines for breast cysts are available not only in the form of tablets, but also in the form of topical ointments. Typically, estrogen binding drugs are produced in this form.
Drug treatment for breast cysts is not complete without vitamins. Vitamins A, E and B are usually prescribed. They are necessary to restore the function of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland and ovaries.
The course of tablets also includes anti-inflammatory therapy for breast cysts. Antibiotics will help kill the infection and avoid suppuration. This course of drugs is indicated if there are obvious pain symptoms. For swelling during menstruation, diuretics are prescribed to reduce discomfort. To reduce swelling, take medications with vitamin P. This way, less fluid accumulates in the tissues.
Since the disease is a stress for the body, when diagnosed with a “breast cyst,” medication treatment complements the use of sedatives. For example, taking valerian tablets. The less stress the patient experiences, the less likely it is that her condition will worsen.
Answers to popular questions
- Why is a breast cyst dangerous? A breast tumor is not life-threatening for a woman. Of course, it can reduce the quality of life with certain symptoms, but it is rarely a pathology that degenerates into a cancerous tumor. Despite this, its nodular forms are capable of stimulating a malignant tumor. Quite often, a breast cyst, taking into account the risk factors for mastopathy, and the entire danger of a malignant process, represents a background for cancer development. According to statistics, every third woman has a cyst in the mammary gland, and many do not even know about it. Faced with the disease, representatives of the fair sex begin to panic, in fear that cancer may develop. There is no need to do this, you just need to start treatment in a timely manner. If the disease is detected in a timely manner, it is necessary to have time to eliminate the cause and carry out complex therapy. (
What is a breast cyst?
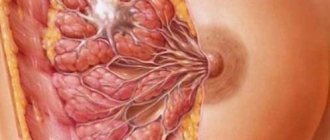
A breast cyst is a cavity-shaped formation that develops from the tissue of the milk duct. It occurs when such ducts expand. When the milk passages expand, the secretion in them stagnates and becomes viscous.
The thickening of this liquid leads to the formation of a plug that blocks the duct. Then, at the site of the blockage, a cyst is formed, which is a sac with liquid contents and clear boundaries.
This formation has walls that can change as the disease progresses. At first they have a slight thickness, and then they are covered with connective tissue and become thick and dense.
The fluid that fills the cyst is in most cases yellowish in color, but sometimes it can acquire brownish or greenish tints. The composition of the old formation may also include calcium salts.
Breast cyst
Such neoplasms in the mammary glands can be single or multiple (more information about the types of cysts in the breast can be found here). They may also vary in size. In most cases, this diagnosis is made to women between 30 and 40 years old. In addition, nulliparous women over the age of 30 are considered at risk.
Types of breast cysts
Neoplasms and breast cysts are determined by several types:
- Cysts are oval, round.
- Cysts of irregular shape.
- Small or large cysts.
- Single or multiple. Polycystic disease is determined not only by the fusion of cysts, but also by the formation of multi-chamber clusters.
- Single-chamber or multi-chamber cysts.
- Cysts with or without inflammation.
- Typical, having smooth internal walls or atypical, having growths on the walls.
There are atypical, fibrous, ductal, solitary, multi-chamber cysts of the mammary glands.
An atypical breast cyst is an accumulation of fluid, when the gland duct expands, in the resulting cavity. Such a cyst has a fibrous capsule, round or oval in shape, of different sizes. An atypical cyst is a benign cyst with growths protruding into the cavity.
The main causes of an atypical cyst:
- Cysts that have existed for a long time.
- Often recurrent breast cysts.
- Inflammatory processes occurring in the cyst.
- The presence of papillomatous (benign) growths.
- The presence of papillomatous formations in the cyst cavity.
Fibrous cyst of the mammary gland occupies a central place in oncology and is a background disease in the development of breast cancer.
Fibrous cyst is: Reclus disease, cystic mastopathy, Schimmelbusch disease, cystic disease, chronic cystic mastitis. At the moment, these terms are not used in medicine. The following forms are distinguished: non-proliferative and proliferative.
Fibrous cyst of the mammary gland is characterized by characteristic symptoms:
- Before menstruation, pain in the mammary glands intensifies.
- There is a presence in the chest, cluster-shaped nodular compactions.
- Liquid is released from the nipples.
The pathogenesis of fibrous mastopathy is not fully understood. There are certain factors that provoke its development:
- Such cysts develop in tissue during menopause due to hormonal imbalance.
- When the immune system is weakened and the functioning of individual organs is impaired.
Read more: Causes, symptoms, stages and treatment of breast cancer
A solitary cyst of the mammary gland is a benign dysplasia that does not pose a particular danger. But this does not mean that you should not pay attention to it and not engage in treatment. It is necessary to contact a mammologist in a timely manner and begin treatment, adjust hormonal levels and the protective system.
A solitary cyst is a formation of round shape and elastic consistency. It is a swelling filled with liquid of various colors. The longer the cyst, the denser its capsule. A solitary cyst is a large cavity that is located in one breast.
Reasons for the development of this form of cyst:
- Heredity.
- Neuroendocrine disorders.
- Abortion.
- Age, after 35 years.
- Heavy weight.
- Late birth.
- Stress, nervous tension.
- Complete refusal of breastfeeding.
- Early puberty.
- Mastitis.
- Breast injuries.
A solitary cyst manifests itself as chest pain, which intensifies in the second phase of menstruation. The pain is stretching, pressing and aching. There is a feeling of burning and itching in the chest area. Such pain is accompanied by compressed nerves of the mammary gland and surrounding tissues. The pain can radiate to the shoulder blade, neck or shoulder. As soon as menstruation ends, the pain stops.
Another characteristic symptom is determined by palpation, which any woman can identify, especially if the solitary cyst is large.
Ductal cysts of the mammary gland develop at any age, but are most often diagnosed after 48 years of age. This disease occurs in 1% of all breast tumors.
The worst thing is that a ductal cyst is a full-fledged precancerous condition, despite the fact that no reliable data has been identified.
A ductal cyst is an intraductal papilloma, a cystoadenopapiloma is small growths inside the mammary gland. Pathology belongs to the group of benign diseases.
Factors causing ductal cysts:
- Hormonal disorders.
- Ovarian dysfunction.
- Abortion.
- Inflammation of the uterine appendages and ovaries.
- Excess body weight.
- Diabetes.
- Endocrine diseases.
- Stress.
Clinically, this pathology is manifested by discharge from the nipples of a clear, brown, bloody or greenish fluid. A ductal cyst can be palpated if it is present in the area of the milk ducts.
A ductal cyst of the mammary gland is palpable as a dense formation; no pain is felt on palpation. The disease is most often discovered by chance, during a routine examination.
Multilocular breast cyst is a very unpleasant diagnosis. First, one cyst develops, then new ones appear nearby, after which they merge. This is how a multi-chamber cyst is formed. The disease is detected by ultrasound.
The main factor in the development of pathology is an incorrect lifestyle, but there are other factors:
- Alcohol abuse.
- Nicotine and drug use.
- Poor nutrition.
- Metabolic disease.
- Frequent taking of medications.
- Stress, anxiety.
- Hormonal imbalances.
- Infectious diseases.
Multilocular cyst of the mammary glands is a dangerous disease that can develop into a malignant tumor.
Symptoms of a breast cyst
The presence of clinical signs of a breast cyst and their severity depend on the size of the formation. Small cysts (and sometimes their size does not exceed 3 mm) in the absence of growth can be asymptomatically present in the mammary gland for years and are discovered by chance. Medium and large (up to 5 cm or more) cysts can cause a feeling of discomfort and mild pain, especially on the eve of the next menstruation due to fluid retention in the tissues of the mammary glands. Sometimes a cyst may be accompanied by periodic discharge from the nipple; this is due to the release of the contents of the cyst into the milk duct of the gland; it has a liquid or thick consistency, yellow, greenish or almost transparent. Such discharge from the breast can accompany other diseases, more often mastopathy, so the symptom is not significant.
Large cysts are often visible during external examination, when a raised area or “bump” is visualized on the surface of the breast.
It has been noted that a cyst of the right breast is less common than a cyst of the left breast in young patients.
Breast cysts often accompany mastopathy, namely its fibrocystic form, so a patient with a cyst often has symptoms of mastopathy, which is the real culprit for the appearance of pain in one or both mammary glands, and not the cyst itself. The nature of the pain is very diverse and varies from mild discomfort to severe pain. In addition to pain due to mastopathy, painful areas of compaction of various sizes, shapes and densities are palpated in the mammary gland, which complicate the initial diagnosis of the cyst.
Both mammary glands have an almost symmetrical structure, so the cyst of the right mammary gland and the cyst of the left mammary gland do not differ in clinical signs and structure.
During self-examination of the mammary glands, women can often discover a medium or large cyst themselves. It is palpated as a round, smooth formation of soft-elastic consistency. However, the exact nature of any formation detected by palpation cannot be determined without additional examination methods.
The presence of a cyst in the mammary gland in most cases is confirmed by two leading diagnostic methods:
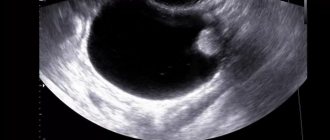
— Method of ultrasound scanning of the mammary glands. It is carried out in the first phase of the cycle in young women (up to 40 years old) who have a dense structure of the mammary glands. It allows you to identify very small (less than 5 mm) cysts and determine their internal structure, and is also able to differentiate a cavity formation from a tumor-like one. When examined, a cyst looks like a round, clearly demarcated formation with liquid contents, having a well-defined capsule, and a solitary breast cyst looks like a cavity separated by septa. All segments of the mammary gland are examined, the condition and size of its ducts are assessed, and the lymph nodes surrounding the gland are scanned.
— X-ray examination (mammography). Indicated for women who have passed the age of forty. It is an accessible and informative method that can detect even the deepest pathological formations in the mammary gland. Allows you to take pictures of the problem area of the gland in several projections with magnification.
In difficult clinical situations, MRI may be performed.
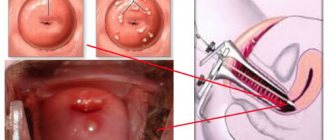
After a cyst is detected using ultrasound or mammography, it is necessary to determine what it is filled with. Since some malignant formations in the breast are disguised as a harmless cyst, you should determine its benignity, that is, look at what cells it consists of. To do this, a puncture (piercing) of the cyst is carried out using a thin needle, followed by evacuation of its contents. The resulting material is sent for research.
Since a breast cyst is considered to be a hormone-dependent process, all patients are shown a laboratory study of the state of hormonal function. If the unfavorable background for the formation of cysts is not eliminated during therapy, the cyst may recur or form in another place.
Breast cysts can become inflamed, infected and fester. In such situations, patients develop signs of acute infectious inflammation.
Large and even giant cysts disrupt the structure of the mammary glands. In addition to the visible deformation of the mammary gland, pain is noted due to compression of the tissues surrounding the gland.
Diagnosis of a cyst
In order to diagnose a medium-sized breast cyst, standard palpation is sometimes sufficient for the doctor. If the formation is smaller, then an ultrasound or mammography will be required.
These two diagnostic methods differ from each other not only in the way they are performed, but also in the results that the doctor receives. Thus, ultrasound makes it possible to clarify whether there are cystic growths inside the mammary gland, and it is also possible to distinguish between a cyst and fibroadenoma. Based on the results of mammography, a conclusion can be made about their size, shape and exact quantity.
In addition, the patient may be recommended to undergo an MRI, however, this is performed only in severe cases. After all, there are still disputes between physicists regarding the safety of this procedure for the human body. Although everywhere this method is positioned as absolutely harmless.
In this regard, before going for diagnostics using a tomograph, you should make sure that it is really needed. If the doctor is not principled in this matter, then it is better to stop at mammography or ultrasound. This will definitely relieve the body of excess stress.
A biopsy is performed when there are papillomas inside the formation. A biopsy is performed under ultrasound control. This method is necessary to enable further histological examination. Based on its results, a cancerous tumor can be suspected (if the substance taken for examination is brown or brown in color, and also if a large number of epithelial cells are detected).
Causes of breast cysts
The functioning of the hormonal system in women is regulated by the central nervous system. This explains the formation of a cyst under the influence of psycho-emotional factors:
- Stressful situations
- Long intellectual overload (exams, scientific work)
- Psychological trauma
One of the common causes of breast pathology is a hormonal imbalance with the predominance of estrogens - female sex hormones as a result of:
- Menopause, menopause;
- Pregnancy, childbirth;
- Lactation;
- Uncontrolled use of hormonal oral contraceptives;
- Abortion;
Injuries and surgical interventions negatively affect the health of the breast. Thermal procedures (bath, sauna, beach, solarium) and exposure to ultraviolet radiation have a negative effect.
One of the provoking factors is poor nutrition, and, as a result, obesity. Excess body weight leads to hormonal imbalance and further health problems.
Treatment of breast cyst
First of all, a woman should contact a mammologist to undergo an examination and determine an effective treatment method. For the treatment of small cysts, adequate conservative treatment is selected. To do this, it is necessary that the size of the cyst does not exceed 0.5 mm. In this case, removal of the tumor is not required. First of all, the doctor directs all his actions to normalize hormonal balance. To do this, you need to undergo examination by a gynecologist, immunologist and endocrinologist.
In order for the cyst to resolve, modern medications or puncture of the cyst are prescribed. The doctor makes a puncture, pumps out the liquid and injects a solution to destroy the capsule. This method is suitable for the treatment of single-chamber cysts. If the cyst has atypical features, then surgery is prescribed, and the tissue removed during surgery is sent for histological examination.
Another method of treating cysts is aspiration. This is a procedure during which a thin cannula is inserted into the cyst cavity and the cystic fluid is pumped out through it. If there are no bloody impurities in this liquid, then treatment is not required. If streaks or even traces of blood are present, then additional research is required.
The cyst can be treated with hormone replacement therapy. To treat cysts, many doctors resort to a course of medications that are aimed at normalizing hormonal levels. In addition to this, this method of treatment also strengthens the immune system. Such treatment can cure the disease and prevent the recurrence of the cyst.
If, based on the results of observation, it becomes clear that the cyst is growing, it is drained. To do this, the cyst is punctured using a thin needle, the contents are aspirated, and either air or ozone is introduced into the resulting cavity. This conservative and low-traumatic method of therapy can be performed only when single-chamber cysts are detected that have not undergone malignancy and do not contain papillomas. In addition, you will need to undergo repeated mammological examinations every 6 months, as well as regular monitoring by a mammologist. This will allow timely detection of a possible relapse. The success of the operation depends on how completely the contents of the cyst are removed, whether there are cells in it that can grow, and ultrasound does not reveal fluid, then the possibility of relapse is reduced to 20%. However, when the fluid is retained and gradually accumulates, it will require repeating the procedure.
It is worth refusing to perform the operation in a clinic where a woman is offered to inject not ozone or air, but ethyl alcohol. This is an unsafe treatment method, which very often causes tissue necrosis. Therefore, it is so important to clarify all the aspects of the upcoming operation. Even air in this case will be preferable to administration than alcohol.
If a simple cyst is discovered, then most often it does not require surgery, but if a parietal formation is detected, a puncture is necessary. This will make it possible to exclude an oncological process. When there are no cancer cells, the woman is offered to undergo a vacuum biopsy. With its help, the growth is removed within half an hour, for which only local anesthesia is used. When cancer cells are still detected, more complex treatment is required in an oncology clinic.
If, after aspiration of the cyst and administration of ozone, relapses still occur, but there are no cancer cells, then such a formation must also be removed using vacuum aspiration.
How safe are such operations? There is no need to worry about having your breast removed if a cyst is found in it. As a rule, even large cysts are removed while preserving the mammary gland.
Surgeons strive to make as few incisions as possible, since every doctor wants to give the woman a minimum of aesthetic discomfort in the future. Therefore, most often such operations do not leave behind any visible traces.
The risk of malignancy varies from 1 to 4%. This is why it is so important to start treatment in a timely manner.
Sectoral resection leaves behind scars. This can further negatively affect breastfeeding due to destruction of the ducts. To avoid congestion, women planning to give birth should, whenever possible, avoid intervention.
Classification of breast cysts
Depending on what type of breast cyst a woman has formed, the clinical picture of the disease will depend.
Atypical breast cyst
Such a cyst has a fibrous capsule of round or oval shape of different sizes. An atypical cyst refers to benign neoplasms that have proliferation. The symptoms of this type of cyst will not be specific; rather, they are general.
Fibrous cyst of the breast
It occupies a central place in oncology and is a background disease in the development of breast cancer. This type of neoplasm in question in the mammary gland will be characterized by the following symptoms:
- increasing chest pain before menstruation;
- feeling of a foreign body in the chest;
- fluid is constantly released from the nipples;
- During manual examination of a breastfeeding woman, cluster-shaped nodular seals can be easily felt.
The reasons for the appearance of fibrous cysts in the mammary glands are not fully understood, but it is known that this process can be triggered by hormonal imbalance during menopause, weakened immunity and disruption of the functioning of certain organs.
Solitary cyst of the mammary gland
A formation of round shape and elastic consistency, containing liquid of various colors. The longer the cyst exists, the denser its capsule. A solitary cyst is a large cavity that is located only in one breast. The reasons for the development of this type of education are:
multiple abortions;
- heredity;
- endocrine disorders;
- late birth;
- heavy weight;
- woman's age over 35 years;
- chronic mastitis;
- complete refusal of breastfeeding;
- stress and psycho-emotional disturbances;
- breast injuries.
This type of breast cyst is manifested by severe pain in the chest, which is especially sensitive in the second phase of the menstrual cycle, burning and itching in the chest area. Interestingly, pain from the mammary gland can “radiate” to the shoulder blade, neck and shoulder, but as soon as a woman’s period ends, all unpleasant sensations disappear on their own.
Please note: a woman can identify a solitary cyst in herself - she just needs to palpate the mammary gland and determine the presence of a dense formation.
Ductal cyst of the mammary gland
Such a cyst develops at any age, but is more often diagnosed in women after 48 years of age. Despite the fact that there are no reliable facts, doctors are confident that a ductal cyst of the mammary gland is a full-fledged precancerous condition , but is classified as a benign neoplasm.
Provoking factors that contribute to the development of ductal cysts of the mammary gland include:
- ovarian dysfunction;
- hormonal disorders;
- a woman is overweight;
- endocrine diseases;
- frequent stress.
The main symptom of the presence of a ductal cyst in the mammary gland will be discharge from the nipples, which may have a green, brown or bloody tint , although it may be completely transparent. If this type of formation has formed in the area of the milk ducts, then it can be absolutely clearly identified by palpation of the mammary gland.
Multilocular breast cyst
A very unpleasant disease, which is characterized by the formation of multiple cavities around the main one. A doctor can determine this disease by conducting an ultrasound examination. The main reason for the development of this type of formation in the mammary gland is an unhealthy lifestyle, but there are also some provoking factors:
- poor nutrition;
- long-term use of medications;
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body;
- disruptions in the hormonal system;
- infectious diseases.
A multilocular breast cyst is dangerous because it can turn into a malignant neoplasm at any time.
Breast cyst: symptoms
Breast cysts are a fairly common benign formation among women. Such a formation very rarely develops into cancer, but it is imperative to carry out timely treatment and further examination by a mammologist.
This disease is encountered mainly by women who have crossed the thirty-year mark. Gynecologists recommend planning a pregnancy before the age of 30 in order to avoid problems with the formation of breast cysts in the future.
A small cyst (up to 2 centimeters) may not be detected and women can live with it all their lives. Only a mammologist can detect it during examination and based on the results of mammography. A larger cyst can be discovered by a woman herself when feeling her breasts before menstruation, or by a gynecologist during a routine examination. If the cyst has reached a large size, then it will definitely make itself felt.
Breast cyst pain
Due to the large tissue content, such a cyst causes pain and burning. As a rule, these symptoms appear before the onset of the menstrual cycle; if the case is severe, then pain always occurs.
It happens that the cyst grows over time. A small cyst the size of a pea can grow within two years to a size of several centimeters. As the cyst grows, pain will appear. At first, women will notice this only before the onset of menstruation, but later the pain will intensify.
Treatment of breast cysts with folk remedies
A neoplasm in a woman's breast made of connective tissue, filled with liquid contents, is called a mammary cyst. More often it is round or oval in shape. It can appear either one or many. The cyst is most often located in the upper part of the chest. It is usually benign in nature, but in advanced cases an inflammatory process occurs.
The reasons for the formation are very different - from untreated chronic gynecological or endocrine disease to unhealthy diet, lifestyle and stress. But the most common factor that provokes the appearance of a cyst is a hormonal imbalance in a woman’s body. Namely, excessive production of estrogen. In the early stages of the disease, symptoms may not be noticeable, but later pain and a burning sensation in the chest appear. A woman can identify a large cyst on her own during a breast examination.
Properties of medicinal plants
Treatment of the disease is carried out conservatively using anti-inflammatory, absorbable or hormonal drugs, as well as homeopathic and herbal medicines. Sometimes it is necessary to puncture the capsule with liquid to exclude the presence of an oncological process or removal by sectoral resection.
Along with the methods of classical medicine, there are a lot of folk methods for getting rid of cysts in the chest.
But it is important to remember that any treatment of the disease should be carried out under the supervision of a qualified doctor, in particular a mammologist. Self-medication of neoplasms is unacceptable, as this is fraught with serious consequences for the woman.
You should take any decoctions of medicinal plants at home only after consulting a doctor and conducting a study of the patient’s hormonal levels. It is important to know the concentration of which hormones are increased or decreased in the blood in order to use the right remedy. Otherwise, you can only harm yourself and worsen the disease. It has long been known that some plants contain phytohormones, which, when entering the body, do not help in the treatment of cysts, but, on the contrary, contribute to its development. But there are a number of medicinal herbs that suppress hormone synthesis.
Types of plants that reduce estrogen production:
- marsh calamus;
- dandelion officinalis;
- ordinary bruise;
- parsley seeds;
- sparrow;
- oxwort officinalis.
All varieties of cabbage (white cabbage, broccoli) have the ability to suppress the secretion of prolactin. They can be consumed boiled or raw (salads), or as compresses on the chest. Cabbage juice also improves metabolism, liver function, and helps reduce weight, which is important when treating cysts, since adipose tissue is a source of estrogen.
It is good to use motherwort herb as a sedative. To do this, infuse in the proportions of two tablespoons of grass (previously dried and crushed) per 400 ml of boiling water. Filter, add boiled water to the initial amount and drink throughout the day.
To improve metabolism during illness, the following is used:
- chamomile;
- fennel;
- black elderberry;
- peppermint;
- Linden blossom.
Treatment of breast cysts with rubbing and compresses
Traditional recipes for the treatment of disease mainly contain components that are available to every person and collecting them will not present any difficulties.
The most common compresses that will help fight the disease at home:
- From cabbage leaf. The preparation is quite simple, you need to take a clean, fresh cabbage leaf, slightly mash it in your hand to release the juice. Then wrap it in gauze and apply it to the affected breast overnight. Secure with a bandage or bra. Cabbage has long been known for its healing properties and relieves inflammation well.
- From beets. To do this you need to prepare beetroot pulp. Grind or grate fresh beets in a blender. Then heat it in a water bath for about 15 minutes and add, stirring well, 9% vinegar (calculated at 1 tablespoon per 100 grams of beet mass). The resulting mixture is applied to the affected area, covered with gauze and bandaged, it is better to leave it overnight. By morning, the breasts should be washed with soap and wrapped in a warm towel or scarf.
- From St. John's wort. It relieves pain well and resolves formation. You need to take 30 grams of dry leaves, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave for about 15 minutes. Prepare cotton napkins, folded in four, moisten them with the solution and apply to the chest for at least 8 hours or until completely dry. St. John's wort can also be replaced with sweet clover.
- From burdock. Take crushed burdock root in a ratio of 10 grams per glass of boiling water. Infuse in a tightly closed container for 2 hours, then strain and also apply a compress. This is exactly how an infusion of large-leaved gentian is prepared (sold in a pharmacy).
- From common toadflax. You just need to grind the grass with sunflower oil and rub it into the skin in the place where the seal is localized.
- From carrots. The root vegetable is crushed on a fine grater, then the resulting mass is spread on gauze and a compress is made on the chest, as in previous cases. You need to change it at least three times a day.
- Celandine ointment. Mix celandine leaves with ghee in equal proportions and lubricate the area where the cyst is located. Wash off no earlier than after 4 hours so that the ointment is well absorbed.
Tinctures for oral administration
The following tinctures have also proven themselves very well in the treatment of breast cysts:
- From walnut shells. You need to take 15 shells, crush them and place them in a half-liter jar, then pour in 500 ml of alcohol or vodka and leave for more than a week in a dark, cool room.
- From chaga (birch mushroom). Slows down cell division in neoplasms. To prepare the infusion, you need to take one part of the crushed mushroom and add five parts of cold water, leave for a day and take orally before meals. This remedy should not be abused, otherwise the growth of healthy cells may slow down.
- From burdock root. The infusion can be used as a compress or taken orally.
- Garlic with sunflower oil. Has properties of accelerating blood circulation and healing. The juice from three cloves of garlic is poured into half a glass of sunflower oil and left for 24 hours in a cool place. Take for 2 weeks.
- Kalanchoe with honey. It is necessary to take the crushed leaves of the plant and liquid honey in equal parts, grind everything until a homogeneous mass is obtained. Take orally before meals. Kalanchoe is a strong natural antiseptic.
Treatment with folk remedies has proven its effectiveness over the years. Very often they are used together with traditional medicine methods. But the maximum positive effect is achieved in complex therapy of breast cysts under the supervision of a doctor.
We recommend reading:
grud03.ru
Causes of inflammation of breast cysts
At the beginning, the cyst does not cause concern to the woman. However, over time, the inflammatory process begins. Also, a benign formation can degenerate into malignant. Various negative factors contribute to this.
The causes of inflammation are:
- progression of the cyst and filling it with viscous secretion
- disruption of the hormonal system
- menopause
- taking certain medications
- poor hygiene
- stress and depression
- hypothermia
- injury
- metabolic disease
- ovarian dysfunction
- endocrine and thyroid diseases
In most situations, the development of the inflammatory process is facilitated by excessive production of estrogen. Hormonal instability is the main cause of inflammation. The use of hormonal contraceptives can also provoke pathology. The use of hormonal contraceptives for more than five years provokes the development of cancer and inflammation in the mammary gland.
The emergence of a pathological process is facilitated by abortion, poor diet, and passion for thermal procedures and tanning. Risk factors also include chest injuries and bruises. A woman should not stay in the sun for a long time without a swimsuit or work near heat sources in workshops.