Description and characteristics
With a hypoplastic uterus, its size does not exceed 7 cm in a nulliparous woman. The pathological condition is often found in gynecological practice and leads to infertility and the inability to bear a child normally. In a newborn girl, the uterine organ is located in the abdominal region and has a length of 30 mm.
The size of the neck and body of the reproductive element is in a ratio of 3:1. The weight of the organ is about 4 g. After reaching the age of 5, the uterus descends into the pelvic area. The size and weight of the organ gradually increase. During pregnancy, smooth muscle tissue stretches.
Uterine hypoplasia is a state of underdevelopment when, at the end of puberty, the size lags behind the normal value and deviations in the anatomical structure of the organ are observed. It is often combined with general infantilism of the ovaries, vaginal cavity and external genitalia.
Anatomically, a hypoplastic organ is manifested by an elongated conical neck, a body that is smaller than age standards, and an abnormal anatomical location called hyperanteflexion.
Degeneration is characterized by atypical bends of the fallopian tubes, which prevents conception and normal childbearing. Hypoplasia is often associated with ectopic pregnancy. The movement of a fertilized egg through the anatomically altered fallopian tubes is complicated.
Causes of pathology
The etiological factors of the hypoplastic state of the uterus are varied. The leading cause is considered to be suppression of the functions of the hypothalamus in childhood and adolescence. This disorder leads to a slowdown and suspension of the development of the organs of the reproductive system.
Predisposing factors include:
- severe infection during puberty;
- secretory dysfunctions;
- hormonal imbalance;
- disorders of the endocrine mechanism;
- chronic intoxication of nicotine, narcotic, chemical and drug origin;
- failure of internal organs;
- abnormalities of intrauterine development;
- genetic and chromosomal diseases;
- unsuccessful surgical operation on the pelvic and abdominal organs.
Uterine infantilism is often observed in patients with disorders of puberty. The hypoplastic condition is caused by congenital pathologies and defects in the development of elements of the reproductive apparatus.
A common cause of underdevelopment of the uterus is hypogonadism, characterized by ovarian failure. Conceptually, it is associated with a decreased level of secretion of sex hormones. This pathological condition is a manifestation of the damaging effects of external factors in the antenatal period.
Underdevelopment of the uterus is one of the symptoms of increased gonadotropic activity of the pituitary appendage of the brain. Infantilism of the main organ of the reproductive mechanism occurs with hypovitaminosis in childhood and adolescence.
It is typical for:
- nervous disorders;
- anorexia;
- exhaustion of the body;
- excessive physical and mental stress;
- low calorie diet.
Infectious causes of uterine hypoplasia include tonsillitis, gonococcal infections, and influenza complications.
Degrees and symptoms
At puberty, when the uterine organ is underdeveloped, suppressed libido is observed. Symptomatically, this anomaly manifests itself as anorgasmia. Clinical signs depend on age.
Infantilism of the main reproductive organ is characterized by amenorrhea - the complete absence or constant delay of menstruation. The cycle is often accompanied by severe pain, heavy bleeding, or, conversely, scanty discharge.
Hypoplasia of the uterus is a dystrophic pathology of the organ, which is manifested by the following external signs of an anatomical nature:
- weak physical development;
- thin build;
- short stature;
- evenly narrowed bones of the hip joint;
- unformed due to low secretion of sex hormones by the mammary glands.
In older women, degenerative changes are manifested by frequent inflammation of the reproductive mechanism - endometritis, cervicitis and others. In young girls with an infantile state of the uterus, secondary sexual characteristics are poorly expressed.
During the period of bearing a child, the hypoplastic condition is characterized by:
- spontaneous termination of pregnancy;
- severe toxicosis;
- ectopic location of the embryo;
- weak or absent labor;
- insufficient opening of the uterine os;
- atonic postpartum hemorrhage.
There are 3 degrees of uterine hypoplasia. Each of them differs in individual symptoms, clinical picture and features of occurrence.
First degree
The development of the uterus stops during the embryonic period. This pathology is called rudimentary or embryonic. The neck of the organ is normally developed in a hypoplastic state of the body.
The first degree is characterized by the size of the uterus not exceeding 30 mm. The ratio of body height to neck is estimated as 1:3. During puberty, the menstrual cycle does not begin.
This degenerative pathology provokes disruption of the functioning of internal organs. Hypoplasia of the 1st degree leads to visible changes in physical development. The patient is morbidly thin.
She has a thin voice and weakly expressed secondary gender characteristics. This pathology is incurable. The tiny size of the uterus makes it impossible to bear a child. Degeneration is of a congenital nature and is extremely rare in gynecological practice.
Second degree
The infantile uterus has a size of 3-5 cm. The pathology is characterized by an inflated placement of the ovaries, long and tortuous fallopian tubes with an extremely narrow lumen.
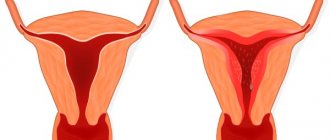
Stages of uterine hypoplasia
Clinically, the 2nd degree of uterine hypoplasia is manifested by an irregular menstrual cycle and severe pain during its passage. A typical symptom is periodic fainting. Menstruation begins no earlier than 16 years of age and occurs intermittently. The delay can be up to 6 months.
Third degree
The mildest form of the disease. The main reproductive organ reaches a size of 7 cm. This pathology is characterized by a hypoplastic state of the cervix with normal development and proper anatomical configuration of the body. Menstruation is regular, problems with conceiving and bearing a child are possible.
Degrees of hypoplasia
The size of the underdeveloped uterus and the stage at which development has stopped determine the degree of the disease. There are 3 degrees of hypoplasia:
I degree or fetal uterus. The organ is in an embryonic state. The dimensions of the uterine cavity are no more than 3 cm. If the pathology is congenital, then in most cases uterine hypoplasia of the 1st degree immediately occurs.
II degree or childish or infantile uterus. The dimensions of the uterine cavity range from 3 to 5.5 cm. The ratio of body length to cervical length changes. It is 1:3.
III degree or teenage uterus. The size of the uterus is slightly smaller than the physiological norm, the ratio of the body to the cervix is normal 3:1. The length of the cavity ranges from 5.5 cm to 7 cm.
Diagnostics
During the initial gynecological examination of patients with suspected hyperplastic condition of the uterine organ, signs of genital infantilism are visually noticeable.
They are expressed in:
- weak hair growth in the pubic area;
- degeneracy of the labia;
- the head of the clitoris protruding beyond the boundaries of the vulva;
- narrowed vaginal cavity with poorly developed smooth muscles.
The cervix of the uterine organ has an abnormal conical shape. The body is flat and poorly developed. Upon further examination, instrumental diagnostic methods reveal anomalies in the anatomical placement of the organ.
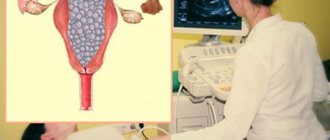
Uterine hypoplasia is a degenerative pathology that is easily determined by ultrasound. With such an examination of the pelvic cavity, the degree of changes in the anatomical structure and location of the organ is determined.
To clarify the diagnosis, echohysterosalpingoscopy (USGSS) is prescribed. Such a hardware examination provides important clinical information about the condition of the organ cavity and the patency of the fallopian tubes.
A special radiopaque substance is injected into the uterine space and its progress through the canals is monitored using ultrasound equipment. Ultrasound ultrasound examination allows us to identify concomitant pathologies of organic origin and adhesive destruction in the pelvic area.
This diagnosis is considered the modern standard for examining women with uterine hypoplasia and various forms of infertility.
A laboratory blood test is prescribed for the content of the following sex hormones:
- follicle-stimulating;
- progesterone;
- prolactin;
- luteinizing;
- estradiol.
If a hypoplastic condition of the reproductive organ is suspected, the uterine space is probed, the bone age of the patient is determined by examining the epiphysis and studying the end sections of solid tubular fibers.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the cerebral zone is considered an important diagnostic method that allows identifying the neuroendocrine causes of pathology. The bone bed of the pituitary gland is specifically studied using x-rays.
The clinical picture is assessed by a detailed analysis of 2 projections - frontal and flanking. Laboratory blood testing for the concentration of sex hormones is key to predicting the possibility of conceiving and bearing a child.
Functional diagnostics is aimed at determining the following ovulation parameters:
- pupillary symptom – anisocoria;
- measuring the temperature of basement membranes and tissues;
- tension of the cervical (cervical) mucus secretion produced by the uterus;
- ability to release an egg.
An X-ray examination of the size of the skull is performed. An important method for diagnosing uterine hypoplasia is the determination of the karyotype - a set of morphological and physiological characteristics of the chromosome set.
Treatment
Therapeutic tactics are developed based on the established degree of hypoplastic changes in the main organ of the reproductive mechanism and the etiological factors for the occurrence of pathological changes.
Basic treatment involves the use of hormone replacement or stimulating medications. Germline hypoplasia cannot be treated. Any methods do not provide adequate clinical effect.
In a rudimentary state, the uterus is not capable of further development and restoration. The second and third degrees require an individual approach to treatment. The duration of therapy ranges from several months to several years.
If necessary, the complex of treatment measures is repeated. It is recommended to correct the diet with an increase in the volume of foods rich in vitamins, microelements, protein and mineral compounds.
Official medicine
Medication, physiotherapy and other techniques are used. When diagnosing a pituitary tumor and various pathologies of the hypothalamic-pituitary apparatus, therapy is aimed at eliminating them.
The main methods of treating uterine hypoplasia offered by official medicine:
- gynecological massage;
- taking vitamin complexes;
- magnetic therapy;
- means of laser exposure;
- high frequency currents;
- mud baths;
- physiotherapy;
- hormonal drugs;
- anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs.
Spa therapy is used as an auxiliary treatment. The main goal is to increase the sensitivity of the external genitalia and internal reproductive organs to the influence of hormonal compounds. The best results are achieved by complex therapeutic tactics using several diverse techniques.
Treatment with hormonal drugs
Hypoplasia of the uterus is eliminated by a course of drugs based on synthetic estrogen or gestagen. This reduces hormonal imbalances, which promotes organ development.
Prescribed:
- Estrofem. The drug replenishes the deficiency of endogenous hormones. The chemical formula is designed based on 17-beta-estradiol. Accelerates the development of the uterine organ, regulates menstruation, improves the condition of the endometrium.
- Duphaston. Progestin medicine in tablets. The active substance is dydrogesterone, which is similar in molecular structure, chemical and pharmacodynamic properties to natural progesterone.
- Femoston. A combined drug used to replace natural hormones. Helps increase the size of the hypoplastic organ, improves blood filling of the genitals.
- Microfollin. An estrogenic drug based on ethinyl estradiol. It is used for uterine hypoplasia of the 2nd and 3rd degrees, dysmenorrhea, menopausal syndrome. Used in medicinal combination with Duphaston, which promotes the release of the egg.
- Ovestin. Hormonal suppositories with a short period of action. The main active component is concentrated for a short time in the nuclei of endometrial cells. Ovestin for uterine hypoplasia is used as an adjuvant in complex therapy. Vaginal suppositories stimulate blood circulation in the pelvic organs, improve the ability of the uterus to grow and develop.
Drugs for hormonal treatment are selected by the doctor individually based on the diagnosed concentration of such substances in the body. The nature of replacement therapy is determined taking into account the content of steroid compounds and the body's response to pharmacologically active components.
For diabetes and hyperthyroidism, a preliminary consultation with an endocrinologist is required. Hormonal drugs used to normalize the menstrual cycle have a large number of contraindications and side effects.
Folk remedies
Non-traditional methods of treating uterine hypoplasia can only be used as auxiliary and preventive measures. They are not able to replace complex, full-fledged therapy. To improve the functional state of the reproductive organ, herbal infusions and extracts of medicinal plants are used.
Such natural remedies normalize hormonal levels, promote cellular regeneration and relieve inflammation.
Medicinal plants used for hypoplastic uterus of the 3rd degree:
| Name | Properties |
| Decoction of boron uterus | Contains plant analogues of estrogen and progesterone. The plant of the heather family rejuvenates the skin, accelerates cell proliferation, stabilizes blood pressure, and strengthens the heart muscle. |
| knotweed | Rich in flavonoids and antioxidants, phylloquinone and tocopherol. Used to treat infertility, strengthens the pelvic muscles, and restores ovarian function. |
| Sage | Contains a vitamin-mineral complex, ursolic, linoleic and chlorogenic acids. It has a pronounced antimicrobial effect, suppresses pain, and relieves inflammation of the reproductive system. |
| Pharmaceutical chamomile | Improves the functions of the hepatobiliary apparatus, has vasodilating properties, and activates neuromuscular activity. Used in the prevention of cancer. |
| St. John's wort | The plant is rich in rutin, quercetin, ascorbic and nicotinic acids, and many other physiologically active compounds. Reduces the spasmodic state of smooth muscles that often accompanies uterine hypoplasia. Improves the filtration capabilities of the kidney organ. |
| Calendula | The chemical composition of the plant includes volatile essential oils, carotenoids, and oleanolic acid glycosides. Calendula tincture is effective for cervical erosion, trichomonas colpitis, and dysmenorrhea. |
| Melissa | It has a sedative and antispasmodic effect, stimulates the motility of the bile ducts. Used for any diseases of the uterine organ and menstrual disorders. |
Uterine hypoplasia is a degenerative pathology, in the treatment of which mud baths and wraps provide a good therapeutic effect. Used to improve the menstrual cycle and reproductive function.
For wrapping, ordinary clay is used. The procedure can be performed at home. Natural plastic material is diluted with cool water, wrapped around the lower abdomen, and food-grade polymer film is placed on top. You need to keep such an improvised compress for 2 hours a day.
The clay should be diluted to a creamy consistency. Instead of water, you can use tincture of boron uterus. Herbal dietary supplements are combined with medications to achieve the best therapeutic result.
To treat a hypoplastic uterus, an infusion of onion peels is used. To prepare a healing decoction, 1 tsp. pour the product into a glass of cold water and boil for 5 minutes. The infusion is filtered through cheesecloth and drunk 1 tbsp. l. every 3 hours
Diet and vitamin therapy
Prescribed drugs containing retinol, ascorbic acid, calciferol. B vitamins are used, which have pronounced neurological properties. Tocopherol has an antioxidant effect, normalizes menstruation, and prevents the development of infertility.
Vitamin D for hypoplasia is valuable because it facilitates the absorption of calcium, which is necessary for the formation of bone fibers and muscle tissue. Ascorbic acid, prescribed as part of complex treatment, reduces the likelihood of vaginal bleeding and strengthens vascular walls.
To normalize reproductive function, diet is important. Nutritionists recommend that women with this pathology consume more cereal porridges, fiber-rich cereals, and vegetables containing a complex of amino acids.
These include:
- Brussels sprouts;
- tomatoes;
- salad;
- spinach.
Fruit purees, which are included in diet therapy for uterine infantility, are useful. It is recommended to add olive oil, red meat, and seafood to the diet.
Physiotherapy
Such methods are used as auxiliary ones in addition to the main treatment.
Widespread:
- exposure of the body to high frequency currents and electromagnetic fields that have an oscillatory effect on the cellular structures of the uterine organ;
- laser therapy - the use of a concentrated beam of optical range, which improves tissue nutrition, suppresses pain during menstruation and stimulates intracellular metabolism;
- ozokerite-paraffin applications - a physiotherapeutic method of thermal treatment that strengthens the immune system, stimulates reproductive function, improves blood supply to tissues and the outflow of lymphatic fluid;
- Abdominal decompression is an effect that eliminates placental insufficiency, underdevelopment and early aging of the reproductive organ.
For genital infantilism, prolapse and hypoplastic condition of the uterus, gynecological massage is prescribed. The course lasts 30-40 days. The session lasts 10 minutes. Massage procedures can eliminate grade 3 hypoplasia. Inductothermy and acupuncture are actively used.
Treatment of uterine hypoplasia, drugs
The basis for correcting uterine hypoplasia is hormonal therapy. Each woman’s body is individual, so some will have a positive effect immediately after the first course of treatment, while for others, even the most intensive therapy will not bring the desired result.
- Hormonal drugs - as a rule, these are oral contraceptives (usually Diana-35), which the doctor prescribes to take from several months to several years - it all depends on how the uterus responds to treatment.
- Physiotherapy – types such as magnetic therapy, diathermy, UHF therapy can be used. The goal is to make the ovaries work and normalize blood circulation in the pelvic cavity.
- Massage – if the uterus is underdeveloped, a woman may be prescribed several courses of gynecological massage, which will have the same goals as physiotherapy – stimulating the ovaries and increasing blood flow to the organs of the reproductive system.
If you know in advance that the size of the uterus is much smaller than normal, then you should not plan a pregnancy before the hypoplasia is treated. Forcing events can lead to the baby dying due to lack of space for further development in the uterine cavity.
But how can you find out about hypoplasia before pregnancy?
Complications with hypoplasia
Degenerative pathology can provoke the occurrence of numerous diseases of the reproductive and genitourinary systems. It affects overall physical development and causes organ failure.
The most typical and common complications:
- infertility;
- miscarriage;
- chronic endometritis and endocervicitis - inflammatory processes of the mucous membrane and cervix of the uterine canal;
- discoordinated labor - an anomaly of the contractile activity of the uterine organ, characterized by an imbalance of its individual parts;
- severe pregnancy and early toxicosis;
- blockage of fallopian tubes by adhesions;
- ectopic embryo placement;
- heavy bleeding during menstruation and after childbirth.
Uterine hypoplasia is a pathological condition that often leads to the development of inflammatory and tumor processes in the reproductive system. At grade 3, premature birth is possible.
Symptoms of the disease
Signs of the disease can be divided into 3 groups:
- Menstrual cycle. One of the main symptoms of hypoplasia is that a girl’s periods begin later than the physiological norm, usually after 16 years. In this case, bleeding can be heavy or insignificant, and the periods themselves can be painful. Menstruation is irregular.
- Physical development. Other signs of the disease are the young girl’s retardation in physical development:
- short stature;
- narrow pelvis and chest;
- poorly developed mammary glands.
- Sexuality. Women with this pathology often experience decreased libido and an inability to experience orgasm.
Is it possible to get pregnant with uterine hypoplasia?
Congenital organ degeneration precludes successful conception. Motherhood is possible only through assisted reproductive medicine technologies. If the functionality of the ovaries is preserved, in vitro fertilization is used for patients with fetal type of hypoplasia.
IVF involves conception and the passage of an early stage of embryogenesis in laboratory conditions. In case of spontaneous abortion syndrome, the birth of a child is possible only within the framework of surrogacy.
With minimal destructive changes in the organ, normal structure and proper functionality of the reproductive apparatus, the chances of pregnancy are assessed as favorable. Such patients must remain under constant gynecological supervision throughout the entire period of bearing a child.
Uterine hypoplasia and pregnancy
The likelihood of getting pregnant depends on the degree of the disease. With grade 1 hyperplasia, pregnancy is impossible in most cases. With stage 2 disease, a woman often experiences spontaneous abortion. With stage 3 disease (if the size of the uterus is slightly reduced and the patient does not have ovarian hypoplasia at the same time), there is a possibility that she will be able to become pregnant and carry a child.
Thus, pregnancy can occur only against the background of normal functioning of the ovaries. If a woman manages to become pregnant with an underdeveloped uterus, the pregnancy can be difficult. Such women are at high risk of miscarriage. While carrying a child, a woman suffers from severe toxicosis. Problems can also be expected during childbirth. An underdeveloped uterus contracts weakly. Intrauterine bleeding occurs very often during childbirth.
If a woman has developed uterine hypoplasia, but there is no ovarian failure, then normal maturation of the egg occurs, but the woman is not able to bear a fetus. In this case, you can resort to surrogacy.
Another danger of hypoplasia is the high risk of ectopic pregnancy. This is a life-threatening condition that, if not detected promptly, can cause severe bleeding and death to the woman.
How is pregnancy going?
There is a high risk of early toxicosis and miscarriage. Before conception, it is recommended to do a blood test for the content of sex hormones, to eliminate inflammatory and infectious processes, if any.
Pregnancy in patients with uterine hypoplasia of the 2nd and 3rd degrees always occurs with complications. Hormonal therapy can increase the chances of having a baby. This increases the likelihood of normal labor. Anticoagulant drugs reduce the risk of heavy bleeding.
How to treat uterine hypoplasia
Depending on the individual health status of each woman, a treatment method for uterine hypoplasia is selected. In addition, the type of hypoplasia, the causes of development and the size of the uterus are taken into account.
The standard treatment for uterine hypoplasia is hormonal therapy, the use of physiotherapeutic procedures and gynecological massage.
When prescribing general treatment, it is necessary to especially note the rationality of nutrition. Moreover, nowadays teenage girls often abuse various diets, driving themselves to complete exhaustion.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account adolescence as a period of intense experiences and avoid stressful situations. The same applies to more mature women with a similar pathology.