For the term "Hypoplasia" see also other meanings.
| Hypoplasia (dentistry) | |
| ICD-10 | 00.400.4. |
| ICD-9 | 520.4 |
Hypoplasia of teeth
(Latin hypoplasia from ancient Greek ὑπο- 'prefix with the meaning of weakened quality' and πλάσις 'formation') is a developmental defect consisting in the underdevelopment of a tooth or its tissues during the period of their formation.
The extreme expression of hypoplasia is aplasia
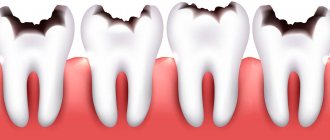
- the congenital absence of a tooth, part or all of the tooth enamel. Most often, hypoplasia affects the enamel of teeth (and permanent teeth suffer more than temporary teeth), in more severe cases - dentin.
Dental hypoplasia in one form or another is a fairly common disease and is observed in approximately 30% of people.
Content
- 1 Etiology/pathogenesis 1.1 Hypoplasia of primary teeth
- 1.2 Hypoplasia of permanent teeth
- 2.1 Main forms of hypoplasia 2.1.1 Discoloration
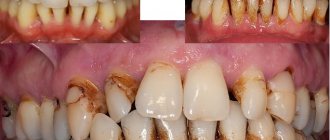
Enamel hypoplasia in a child
Hypoplasia of primary teeth occurs in almost every child, which can be caused by problems during pregnancy. This condition cannot affect the condition of the enamel of permanent teeth; this can only happen if the child was often and seriously ill in childhood. Hypoplasia of non-permanent teeth is a problem before the bite changes. But this does not mean that you should ignore visiting the dental office and treatment.
Symptoms of hypoplasia in children that you should pay attention to and begin timely treatment:
- Yellow or white spots on the surface of the enamel, dotted or furrowed depressions on the surface of the enamel.
- Lack of enamel on the crown of the tooth.
- Teeth of an incomprehensible shape, which explains the lack of enamel
Below are recommendations for parents related to the treatment of this pathology in children:
- Proper and balanced nutrition for the child. It is recommended to exclude sweet and sour foods from the diet.
- Using high-quality and proven toothpaste, which helps strengthen the enamel of baby teeth.
- Brushing children's teeth should be done with a cotton swab, and then only with a soft children's toothbrush.
- Silvering of affected areas, which helps protect teeth from carious lesions. The decision to carry out this procedure is made exclusively by a specialist based on a dental examination of the child’s oral cavity.
- Filling teeth that are located further than threes.
Etiology/pathogenesis
Hypoplasia of dental tissue (most often enamel) occurs when metabolic processes in the tooth buds are disrupted under the influence of disturbances in mineral and protein metabolism in the body of the fetus or child. Underdevelopment of enamel due to hypoplasia is irreversible. Often, enamel hypoplasia is accompanied by a violation of the structure of dentin and dental pulp.
Hypoplasia of primary teeth
Examination in the dentist's office
Hypoplasia of baby teeth, which form during the prenatal period, is caused by disorders in the body of a pregnant woman (rubella, toxoplasmosis, toxicosis, Rh conflicts). In children suffering from chronic somatic diseases that began before or shortly after birth, dental hypoplasia is observed in 50% of cases.
Hypoplasia of permanent teeth
Hypoplasia of permanent teeth develops under the influence of various diseases (rickets, tetany, acute infectious diseases, gastrointestinal diseases, toxic dyspepsia, nutritional dystrophy, brain disorders) that arose during the period of formation and mineralization of these teeth, that is, in the period from 6 months to 1-1 ,5 years. The localization of hypoplasia on the crown of the tooth largely depends on the age at which the child suffered the disease (see Teething).
The severity of hypoplasia depends on the severity of the disease.
The following types of hypoplasia also differ:
systemic hypoplasia
- manifests itself in a change in the color of tooth enamel, its insufficient development or complete absence;
local hypoplasia
- occurs when the rudiments of permanent teeth are involved in the inflammatory process or in the event of mechanical trauma.
Prevention
Prevention of enamel hypoplasia includes the following measures:
- prevention of rickets (taking vitamin D3);
- timely treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases when planning pregnancy;
- nutritious nutrition for a young child;
- mandatory systematic hygienic procedures for oral care in young children;
- periodic sanitation of the oral cavity.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Education: higher education, 2004 (State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “Kursk State Medical University”), specialty “General Medicine”, qualification “Doctor”. 2008-2012 – postgraduate student of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, KSMU, Candidate of Medical Sciences (2013, specialty “pharmacology, clinical pharmacology”). 2014-2015 – professional retraining, specialty “Management in Education”, Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “KSU”.
The information is generalized and is provided for informational purposes. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous to health!
74-year-old Australian resident James Harrison has donated blood about 1,000 times. He has a rare blood type whose antibodies help newborns with severe anemia survive. Thus, the Australian saved about two million children.
Tooth decay is the most common infectious disease in the world, which even the flu cannot compete with.
When lovers kiss, each of them loses 6.4 calories per minute, but at the same time they exchange almost 300 types of different bacteria.
Even if a person's heart does not beat, he can still live for a long period of time, as the Norwegian fisherman Jan Revsdal demonstrated to us. His “engine” stopped for 4 hours after a fisherman got lost and fell asleep in the snow.
Read also: Dental treatment without a drill for children
Research shows that women who drink several glasses of beer or wine per week have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
It was previously believed that yawning enriches the body with oxygen. However, this opinion has been refuted. Scientists have proven that yawning cools the brain and improves its performance.
In order to say even the shortest and simplest words, we use 72 muscles.
Many drugs were initially marketed as medicines. Heroin, for example, was originally brought to market as a cure for children's coughs. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as an anesthesia and as a means of increasing endurance.
Millions of bacteria are born, live and die in our intestines. They can only be seen under high magnification, but if they were put together, they would fit in a regular coffee cup.
American scientists conducted experiments on mice and came to the conclusion that watermelon juice prevents the development of vascular atherosclerosis. One group of mice drank plain water, and the second group drank watermelon juice. As a result, the vessels of the second group were free of cholesterol plaques.
Our kidneys are capable of purifying three liters of blood in one minute.
According to statistics, on Mondays the risk of back injuries increases by 25%, and the risk of a heart attack by 33%. Be careful.
Regular use of a solarium increases your chance of developing skin cancer by 60%.
The first vibrator was invented in the 19th century. It was powered by a steam engine and was intended to treat female hysteria.
Besides people, only one living creature on planet Earth suffers from prostatitis - dogs. These are truly our most faithful friends.
Malignant neoplasms of the genital organs represent a serious socio-medical problem. Penile cancer – malignant formation, l.
Systemic hypoplasia
Main forms of hypoplasia
Clinically, three forms of systemic hypoplasia are distinguished:
Color change
A weak degree of enamel underdevelopment manifests itself in the form of spots, often white, less often yellowish in color, with clear boundaries and the same size on the teeth of the same name. The spots are usually found on the vestibular surface and are not accompanied by any unpleasant sensations. Spots with hypoplasia are not stained with dyes (unlike caries at the spot stage).
Underdevelopment
A more severe form of enamel hypoplasia is its underdevelopment, which manifests itself in different ways (wavy, dotted, grooved enamel). Indentations or grooves are found on the surface of the enamel. The enamel in the recesses remains dense and smooth.
Lack of enamel
The most rare form of hypoplasia is its absence (aplasia) in a certain area. With this form, there may be complaints of pain from thermal and chemical irritants.
Hypoplasia in congenital syphilis
Congenital syphilis is characterized by “Hutchinson’s”, “Fournier” and “Pfluger” teeth. These signs are included in the triad of congenital syphilis: parenchymal keratitis, congenital deafness and Hutchinson's teeth. However, it was later found that these anomalies can occur not only with syphilis.
Hutchinson's teeth
An anomaly of tooth development in which the upper central incisors have a screw-shaped or barrel-shaped crown (the size at the neck is larger than that of the cutting edge) and a semilunar notch on the cutting edge. Sometimes the semilunar recess is not covered with enamel.
Fournier's teeth
The central incisors are similar to Hutchinson's teeth, but without the lunate notch.
Pflueger's teeth
An anomaly of the first molars, in which the size of the crown at the neck of the tooth is larger than that of the chewing surface, and the cusps are underdeveloped.
"Tetracycline" teeth
“Tetracycline” teeth are teeth that have a changed color as a result of taking tetracycline during the formation and mineralization of tooth tissue. Tetracycline is deposited in the enamel and dentin of tooth germs, as well as in the bones of a fetus or child if administered to a pregnant woman or child. Depending on the dose, tetracycline can change not only the color of the enamel, but also lead to underdevelopment of tooth enamel. When taking dimethylchlortetracycline, the color change is more significant.
When taking tetracycline during pregnancy, the child's baby teeth are stained, namely 1/3 of the crowns of the incisors, starting from the cutting edge and the chewing surface of the large molars. Taking tetracycline by a child older than 6 months already leads to staining of permanent teeth. As a rule, only the part of the tooth crown that is formed during the period of taking the drug is stained.
The intensity of staining and color depend on the type of tetracycline and its amount. Teeth colored yellow have the ability to fluoresce under the influence of ultraviolet rays. This property can be used to differentiate tooth staining caused by other causes, such as bilirubin in hemolytic disease of the newborn.
Special forms of dental hypoplasia
Special forms of the variety of systemic dental hypoplasia are the teeth of Fournier, Pfluger and Hutchinson. Each of these forms is characterized by its own special shape of the dental crown. Not so long ago it was believed that all these developmental anomalies were one of the symptoms of congenital syphilis. It has now been established that the appearance of Fournier and Hutchinson teeth may be caused by some other diseases. But “Pfluger’s teeth” appear only under the negative influence of a syphilitic infection.
Gnomik.ru recommends the company Kholod Group Repair of Maytag refrigerators inexpensively! We professionally and quickly repair Maytag refrigerators + any other manufacturers. More than 5 years of experience. Free visit of a specialist and diagnostics!
All repair and maintenance services for refrigeration equipment.
Use promo code: Gnomic.ru
and get a guaranteed 10% discount
We work in Moscow and the region. More details by service area.
Call
Call a technician for free
Local hypoplasia
This is a disruption of the formation of enamel on permanent teeth as a result of the involvement of tooth buds in the inflammatory process or due to their mechanical trauma.
Local hypoplasia appears in the form of whitish-yellowish spots and depressions located on all surfaces. In severe cases, there may be aplasia (absence) of enamel.
Local hypoplasia is more often observed on permanent small molars, the rudiments of which are located between the roots of milk teeth.
This disease can be prevented by taking preventive measures against caries of primary teeth or treating them at an early stage of the lesion.
This pathology is formed as a result of a disruption in the activity of the cells that build the enamel, but the causes of this disruption are not related to mineral metabolism in the body - local enamel hypoplasia occurs as a result of mechanical trauma to the germ of a permanent tooth or an inflammatory process in it under the influence of biogenic amines and infections entering the follicle during chronic periodontitis of the baby tooth. Local hypoplasia is not observed on temporary teeth.
More often, the cause of local hypoplasia is an inflammatory process spreading from the area of the apex of the root of a temporary tooth or from an osteomyelitic lesion of the jaw. The rudiment of any permanent tooth may be involved in the inflammatory process, but more often it is the rudiments of premolars located between the roots of temporary molars that suffer. As is known, temporary molars are most often affected by caries, and therefore by apical periodontitis.
With an intense and prolonged inflammatory process, as well as with a deep impacted dislocation, the cells that build dentin can be damaged. In this case, both tissues - enamel and dentin - are formed incorrectly, while the permanent tooth has an irregular shape - with a curved or barrel-shaped crown, bizarre outlines.
Diagnostics
Hypoplasia of enamel and dentin is diagnosed based on:
- characteristic clinical picture;
- X-ray examination (changes in tooth roots, canals, hard tissues are revealed);
- fluorescent stomatoscopy (there is no quenching of the glow in places where spots are localized);
- results of vital staining (no staining of enamel defects with dyes);
- assessing the dynamics of the process (the stability of pathological changes is established).
The choice of treatment for hypoplasia in each specific case depends on the depth and extent of the defect, the severity of the disturbance of mineral metabolism, and the degree of deterioration in the aesthetic appearance of the teeth.
Conservative treatment of enamel and dentin hypoplasia consists of saturating tooth tissues with minerals (remineralizing therapy).
Microabrasion or bleaching of hypoplastic areas is used when the affected area is small and allows you to eliminate small superficial cosmetic defects of the enamel.
Replacement of affected tissues is carried out if it is impossible to eliminate the defect in a low-traumatic way. The main directions in this case are restoration of hypoplastic areas with composite material, installation of veneers and lumineers, metal-ceramic, ceramic, metal-plastic crowns.
Treatment
For single white spots, treatment may not be necessary. But if the spots are visible when talking, smiling, etc., and even more so if the disease leads to the destruction of tooth tissue, treatment of hypoplasia must be carried out, and as soon as possible, since severe dental hypoplasia can cause very serious consequences:
- Increased tooth wear
- Destruction of tooth tissue
- Complete loss of affected teeth
- Development of malocclusions
The main method of treatment is teeth whitening for mild cases of the disease or filling teeth with composite materials. In case of pronounced changes, orthopedic treatment is indicated. In some cases, uneven tooth enamel may be sanded down to smooth out the surface of the teeth.
Along the way, as a rule, the enamel is remineralized using special preparations (remodent, calcium gluconate solution, etc.).
Hypoplasia of tooth enamel: etiology and classification
The purpose of the outer enamel layer is to protect the tooth from harmful external influences, so in a healthy person it is quite thick and durable. In the case of hypoplasia, when the source of the disease is internal malformations, any tissue can be affected. In the vast majority of clinical cases, this is tooth enamel. The lesion is non-carious in nature and is caused by genetic abnormalities, and its result is the thinning of tooth enamel of varying degrees of severity.
Enamel hypoplasia is a specific hereditary disease affecting both primary and molar teeth.
Note: most often, hypoplasia is detected at an early age; much less often, the first symptoms appear in adults.
In modern dentistry, it is customary to distinguish three types of hypoplasia:
- systemic, in which the lesion covers the entire surface of the teeth. It is characterized by serious underdevelopment of the enamel (and not just its thinning) and appears pointwise, grooved or wavy;
Systemic enamel hypoplasia – mild severity
Aplasia of tooth enamel is less common than the tooth itself; it manifests itself as a complete or partial absence of enamel on the crown of the tooth.
Pathological changes in the enamel layer outwardly look like a cosmetic defect and often cause psychological discomfort. In addition, this causes tooth weakness and provokes the development of other pathological processes, in particular caries.
Doctors have different opinions about the causes of hypoplasia. Some consider the main cause of impaired mineralization in dental tissues, others believe that the main risk factor is associated with dysfunction of the epithelial cells of the dental germ. At the same time, both sides recognize that changes at the cellular level can be provoked by external causes that create favorable conditions for the development of hypoplasia.
Pathology is a congenital defect and develops in the womb
Reasons for appearance
Often, enamel hypoplasia begins to form already at the moment of formation of tooth germs, that is, during the embryonic period.
The cause of this phenomenon is unfavorable factors affecting a pregnant woman:
- infectious and viral diseases, such as toxoplasmosis, rubella, acute respiratory infections;
- the presence of toxicosis and gestosis;
- exacerbation of certain chronic diseases;
- poor nutrition, which results in a deficiency of nutrients;
- the presence of bad habits such as smoking, drinking alcohol or drugs.
The development of hypoplasia is not necessarily associated with diseases of the woman during pregnancy. Often the cause of the development of pathology is a negative impact on the child during the birth and postpartum period:
- premature birth;
- injury during labor;
- development of jaundice in an infant;
- the presence of congenital defects of the cardiovascular system;
- lactation problems, as a result of which the quantity of milk decreases and its quality composition deteriorates.
Exposure leading to the development of hypoplasia can also occur during the first years of a child’s life.
Experts note the following unfavorable factors affecting the condition of the enamel:
- unbalanced diet;
- systemic diseases and various pathologies of the structure and development of internal organs;
- blood diseases causing iron deficiency;
- excess fluoride intake into the body;
- taking certain medications;
- damage to the integrity of the elements of the jaw row as a result of mechanical trauma, as well as the occurrence of dental diseases, such as pulpitis, periodontitis.
Concept
Enamel hypoplasia is a non-carious lesion. The problem is that the formation of the matrix of the protective layer itself is disrupted, as a result of which it is damaged.
This disease can be found in people of all ages, including children. There are statistics that enamel hypoplasia occurs in 30% of people on earth.
Patients who already have permanent teeth suffer most often.
, the disease can be congenital or even acquired. The disease is inherited as a dominant trait linked to the X chromosome.
Hypoplasia affects both incisors and molars, depending on the severity of the disease. It can be localized to one or two or spread to all teeth in a row.
This is due to the stage of life at which the disease occurred.
For example, if the onset of the disease occurs before the age of 3-5 months, hypoplasia will affect the cutting edges of the cusps of the third molars and central incisors. If the baby gets sick between 8-9 months, pathological spots appear on the lateral incisors and on the cutting edges of the canines.