Diabetes mellitus is a serious disease that causes dangerous complications and can make a person disabled and shorten his life. Men are usually concerned that impaired glucose metabolism reduces potency and leads to other urological problems. Although they should be afraid of truly serious complications - blindness, leg amputation, kidney failure, heart attack or stroke. Below you will learn in detail what are the common symptoms of diabetes in men, how the signs of this disease differ in people of different ages. On the Diabet-Med.Com website you will find all the information you need to quickly and accurately make a diagnosis, and then bring your sugar levels back to normal.
Men who suspect that they have high blood sugar are usually interested in how the symptoms of this disease differ among people of different ages. For example, what symptoms indicate diabetes in men after 30 years of age? Are they different from the signs of diabetes in a man at 40, 50 or 60? In fact, in men at any age, the symptoms of the disease are almost no different from the symptoms in women. Diabetes causes virtually the same problems in adults, younger children and adolescents. Therefore, you need to study the article “Symptoms of Diabetes” - it is universal for all categories of patients. Signs in men have minor features, which are described in detail below.
Primary signs
The causes of the disease are practically independent of gender. These include:
- heredity;
- low physical activity;
- poor nutrition;
- obesity;
- regular stress;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- chronic diseases;
- long-term use of certain medications: antihypertensive drugs, diuretics, synthetic hormones, etc.;
- hormonal disorders.
In addition to common provoking factors in men, bad habits often play a negative role in the appearance and development of diabetes. In addition, they are more carefree about their health. Not many of them monitor their blood counts as shown in the photo.
Unfortunately, they rarely pay attention to the first symptoms of diabetes in men:
- suddenly appeared pigmentation on the skin;
- periodic unexplained itching in the groin area;
- excessive sweating;
- sudden changes in weight;
- significant increase in appetite;
- extreme thirst;
- drowsiness;
- restless sleep;
- pressure surges;
- frequent need to go to the toilet to urinate;
- baldness;
- high fatigue even without load;
- slower wound healing.
If you notice at least two of the listed symptoms, it is better not to delay a visit to your doctor in order to avoid the consequences of diabetes in men. Primary symptoms can be observed for years, and then the disease takes on a chronic stage.
Secondary signs
If the first symptoms were not noticed and treatment was not carried out, a drop in testosterone may begin, leading to disturbances in the blood supply to the pelvic organs. Insufficient supply of nutrients to the genitals can lead to progressive impotence. Men's health is impaired, which is manifested in the clinical signs of diabetes in the form of:
- decreased potency;
- decreased libido;
- premature ejaculation;
- defects in reproductive function (decreased quantity and quality of sperm).
How do other problems besides male ones manifest themselves? The patient suffers from unpleasant conditions:
- microcracks in mucous membranes;
- peeling of the skin;
- the occurrence of fungal diseases and viral infections due to poor wound healing;
- incessant itching.
In addition to external signs of diabetes mellitus, an experienced patient may experience damage to DNA, the carrier of hereditary information. Over time, if diabetes is not treated, it can cause a number of associated diseases: gangrene, polyneuropathy, vision problems and others.
Manifestations of type I disease
The first signs of diabetes in men after 30 years of age may initially be subtle, and the disease itself may have hereditary causes. More often at this age, type 1 diabetes mellitus occurs, which is characterized by insufficient or zero production of insulin by the pancreas. In this case, the hormone is administered artificially to neutralize glucose in the blood. This is necessary so that the patient does not fall into a coma and die. This form of diabetes is typical for adolescence and occupies a leading place in patients under 40 years of age.
Often, symptoms, under the influence of infections or exacerbation of chronic diseases, can increase rapidly and become obvious in a few weeks. Patients suffer from symptoms:
- extreme thirst;
- skin itching;
- a sharp drop in body weight;
- frequent need to go to the toilet to urinate;
- chronic fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- increased appetite, followed by its complete absence;
- reduced ability to work;
- specific odor from the mouth;
- vomiting or nausea;
- discomfort or pain in the intestines;
- decrease or absence of potency.
Such manifestations should alert a man who considered himself healthy and encourage him to monitor his blood for the presence of sugar in it.
Manifestation of diabetes in women
First of all, it should be noted that high sugar content poses a higher danger for women than for men. This is due to the fact that complications in the form of a heart attack, according to statistics, increase 2-3 times for men, and 6 times for women. This trend is also observed for other types of complications.
Causes
In medicine, there are two types of diabetes:
- Type I diabetes;
- Type II diabetes.
Table No. 2. Types of diabetes:
| Type of diabetes | Degree of development | Clinical manifestations | Risk group |
| Type I diabetes | Extremely aggressive | The first signs of diabetes in women quickly change to the main clinical picture, leading to coma in a short time. | Young ladies aged 20 to 30 years. |
| Type II diabetes | Low intensity | Sugar levels rise less rapidly, and the hormone insulin is not perceived by cells, which does not stimulate the normal removal of sugar from the body. | Representatives of the fairer sex aged from 30 to 60 years. |
It is worth saying that signs of diabetes mellitus in women of type 2 do not manifest themselves at the early stage of development of the pathology. Very often, patients do not even suspect for a long time that they are already at risk of the disease.
Diabetes mellitus in women can occur in a latent form for a long time.
The main reasons influencing the process of increasing the concentration of glucose in the blood are:
- hereditary predisposition;
- regularly tormenting insomnia;
- permanent stress;
- lack of physical activity;
- abuse of bad habits (drug addiction, alcoholism, smoking);
- excess weight.
Attention. A disease will be considered hereditary if one of the parents has diabetes, in which case the probability of developing the pathology is 50%. If both parents are diagnosed with diabetes, the likelihood of the child developing the disease is 100%.
The hereditary factor in the development of endocrine pathology affects both the female and male bodies equally. However, there are specific factors that are unique to women.
Table No. 3. Specific features of the female body that can cause diabetes:
| Factor | Effect on disease |
Polycystic ovary syndrome. | With polycystic disease, the eggs remain in the ovary and do not leave it; this circumstance directly affects the sensitivity of the cells to insulin, which in turn causes a high concentration of sugar. |
Uncontrolled weight gain during pregnancy. | There are specially developed norms for weight gain during pregnancy; they must strictly not be exceeded, as the likelihood of obesity (a direct factor in diabetes) increases. |
Jumps in glucose levels during pregnancy and lactation. | The female body during pregnancy and lactation is subject to hormonal changes. It is believed that this factor can have a negative impact even after 5-10 years. |
The birth of a baby weighing more than 4 kg. | It is believed that childbirth with a fairly large fetus is difficult, the woman’s body is exposed to high stress, and as we know, stress is one of the first sources of diabetes. |
You can also note some features of the female body at a later age (after 65 years):
- excessive overeating of sweets;
- presence of hyperglycemia;
- hereditary heart defects;
- presence of hypertension.
The main feature of female diabetes is that its causes simultaneously act as a clinical picture and complications. Therefore, after the first symptoms of diabetes appear in women, the pathological condition begins to develop in direct dependence on the cause, while activating its clinical picture.
Interesting fact. A high incidence of diabetes is observed in the population with average and low incomes, since such categories of citizens sometimes cannot afford to eat properly. The risk group also includes able-bodied people, especially those employed in difficult working conditions. For these two reasons, the problem of diabetes treatment concerns not only each individual patient, but also the entire state.
Acute clinical picture of type I and II diabetes
Acute signs of type 1 diabetes mellitus in women are characteristic of acute signs of type 2 diabetes mellitus, they manifest themselves as follows:
- frequent urination;
- strong feeling of unquenchable thirst;
- nausea;
- gagging;
- bad breath;
- unreasonable irritability;
- numbness of the extremities (especially the lower ones);
- a sharp deterioration in vision, sometimes so-called double vision.
Clinical manifestation of type II diabetes
If a woman develops type II diabetes, it may not manifest itself for several years. The signs of incipient diabetes of this type are quite mild; the patient’s overall health gradually worsens and her quality of life changes.
But such a manifestation is characteristic of the symptoms of aging of the body, which is why the alarm is not always raised, and the diagnosis is made already in the presence of obvious manifestations.
The first signs of diabetes in women are as follows:
- rapid fatigue of the body;
- muscle weakness;
- blurred vision;
- loss of concentration.
Deterioration of vision is one of the main signs of onset diabetes.
Attention. When acute symptoms appear, the patient’s health is at risk, since the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream reaches a critical level, which can subsequently lead to coma.
Symptoms of the initial stage
Very often, type 2 diabetes begins with a call to the ambulance, when the patient’s condition worsens to critical, and loss of consciousness is possible. Therefore, this diabetes mellitus is very insidious; signs in women are recognized only when the glucose level rises to more than 6.7 mmol/l.
Fact. When an acute clinical picture of diabetes develops, doctors fail to save up to 5% of those who seek help from death.
Despite the hidden picture of the disease, type II diabetes usually manifests itself with symptoms of various complications. This:
- Thrush. The main symptom is vaginal itching and cheesy discharge. You can get rid of thrush caused by diabetes without using special antifungal drugs, just follow a proper diet and reduce your carbohydrate intake.
- The proliferation of yeast caused by elevated glucose levels causes urinary tract infections. In frequent cases, cystitis (an inflammatory process in the bladder) becomes a manifestation of such an infection. Women, due to their distinctive anatomical structure, are more susceptible to this complication. The pathology manifests itself as acute pain when urinating, a feeling of discomfort in the lower abdomen, and high fever.
- Another dangerous complication is pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys). Develops against the background of the negative effects of pathogenic bacteria. This disease is very difficult to treat.
Attention. In some cases, thrush caused by a fungus of the genus candida albicans subspecies spreads to the oral cavity. It can be recognized by a white coating on the tongue and palate.
Skin manifestations
Signs of diabetes in women on the skin speak about themselves as follows:
- dryness;
- peeling;
- itching;
- darkening;
- non-healing wounds and cuts.
External signs do not always determine impaired glucose synthesis; focusing only on them is a mistake. Sometimes, even with critically high glucose levels, there are no skin problems.
Important. One of the signs of type II diabetes is premature aging and aging of the skin. But due to the fact that the symptoms of diabetes in women are mild and gradual, this factor can simply not be noticed.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes
As we have noted more than once, type I diabetes can only occur in young girls under 30 years of age, and in rare situations after the age of thirty. To recognize the onset of the disease, let's look at its main obvious signs.
Table No. 4. Signs of type 1 diabetes:
| Sign | Description |
Feeling thirsty. | A woman’s desire to get drunk is constantly present; this is not an ordinary thirst that is quenched by one glass of water. The patient drinks as much liquid as a healthy person simply cannot drink. This symptom is facilitated by a disturbed hormonal balance, in which incoming glucose is not absorbed in the body, hence a sore throat and unquenchable thirst. |
Sudden weight loss. | Type I diabetes is characterized by rapid weight loss. This occurs due to the body not absorbing nutrients. The body, having not received a sufficient amount of energy, begins to actively use the existing supply, leading to the decomposition of adipose tissue. The rate of weight loss is 5 kg per month or more. |
Hunger. | A distinctive feature of diabetes is that with a constant feeling of hunger and its satisfaction, a woman still continues to lose weight. |
Frequent urge to urinate. | Due to constant thirst and regular consumption of a huge volume of liquid, the body is forced to eliminate it. The amount of fluid removed is 3 liters per day, which is several times higher than the norm. More than 10 urges to urinate are a reason to sound the alarm. |
Bad breath. | As a result of the breakdown of proteins, acetone is released in very small quantities, but due to dysfunction of metabolic processes, acetone increases. A high content of this substance poisons the body, which is where the smell comes from. |
Low body temperature. | The temperature of diabetics drops to 35.6-36.2 ⁰C. As is known, the body maintains heat due to the energy consumed, but as a result of dysfunction of all metabolic mechanisms, energy accumulates in insufficient quantities. |
Decreased libido. | In both the weaker and stronger sex, diabetes contributes to a decrease in sexual desire and need for it. The main reason is regular hormonal imbalances and the general condition of the patient. |
But in addition to obvious physical symptoms, type I diabetes is reflected by objective changes in the body, which can be recognized by laboratory tests.
This:
- sugar concentration in the bloodstream. They take the test in a laboratory on the direction of a doctor or at home using a glucometer. For women, the sugar level depends on her age and meal time.
- Test for ketone bodies. This analysis allows you to determine the content of ketone bodies (protein breakdown products, including acetone) in the urine.
Manifestation of diabetes in patients aged 30 years
Dysfunction of glucose synthesis in the body of a woman under 30 years of age means the appearance of type I diabetes, a complex autoimmune disease. Symptoms manifest as the acute picture described above. But young women are not at risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
To confirm concerns about the development of type I diabetes, it is necessary to conduct a laboratory blood test for sugar concentration. This is done in the laboratory as prescribed or at home using a glucometer. If your sugar level is still higher than normal, then take care of your health. First of all, you need to study the type 1 diabetes control program and follow your doctor’s recommendations.
Manifestation of diabetes in women at 40 years of age
Forty-year-old women can be diagnosed with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Sugar levels at this age increase from eating the wrong foods and a sedentary lifestyle. Note that the body is also susceptible to autoimmune attacks on β-cells that produce insulin. Thin women are at risk for attacks.
Interesting. Autoimmune diabetes, which affects not only the female population but also the male population at the age of forty, is called LADA. After 2010, scientists determined that this pathology appears much more often than previously thought. Modern medicine has already begun to change the standard tactics of treating autoimmune pathology.
In the vast majority of forty-year-old women, it is type I diabetes that develops, and type II diabetes often develops after 45 years. Type II diabetes is easier to treat than type I diabetes.
For positive dynamics of treatment, it is enough to maintain normal glucose concentrations by following a low-carbohydrate diet and taking sugar-lowering medications. But with type II diabetes, autoimmune attacks are also observed, and in this case the patient may already need insulin injections. Various infectious diseases can serve as a prerequisite for attacks.
What are the symptoms of diabetes in women after 40? We present the most basic signs in the table below.
Table No. 5. Signs of diabetes in forty-year-old women:
| Sign | Description |
Osteoporosis. | Osteoporosis is the fragility of bone tissue that occurs due to a lack of nutrients. Basically, the disease occurs in old age, but due to the development of diabetes, this process begins at the age of 30, since the mechanism of bone aging increases tenfold. |
Muscle weakness. | Diabetes negatively affects the peripheral nervous system, which immediately affects muscle mass. |
Obesity. | Type 2 diabetes is usually characterized by active weight gain. If you do not control your food intake, you can bring your body to a large number of extra pounds. |
Attention. In a woman, the risk of developing type 2 endocrine pathology after 40 years of age increases if during pregnancy she periodically increased the concentration of glucose in the bloodstream above the normal level.
Manifestations of diabetes in women at 50 years of age
Autoimmune DM LADA, which we talked about earlier, very rarely develops in women fifty years old and older, but it can develop even before this age and occur in a latent form. However, in medical practice, type II diabetes becomes a common cause of increased glucose concentrations in women after 50.
During this period, the female body experiences severe stress caused by menopause. This disrupts metabolic processes, creates preconditions for the development of obesity, and also increases the risk of cardiovascular failure.
Symptoms are characteristic of accompanying complications. To normalize their condition, patients should strictly follow the recommendations of a diabetes doctor and carry out appropriate diabetes therapy.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes (GDM) is a disease of the pancreas of an endocrine nature that occurs in women during pregnancy. With each month of pregnancy, the organ is subjected to more and more stress, and therefore cell tolerance to insulin develops.
The trigger mechanism for the disease is the level of maturation of the placenta, which actively produces hormones. These hormones have a direct effect on increasing glucose concentrations.
Each trimester of pregnancy is characterized by a high concentration of hormones such as progesterone and estrogen, which further aggravate the picture of the disease. As a result, the pancreas cannot cope with its functions and does not produce insulin in the amount required by the body, and dysfunction of carbohydrate metabolism develops.
GDM increases the risk of developing true type II diabetes.
As the fetus begins to develop in the mother's womb, the sensitivity of cells to insulin is disrupted in her body.
The reason for this may be the following factors:
- hereditary predisposition (at least one of the parents has a diagnosis of diabetes);
- sedentary life, especially in the last trimester of pregnancy;
- increased food consumption, and at the same time calories and carbohydrates;
- excessive weight gain.
The above factors influence the appearance of persistent hyperglycemia.
Important. Treatment of gestational diabetes is complicated due to the fact that it occurs in a mild form, without any obvious signs. It is often diagnosed only in the third trimester of pregnancy.
GDM can be recognized by indirect symptoms. This:
- sudden weight gain;
- strong thirst;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- loss of appetite;
- depression.
Attention. If the pathology was identified in the mother during pregnancy, or suspicious symptoms indicating it were noticed, then the newborn baby should undergo a full examination for the possible development of complications. The purpose of the examination is to promptly identify abnormalities in the newborn’s health and begin treatment while the processes are considered completely reversible.
Manifestations of type II disease
Type 2 diabetes mellitus occurs more often in men after 40 years of age and is initially so asymptomatic that the disease can only be detected during a clinical examination. The body produces enough insulin, but tissue susceptibility to glucose and the transport of sugar into cells are disrupted, as a result of which it accumulates in the blood. Since insulin is partially absorbed, the disease does not occur as clearly as in type I diabetes mellitus in men.
Type II diabetes is characterized by:
- weight gain up to obesity;
- constant thirst;
- increased appetite;
- lack of feeling of satiety;
- copious and frequent urination;
- memory impairment;
- blurred vision;
- poor wound healing;
- bleeding gums;
- feeling tired;
- baldness;
- impaired finger flexibility.
- destruction of tooth enamel.
Similar symptoms of diabetes mellitus often appear in men after 50 years of age. At 60 years of age, secondary signs often appear:
- cataracts;
- glaucoma;
- increased sweating.
The symptom of impaired finger flexibility is often a clear sign of diabetes in men after 50 years of age. One of the methods for diagnosing the disease is based on it. At the appointment, the doctor asks you to raise your big toes 45 degrees relative to the surface or to bring your palms together tightly, without gaps. Diabetics with experience over fifty cannot perform both operations.
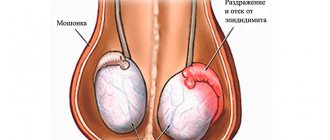
Men with an advanced form of the disease often experience secondary symptoms - fungal infections and problems in the genitourinary area. Sometimes they suffer from problems with the penis:
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- redness;
- itching;
- peeling of the skin;
- unpleasant odor;
- erectile dysfunction.
Treatment of diabetes mellitus in men, if the disease occurs in type II, is carried out without the administration of insulin. Sometimes following a diet, giving up bad habits and increasing physical activity is enough. If this turns out to be not enough, treatment with glucose-lowering drugs is introduced, of which metformin is now recognized as the most popular.
The consequences of diabetes in men who do not follow doctor's recommendations can be the most severe.
How does diabetes manifest itself?
The course of the “sweet” disease depends on the type of disease. Patients with type 1 pathology are characterized by a rapid and acute onset, especially for children, adolescents and young adults. There is rapid loss of kilograms, dry skin, thirst, and polyuria. Early symptoms of type 2 diabetes are not noticeable at all. It is usually discovered in adult men and women by chance during a preventive examination. The disease is characterized by a stable course, slow onset, and the presence of nonspecific symptoms that are also suitable for other ailments:
- general weakness;
- periodontal disease;
- itching of the genitals;
- Athlete's foot.
- What is the hormone prolactin?
- Treatment of diabetes mellitus with folk remedies - diet. Diabetes mellitus - folk remedies for treatment
- How much does YouTube pay for video views? How much can you earn on a YouTube channel for
Complications of diabetes in men
The most severe consequence of diabetes, affecting patients regardless of gender, is diabetic coma, which can cause death. Therefore, it is necessary to promptly recognize the first symptoms of a precomatose state:
- clouding of mind;
- frequent dizziness;
- lethargy.
If such symptoms occur, hospitalization cannot be delayed. The onset of renal dysfunction due to diabetes is indicated by local or general edema, which may also indicate heart failure.
Men are more likely to experience complications such as:
- cardiovascular diseases with the development of strokes and heart attacks;
- dysfunction of the kidneys, gastrointestinal tract, liver;
- disruptions in the functioning of the reproductive and sexual spheres up to complete impotence;
- diabetic foot.
Why is the last symptom dangerous? This complication may lead to the need for amputation. To avoid this, it is important to distinguish its main signs:
- goosebumps on the legs;
- leg cramps;
- decreased sensitivity in the area of the feet;
- the occurrence of necrosis or suppuration after the slightest damage.
What other undesirable consequences can diabetes cause? They can be specific forms of diseases:
- atherosclerosis,
- encephalopathy,
- angiopathy,
- nephropathy,
- angina pectoris
- polyneuropathy, etc.
To prevent the development of complications, it is important to diagnose the disease in time.
Dangerous consequences and diabetic complications
The consequences of diabetes for men are:
- Sexual function suffers (with any type of diabetes): testosterone is poorly produced, ejaculation weakens, blood saturation of the genital organs is insufficient. The use of drugs to improve potency with existing diabetes is inappropriate;
- balanoposthitis (with the first form of diabetes);
- diabetic foot;
- encephalopathy . Manifestation: fainting, migraine and dizziness, poor sleep.
- atherosclerosis of blood vessels in the head (narrowing occurs due to high cholesterol). Progressive pathology leads to heart attack and ischemia, nephrosclerosis;
- angiopathy . Starting with paresis of the ocular vessels, it can develop into retinal detachment and blindness;
- nephropathy . Damage to the renal vessels with subsequent sclerosis of the filtering units - glomerunculi;
- pyelonephritis and cystitis;
- polyneuropathy . In this case, the functioning of the nerve endings of the arms and legs is disrupted. The patient experiences various parasthenias: burning or tingling. It’s hard for him to run and stand, his feet are constantly cold;
- diabetic coma is perhaps the most severe consequence of diabetes.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Impaired finger flexibility occurs in the later stages of diabetes. Earlier diagnosis is carried out based on test results:
- blood and urine glucose levels;
- blood biochemistry for glycosylated hemoglobin";
- to detect insulin and peptides in plasma.
The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in men is made when the blood sugar value is more than 7.7 mmol/liter. In old age, the threshold values may be slightly higher.
In type I diabetes, treatment is necessarily associated with insulin injections, and in type II – with proper nutrition and physical activity. In difficult cases, medications are prescribed:
- hypoglycemic agents (metformin or its analogues);
- from overeating (glucophage, siofor);
- receptor stimulants (byeta, victoza).
Measures to prevent type 2 disease in men include a diet containing foods with a low glycemic index; increased physical activity; sufficient water consumption, avoidance of alcoholic beverages and tobacco. Those who have a family history of diabetics should monitor their blood counts. Men after forty should also do this once every six months. And, most importantly, a positive attitude and understanding that if you follow your doctor’s recommendations, diabetes allows you to lead a full life is important.
Sugar norm
Checking diabetes
Of course, the most reliable determination of the development of diabetes is a blood sugar test. There are different indicators of the norm and they depend on many factors. Glucose levels are primarily affected by food intake.
If you carry out the analysis in the morning on an empty stomach, the norm will be significantly lower than after a meal. The same can be said about physical activity, for example, after active exercise, the sugar content decreases sharply, helping to activate energy reserves.
Sugar levels depend on the patient’s age and a number of other factors.
Please note that children's sugar levels will always be lower than adults'. But if we consider two sexes, then the sugar level should be determined within a general framework. But there are a number of trends in which the sugar norms for women and men will not be the same. This is affected, for example, by pregnancy, when a woman experiences jumps in glucose levels, and this does not always mean the development of pathology.
We all know that diabetes is diagnosed based on the main symptom - blood sugar level. But there are some methods to determine the development of the disease.
This method consists of checking the flexibility of the fingers on the limbs:
- Raises your big toe if it cannot come off the surface 50 or 60 degrees - this is a reason to check your sugar level. If the process of diabetes has been running for a long time, then it will be difficult for a person to even simply lift a finger from the floor.
- Checking the flexibility of your fingers. To do this, you need to connect your palms so that all fingers touch each other right up to the pads. In diabetics, the fingers will be bent at the joints, this is due to the contraction of the tendons, which prevents the action from being performed.
Testing finger flexibility can help determine diabetes.
Attention. If the finger flexibility test fails, this does not always indicate diabetes. The action will also not be feasible for a disease such as gout.