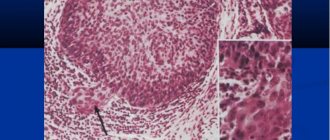
The symptom of itching a certain part of the body is called pruritus in medicine. It, like pain, is an attempt by the body to convey to a person’s consciousness that there is a problem in him that requires an urgent solution. To some extent, itching can be called a protective reaction, since such mechanical stimulation of the pathological focus helps to shake off parasites, poisonous plants or stinging insects.
Often itching is caused by individual intolerance to some substance that gets either on the skin or inside the body - through the mouth or by injection. It can occur due to thermal, mechanical or electrical stimulation of skin receptors. The symptom also indicates an excess of substances in the blood other than histamine, which appears during allergies. Some of these diseases can be life-threatening.
Where does the itching sensation come from?
The imperative desire to scratch an area of skin occurs when blood with a high concentration of dissolved substances flows to the pain receptors (nociceptors), spread out in the form of a network under a layer of epithelial cells:
- histamine and/or histidine. These substances are formed in excess by immune cells when certain – specific to each organism – foreign proteins enter the body;
- bile acids produced in the liver. They enter the skin cells and cannot leave them when a condition such as cholestasis develops - when bile cannot completely enter the duodenum and is forced to stagnate in the cells of the liver and biliary tract;
- serotonin is a substance formed from an amino acid, which, when released, leads to a significant contraction of smooth muscles located in blood vessels and internal organs. This is a neurotransmitter, that is, a chemical compound that allows communication between nerve endings (the signal passes from nerve to nerve not like electricity, but rather like a bubble with a chemical substance, depending on the structure of which the activity of a neuron can be inhibited or activated). Its structure is very similar to the psychoactive hallucinogen LSD;
- cytokines – molecules that enable “communication” between immune cells;
- endorphins – natural pain-relieving molecules;
- nitrogenous wastes that accumulate in the blood during kidney disease;
- some other bioactive substances: thyroid hormone calcitonin, pancreatic enzymes (trypsin, kallikrein), VIP neuropeptides and substance P.
Since each person’s body has its own characteristics, no direct connection has been identified between the concentration of the above substances and the severity of the need to perform mechanical stimulation. Thus, severe itching in one individual may accompany the initial stage of renal failure, while in another it will not appear even with the terminal stage of uremia.
Only the skin and those mucous membranes, the layer of epithelial cells in which is in contact with the external environment and is located near the skin: gums, tongue, genitals, are “subject to itching”. The signal from the pain receptors located underneath them travels along type C and A-delta nerve fibers, reaches the spinal cord and, together with its structures, is delivered to the brain, to its sensitive zone.
Itching can be of a different nature: from a mild “tickling” to severe, painful. Its nature dictates to a person how to “process” its localization:
- scratch: this is more typical for skin pathologies such as neurodermatitis or eczema;
- rub gently: inherent in lichen planus;
- cool (typical for acute urticaria).
However, a diagnosis cannot be made based on these characteristics alone. In determining the cause of itchy body skin, the following are important:
- its localization;
- the condition of the skin at the site of such sensations;
- conditions for the appearance and relief of itching;
- additional symptoms.
Let’s consider the combination of these factors to make it easier to get examined and choose exactly the specialist who can quickly alleviate your condition.
Why do people itch?
During the scratching process, a person performs a kind of massage on the affected area of the body. It accelerates blood flow and lymph movement, removes dangerous substances and irritation of nerve endings. Itchy skin can be a physiological sensation in a completely healthy area of the body, which occurs due to the fact that metabolic products have simply accumulated in one area. There are no visual manifestations here, the feeling of discomfort passes quickly.
In the world of medicine, itching of the skin is usually divided into several types:
- Common, when the whole body will itch;
- Universal, when unpleasant sensations will be localized in a specific area.
Both types can be periodic or permanent. The intensity of itching can vary, from insignificant to very significant. If the manifestation is strong, the person may lose appetite and sleep. He will want to scratch the affected areas constantly, tearing the skin until it bleeds.
Most often the “itch comes” at night and in the evening hours. Why? Because at this time blood circulation is increased due to vasodilation. Cells receive more heat, especially when a person lies in bed. The breakdown products of substances enter the tissues and cells of the epidermis faster.
Types of itching
The prevalence of the symptom is the main criterion from which the diagnosis of the cause of skin itching begins. Based on this measure, pruritus (the so-called itching in medicine) may be:
- Localized (a person can indicate a specific place where itching is felt).
- Generalized (throughout the whole body, not necessarily at the same time).
Generalized itching
- Diseases of the liver and biliary tract: hepatitis, cirrhosis, pancreatic cancer, cholestasis of pregnancy, giardiasis.
- Kidney failure.
- Presence of worms in the intestines.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Gout.
- Diabetes.
- Hypovitaminosis A.
- HIV infection.
- Oncological diseases: stomach cancer, multiple myeloma, erythremia, iron deficiency anemia, leukemia, lymphogranulomatosis, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Mental illnesses: depression, phobias, mnemoderma (itching associated with the mention of biting and stinging parasites).
- Senile itching.
- Itching when going up to altitude.
- Associated with neurological diseases: brain tumors, multiple sclerosis.
- Seasonal itching.
- For systemic pathologies, for example, periarteritis nodosa.
Localized itching
| Localization | Causes |
| On the face |
|
| On the head |
|
| In areas subject to friction | Bullous pemphigoid |
| On the crooks of your wrists | Atopic dermatitis, lichen planus |
| In the anal area |
|
| In the genital area |
|
| In areas covered by clothing most of the year | T cell lymphoma |
| On the back, on the hips | Folliculitis |
| On the knees | Atopic dermatitis |
| On hands | Scabies |
| Anywhere | Neurodermatitis, eczema, contact dermatitis, insect bites |
Itching accompanied by changes in the skin
This symptom indicates pathologies that are within the competence of dermatologists. That is, local changes are accompanied by skin diseases that are less dangerous than systemic diseases.
Diseases accompanied by redness of the skin
Itching and redness of the skin are more typical for inflammatory or allergic diseases. This:
- Contact dermatitis: irritation and itching located in the area that came into contact with the allergen. The boundaries of redness are clear. To diagnose, you need to remember what new places you have been to, what new household chemicals you started using, what clothes or accessory you put directly on your skin. So, redness in the armpits may be associated with wearing a new woolen sweater/dress or clothes that are familiar, but washed with a new powder. And itching of the skin of the hands - using a new cream or other chemical product. A characteristic feature of this disease is the complete disappearance of symptoms after the allergen ends.
- Atopic dermatitis is a disease that most often affects children, but atopic dermatitis can also occur in adults. Its causes are an allergen, most often taken orally with food. In children, redness is located mainly on the skin of the face (on the cheeks), the flexor surface of the knees and elbows. In adults: the face is excluded, wrists, knees and elbows may turn red - on their bends.
Combination of itching and rash
If such blisters protruding above the cover appear after mechanical friction of this area - dermographic urticaria
| Disease | Type of rash | Localization, features |
| Contact dermatitis | Redness with a clearly defined border; there may be blisters at the top of the redness | Anywhere. Can recall contact with clothing/accessory/chemical |
| Redness that has a border, protrudes above the skin level, and tends to merge with each other, similar to a mark left by a nettle. | Anywhere | |
| Bullous pemphigoid | Initially, redness rises above the skin, after which a bubble of tense properties appears in this place | In places where friction occurs with clothing or accessories (bag belt, watch belt) |
| Eczema | At first there is redness and swelling, which have a clear shape, then bubbles appear, some of which open, and crusts develop in their place. Elements of several stages are observed in one place (redness, blisters, crusts) | Symmetrical areas of skin, most often on the extremities (especially the upper ones), as well as the face |
| Limited neurodermatitis | Dry plaques, around which there may be red spots that do not have clear boundaries with healthy skin | On the sides of the neck, in the folds |
| Neurodermatitis diffuse | In adults - dried spots on the skin, surrounded by a reddish rim, without a sharp transition to healthy skin | Eyelids, feet, lips, hands. May be all over the body. |
| Swelling and redness, swelling and peeling, there may be red rashes, blisters or crusts on top | In children - after the introduction of complementary foods - on the cheeks, collar area, upper limbs | |
| Small spots of various shapes protruding above the skin, shiny | At the 2nd year of life, located in the area of the folds | |
| T cell lymphoma | Red rash on the skin, accompanied by itching, oval | In places not exposed to sunlight |
| Lichen planus | Violet, polygonal shaped polygonal polygonal granules with scales that rise above the healthy cover | Flexion surface of the wrists |
| Folliculitis | Bubbles and pustules | Hips, back, chest |
| Psoriasis | Silvery plaques with peeling on top | Extensor surface of the extremities, itching of the scalp and neck, palms and soles |
| Scabies | Paired black dots are visible | Arms, armpits, stomach, genitals |
Treatment
Treatment for itchy skin is prescribed after an examination, the purpose of which is to identify the cause of this condition. The main tests that will help clarify the ethology will be:
- general urine and blood tests;
- blood glucose;
- skin scraping to identify fungi;
- liver and kidney tests (blood);
- test for occult blood in stool;
- detection of helminth eggs in feces.
While the tests are being performed, to alleviate the symptoms of itching - if there are no signs of renal or liver failure, which the doctor must tell you about - antihistamines are prescribed: "Eden", "Fenistil", "Diazolin", which do not cause drowsiness, or more powerful drugs, but with this effect (“Suprastin”, “Tavegil”).
For a localized lesion, an antiallergic ointment for skin itching can be used, for example, Sinaflan, Akriderm, Apulein, hydrocortisone ointment or other corticosteroids. Sometimes other local drugs of non-hormonal origin are prescribed - “Prograf” or “Elidel”.
If itching is caused by cholestasis, bile acid-absorbing drugs have been used successfully. When the cause of the symptom lies in a blood disease, specific drugs are used - monoclonal antibody inhibitors. Psoriasis is treated by combining local and systemic medications that normalize skin cell division.
In case of extremely severe itching, weak opiates are prescribed, and treatment is supplemented with hirudotherapy, ultraviolet irradiation of the skin and acupuncture.
Thus, the causes of itching of the scalp and body are varied. Most often, these are various allergic reactions both to a substance that has entered the body and to a substance that has touched the skin. But there may also be life-threatening kidney diseases, liver diseases, or even blood diseases. To clarify the cause and select treatment, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination.
Skin itching is a specific unpleasant sensation that causes the need to scratch the affected area. This is not an independent disease, but only a symptom, which most often indicates damage to the skin, nervous system or internal organs.
Do I need to contact specialists?
Sores on the head in the hair require competent consultation with a specialist. Only a doctor can determine the cause of the pathology. If you have a problem with the scalp, you should contact a trichologist. The doctor will conduct appropriate studies and prescribe a treatment regimen.
You should contact a trichologist in the following cases:
- excessive hair loss;
- the appearance of coarse hair;
- excessive oily scalp;
- hair gluing;
- dry skin;
- peeling;
- a feeling of tightness and discomfort in the scalp;
- redness;
- the appearance of oval or round plaques;
- itching
A visit to a trichologist is also necessary if inflammation in the form of pads filled with pus is visually visible. This indicates pathology of the hair follicle.
If your head starts to itch, you should get examined by a trichologist.
Doctors who deal with such problems are a trichologist and a dermatologist. As a rule, people are reluctant to go to the doctor if they have an itchy head. They try to eliminate the discomfort on their own, although at this time special drug treatment may be needed.
Parasitic diseases are not only very unpleasant, but also fraught with complications in the form of various infections. For example, typhus is transmitted by lice from an infected person to a healthy person. Therefore, when identifying insects or nits themselves, you should contact a specialist, especially if we are talking about a child. If your baby has been actively scratching her head lately, you need to go to the doctor as soon as possible.
When your head itches but there are no lice, you need to be tested for the presence of demodex mites. These mites do not appear on the surface of the head and are difficult to identify. But it is undoubtedly necessary to treat this disease, since it leads to skin poisoning by the waste products of the parasite.
Other, non-parasitic diseases also adversely affect the appearance and health of skin and hair. They can weaken the local immune defense, and when scratched, they can contribute to the introduction of infections into the wound. Left unattended, burning and itching of the head, provoked by internal diseases and hormonal changes, can cause complications.
Infections of bacterial or fungal origin lead to a weakening of the general immune system and can cause a violent inflammatory process not only on the scalp, but also in other organs. An itchy area of the head becomes a source of pathogens spreading throughout the body.
And one more aspect, also important for any person who cares about his appearance. Diseases accompanied by severe itching of the scalp have a bad effect on hair growth and nutrition, so the hair becomes unhealthy in appearance and seems unkempt. And people who scratch their heads all the time, even if there are no lice, look completely unaesthetic.
Causes of itchy skin
The mechanism of skin itching is not as simple as it might seem at first glance. It is based on a chain of successive nervous and humoral reactions in the skin, and this chain can be triggered by many different factors.
It is known that pain and itching are perceived by the same receptors in the skin. Biologically active substances secreted by leukocytes and other cells of the immune system play a huge role in the origin of skin itching. These include histamine, leukotrienes, bradykinin, serotonin, etc. In another way, these substances are also called inflammatory mediators.
Itching of the skin in some diseases
Itchy skin on your hands can be a symptom of scabies, which is caused by the scabies mite. In this case, itching of the skin of the hands is determined between the fingers, on the wrists (flexion side), often moving to the skin of the abdomen and scrotum in men. The tick chooses places with the most delicate and thin skin for reproduction. In the evening and at night, the itching of scabies intensifies. Scabies is not characterized by itching of the scalp and face.
With diabetes, there is itching of the skin of the body in the anus and genital area. The reason for this is the activation of candida fungus, which feeds on glucose. In children, itching of the skin near the anus occurs with enterobiasis.
Itching of the scalp is possible with seborrhea (when the skin is very oily) or pediculosis. Seborrhea is also characterized by oily hair that quickly gets dirty, dandruff and crusts. If lice live on a person’s head, then you can see their whitish nits glued to the hair, the insects themselves, which move relatively quickly, as well as traces of scratching on the skin.
Itchy skin in the lower legs occurs due to stagnation of blood in the vasculature of the legs.
With psoriasis, the skin itches in limited areas, covered with red psoriatic plaques with an easily removable whitish coating.
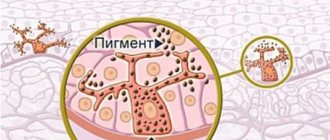
With liver diseases and stagnation of bile in the liver, bile acids begin to be deposited deep in the skin, which irritate the receptors of nerve endings, causing itching of the skin of the body. Typically, in these cases, the levels of bilirubin and liver enzymes are also elevated, and the skin itself is colored various shades of yellowish.
The last stages of renal failure are often also accompanied by itching of the skin of the body due to the deposition of excess urea and urochromes in the skin.
Skin itching in certain conditions
During pregnancy in the third trimester, due to toxicosis, a woman can often be bothered by itchy body skin. It is believed that the reason for this is stagnation of bile inside the liver.
Senile itching is caused by the fact that the functions of the sebaceous glands decrease with age. Because of this, older people suffer from excessive dry skin and itching.
During chemotherapy and radiation therapy, cancer patients also suffer from itchy skin due to the side effects of the drugs and radiation.
Treatment for itchy skin
Before following recommendations for treating itchy skin, factors that cause excessive dryness should be eliminated. These include: washing hands with too hot water and soap, wearing synthetic clothing, emotional distress, and using certain medications (antibiotics, a number of narcotic drugs). Only if all these influences are excluded will the treatment of itchy skin be effective. In case of infectious and parasitic skin lesions, the cause that causes itching of the skin should be directly affected. These are local antiseptics and antibiotics, remedies for lice and helminths.
In case of allergic origin of skin itching, antihistamines, both for oral use and external forms in the form of lotion, ointment, and gel, have a good effect. Your doctor may prescribe topical glucocorticoids for a short period of time. The complex of treatment for skin itching often includes sedatives and sedatives. When bile stagnation, agents that bind bile acids (urodeoxycholic acid preparations) are used.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
The information is generalized and is provided for informational purposes. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous to health!
Itching of the scalp and body, the causes, diagnosis and treatment of which we will try to consider in our publication, is only a symptom and not a disease.
In most cases, the cause of itching of the head and body is some kind of disease. And in order to choose the right treatment, it is first necessary to find out the cause of such an unpleasant symptom.
What does itching without symptoms mean?
If itching appears, but there are no spots or color changes, this may indicate the following pathologies:
- Diseases of the hematopoietic system, for example, lymphogranulomatosis. In this case, you need to consult a therapist who can palpate the lymph nodes, prescribe and interpret a hemogram and other blood tests, and then refer you to a hematologist or oncologist.
- Senile itching. It appears after 60 years of age for unknown reasons. But even if you fit into this category, other pathologies cannot be ruled out.
- Helminths in the intestines. This pathology can be excluded by taking a stool test for helminth eggs and a blood test for antibodies to parasites. To prescribe a diagnosis, you need to visit an infectious disease specialist.
- Mental or neurological pathologies. In this case, you may simply not notice the symptoms.
In any case, only a doctor can prescribe diagnosis and subsequent treatment, so if an unpleasant symptom appears, you must contact him.
Main reasons
This kind of scabies, in most cases, manifests itself locally - on the head, arms, in the bends of the legs, arms, etc. But sometimes the whole body itches.
The reasons for the development of such a symptom can be different, ranging from a banal allergy to the development of a certain disease in the body. Let's look at the most common causes of itching of the head and body.
Seborrhea as a cause of itchy scalp
One of the causes of itchy scalp is a disease such as seborrhea. In classical practice, this disease is classified into 3 types:
Regardless of the type of seborrhea, one of the first signs of the onset of this disease is scalp itching.
In the case of oily seborrhea, the reason is this: due to the high increase in the concentration of androgens in the blood, which occurs during hormonal fluctuations, a change in the composition of the secretion of the sebaceous glands is observed.
Due to this, sebum secretion increases and its bactericidal properties decrease. This condition causes the activation of a yeast-like fungus, which is a permanent inhabitant of the epidermis of the scalp.
Due to the proliferation of fungal organisms, the sebaceous glands become clogged and, as a result, severe itching develops in the area of hair growth on the head.
Against this background, favorable conditions are created for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms that contribute to the development of purulent skin diseases, which are frequent companions of seborrhea.
If we are talking about the dry type of seborrhea, then itching on the head appears against the background of the accumulation of a large amount of dandruff caused by blockage of the sebaceous glands.
The mixed type of seborrhea is characterized by uneven secretion of the scalp: in the middle part in the area of the forehead, nose, chin - the epidermis is oily, on the cheeks - dry, in the frontal and parietal region - sebum secretion is too increased, and in other parts of the head - moderately pronounced or reduced .
Therefore, in areas of the head where the skin is dry, itching develops due to a lack of moisture, and, as is clear, where sebum secretion is increased - itching of the head develops against the background of blockage of the glands or due to the appearance of dandruff.
Diseases of the biliary tract and liver
Sometimes the body itches due to developing liver diseases:
- primary biliary cirrhosis;
- extrahepatic blockage of the bile ducts;
- hepatitis of various etiologies;
- chronic cholestasis.
For reference! A symptom in the form of body itching is observed in 20-25% of patients with jaundice, and in all those with primary biliary cirrhosis. Moreover, in 60-75% of patients with biliary cirrhosis, body itching is the primary symptom indicating the presence of liver disease.
The body may itch 1-2 years before the active development of jaundice. And a sharp retreat of itching on the body in liver diseases is often regarded as a poor prognostic sign, indicating liver failure.
If body itching is directly related to liver diseases, then against this background satiety, skin pigmentation, and liver stars may also develop. And it is in combination that all these signs clearly draw the doctor’s attention to the fact that the patient’s body has problems with the functioning of the liver.
The causes of itching of the body and head in diseases of the liver and biliary tract are the following factors:
- the use of medications that are not suitable for the patient, especially when they are taken uncontrolled - this happens when a person begins to self-medicate;
- increased levels of bile salts in plasma;
- extrahepatic obstruction of the biliary tract;
- use of unfamiliar cholesterol metabolites.
Some doctors argue that cholestatic itching of the body itself is most likely not associated with the level of bile acids in the tissues of the body, but at the same time, this symptom can be provoked by certain inflammatory mediators released in the skin under the influence of these same bile acids.
You need to know this! The main difference between hepatic itching of the body and head and allergic one is that the former is not relieved or is only slightly reduced by taking antihistamines.
Regardless of the cause of skin itching on the body and head in diseases of the biliary tract and liver, only through active treatment of the disease and the use of hepatoprotective medications is it possible to get rid of this symptom, since they contribute to the restoration and full functioning of the cells of the liver parenchyma and biliary elements.
The back of the head itches due to fungal diseases and lichen: signs, treatment
Sometimes a burning sensation in the skin occurs after receiving any scratches or cuts. The head itches due to wound healing. You should not comb them, you can only delay the healing process. In this case, specific treatment is not required. But you can use a variety of soothing oils and ointments.
Frequent use of hair dryers, straightening irons and curling irons negatively affect the condition of the epidermis. They dry it out greatly and cause various unpleasant symptoms. Also, these devices worsen the condition of women's hair. Try to use them no more than three times a week, and completely abandon them during treatment.
Parasites
If you are concerned about severe itching of the scalp, then you need to check it for the presence of parasites (you can use a magnifying glass). Most often, the following parasitic organisms are found on the hairline: lice, mites, etc. They can be picked up in public places, through contact with an infected person, or after visiting a forest. Parasites also appear on the skin due to poor personal hygiene.
Lice most often lay their eggs in the area of the back of the head and ears. They are attached to the roots of the hair and have a white or light yellow tint.
It is not recommended to scratch the scalp as this leads to infection.
The cause of severe itching in the area of hair growth can be seborrhea. Seborrheic dermatitis occurs due to a failure in the production of the sebaceous glands. This disease is characterized by the presence of dandruff, acne and increased burning of the dermis (dry appearance). With the oily type of seborrhea, excess sebum and small scales form on the scalp. It occurs due to problems with the human digestive or immune system.
Psoriasis is a non-infectious disease. Its main symptom is the formation of pink plaques covered with white scales. If left untreated, the disease will spread to the skin of the neck and ears.
Eczema and atopic dermatitis have similar symptoms. If you do not consult a doctor in time, these diseases can provoke active hair loss.
All of the above skin diseases require medical intervention. You should not do nothing or self-medicate, as this will only worsen the condition of your scalp.
Xerosis
This disease occurs due to insufficient secretion of the sebaceous glands. As a result, the scalp dries out and small cracks may appear on its surface. The patient is bothered by a burning sensation and develops peeling of the epidermis.
The scalp itches and itches with xerosis for two reasons:
- Using aggressive detergents and frequent hair washing.
- Hormonal imbalance in the body.
In the first case, it is recommended to replace the shampoo with a more gentle one. It is advisable to use a hypoallergenic detergent. If you have a hormonal disorder, you should consult a doctor. He will conduct an examination and prescribe the most appropriate medications.
Itching of the scalp occurs due to fungal microorganisms entering the epidermis. The patient experiences several serious symptoms at once: skin irritation and hair loss. Trichophytosis causes excessive peeling, itching and redness of small areas of the epidermis. Also, due to the disease, the hair loses its former strength, breaks easily and falls out a lot when combing.
It is impossible to detect parasitic fungal microorganisms on your own. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis after first taking a scraping.
This fungal disease is most often diagnosed in children. Ringworm occurs through contact with infected people or animals. The main symptoms are the appearance of itchy plaques on the epidermis. Over time, they swell, fester and become covered with a thick crust. If left untreated, the headache will spread to the skin of the ears (itching behind the ear), neck, chest and back.
Diabetes
Increased blood sugar provokes disruptions in the production of sebaceous glands and causes dehydration. Severe dryness, flaking and itching of the skin extend not only to the scalp, but to the entire body.
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, you must contact a qualified specialist. He will prescribe you a special diet and medications. You will first need to donate blood to check your sugar level.
Neurodermatitis
This serious neurological disease can cause itching and other changes in the skin. Exacerbations occur due to stressful situations. Unpleasant symptoms become most pronounced in the evening.
Scientists have proven that stressful situations (tense situations at home or at work, depression, severe shock) can cause itching of the scalp (the top and back of the head often itch). Stress triggers the production of cortisol, adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body. To remove them, you need to engage in physical activity, otherwise they will accumulate in the blood. This, in turn, causes severe itching.
Avitaminosis
Itching of the scalp and neck appears due to a lack of macro- and microelements in the body. A lack of certain vitamins affects the skin as follows:
- With a deficiency of vitamin B2 in the body, excessive production of sebaceous glands occurs. This can lead to the development of seborrhea (oily type).
- Lack of vitamins A and C leads to excessive hair loss.
- Insufficient vitamin D intake causes premature skin aging. The epidermis becomes dry, peeling and itching appears.
- Deficiency of vitamins E and B6 impairs the regeneration of skin cells.
Distinctive symptoms of vitamin deficiency: lack of performance, frequent colds, weakness. The patient’s nail plates and hair may also deteriorate in appearance.
Externally, psoriasis is very similar to seborrhea. That is, in addition to the frequent urge to scratch your head, you may notice the appearance of scales. Hair will not fall out, but if you comb diligently, there is a high risk of developing wounds that will begin to bleed.
This is what psoriasis can look like and cause itching
What can help with psoriasis?
- Moisturizing medicated shampoos, which serve as good assistants in the matter of moisturizing the skin. They may contain ichthionol, zinc, salicylic acid.
- Medicines that are administered intramuscularly or taken orally in a more conventional way.
- Sometimes steroid drugs, which are classified as hormonal, are also prescribed. True, they must be taken extremely carefully. Failure to comply with the dosage can have the opposite effect to the desired effect - the skin will become even more vulnerable.
Read more about psoriasis in the article: Psoriasis: stages, symptoms, signs, causes. Treatment of psoriasis in children and adults with drugs and folk remedies
It is also recommended to choose special shampoos and lotions. They should contain selenium sulfide, zinc pyrithione, piroctone olamine, climbazole.
Tea tree oil may be useful as a folk remedy. It is recommended to add it to your usual shampoo or conditioner. As a rule, a few drops are enough.
Read more about lichen in the article: Lichen in a child. What does lichen look like in children and how to treat it?
This is what itchy ringworm may look like
Hair itches also due to nervous shock and lack of vitamins. In this case, the itching will intensify in the evening and at night.
If stressful situations have often occurred lately, then it is worth reducing the load and introducing into your diet foods rich in calcium, vitamins A, E, B2, B3, B6, B12, for example, dairy products, fish, fresh vegetables and fruits.
Decoctions and herbal teas with mint, motherwort, valerian, and hops also have a beneficial effect. In severe cases, sedatives and ointments are used to relieve the symptom of itching.
When the body is not under excessive stress, the nervous system and sensory organs function normally. Stress forces the body to activate a defensive reaction, and dissonance arises between the functioning of the nervous system and sensory organs. The result is a wide range of neural sensory symptoms.
For example, a burning and itching sensation on the skin of the body, a very itchy head. In this case, the itching itself is not dangerous and there is no need to treat it. As stress subsides, this symptom decreases and eventually disappears. But reducing stress in the body often takes much longer than we think. However, once the body has fully recovered from the overstimulation of the stress response, this burning and itching sensation on the skin will completely disappear.
Seborrheic dermatitis
The main provoking factor of the disease is dysfunction of the sebaceous glands. Dry seborrhea develops as a result of decreased secretion production, oily seborrhea - due to its excessive secretion. Severe itching, accompanied by dandruff and acne, occurs with dry seborrhea.
Various means are used to solve the problem. Sulsena pasta is popular. The product is applied to washed hair. Using your fingertips, rub the composition into the skin with light movements, then leave under a plastic cap for 15 minutes. After removing the medication, the hair is no longer washed with soap or shampoo.
Pastes that are no less effective are:
- Sulfur-zinc;
- Zinc;
- Tar tea tree.
Ginger hair balm can cope with pathogenic microflora. The composition is designed specifically to combat dandruff. It is used in combination with drugs and independently. In the second case, it is advisable to limit ourselves to preventive measures.
Zdrave Forte shampoo has fungicidal properties. The composition contains a high concentration of active components, which provides an intense effect against seborrhea. After the first treatment, the itching sensation disappears. According to reviews, the product effectively copes with all manifestations of fungal disease. Ducray Kelual shampoo, which is developed based on zinc pyrithione, has similar qualities.
Psoriasis
The disease is also called scaly lichen. The problem is recognized by spots framed by a clear boundary. The surface layer of the neoplasm is a crust. When the scales are rejected, hair loss occurs. There is no point in delaying treatment; after 2-3 weeks, focal baldness appears on the head.
- Hereditary predisposition of a person.
- Allergic reactions caused by the use of shampoos and other hair care products. In this case, severe itching appears.
- Ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
- A fungal infection that is located on the scalp. It is characterized by itchy skin, the appearance of small scales and unsightly appearance of the hair.
- Vitamin deficiency caused by a lack of vitamins and minerals in the body.
- Disruption of metabolic processes in the body.
- The appearance of serious diseases in the form of eczema, lichen and psoriasis.
- Liver dysfunction, sometimes due to poor diet.
- Washing them too often. You should try to do this as little as possible. At the very least, you definitely shouldn’t introduce your hair to the shower every day.
- Irons, hair dryers, and curling irons can not only negatively affect the condition of your hair, but also dry out your skin. It is preferable to use them less often.
- Using balms, shampoos, masks for oily hair. Sometimes increased sebum production is the body’s reaction to something - stress, negative environmental factors. By producing more oil, the skin protects itself. A person, without understanding the root cause, begins to use special products for oily hair, which will only dry out the skin and aggravate the problem.
A moisturizing hair mask will save your scalp from itching
- Lack of sufficient amounts of microelements, vitamins, and acids in the body. Vitamin deficiency must be combated comprehensively, not only using products with useful additives, but also including healthy foods in the diet.
- Pediculosis;
- Excessive dry skin;
- Fungal and lichen infections;
- Dandruff and many other options.
Pediculosis
Treatment of itching of the body and head with folk remedies
Before self-medicating, be sure to consult your doctor. Incorrectly selected therapy will not only fail to eliminate the cause of the development of itching, but can also worsen the course of the disease that provoked this symptom.
There are many folk recipes, the action of which is aimed at eliminating this unpleasant symptom. Let's look at the most common of them.
Celandine in the form of tincture or decoction
Tincture and decoction of celandine are suitable exclusively for external use. Such folk remedies help get rid of itching all over the body and skin rashes.
To prepare a decoction of celandine, take a teaspoon of the plant - the recipe uses only dried raw materials, and pour 200 ml of boiling water. After a quarter of an hour, the broth is filtered and can already be used as a basis for compresses.
The infusion together with plant materials is used as a basis for baths. To prepare it, take 10 grams. dried celandine and add 100 ml of hot water.
If necessary, the proportion is increased. The finished infusion is cooled to a temperature of 36-40°C and baths are made - the procedure time is 10-15 minutes, and the intensity depends on the degree of manifestation of the symptom and is regulated by the doctor.
In addition to the recipes described above, alcohol tincture from celandine also helps in the fight against itching of the body and head. It is prepared from the proportion of 1 part crushed celandine to 5 parts vodka.
The tincture is used as a basis for a compress - the procedure time does not exceed a quarter of an hour. And in order to eliminate the appearance of irritation caused by alcohol, the tincture is diluted with boiled water in a ratio of 3 to 1, respectively.
Melissa tea
As you know, lemon balm has a calming effect on the body, and when prepared as tea, it can relieve irritation from the skin of the head and body, as well as reduce itching.
To prepare lemon balm tea, take 1 tablespoon of plant material and brew it with 200 ml of boiling water. This tea is consumed 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 30 days.
What to do if your whole body itches
Considering that there is only one itching, but there are many causes, its treatment must be approached differently. What to do if your whole body itches? You can use ointments and creams that can relieve discomfort, but if the causes lie in liver disease or endocrine system disorders, then self-medication with local remedies can only aggravate the problem and complicate further treatment. Indeed, in this case, itching on the skin is just the tip of the iceberg, under which lies a serious illness, possibly fraught with tragic consequences.
Diagnostics
Determining the root cause will require diagnosing the itchy areas. First contact a dermatologist to prescribe tests and a detailed examination. If the dermatologist finds it difficult to name the cause, consultation with a therapist, endocrinologist, allergist, gastroenterologist and other specialists will be required. Principles of treating itchy skin:
- eliminating the cause;
- local treatment;
- systemic treatment.
Depending on the reasons that caused the unpleasant symptoms, treatment for itching of the body skin is prescribed. For allergic scratching, antihistamines are prescribed: Zyrtec, Loratidine, Erius, Zyrtec, Suprastin, Tavegil. Additionally, it is recommended to take sedatives: Novo-Passit, valerian, mint tea, motherwort tincture, since the constant desire to itch disrupts sleep and makes the patient irritable. Complex manifestations are treated only under the supervision of a doctor.
However, this will take some time, and you want to relieve the itching as quickly as possible. Therefore, there are general recommendations:
- The diet should not contain salty, hot, spicy foods. It is undesirable to drink strong tea, coffee, and alcohol.
- If an elderly person has body itching (senile, worse in the evening and at night), then iodine preparations will alleviate the condition.
- Take warm baths with sea salt.
- Wipe the skin with calendula tincture in alcohol, lubricate with menthol-based antihistamine ointments.
Folk remedies
Along with drug therapy, folk remedies for body itching are used:
- A quick effect is achieved by taking baths with decoctions of plants: nettle, chamomile, mint, celandine, pine needles.
- Pruritoceptive (insect bites) are removed with coconut oil baths. To do this, dissolve 50 g of oil in a water bath and pour into warm water. The procedure time is 15 minutes.
- Lemon juice works great for itching, but it should not be applied to areas with damaged skin.
- Vaseline will help quickly relieve itching, as it will additionally moisturize and soften.
- To soothe irritations, you should use basil. It contains vitamins A, C, P, which are very important for skin health. You need to wipe the irritated areas with a clean fresh leaf or prepare a decoction of basil and make lotions.
- Apple cider vinegar and celandine are used as applications (do not use celandine for chemical or sunburn).