- Menstrual irregularities
- Infertility
- Pain during intercourse
- Painful periods
- Bloody discharge after sexual intercourse
- Increased vaginal leucorrhoea
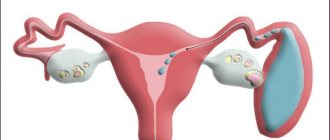
Cervical ectopia is a disease that develops in women when columnar epithelium moves to the part of the uterus located directly from the vagina. Normally, columnar epithelium lines the cervical canal, and only when it is influenced by various unfavorable etiological factors of the endogenous and exogenous type can it begin to grow.
- Etiological factors
- Varieties
- Symptoms
- Ectopia and pregnancy
- Diagnostics
- Therapeutic measures
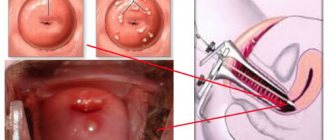
This disease can be detected through a gynecological examination. Visually, an area of overgrown columnar epithelium will appear on the neck as a large red spot that does not have clear boundaries. It is worth noting the fact that in case of progression of cervical ectopia, the epithelium of the cervix of the reproductive organ will not be damaged.
In the medical literature you can also often find other names for this pathological process, such as:
- glandular muscle hyperplasia;
- endocervicosis;
- false erosion;
- pseudo-erosion.
Medical statistics today are such that cervical ectopia is diagnosed in 40% of the total number of representatives of the fair sex. It is also worth noting that 11% have a congenital form of this pathology. Most often, the disease is detected in women who have not yet reached the age of thirty - this is the main risk group. Many people are sure that cervical ectopia is a precancerous condition. This is actually not true. This pathology does not independently develop into oncology, but against its background the chance of progression of the malignant process increases several times.
What is cervical ectopia
Ectopia (pseudo-erosion, false erosion, endocervicosis, glandular-muscular hyperplasia) is a lesion of the mucous membrane in the cavity of the uterine cervix. The pathology is characterized by displacement of the columnar epithelium (which lines the cervical canal) to the vaginal part of the cervix. In 12% of all identified cases, false erosion is congenital. If she has no symptoms, treatment is usually not required. In the complicated stage of progression, rapid and appropriate therapy is necessary. Ignoring the advanced stage of cervical ectopia is the first step towards the development of cancer and various inflammatory processes.
Ectopic formation
There are two ways to form ectopia. The first is considered the main one, when on the vaginal surface of the cervix (ectocervix) a cylindrical epithelium is formed from reserve cells, lining the canal of the cervix (endocervix).
In the second case, ectopia occurs as a result of the replacement of stratified squamous epithelium with single-layer columnar epithelium originating from the cervical canal against the background of cervical diseases (inflammatory or traumatic origin). This is a secondary way of forming ectopia.
Indeed, during a routine examination of the cervix in the speculum, erosion looks like a defect in the mucous membrane, where the epithelium is supposedly absent, i.e., “corroded” or “ulcerated.” Therefore, before the latest research methods began to be used, cervical erosion was considered a pathology.
It was believed that erosion needed urgent treatment. Moreover, a defect in the mucosa was given great importance as a disease leading to cervical cancer.
When cervical erosion was detected, treatment procedures were immediately prescribed. Doctors feared that, against the background of untreated cervical erosion, a cancerous tumor would sooner or later arise, so they recommended not to delay treatment. But this is far from true.
In fact, this area, as we found out above, is covered with red columnar epithelium. This is his normal color. The epithelium of the ectocervix is pale pink.
Columnar epithelium appears in a place not intended by nature. This is a kind of seizure of territory under the influence of a disruption in the formation and release of sex hormones or as a consequence of hormonal “feeding” of the body.
Moreover, the transformation zone can either increase or decrease. The observed island with ectopia is like a scarlet rose petal lying alone among densely scattered light pink petals.
Thus, the area replaced by columnar epithelium only superficially resembles erosion, standing out in bright red color against the gray-pink background of the mucous membrane.
Ectopia is clearly visible during colposcopy (under magnification). In the absence of an inflammatory reaction, treatment of ectopia as such is not carried out. Currently, the treatment of erosion is approached individually, in accordance with the characteristics of the functioning of the female body, taking into account different age stages, detection of signs of the presence of human papillomavirus infection (genital warts), etc.
Top
Classification
Depending on the origin, the disease is divided as follows:
- Congenital (present from birth and does not cause discomfort);
- Acquired (occurs as a result of exposure to any negative factors).
In addition, ectopia can be:
- Uncomplicated – considered an individual physiological condition, not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms and does not require urgent treatment;
- Complicated – formed as a result of exposure to external factors (trauma, infection). Requires immediate therapeutic intervention.
Pathomorphology
Histologically, glandular, papillary ectopia of the cervix and pseudoerosion with squamous metaplasia are distinguished. With glandular ectopia, accumulations of glands with an extensive network of glandular ducts and signs of inflammation are detected. With papillary ectopia, there is a proliferation of stromal components and the formation of papillary structures covered with columnar epithelium.
Healing of cervical ectopia is accompanied by the reverse replacement of the columnar epithelium with cells of mature squamous epithelium, i.e., the formation of a transformation zone. This process involves reserve cells, which, as a result of differentiation, first turn into immature and then mature metaplastic epithelium.
Causes
The causes that provoke the occurrence of the disease are considered:
- Hormonal imbalance (pregnancy, menopause, puberty);
- Incorrect use of hormonal contraceptives;
- Entry of dangerous microorganisms into the female body (streptococci, chlamydia, human papillomavirus (HPV), E. coli, etc.);
- Surgical interventions in the pelvic organs (artificial termination of pregnancy, diagnostic procedures, operations).
Often, cervical ectopia occurs after childbirth. This may occur due to intense hormone synthesis during this period or due to mechanical damage to the mucous membrane of the uterine cervix.
Treat or observe ectopia
Ectopia in reproductive age, as in puberty, is not a disease, but rather a deviation from the normal state of the cervix, but only if it occurs without signs of inflammation and dysplasia.
However, we must not forget that the cervix with ectopia is more susceptible to infection than the cervix without ectopia. Single-layer columnar epithelium is not adapted to protect the mucous membrane of the cervix from infection, unlike stratified squamous epithelium.
Erosion can become complicated, so it is necessary to undergo regular monitoring by a gynecologist. The absence of inflammatory and pathological processes is determined by colposcopy.
Treatment is required in the presence of symptoms (excessive mucus secretion, bleeding) or in the case of complicated erosion, when an infection is attached, in combination with dysplasia, etc.
If there is no effect from conservative or drug treatment, other methods are used to destroy the focus of ectopia, including coagulation and surgery (laser therapy, diathermocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser destruction, etc.).
Top
Symptoms
In an uncomplicated course of the disease, there are no symptoms. In this case, it is possible to detect the presence of ectopia only during a routine gynecological examination. If a complicated form of pathology progresses, the woman may be worried about the following signs:
- Increased secretion of secretory fluid from the vagina, which is accompanied by a strong and unpleasant odor;
- Menstrual irregularities;
- Feeling of discomfort in the affected area;
- Pain and minor bleeding during mechanical impact on ectopia (sexual intercourse, gynecological examination, etc.);
- Feeling of itching and pain in the area of the external genitalia;
- Long-term inability to conceive a child.
If the symptoms described above appear, you should visit a doctor who will conduct a diagnostic examination and give the necessary clinical recommendations for eliminating cervical ectopia.
Severe disease is considered a precancerous condition of the body. If treatment is not carried out in time, false erosion can lead to cancer.
Ectopia and pregnancy
Ectopia can be diagnosed during pregnancy. Some women believe that this is not a dangerous condition, but in fact, everything is exactly the opposite. It is important to understand that the disease often manifests itself due to the presence of inflammatory or infectious pathologies, which can aggravate the course of pregnancy. The reason is that from the vagina, through the affected cervix, infectious agents can penetrate directly into the reproductive organ, which will cause infection of the amniotic fluid and the fetus itself. Ectopia during pregnancy is fraught with the following consequences:
- abortion;
- fetal death;
- premature birth;
- infection of the child during its passage through the mother’s birth canal;
- child development delay;
- the formation of various defects in the fetus.
It is also worth noting that the presence of ectopia during pregnancy increases the likelihood of rupture several times.
Pregnancy occurs with constant hormonal changes, and as mentioned above, the epithelium can also grow due to a hormonal imbalance. From this we can conclude that pregnancy, in some way, increases the likelihood of aggravation of the disease. This often leads to dysplasia and precancerous pathologies.
It is important to constantly monitor the situation during pregnancy - regularly visit specialists in order to blunt the progression of the pathology and not start it. Also, during pregnancy, self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Diagnostics
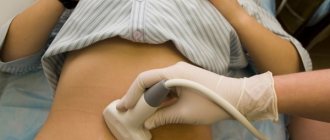
To diagnose ectopia, an examination is first performed on a gynecological chair. Secretory fluid from the vagina and a cytological scraping of the affected area are taken for analysis to study its structure and the possibility of transformation into a malignant tumor. To confirm the diagnosis, additional procedures are performed:
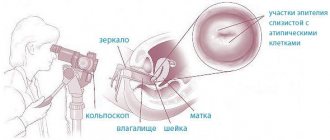
- Extended colposcopy (examination of the cervix using a magnifying optical instrument).
- Polymerase chain reaction test (detects the presence of infectious microorganisms).
- Biopsy. Using a special instrument, a small part of the damaged epithelium is taken from the cervical cavity for analysis to identify cancer cells and infectious agents.
- Diagnostic curettage. Using an endoscope, the doctor scrapes off the mucous layer of the cervix and sends it for a detailed examination.
The material obtained during a biopsy or diagnostic curettage is submitted for histological examination; it is studied under a microscope to detect changes in the structure of the tissues.
Based on the results of the diagnostic examination, the most appropriate method of therapy is determined.
Diagnostic methods
In most cases, the diagnosis of cervical ectopia is made during a routine preventive examination.
When making a diagnosis, pay attention to complaints (bleeding, pain, increased vaginal discharge, etc.), life history (use of contraceptives, abortion, gynecological diseases. After collecting the history, a physical examination of the patient is performed.
Bimanual examination does not reveal any deviations from the norm. When examined in a mirror, ectopia looks like a bright red spot, may bleed, and the vaginal part of the cervix is swollen.
Additional research methods:
- Cytological smear (Pap test, Papanicolaou smear) is a method of examining the cervix, used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes. Cytological examination is carried out by opening the vagina using speculum, collecting material with a special brush, and then examining slides under a microscope. The test is considered an effective, widely used method for the early detection of precancerous lesions and cervical cancer.
- Colposcopy is a diagnostic procedure that is performed using a colposcope (an optical instrument equipped with a camera and lighting). The colposcope provides multiple magnification of the areas needed for study and allows you to visually distinguish normal cells from altered ones.
- Extended colposcopy is a method of examining the mucous membrane of the cervix, which involves the use of various special tests. Among them is the use of various solutions and filters (chromoscopy): Extended colposcopy using a 3% acetic acid solution : after examination with a colposcope, “suspicious” areas are treated with acetic acid. Fragments with dysplasia change their color to white, healthy areas remain pale pink.
- Schiller test: after examination, pathological areas are treated with iodine. In this case, normal areas of the mucous membrane change their color to brown, as they contain a sufficient amount of glycogen. Atypical areas lacking this substance do not change their color.
- Chromoscopy: during this manipulation, a green and blue filter is used. The more dangerous the pathology of the cervix, the thicker the capillaries and the more randomly they are located.
All of the above research methods play a certain role in deciding on treatment tactics.
Treatment
Treatment methods are selected individually for each woman, depending on her age, general health and desire to have a child in the future.
The asymptomatic course of the disease most often does not require therapy. The doctor simply recommends that the patient undergo periodic gynecological examinations and monitor the condition of the affected mucous membrane of the uterine cervix.
If cervical ectopia rapidly develops in a nulliparous woman, then a treatment method is selected that does not affect reproductive function. As a rule, conservative therapy is prescribed - taking pharmacological drugs aimed at regenerating altered tissues, eliminating unpleasant symptoms and combating pathogenic microorganisms. For this, vaginal suppositories are prescribed, which have an antimicrobial, regenerating, soothing and anti-inflammatory effect. Doctors may also prescribe tampons containing special medications to be inserted into the vagina. They eliminate inflammatory reactions and provoke rapid restoration of the epithelial layer of the damaged area. If cervical ectopia is diagnosed, which is provoked by pathogenic microorganisms (streptococci, staphylococci, HPV, chlamydia), then in addition to the main treatment, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
If conservative therapy does not help, then physiosurgical treatment is carried out, which accelerates tissue regeneration and does not in any way affect the woman’s reproductive function. The following are considered safe and highly effective methods:
- Cryodestruction is the effect of liquid nitrogen on the affected area, during which atypical tissues are frozen;
- Laser coagulation is a non-contact treatment method in which the ectopia is cauterized with a laser beam;
- Radio wave coagulation is the effect on atypical tissues using radio wave rays, which provoke sealing of the injured area of the uterine cervix.
The use of these methods is not fraught with the formation of scars and other defects on the mucous membranes, which may further interfere with normal conception, gestation and birth of a child.
If a woman does not plan a pregnancy in the future, then other methods are used. They are widely used in medicine, but provoke the formation of scars, which can negatively affect the dilation of the cervix during childbirth. These include:
- Diathermocoagulation is a quick and highly effective elimination of pathology by exposing it to high-frequency current. As a result of the procedure, the cervix may undergo narrowing or scarring of the mucous tissue;
- Surgical intervention - the doctor, using a scalpel, independently removes the atypical tissue of the uterine cervix. This type of therapy is also fraught with damage to the epithelium.
If cervical ectopia is detected during pregnancy, the doctor recommends postponing treatment measures for a while so as not to harm the fetus.
During pregnancy
During the period of bearing a baby, a woman’s hormonal levels change significantly, which may well provoke the appearance of disorders.
This situation is considered as a variant of the norm, and in the absence of other pathologies of the female genital organs, there is no need to worry about the presence of this disease.
With cervical ectopia, both pregnancy and childbirth can proceed quite normally, without posing a threat to the health of the mother or fetus.
In addition, the appearance of a red spot on the cervix is a consequence of the body’s normal preparation for the birth of a child.
After the baby is born, there will be no trace of the pathology left - the tissue of the epithelial layer will return to normal on its own, without medical intervention.
The disorder does not cause any specific symptoms in pregnant women. The place does not bleed, does not hurt, does not itch.
The appearance of columnar epithelium in pregnant women on the surface of the cervix during pregnancy can only be detected through a gynecological examination or using colposcopy.
The disorder can make itself felt if it is joined by other abnormalities - inflammatory processes, cancerous degeneration of tissues.
Electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, physiotherapy for endometriosis Vacuum aspiration of the contents of the uterine cavity Bend of the cervix - causes and consequences Interpretation of cytological examination of cervical smears
Prevention and prognosis
Prevention of ectopia is aimed at observing the following rules:
- Visit a gynecologist systematically (at least 2 times a year);
- Monitor genital hygiene;
- Avoid frequent changes of sexual partners;
- When using oral contraceptives and medications containing hormones, strictly adhere to the instructions for their use;
- Use condoms during unplanned sexual intercourse (they will help prevent sexually transmitted diseases);
- Consult a doctor promptly if any symptoms of pathology appear.
In most cases, with timely treatment, ectopia is completely eliminated without health complications.
Causes of combined pathology
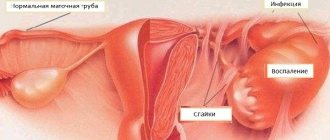
Cervical ectopia of the cervix together with chronic cervicitis can have a different nature, arising due to:
- Viral infection. The most dangerous among all is the papillomavirus, because it easily invades epithelial cells and causes dangerous changes leading to precancerous conditions, primarily;
- Bacterial infections, most often transmitted from a sexual partner. The most common cause of cervicitis with ectopic lesions of the cervix is;
- Inflammation of the external genitalia and vagina. , colpitis, easily turns into cervicitis and subsequent ectopia;
- Changes in vaginal microflora due to lack of cleanliness. The proliferation of pathogenic bacteria and a decrease in the activity of the protective biocenosis leads to a weakening of the mucous membrane of not only this organ, but also the cervical canal, and therefore its external part;
- Incorrect antibiotic therapy. These drugs can also negatively affect the vaginal microflora. The disturbed balance of beneficial and opportunistic bacteria reduces the protection of tissues and their proper development;
- . Excessive growth of cervical canal epithelial cells is caused by high concentrations of estrogen. The reason for this may also be an incorrectly chosen contraceptive;
- Associated pathologies. These are mainly diseases of the urinary system. Located close to the reproductive organs, it easily transmits bacteria to them. Other systemic diseases that affect metabolic processes and hormonal levels also weaken the epithelium.
Cervical ectopia can cause chronic cervicitis itself if it is congenital. Columnar cells are more susceptible to destruction than squamous epithelium. Their presence on the cervix makes it more vulnerable even to bacteria present in the vagina. The onset of sexual activity can also be marked by mechanical damage to the epithelium. As a result, inflammation spreads from the outer part of the cervix and passes into the cervical canal.
Symptoms of the disease
The development of ectopia, in other words, erosion, is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Appearing uncharacteristic pathological discharge after menstruation.
- Unpleasant odor from the vaginal area.
- Changes in discharge of ambiguous color.
- Painful sensations during sex.
- Constant itching in the vagina.
With ectopia, itching appears in the vagina
The difference between ectopia and erosion
Ectopic cervix occurs when columnar epithelial cells, normally located inside the cervical canal (the entrance to the uterus), grow to replace the squamous epithelium, the upper layer of the cervix.
Tissues formed by columnar epithelium produce a secretion that protects the uterus from infections and bacteria. The role of flat epithelial cells is protection from mechanical damage and maintaining the shape of the organ. In 40% of women, changes occur in the cellular composition, and cylindrical cells move to the lower part of the cervix.
These signs may indicate cystitis, adhesions, and many other urogenital diseases.
Ectopia of the cervix in the photo
Variants of ectopia
Ectopia in the cervical canal
Treatment methods for Ectopia
Many women believe that ectopia and erosion are the same thing. These are two completely different conditions that require different treatment approaches, so determining which one you are diagnosed with is very important.
With ectopia, the tissue of the cervical canal shifts closer to the vagina, which leads to eversion of the inner layer and its visualization during a gynecological examination. In itself, the mechanical shift of the epithelium is not dangerous and may not interfere with the quality of a woman’s daily life.
With erosive lesions, injury to the mucosa and disruption of its integrity are observed. This is accompanied by an inflammatory process, and often infection. Simultaneously with erosion, a woman may be diagnosed with cervicitis and colpitis. Erosion requires treatment and during pregnancy can pose a danger to the health of the fetus; an infection develops at the site of inflammation.
Types of pathology
- Congenital erosion of the cervix. Ectopia can be found in newborn girls or in adolescents during menarche. This is considered a variant of the norm until full puberty. Gradually, the columnar epithelium is replaced by stratified squamous epithelium; if this does not happen, a diagnosis of congenital pseudoerosion is made. In this case, treatment is not required, it is only important to undergo observation every six months to a year. Congenital erosion can be compared to congenital skin defects, such as birthmarks, that do not affect body functions.
- Acquired pseudo-erosion. Pathology appears over time. The area with replaced cells looks like a red spot. The affected area may increase over time, and cysts and papillomas may form on it.
- True erosion. Reaction to inflammation or injury. The cylindrical cells covering the neck are destroyed, exposing the lower layers of tissue. Erosive lesions resemble shallow ulcers. Because mucosal cells regenerate (restore) well; erosion usually heals in 5-7 days. Non-healing true erosion is rare and requires observation and treatment.