Diabetic coma is a condition in the body of a person with diabetes mellitus, manifested by severe changes in metabolic phenomena. A coma can occur if there is an excessive decrease or increase in sugar levels in the circulatory system. An emerging diabetic coma must be treated urgently. Due to the lack of long-term medical care, severe complications can occur, including the death of the patient.
diabetic coma
Types of diabetic coma
Several types of diabetic coma are recorded, each of which has an individual therapeutic approach. The development of comas is provoked by different factors and have different mechanisms of appearance.
Doctors distinguish the following types:
- ketoacidotic – occurs in people who suffer from type 1 diabetes. The problem is caused by the release of large quantities of ketones, which develop in the body due to the enrichment of fatty acids. Due to the high saturation of these elements, the patient falls into a coma. During a coma, sugar rises sharply, health deteriorates, manifesting itself with characteristic symptoms. Complete loss of reason occurs after 2 days, possibly earlier. Diabetic coma of the ketoacidotic form is characterized by elevated glucose levels, reaching 15-35 mmol/l;
- hyperosmolar – formed in diabetics with type 2 disease. Coma is provoked due to dehydration of the body, increased urea, sodium ions, and a sharp rise in sugar. The sugar ratio can reach 30 mmol/l, no ketones are observed;
- hypoglycemic coma - observed in patients who administer the wrong dosage of insulin or do not follow the rules of the diet. During this coma, the sugar level reaches 2.5 mmol/l;
- Lactic acidosis is a rare type of coma that appears as a result of anaerobic glycolysis, leading to a change in lactate-pyruvate balance.
coma due to diabetes
Non-ketoacidotic coma
Patients with type 2 diabetes should carefully study the symptoms of hyperosmolar or non-ketoacidotic coma. Against the background of significant insulin deficiency, in such patients the levels of glucose, sodium and urea in the blood greatly increase, which leads to malfunctions of organs and systems. The main cause of coma is dehydration caused by:
- Inability to quench thirst;
- Diarrhea, severe vomiting;
- Using diuretics.
The formation of hyperosmolar coma is significantly influenced by the following factors:
- Lack of insulin in the blood;
- Excess glucose in the blood;
- Eating foods rich in carbohydrates;
- Diabetes insipidus;
- Major blood loss.
Thus, in order to avoid the negative consequences of a coma, it is necessary to strictly follow all the recommendations of doctors.
Non-ketoacidotic coma is accompanied by hyperosmolar syndrome, which is characterized by high glucose levels (up to 30 mmol/l). Often this condition progresses to ketoacidosis. For experienced diabetics and elderly people, mandatory hospitalization is recommended. Hyperosmolar coma begins to manifest itself in a frequent urge to urinate. The following symptoms are observed:
- Thirst;
- General malaise;
- Nystagmus;
- Difficulty urinating;
- Slurred speech;
- Convulsions;
- Partial paralysis.
Obvious signs of coma form within a few days, but slower processes are also observed.
Hyperosmolar coma occurs much less frequently than other similar pathological conditions. However, in 50% of its manifestations it ends in death.
Etiology
Coma in diabetes develops for various reasons. For the development of diabetic coma, the patients themselves become to blame for not caring about their health, or disruptions in the body provoked by a number of factors.
- If the drug is not taken, complete refusal of therapy leads to an increase in glucose to a high level, which provokes a loss of reason and a fall into diabetic precoma.
- Incorrect dosage of medications will become insufficient or excessive to regulate sugar, leading to high or low values.
- By replacing one type of insulin with another, it happens that the body is insensitive to the new drug.
- If the patient refuses the diet, eat dishes that are rich in sugar, simple carbohydrates, and fats.
- The period of gestation and birth can cause rapid disturbances in the endocrine structure, which leads to hyperglycemic coma.
- The occurrence of concomitant pathologies of various types, including infectious lesions, leads to the formation of an increase in glucose levels.
- Prolonged disruptions of the nervous system and stress lead to complications in the course of diabetic pathology.
- Sudden jumps in sugar levels can be observed during surgical treatment. There are cases when the patient fell into a coma after surgery.
reasons for the development of coma
Symptoms
Each type of diabetic coma has its own symptoms. It is important to have an idea of how they develop in order to provide first aid to the patient in a timely manner. If you delay in this matter, it may cost the patient his life.
Signs of a diabetic coma are manifested by dry skin and mucous membranes, their elasticity is lost. Glucose is not able to penetrate into the tissue, therefore the fat reserves of energy material inside the cells are consumed. A diabetic rapidly loses body weight. During the breakdown of adipose tissue, a large volume of ketone bodies and free fatty acids is released.
These elements accumulate in excessive amounts in the circulatory system. The acid-base balance changes, acid in the bloodstream leads to irritation of the respiratory center. The patient experiences the development of shortness of breath and deep noisy breathing. When exhaling air, an admixture of ketone bodies appears, and the smell of acetone is felt at the location of the diabetic.
The development of ketoacidosis occurs over several days, rarely hours. The diabetic’s well-being gradually changes. As complications develop, the patient:
- communicates less;
- severe vomiting;
- severe stomach pain;
- breathing is deep, noisy;
- answers questions in monosyllables;
- sleeps most of the time.
abdominal pain
In severe situations, loss of reason and coma occur.
In hyperosmolar coma, the patient is severely dehydrated. During the period of developing a diabetic state, a diabetic loses about 10% of his weight.
With this diabetic coma, symptoms develop as follows:
- excessive dehydration;
- speech function is impaired;
- the patient is inhibited;
- drowsy;
- there is thirst;
- within a few days the patient weakens;
- hallucinations appear;
- muscle tone increases;
- convulsions appear;
- areflexia.
Features of the development of symptoms of diabetic coma lactic acidosis are:
- muscle pain;
- discomfort in the sternum area;
- severe weakness;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- I have a stomachache;
- vomiting develops;
- nausea;
- performance decreases.
dyspnea
Also, with lactic acid diabetic coma, irritation of the respiratory center with a high saturation of lactic acid occurs, which leads to deep noisy breathing. The smell of acetone is not released into the air.
The development of hypoglycemic coma is associated with a lack of energy in the cells of the cerebral cortex and the release of large amounts of stress hormones into the bloodstream.
- It hurts and I feel dizzy.
- Lips and tongue go numb.
- The diabetic is worried.
- Concentration decreases.
- There is a feeling of fear and anxiety.
- Speech is impaired.
- Spasms.
- Hunger strikes.
- Saliva is released.
- The heart beats frequently.
- The patient is irritable.
- Hands and body are shaking.
- Cold sweat appears.
- The diabetic is sick and vomits.
- Goes to the toilet frequently and copiously.
- Visual ability to see drops sharply.
The progression of symptoms is rapid, so help is provided to the diabetic to prevent long-term loss of sanity.
Symptoms of diabetic coma, signs, consequences, first aid
Diabetes is an extremely dangerous disease.
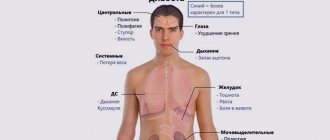
It is characterized by an increased or high level of sugar in the patient’s blood plasma due to a lack of insulin secretion and insulin resistance at the cellular level, which provokes disruptions in many body systems.
The most serious complication of this pathology is diabetic coma. If untimely and urgent intervention is not performed, it can even lead to death. Moreover, symptoms of diabetic coma can occur in both types of diabetes, with hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
What is a diabetic coma?
Coma is a critical, very serious condition when metabolism and metabolic processes are disrupted. As a result, the diabetic accumulates harmful and toxic metabolites, which adversely affect the functioning of all systems, including the central nervous system.
Types and causes of occurrence
Diabetes causes serious hormonal imbalance.
Depending on the balance of certain compensatory mechanisms in the body, several types of coma are distinguished:
- ketoacidotic;
- hyperosmolar;
- lactacidemic;
- hypoglycemic.
This or that type of coma characterizes the severity and danger of diabetes in the event of untimely, illiterate treatment or complete absence of medication.
Ketoacidotic coma occurs in type 1 (less commonly type 2) diabetes. It develops slowly due to the almost complete absence of natural insulin due to a severe imbalance in carbohydrate metabolism.
In this condition, cells cannot absorb the glucose they need, since insulin is a specific conductor of sugar through their membrane. That is, the level of glucose in the plasma increases, but the cells do not receive it. This leads to energy deficiency and exhaustion at the cellular level.
Mycelix - for diabetes. Hurry up to get it for free! Read more The mechanism of fat breakdown (lipolysis) is activated compensatoryly, the metabolism of fatty acids and the accumulation of lipid metabolism metabolites, which are ketone bodies, are enhanced.
During normal metabolism of carbohydrates and fats, the resulting ketone bodies are excreted by the kidneys, but with diabetic ketosis, they accumulate sharply in the blood.
The kidneys cannot cope with the release of so many lipid metabolism metabolites. In this condition, ketone bodies exert their toxic effect on the central nervous system and other systems, which leads to the occurrence of ketoacidotic coma .
With this pathology, the patient has a very high glucose level. Such a coma is a serious and extremely dangerous condition that requires immediate medical intervention.
Without this, it can quickly lead to irreversible severe damage to the central nervous system and death. Coma of this type occurs mainly in patients with incorrect treatment, as well as with independent withdrawal of insulin therapy.
Mycelix - for diabetes. Hurry up to get it for free! More details
The process of manifestation and occurrence of ketoacidotic coma can be divided into three stages:
- moderate or early, when symptoms are uncharacteristic or mild, can last up to several weeks;
- decompensation, when the patient exhibits pronounced symptoms of ketoacidosis;
- coma.
Hyperosmolar coma is manifested by pronounced hyperglycemia . Symptoms are characterized by negative dynamics of carbohydrate metabolism and are manifested by a violation of osmotic pressure in the plasma.
This leads to a change in its biochemical properties and, accordingly, to malfunctions in the functioning of all vital systems in the body. This type of coma occurs due to insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes and is most often found in elderly patients (over 50 years of age).
Hyperglycemic coma develops slowly, with a gradual increase in symptoms. This pathology requires emergency hospitalization and therapeutic measures to correct the patient’s condition.
Delayed medical intervention can lead to fatal brain damage.
Hyperglycemic coma is an extremely serious condition, the mortality rate is 50%. Therefore, the time elapsed from the detection of pathology to the start of the necessary treatment measures is of great importance.
Lactic acid coma is an extremely dangerous and serious condition in which death occurs in 75% of cases . It is less common than other severe complications of diabetes and is otherwise called lactic coma.
Northern Lights - diabetes prevention (consultation) More details
This coma develops in diabetes against the background of concomitant diseases (large blood loss, extensive myocardial infarction, acute infectious process, acute renal and liver failure, chronic exhaustion and heavy physical activity).
The peculiarity of lactic acidemia coma is that the symptoms develop suddenly and very quickly with pathological negative dynamics. Hypoglycemic coma is characterized by a decrease in sugar levels and most often occurs in type 1 diabetes.
It occurs due to the fact that the patient begins to inject an excessive dosage of insulin and exposes himself to excessive physical exertion.
Another reason is pancreatic insulinoma, which begins to produce too much insulin, the concentration of glucose in the plasma decreases, and all of it passes into the cells.
Nervous tissue (in particular, the brain) suffers from this, which causes the symptoms and clinical manifestations of this type of coma. With timely treatment, hypoglycemic coma stops quite quickly.
For this purpose, intravenous administration of 40% glucose can be used. If you do not provide assistance to the patient, severe damage to the central nervous system may develop, including loss of some body functions.
Any coma is extremely dangerous; often only timely contact with a doctor can save the patient’s life, so self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
What symptoms and signs are characteristic of coma in diabetes mellitus types 1 and 2?
Each type of coma is preceded by certain symptoms. In type 1 diabetes they are usually more pronounced, but not necessarily. You should pay attention to them and, if you feel unwell, immediately call a doctor.
Here are the signs that are harbingers of a critical condition:
- Before a ketoacidotic coma, a person experiences progressive weakness, debilitating thirst with increased diuresis, the urge to vomit, and loss of appetite. There is a strong odor of acetone on breath and urine (acidosis). Red spots appear on the cheeks, similar to blush (facial hyperemia);
- hyperosmolar coma is preceded by rapid fatigue and weakness, debilitating thirst with dry mucous membranes, drowsiness, frequent urination, dryness and decreased elasticity of the skin, shortness of breath with asphyxia;
- Before lactic acidemia coma, weakness and pronounced muscle pain, anxiety, drowsiness alternating with insomnia, and antispasmodic abdominal pain with vomiting are noted. With negative dynamics, loss of reflexes and paresis due to brain damage is observed;
- Before a hypoglycemic coma, the patient experiences a feeling of hunger, weakness, lethargy, numbness of the limbs, trembling, sweating, dizziness. Breathing is rare and slow. Possible loss of consciousness.
But there are signs characteristic of most types of coma. They should definitely alert a person suffering from diabetes, even if he has no other symptoms:
- extreme thirst and frequent urination . One of the most important external signs that a person has diabetes. It may also be a harbinger of ketoacidotic or hyperosmolar coma;
- headaches and low blood pressure . Signs that indicate the onset of lactic acidemic or hypoglycemic coma. Symptoms that require urgent medical intervention;
- confusion, weakness . If the patient experiences weakness, lethargy, his movements are slow, and his thoughts are confused, this condition may portend a ketoacidotic or hypoglycemic coma;
- deep noisy breathing . This symptom is observed in lactic acidemic coma and requires immediate intervention;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting . They occur in ketoacidotic and lactic acidemic coma and are very alarming symptoms;
- smell of acetone from the mouth . A classic diagnostic sign, it is the main symptom of diabetic ketosis. The patient’s urine may also smell like acetone;
- other manifestations of coma in diabetics . In addition to the symptoms listed above, patients may experience sudden loss of vision, drooling, irritability, decreased concentration, rapid heartbeat, tremors, speech disorders, feelings of fear and anxiety, and numbness of the tongue.
If you have diabetes, you must constantly monitor your sugar levels, see a doctor, and if any alarming symptoms appear, immediately contact the clinic.
Possible effects on the brain and other organs
Diabetic coma is a severe pathology that is a serious stress factor for the entire body.
In a comatose state and elevated blood sugar levels, lipid metabolism is disrupted, fat peroxidation increases, which has a detrimental and destructive effect on neurons, provoking a cerebral stroke, as well as the development of dementia (Alzheimer’s disease can begin in women in old age).
Glucosuria in urine leads to kidney damage and the development of acute renal failure. In this case, the electrolyte balance of the blood is disrupted (towards acidification), which provokes various types of arrhythmias. The accumulation of toxic metabolic metabolites in the body leads to serious liver damage (cirrhosis, hepatic coma).
With a hypoglycemic coma, the main threat is irreversible brain damage, since neurons do not receive enough energy in the form of glucose and begin to quickly die, which leads to personality changes, dementia, and the child may have a lack of intelligence.
First aid
Diabetic coma can have various causes and symptoms. It is difficult for an ordinary person to understand this, but in an emergency situation, unprofessional actions can cause very serious harm.
Therefore, in a comatose state, the best first aid for the patient would be to urgently call a doctor.
Forecast
With all types of diabetic coma, the prognosis always remains very cautious, since everything depends on qualified medical care. In the lactic acidemic form it is almost always unfavorable.
on this topic
Symptoms and first aid for diabetic coma:
Every person suffering from diabetes needs to know that diabetic coma is not a necessary and inevitable result of this disease. As a rule, it develops due to the fault of the patient himself.
If you have diabetes, you must carefully understand the causes of this disease and follow all the recommendations of doctors. Only an integrated approach and taking care of your own health will help improve your quality of life and avoid coma.
PreviousNext
Source: https://AboutDiabetes.ru/simptomy-diabeticheskoi-komy-priznaki-posledstviia-pervaia-pomosh.html
Emergency care for diabetic coma
If you have an idea of the signs of diabetic types of coma, then you can immediately prevent their progression. It is important to immediately call an ambulance to summon a medical team, and before their arrival, independently carry out measures to provide emergency assistance to the victim.
First aid for different types of diabetic coma has distinctive processes.
So, in case of hyperosmolar coma, it is necessary to turn the diabetic on his side, control his tongue so that it does not stick, and let fresh air into the room.
If a ketoacidotic coma overtakes the patient, then you need to immediately call a doctor, since this condition cannot be prevented on your own. Before doctors arrive, monitor your breathing and heartbeat. Such measures are acceptable if lactic acidotic coma develops.
Due to the development of signs of a hypoglycemic coma, first aid for diabetic coma is to supply the patient with sugar or sweet tea.
Diagnostic measures
It is unrealistic to identify hypoglycemic coma, like any other type, only by visually examining the patient. To do this, you will need to undergo laboratory tests, the most practical of which is a general blood test, which reveals the sugar level. Biochemical analysis of blood and urine is also carried out.
blood test for diabetes
Any type of coma in type 2 diabetes mellitus is accompanied by a high increase in blood sugar saturation of more than 33 mmol/l. The only exception is hypoglycemic, characterized by a decrease in glucose levels to 2.5 mmol/l. When a hyperglycemic coma develops, the patient will not feel any distinctive signs. It is possible to calculate a ketoacidotic state by the appearance of ketone bodies in the urine; a hyperosmolar state is when plasma osmolarity increases. The lactic acidemic type of diabetic coma is diagnosed as a result of an increase in the saturation of lactic acid in the bloodstream.
After diagnosis, treatment is prescribed.
Hypoglycemic coma in diabetes mellitus
Occurs with a sharp decrease in blood glucose concentration (up to 2-1 mmol/l). Risk factors:
- violation of the therapeutic diet;
- insulin overdose;
- hormonal tumor (insulinoma);
- intense physical activity.
Hypoglycemic coma manifests itself very quickly. The first symptoms occur within half an hour after the action of the provoking factor.
Increasing signs:
- severe hunger;
- general weakness;
- increased sweating;
- moist pale skin;
- tense muscles;
- strong tendon reflexes, clonic and tonic convulsions;
- dilated pupils;
- mental inadequacy, hallucinations;
- loss of consciousness (blood pressure, respiration and pulse remain within normal limits).
Treatment
Before starting treatment for diabetic coma, the doctor collects a complete medical history and determines the type of condition. Diabetics have their blood pressure and pulse measured.
Various treatment options are used to avoid coma in diabetes mellitus.
- If sugar is low, emergency treatment is required, including the injection of insulin into a vein along with glucose. In addition, Adrenaline, Vitamin C, Cocarboxylase, and Hydrocortisone are prescribed. To prevent pulmonary edema, artificial ventilation of the lungs is carried out, and systems with diuretics are installed.
- In case of elevated glucose, short-acting insulin treatment is prescribed. At the same time, the sugar value is measured at certain intervals so that the coefficient decreases gradually.
- In both cases, the water balance is restored and the missing lost fluid is introduced to prevent dehydration. By injecting liquid into a vein, the total volume of circulating blood, pressure, and plasma composition are controlled. The introduction of fluid occurs in stages, the total amount often reaches 7 liters on the first day.
- If there is a large loss of microelements, therapy is prescribed with their introduction into the body.
pathology treatment
Types of comatose states
Comas with diabetes mellitus always begin with a precomatous state. During this period, there are already obvious deviations of sugar levels from the norm, but they have not yet reached critical values. On the eve of hypoglycemia, the sugar level drops to 2.8 mmol/l. If a subsequent decrease occurs, a hypoglycemic coma develops. Approaching a sugar coma means an increase in blood sugar above 13.9 mmol/l. Hypoglycemic and diabetic coma are equally dangerous to human life.
Comas with diabetes can be different. Experts distinguish several types of them:
- Hypoglycemic. This type can develop in a short period of time and indicates a nutritional deficiency or an overdose of insulin. Occurs when the amount of insulin is excessive. The fatal outcome of this condition occurs much less frequently than with various types of sugar coma. Symptoms of a hypoglycemic type diabetic coma are: weakness, dizziness, confusion, indifference to external factors, lethargy, low blood pressure and tremor.
- Diabetic ketoacidotic coma is the most common type of coma in diabetes mellitus. If there is enough sugar in the blood, it cannot be absorbed by the cells, since this requires insulin. Starving the cells forces the liver to synthesize glucose from fats and proteins in the body. The synthesis is accompanied by the release of acetoneacetic acid and ketones, and ketoacidosis occurs - acute intoxication of the body not only with sugar, but also with toxic substances. Symptoms of such a coma include general lethargy of the body, lack of reflexes, nausea accompanied by vomiting, dizziness, there may be seizures of the epileptic type, the patient smells of acetone or rotten apples, dry skin accompanied by itching, deep rapid breathing. Diabetic ketoacidotic coma is accompanied by sugar levels of 30-40 mmol/l.
- Hypersmolar. It also develops according to the principle of increased blood sugar. Its peculiarity is dehydration of the body, during which the glucose level increases along with the concentration of electrolytes, but the release of ketones does not occur. This type of development of diabetic coma leads to death in 45% of cases, but this option is 6 times less common than diabetic ketoacidotic coma. The course of coma of the hypersmolar type is characterized by such manifestations as confusion, dry skin, convulsions, muscle tone, decreased blood pressure, accompanied by severe dehydration and lack of urine.
- Hyperlactacidemic. It can occur in older diabetics who already have problems with the liver, kidneys or heart. In this case, there is an increased concentration of lactates in the blood, and as a result, accumulation of lactic acid and acidosis. Symptoms will be all the signs of a diabetic coma, plus muscle tissue soreness.
After the development of the main stage of a comatose state, when it is clearly possible to understand its type, in the absence of adequate help, the last stage develops - a true coma, which can last several months, and its prognosis is not always reassuring.
Prevention
Follow a number of recommendations that will reduce the threat of coma formation in diabetes mellitus.
- Be systematically examined.
- Follow the doctor's advice.
- To eat well.
- Control your sugar all the time
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Minimize stress and worries.
- Monitor breathing in diabetic coma and heart function until doctors arrive.