Rhinopharyngitis is an inflammatory process localized on the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and larynx. Pathology should be differentiated from inflammation of a more limited area: rhinitis or pharyngitis.
Most often, the disease develops in adults and children as a complication of acute damage to the nasal mucosa and is manifested by the addition of damage to the pharynx.
Pain syndrome occurs, the mucous membrane thickens and becomes covered with plaque.
What is rhinopharyngitis?
Most cases of this disease are consequences of acute respiratory viral infection. Doctors put him in a separate category. Rhinopharyngitis is an inflammation of the nasal sinuses (rhinitis) and the laryngeal mucosa (pharyngitis).
Rhinopharyngitis
Before starting treatment, you need to know the characteristics of the disease:
- Pharyngitis is a disease that occurs as a complication after an acute respiratory viral infection. In more rare cases, the causative agent is bacteria. Accompanied by symptoms: sore throat, dry cough, pain when swallowing.
- Rhinitis is a runny nose that occurs when the mucous membranes of the nose become inflamed. There are several stages of the disease: The first stage is characterized by specific symptoms: sneezing, headaches, body aches, slight soreness in the larynx, slightly elevated temperature, mild cough. The second stage is accompanied by copious nasal discharge, increased temperature and severe nasal congestion. The last stage is thick discharge and general nasal congestion. If the disease proceeds without complications, you can get rid of rhinitis after 7 days.
Antiviral agents
If a child is diagnosed with viral rhinopharyngitis, antiviral drugs should be started immediately. The sooner treatment is prescribed (in the first 3 days), the more effective and fleeting the results from taking the drugs will be.
Antiviral drugs recommended for children:
- Anaferon;
- Interferon;
- Arbidol;
- Kagocel;
- Grippferon;
- Viferon;
- Orvirem;
- Cytovir-3;
- Remantadine;
- Tamiflu;
- Famciclovir;
- Acyclovir.
Clinical studies have shown that anti-influenza and anti-herpetic drugs have proven effectiveness in the treatment of viral nasopharyngitis.
Interferons will affect the virus only in the first 72 hours from the moment of illness; in the future, the feasibility of their use has not been proven.
Some sprays, lozenges and tablets have an antiviral effect: Lizobact, Strepsils, Ingalipt.
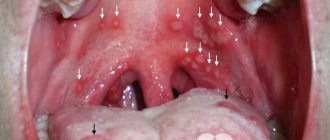
Symptoms of nasopharyngitis
The disease nasopharyngitis has similar symptoms to pharyngitis and rhinitis, in which the following are observed:
- Dryness, soreness and burning in the nasopharynx;
- Breathing through the nose is difficult, nasal sounds appear (this is especially typical in children).
- Periodically, mucus accumulates in the nasopharynx, which is difficult to separate. Sometimes blood is found in the mucus.
- The larynx is inflamed and swollen. The discharge has a viscous consistency.
- There is an increase in lymphoid tissue in the back of the head and neck.
- Sometimes the disease causes complications on the hearing aid, in which case the patient’s hearing deteriorates, pain and clicking in the ears occurs.
Symptoms of nasopharyngitis
Inflammation of the nasopharynx can be caused by various viruses (influenza, rhinovirus, adenovirus, etc.) and bacteria (chlamydia, mycoplasma, diphtheria bacillus, and others). Less commonly, inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx can be caused by allergic reactions (plant pollen, animal hair, household dust mites, etc.).
Inhalations
Inhalations are one of the effective physiotherapeutic procedures that will help you quickly get rid of nasopharyngitis.
If a child, due to age, is not able to gargle independently, inhalations with salt, mineral water, and medications are used.
Inhalations are prescribed to children no more than 2 times a day, and the doctor may prescribe the following solutions:
- Lazolvan;
- Eufilin;
- Berodual;
- Gentamicin;
- Furacilin;
- Saline;
- Borjomi;
- Essentuki.
If you have a special inhaler (nebulizer) at home, inhalations are carried out using ready-made pharmaceutical solutions, which should be diluted with saline solution in a 1:1 ratio, or pure saline solution, or still mineral water.
Solutions containing large particles (with Furacilin) or essential oils are not used in home nebulizers, as they can damage the inhaler. Gentamicin solution is prescribed only in the presence of a bacterial infection.
Inhalations with essential oils are carried out in older children, since they can cause an allergic reaction and aggravate the condition of a small child. Eucalyptus, tea tree, and thyme oils are used.
Rhinopharyngitis in children
A child's body is weaker than that of adults, as a result of which the disease in young patients is more complex and is often accompanied by complications. Therefore, at the first signs of nasopharyngitis, you must immediately consult a doctor. The first symptom that should alert parents is complaints of a sore throat . In children, the disease is accompanied by a runny nose, this is due to the structural features of the nasopharynx and the characteristic properties of the mucous membrane.
To prevent nasopharyngitis, symptoms and treatment for children, every mother needs to know. Let's look at the main signs of the disease in children :
- Breathing through the nose is impaired, congestion is felt.
- The child sneezes frequently.
- The throat has noticeable redness and swelling.
- During the swallowing process, the child feels severe pain.
- At night, a cough occurs. This is due to the fact that mucus drains from the nose into the larynx, thereby irritating the mucous membrane. The cough is dry, hacking.
- The child experiences weakness and malaise.
- Temperature increase.
Rhinopharyngitis in children
Treatment of viral nasopharyngitis is prescribed depending on the symptoms accompanying the course of the disease. Basic means for treating the disease:
- The diet should be balanced, a gentle diet is recommended.
- Drinking should be warm and plentiful.
- The nose is washed with a warm, salty solution.
- To ease breathing, vasoconstrictor drugs are prescribed.
- To relieve swelling of the mucous membrane, antihistamines, such as Loratadine, are used.
- Painkillers to reduce pain in the throat (lozenges, sprays, etc.).
- At high temperatures, antipyretic drugs (ibuprofen, paracetamol, nurofen) are used.
- Bioparox is an antimicrobial drug.
A course of antibiotics can be prescribed only if nasopharyngitis is bacterial in nature . If the disease is caused by an allergen, you must first of all completely eliminate contact with the causative agent of the disease. For treatment, steroids and antihistamines are used, which are prescribed by a doctor.
Antipyretics for children
There are several stages of nasopharyngitis: acute, chronic, allergic. Let's take a closer look at the symptoms of each of them.
Prognosis and prevention
With timely treatment, acute rhinopharyngitis does not pose a threat to the health and life of the patient. The risk of developing severe consequences increases if therapy is not started on time or is absent, since in this case there is a high probability of dangerous complications (bronchitis, pneumonia, sinusitis).
Chronic nasopharyngitis requires constant monitoring by doctors, since it is a source of infection and can cause other diseases of the respiratory system and internal organs. Several times a year, it is recommended to conduct courses of maintenance therapy to avoid the spread of the pathological process and deterioration of the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
To prevent the development of nasopharyngitis, it is necessary to avoid infection with viral and bacterial infections and, if necessary, begin treatment for ARVI and other respiratory diseases as early as possible. It is important to regularly take care of strengthening the immune system, eat right, protect the body from hypothermia and stop smoking. Persons prone to developing allergic reactions should avoid contact with allergens.
Chronic stage of the disease
To figure out how to deal with the disease, you need to know what chronic nasopharyngitis is, symptoms and treatment in adults.
Untreated rhinitis or acute nasopharyngitis cause the chronic form of the disease.
The course of the disease is long and can last for months or even years. The patient has a constant runny nose and cough. Frequent complaints of sleep dysfunction due to difficulty breathing. Often the patient is unable to distinguish odors. A characteristic feature of the disease is the presence of a permanent focus of infection in the nose and teeth (in the form of caries).
Chronic nasopharyngitis, divided into three categories:
- Catarrhal nasopharyngitis .
With this form of the disease, the patient feels like a foreign body in his larynx. Discharge from the nasopharynx is profuse, sometimes purulent in nature. In the morning, when the position of the body changes, mucus flows especially intensely and may be accompanied by expectoration and vomiting. The tonsils are enlarged and inflamed. Chronic catarrhal nasopharyngitis - Atrophic – has symptoms such as: hoarseness; soreness and pain when swallowing, in the throat; mucous membranes are pale, with a specific shine. The atrophic form of the disease develops against the background of gastrointestinal pathologies. If subatrophic rhinopharyngitis is detected, the reasons are as follows: halicystitis; hiatal hernia; inflammatory processes in the stomach (gastritis); pancreatitis. Inflammation of the larynx is caused by the release of stomach acid into the pharynx. Before starting treatment for atrophic rhinopharyngitis, the primary cause of the disease should be eliminated, after which the inflammation of the larynx will go away without any intervention.
- Granular . The main symptoms are a loose surface of the mucous membrane, with obvious swelling. Inflammation of the tonsils and other lymphatic tissues.
What viruses cause such damage?
Rhinovirus
Let's start with rhinovirus. Rarely, the disease is complicated by severe intoxication and damage to the bronchi and lungs.
MS infection
This could be exactly how it goes. But it is much more often complicated by bronchitis and pneumonia.
Metapneumo and adeno viruses
Metapneumovirus in adults and adolescents does not descend further than the pharynx. Causes pneumonia in young children and weakened adults.
Adenoviral infection sometimes occurs as nasopharyngitis with a reaction of peripheral lymph nodes.
Corona and parvo viruses
Corona virus, if it gets on the nasal mucosa, then this is how the disease will progress in the majority of patients. Severe pneumonia rarely develops. And if it gets into the stomach, the disease will develop like an intestinal disorder.
Parvovirus infection in adults affects the nose and throat. Children experience typical rashes.
Reoviruses
They love the mucous membrane of these organs. But they can also settle in the intestines. Almost always the disease ends within 5-7 days. No progression is noted.
This is exactly how people still say catching a cold, an acute respiratory disease most often occurs.
The listed viruses are the cause of frequent, as people say, colds, but essentially respiratory infections.
Acute form of the disease
Acute nasopharyngitis, what is it and what symptoms accompany it? Inflammation of the mucous tissues of the nasopharynx is called nasopharyngitis.
Acute nasopharyngitis symptoms
In the acute form, the following symptoms are observed::
- Itching in the nasal cavity and frequent sneezing.
- Copious mucus discharge, often purulent.
- Changes in voice timbre.
- Soreness, hoarseness and pain during swallowing.
- Temperature rises to 38 degrees.
- Dizziness and general malaise.
- Inflammation of the lymphatic tissues on the back wall of the larynx.
The disease has its own code in the international classification of diseases (ICD-10).
Rhinopharyngitis IBC code 10 – (acute nasopharyngitis) J00.
Kalanchoe juice
Kalanchoe is used for nasopharyngitis as an irritant that causes the patient to sneeze and clears the nasal passages of accumulated mucus. Children are treated with Kalanchoe juice or a decoction of the leaves of the plant. The decoction is recommended for babies in the first year of life.
Before using Kalanchoe juice drops, you need to find out whether the child is allergic to this plant. To do this, you need to lubricate the space above the upper lip near the nose with a small amount of juice. If the area of skin does not turn red within 1-2 hours, then the child is not allergic to the juice. Treatment should begin with a small dosage, 1 drop in each nasal passage.
- Children under 2 years old are recommended to dilute Kalanchoe juice with boiled water in a ratio of 1:3 and instill 1-2 drops of the solution 3 times a day.
- For older children, undiluted juice can be instilled 3 times a day.
- Kalanchoe juice for instillation into the nose can be used in combination with onion juice and aloe.
- Infusions for oral administration are prepared from Kalanchoe juice to help get rid of cough. Infusions can be used from 3 years of age.
- One of the popular recipes: 3 parts Kalanchoe juice, 1 part honey and 1 part aloe juice. The mixture is heated to a liquid state and taken orally, ½ tsp. no more than 2 times a day.
Improper use of Kalanchoe juice can lead to complications, including burns of the mucous membrane and allergic bronchospasm. Therefore, for the treatment of children, the plant is used with caution and always fresh.