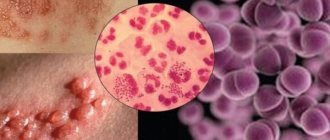
Throat gonorrhea
Gonorrhea of the throat is a specific infectious process affecting the mucous membrane of the pharynx, tonsils and larynx.
The causative agent of this infection is the bacterium gonococcus, which mainly parasitizes the human reproductive system and is transmitted sexually.
The throat is a fairly rare localization of pathology, but it is difficult to diagnose.
This occurs due to its disguise as a purulent sore throat caused by other pathogens.
Causes and mechanism of development of throat gonorrhea
The main cause of the infectious process is a gram-negative spherical bacterium - gonococcus.
It parasitizes primarily in the mucous membrane of the urethra, leading to the development of purulent urethritis.
When the pathogen gets on the surface of the pharynx, tonsils and larynx, the bacteria begin to actively multiply.
Factors of nonspecific immunity are suppressed, which leads to the development of a purulent process.
Bacteria in the environment quickly die, so the main route of infection for throat gonorrhea is direct contact of mucous membranes during oral sex.
This is facilitated by frequent changes of sexual partners and having sex without using personal protective equipment (condoms).
Gonorrhea of the throat: symptoms
According to the patient's complaints, the disease can be confused with purulent tonsillitis or tonsillitis.
The time from infection to the appearance of the first symptoms can range from five days to two weeks.
Lieutenant Colonel of the Medical Service, doctor Sergey Gennadievich Lenkin talks about the causes and mechanism of development of throat gonorrhea
The content of this article has been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by a dermatovenerologist, urologist, candidate of medical sciences.
Lenkin Sergei Gennadievich
| Name | Term | Price |
| Venereologist appointment | 900.00 rub. | |
| Neisseria gonorrhoeae DNA | 1 day | 300.00 rub. |
Gonorrhea
- Manifestations of gonococcal infection
- Diagnosis of gonococcal infection
- Treatment of gonococcal infection
Gonorrhea is an infectious disease caused by gonococcus (Neisseria gonorrhoeae), which is classified as a sexually transmitted disease.
Gonorrhea is transmitted primarily through sexual contact. The main sources of infection are men and women with an erased or chronic form of infection. Infection from a person with gonorrhea can occur through direct contact of the external genitalia, even if the penis is not inserted into the woman’s vagina. The contact and household route of transmission (through household items, toilet seats, towels, etc.) has not been proven. Children can become infected during childbirth, when passing through the birth canal of a mother with gonorrhea. Immunity to gonococcus is not formed. Therefore, repeated infections are possible throughout life. Women become infected with gonorrhea more easily, due to the structural features of their genital organs; they more often suffer from erased forms of the infection and more often infect men. It is probably not worth saying that this disease is most widespread among people who are sexually active and have promiscuous sex.
Manifestations of gonococcal infection
The incubation (latent) period of the disease lasts from 12 hours to 7 days, on average 72 hours. At this time, the patient is already contagious and is capable of transmitting the disease to sexual partners.
Gonococci affect the especially delicate mucous membranes of the genital organs, causing inflammation. In women, the mucous membranes of the urethra (urethra), lower rectum, ducts of the Bartholin's glands (glands of the vestibule of the vagina), cervical canal (cervical canal), uterine cavity (endometrium) and lumens of the fallopian tubes are affected. Thus, women are more likely to develop gonorrheal urethritis (inflammation of the urethra), proctitis (inflammation of the rectum), endocervicitis (inflammation of the cervical canal), endometritis (inflammation of the lining of the uterus) and adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine appendages - ovaries and fallopian tubes) . The remaining forms of lesions, that is, vulvitis and colpitis, occur mainly secondary to the presence of damage to the surface of the mucous membrane. In severe cases, it is possible to develop gonorrheal peritonitis, spread the infection through the bloodstream and damage the eyes, joints, heart and other organs.
A few days after infection, the first signs of gonorrhea begin to appear. More often, the development of infection begins with the phenomena of urethritis. The woman begins to experience pain and pain when urinating. The area around the external opening of the urethra becomes swollen and red, and a drop of pus may be released from the canal. At the same time, the cervical canal is involved in the inflammatory process. Here, too, signs of gonorrheal infection are observed. A woman notices the appearance of purulent, moderate or heavy vaginal discharge. If the mucous membrane of the rectum is affected, proctitis occurs, and this is accompanied by complaints of pain in the anus and false urge to have a bowel movement. Sometimes the glands of the vaginal vestibule are involved in the infectious process. Bartholinitis develops in its various forms and manifestations.
However, gonorrhea does not always manifest itself so clearly; quite often in women the disease is almost asymptomatic, which leads to further spread of the infection and serious complications.
In the absence of timely treatment, the inflammatory process extends beyond the external genitalia and spreads to the mucous membrane of the uterine cavity. This disease is called ascending gonorrhea. The development of ascending gonorrhea is promoted by sexual intercourse, decreased immunity and intrauterine interventions. Inflammation of the uterine mucosa (endometritis) with gonorrhea manifests itself in the same way as an inflammatory process of a nonspecific nature. Body temperature rises, general well-being sharply worsens, and nagging pain in the lower abdomen occurs. The woman begins to be bothered by purulent vaginal discharge mixed with blood. Sometimes bleeding occurs that is not associated with menstruation. Menstruation becomes prolonged, heavy and painful.
The spread of gonorrheal inflammation to the area of the appendages causes the development of gonorrheal adnexitis. Severe general condition, high temperature, intoxication, severe pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the lower back and hips - these are the worries that gonorrheal infection of the appendages causes. A characteristic feature of inflammation caused by gonococcus is damage to the appendages on both sides, the rapid occurrence of irreversible changes in the fallopian tubes, with the development of their complete obstruction.
Acute manifestations of the disease do not last long. After just two weeks, the number of complaints decreases, and after 2 months, acute gonorrhea becomes chronic. There are few manifestations of the disease during the calm period, and they are no longer as pronounced. Inflammation of the urethra may practically not bother a woman; endocervicitis (inflammation of the cervical canal) may not manifest itself at all. Minor purulent discharge by a sick woman may go unnoticed.
With a long course of gonorrhea, the likelihood of infection spreading into the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes and the development of a large number of adhesions in the pelvis increases sharply. Chronic inflammation of the uterine mucosa (endometritis) and uterine appendages (adnexitis) is accompanied by patient complaints of constant dull aching pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, intensifying after sexual intercourse or gynecological examination. Periodically, spotting from the genital tract and menstrual irregularities are a concern. Menstruation becomes frequent, painful, and heavy. Infertility almost always occurs.
Chronic gonorrhea is prone to exacerbations. Most often they are provoked by hypothermia, sexual intercourse, gynecological intrauterine manipulation, and decreased immunity as a result of common infections. Exacerbations occur as a full-blown inflammatory process with a large number of manifestations.
Diagnosis of gonococcal infection
During a gynecological examination, the doctor detects all signs of inflammation, depending on their prevalence and the colorfulness of the manifestations. In general, the picture does not differ from that of diseases caused by nonspecific pyogenic flora. Decisive in the diagnosis of gonorrhea will be the detection of gonococcus during laboratory examination of smears and cultures from the urethra, cervical canal and rectum. To diagnose gonorrhea, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is also currently used, which makes it possible to detect the presence of gonococcus heme in various biological fluids. In addition, the patient's blood is tested for syphilis and HIV.
Considering that gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease, further examination and treatment of the woman and her sexual partner, or partners, are carried out at a dermatovenerological dispensary.
Treatment of gonococcal infection
So, the woman receives a referral to the skin and venereal disease clinic. A notification is sent there when a case of gonorrhea is detected.
At the venereology clinic, a woman is questioned about her sexual contacts, and, if necessary, search activities are carried out. Treatment in a venereology hospital is often required. All this is necessary to suppress the spread of infection among people and it is in the interests of a woman not to hide anything from the details of her intimate life.
When treating gonorrhea, a course of specific antimicrobial therapy is prescribed. A prerequisite for successful treatment is abstinence from sexual activity. After completing the course of treatment, control of cure for gonorrheal infection is carried out 2 and 14 days after the end of treatment. If gonococci (Neisseria gonorrhoeae) are detected, treatment is repeated. Remember that timely treatment for gonorrhea will help you recover and avoid complications.
An infection in the throat has an acute onset
In most cases, the infectious process in the throat has an acute onset.
General symptoms of the disease:
- body temperature rises
- general weakness develops
- appetite decreases
- muscle aches are observed
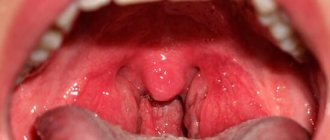
The mucous membrane of the larynx, tonsils and pharynx becomes deep red (hyperemia).
Over time, purulent plaques appear on it, which have a viscous consistency and a yellow-green color (pus is dead leukocytes with gonococci that are localized inside them).
The following local symptoms can be detected:
- Dry mouth
- Redness and swelling of the throat
- Pain occurs when swallowing and speaking
- Hoarseness of voice
- There is a foul odor from the throat
- Salivation increases
There are complaints of general malaise, body temperature increases.
Lymph nodes may be enlarged.
Remember! If you experience the above symptoms, contact your venereologist immediately.
If the pathological process is not treated correctly, gonorrhea of the throat can lead to a number of complications.
These include:
- purulent encephalitis - occurs when bacteria penetrate into the substance of the brain
- purulent meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord with accumulation of pus in the space between them
- abscess of the soft tissues of the retropharyngeal and paratonsillar space - is a limited cavity filled with pus, which often forms after the addition of a concomitant infection caused by other bacteria
- chronic course of throat gonorrhea, which leads to decreased immunity and complicates the treatment of the disease
Gonorrhea of the throat has nonspecific symptoms
Such a specific infectious process as gonorrhea of the throat has nonspecific symptoms, which makes diagnosis difficult.
To prevent the development of complications, it is very important to promptly consult a venereologist, who will prescribe appropriate laboratory examination and treatment.
Methods for diagnosing gonorrhea of the throat
Gonorrhea of the throat has similar symptoms to many colds and other diseases.
According to clinical manifestations, it can be compared with diseases such as:
In order to accurately diagnose and differentiate gonorrhea, a number of laboratory tests are used.
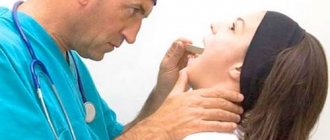
After a thorough examination, the doctor takes material from the oral cavity (smear) and blood for analysis.
Additionally, the doctor may refer you for examination to a venereologist.
Diagnosis is carried out using the following methods:
- PCR diagnostics
- Bacteriological culture
- Microscopy
- Serology
Let's consider each method separately.
Bacteriology is characterized by inoculating pathological material on a special nutrient medium.
Pathogenic microorganisms are cultivated on it.
At the same time, sensitivity to antibiotics is tested in order to find out which drug the pathogen is sensitive to.
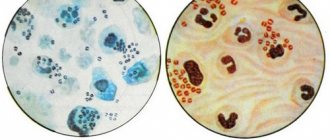
By microscopy of a smear, you can see characteristic signs of gonococcus.
Treatment of throat gonorrhea
After a diagnosis of throat gonorrhea is made, treatment is aimed at destroying the pathogen.
Treatment should be carried out as quickly as possible to prevent the pathogen from damaging the entire body.
For this purpose, antibiotics active against gonococcus are used.
These include:
- representatives of the penicillin group (amoxicillin, ampicillin)
- cephalosporins (cefazolin, rocephin)
Depending on the severity of throat gonorrhea, these antibiotics are used in the form of tablets or solutions for parenteral (intramuscular or intravenous) administration.
Additionally, local antiseptics are used in the form of:
- gargling (furatsilin solution)
- lozenges (septrefril, septolete)
- aerosol (inhalipt, chlorophyllipt)
It is very important to carry out correct and adequate treatment of gonorrhea of the throat, since independent use of antibiotics can lead to the development of gonococcus resistance and the development of purulent complications.
The patient's sexual partners are examined for the presence of gonorrhea and appropriate therapy is administered.
This is an integral part of preventing the recurrence of the disease.
Note! Do not self-medicate, entrust it to a qualified specialist.
After treatment with antibacterial drugs, eubiotics must be prescribed to restore normal intestinal microflora.
To strengthen the body, you should drink mineral and vitamin complexes.
Complications of gonorrhea throat
If the pathological process is not treated correctly, gonorrhea of the throat can lead to a number of complications.
The main complications of sexually transmitted diseases are infertility and impotence.
It is worth noting that further consequences of the disease depend on the chosen treatment tactics.
The functioning of the immune system also plays a leading role.
Complications of gonorrhea include:
- purulent encephalitis - occurs when bacteria penetrate into the substance of the brain
- purulent meningitis - inflammation of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord with accumulation of pus in the space between them
- abscess of the soft tissues of the retropharyngeal and paratonsillar space - is a limited cavity filled with pus, which often forms after the addition of a concomitant infection caused by other bacteria
- chronic course of throat gonorrhea, which leads to decreased immunity and complicates the treatment of the disease
Severe complications include damage to the entire body by the gonorrhea pathogen.
Gonococcal sepsis occurs, which can have an unfavorable outcome.
To prevent complications from occurring, timely treatment should be carried out and all instructions of the attending physician should be followed.
Prevention of throat gonorrhea
Preventing a disease is easier than continuing long-term treatment.
It is very important to avoid unprotected sex with casual partners.
Do not have sexual intercourse if your partner has rashes or sores on the genitals.
Do not have a promiscuous sex life, this can lead to serious illnesses!
After oral-genital contact, you should definitely rinse your mouth with a 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine digluconate.
This will help you reduce the risk of possible infection.
It is important to know! If a solution with a disinfectant is intended for external use, it is strictly forbidden to swallow it.
Be sure to follow the rules of personal hygiene.
If you experience any signs and symptoms of throat gonorrhea, contact the author of this article - a venereologist, a urologist in Moscow with 15 years of experience.
Differences between gonorrhea and other infections
The symptoms that appear when infected with gonorrhea are so similar to sore throat and other ailments that it is very difficult to establish the correct diagnosis. Especially if the patient turned to an ENT specialist, but kept silent about the new partner and oral sex.
Oral gonorrhea can be suspected first of all in the absence of a positive result from the treatment of pharyngitis. After all, rinsing and other methods of treatment will not help get rid of the causative agent of clap.
The main distinguishing feature of gonorrhea is that only the mucous membrane of the throat and nearby areas is affected. Symptoms include:
- a sore throat;
- hoarseness;
- purulent plaque.
At the same time, the typical symptoms of respiratory infections and sore throat in the form of inflammation of the nasopharynx are absent. The person does not have a stuffy nose, no rhinorrhea, lacrimation, sneezing and other similar manifestations.
When carrying out differential diagnosis with infectious mononucleosis, attention is drawn to the fact that with gonorrhoea only the cervical, submandibular and occipital lymph nodes become enlarged. In mononucleosis, axillary, inguinal and other peripheral nodes are affected.
Despite the fact that the disease is very similar to follicular or purulent tonsillitis, gonorrhea can be distinguished from them. First of all, because gonorrhea is characterized by 2-sided damage to the tonsils. In addition, with this disease, purulent plugs do not form, but only a massive plaque.
If you experience a sore throat, hoarseness and other typical signs of a sore throat soon after unconventional sexual intercourse, you should definitely consult a specialist. After all, this may not be ordinary pharyngitis, but gonorrheal infection of the oral cavity. This condition requires immediate specific treatment to prevent the development of complications.
Not many people know that gonococcal pharyngitis develops against the background of gonorrhea - a severe pathology that affects the oropharynx. Gonorrhea is accompanied not only by urogenital symptoms. When the pharynx is infected with gonococci, the clinical picture of this sexually transmitted infection includes symptoms of tonsillitis. The disease develops in a special way and requires specific treatment.
How does gonorrhea manifest when it affects the oral cavity?
Most sexually transmitted diseases can spread not only to the genitals, but also to other parts of the body. Gonococcal infection can be localized in the eyes, rectum, pharynx and larynx. With gonorrhea in the mouth, a person experiences purulent plaque and pain when swallowing. We will discuss below what symptoms, routes of infection and methods of treating this pathology exist.
Oral gonorrhea
Oral gonorrhea is detected mainly in people who prefer oral sex; the course of the disease is often asymptomatic. In rare cases, a sore throat and fever may occur. With orogenital infection, gonococcal stomatitis and pharyngitis can develop:
- Gonococcal stomatitis is manifested by swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane, the release of viscous-purulent secretion. If left untreated, the mucous membranes of the cheeks, tongue and gums become covered with ulcers and erosions. The ulcerations are small in size and do not particularly bother them; yellow-gray mucus is released from them, in which gonococci are found.
Gonococcal pharyngitis most often occurs without any symptoms; sometimes patients complain of a sore throat, excessive salivation, and difficulty swallowing. A purulent-mucous plaque forms on the reddened throat and tonsils, the uvula and palatine arches swell.
When oral gonorrhea is infected through household means, the symptoms of the disease are also similar to stomatitis - similar purulent inflammations occur in the mouth. Just 3 days is enough for gonococci to completely affect the mucous membrane of the larynx and palatine tonsils. The patient's body temperature rises, headaches and chills appear. The tonsils become covered with purulent plaque.
Fortunately, there are several very effective ways to prevent gonorrhea - a regular sexual partner and the use of protective intimate products during sexual intercourse. The methods, although conservative, are very effective and time-tested.
Signs and symptoms of gonorrhea in the mouth
The manifestation of the disease does not begin immediately after infection, but some time after. The first symptoms become visible after 3-7 days, but sometimes the pathology does not manifest itself for 6 months.
The main symptom of the disease is burning and dry mouth. Patients also experience itching quite often. As the disease progresses, the body becomes intoxicated and fever appears. At this point, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- constant pain that worsens when swallowing;
- excessive salivation;
- hoarse voice;
- unpleasant odor that cannot be eliminated with chewing gum or other means;
- enlarged lymph nodes, pain is felt when pressing on them.
In the early stages of the development of gonorrhea, the symptoms are practically no different from ordinary sore throat, so patients do not attach importance to their well-being and try to improve their health on their own. The photo in our article clearly shows what oral gonorrhea looks like.
Symptoms will appear suddenly, since the oral mucosa is a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria.
In just a few days, plaque will appear throughout the entire mouth and throat.
If you notice a clear manifestation of the symptoms described above, you should urgently consult a doctor who will draw up a treatment plan. It should be understood that in the absence of medical care, gonococcus will quickly spread to internal organs and can enter the brain. In such a situation, there is a high risk of death.
Cultures for throat gonorrhea
The cultural method is the “gold standard” in the diagnosis of oropharyngeal gonorrhea.
This test is not as sensitive as PCR.
But it has higher specificity.
Culture almost never gives false positive results.
Because it allows you to differentiate different types of Neisseria by morphological, tinctorial, and biochemical properties.
Gonococci are grown on nutrient media that contain:
- purines
- amino acids
- pyrimidines
- glucose
- pyruvate and lactate
They contain antibiotics that suppress other flora: fungal and bacterial.
Vancomycin and amphotericin B are usually added.
Most often, colonies appear on the medium within a day.
If after 3 days they are not present, the study is considered negative.
After the colonies appear, their appearance is assessed.
Gonococci create colonies up to 1 mm in diameter, gray or white.
With further incubation, they become less convex and increase their diameter to 3 mm.
In appearance, they are somewhat different from meningococcal colonies.
They look bluish.
Non-pathogenic Neisseria usually produces colorless, transparent colonies.
But bacteria cannot be identified by external signs alone.
Not only gonococci live in the mouth and throat, but also other microorganisms that form similar colonies.
Therefore, identification is carried out by determining the saccharolytic properties of crops.
An oxidase test is performed.
Microscopy with Gram staining may be used.
Immunological or antigen confirmatory tests are performed.
Methods of infection
Gonorrhea in the mouth appears only when the corresponding bacteria enter the mucous membrane. According to statistics, women are much more likely to experience this pathology than men. Gonorrhea can be transmitted in 3 main ways:
- Kisses. Many people believe that it is impossible to become infected with anything through an ordinary kiss. However, this is just a misconception. With a passionate kiss with tongue penetration, the risk of infection increases significantly. If during sexual intercourse oral sex alternates with kisses, then it is almost impossible to avoid infection.
- Hygiene. Gonococcus cannot exist in a clean environment. In this regard, doctors insist that people wash dishes well, regularly change bed linen, wash towels and observe personal hygiene rules.
- Oral sex. This method of infection with gonorrhea is the most common. During oral sex, bacteria from diseased genital organs enter the mouth, so the development of the disease begins immediately. In this case, symptoms are noticeable already 3-4 days after contact with the patient.
Gonorrhea of the throat in children
If a pregnant woman has a gonococcal infection, she can infect her baby.
Infection usually occurs during childbirth.
The course of inflammation of the throat and oral mucosa in children is usually asymptomatic.
Signs of the inflammatory process can be identified objectively.
On examination, redness of the mucous membrane of the mouth or throat is noted.
The act of sucking in such newborns is not disturbed.
Occasionally, the disease occurs with severe symptoms.
There is significant hyperemia and edema.
Erosion and sometimes ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and gums.
They can also occur on the sides of the tongue.
In rare cases, gonorrhea of the throat in children becomes more complicated.
Sometimes deep ulcers appear with yellow purulent discharge.
Cases of gonococcal abscesses forming in children have been reported.
Gonorrheal pharyngitis and laryngitis
Quite often people confuse gonorrheal pharyngitis with other types of diseases.
Few people think that unpleasant symptoms can be caused by a sexually transmitted infection; moreover, the throat can look completely different. In the acute course of gonorrhea, a high temperature may appear, which further convinces the patient of a cold. Against this background, malaise and weakness appear.
If medical care is not provided in a timely manner, gonorrheal pharyngitis will begin to penetrate the respiratory tract. This in turn will cause damage to the larynx, which is practically no different from ordinary laryngitis. The patient will experience shortness of breath, it will become difficult for him to take breaths, and a severe cough will occur. Therefore, if you feel changes in your health, do not try to eliminate the symptoms on your own. Contact a specialist, as only he can identify the disease.
Diagnostics
No matter how obvious the symptoms of gonorrhea seem, the doctor is obliged to diagnose and make sure what exactly the patient is suffering from. First, the specialist examines and interviews the person, and then moves on to other methods that make it possible to establish the exact cause and stage of progression of the disease. This includes:
- mutual fund analysis;
- bacterioscopic method, antibiotics and other medications should not be taken before this study;
- PRC analysis (DNA is analyzed);
- enzyme immunoassay.
In rare cases, when a person has concomitant diseases or gonorrhea has affected internal organs, instrumental diagnostics are also prescribed.
Treatment of the disease
Gonorrhea found in the oral cavity can be completely cured with a course of antibiotics if treatment is started on time. The course prescribed by your doctor must be completed even if all your symptoms of the disease have disappeared.
Medicines are selected depending on individual characteristics. The doctor will select a comprehensive therapy, which includes tablets and, if necessary, injections.
The basis of treatment is medications that include penicillin. The most popular and effective are ampiox, bicillin and ampicillin. In addition, sulnilamide, minoglycose and cyphalosporin medications are required.
Particular attention is paid to the patient's immunity, since gonorrhea makes a person more susceptible to HIV infection.
For this purpose, complexes with a high content of vitamin B and C are prescribed.
An adult must take his or her health seriously in order to begin treatment at an early stage and not face serious complications.
Treatment of gonorrhea of the throat: basic principles
1. Antibiotics are prescribed, which should destroy pathogenic microorganisms. The doctor may use medications
2. Specific immunotherapy in the form of gonovaccine.
3. Autohemotherapy. The doctor may prescribe biogenic stimulants:
4. To treat the throat, pharmacological and folk solutions of antiseptics (Lugol's, Chlorhexidine, oak bark, chamomile, sage, etc.) are used.
5. For the treatment of deep lesions, wound healing and antibiotic ointments (erythromycin, tetracycline, methyluracil) are prescribed.
6. To prevent candidiasis, hepatoprotectors are prescribed.
It often makes sense to use detoxification drugs, antihistamines; means that strengthen blood vessels. Vitamin therapy is of great importance. When treating throat gonorrhea, an increased amount of vitamins B and C is required.
A speedy recovery depends on an integrated approach and the responsibility of the patient himself. The sooner throat gonorrhea is diagnosed, the fewer negative consequences it will leave in the body.
Share this article with your friends:
Source: https://tvoyaybolit.ru/gonoreya-gorla.html
Popular:
- Gonorrhea in the tongue photo How to treat and prevent gonorrhea of the throat? Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that is sexually transmitted. Gonococcus is the causative agent of this disease; it can also infect the oral cavity. This manifests itself in a pale yellow coating on the mucous membrane of the pharynx. This disease appears as a result of sexual contact with an infected partner, or more precisely, during oral sex. In […]
- Gonorrhea of the throat treatment How to treat and prevent gonorrhea of the throat? Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that is sexually transmitted. Gonococcus is the causative agent of this disease; it can also infect the oral cavity. This manifests itself in a pale yellow coating on the mucous membrane of the pharynx. This disease appears as a result of sexual contact with an infected partner, or more precisely, during oral sex. In […]
- Gonorrhea in the throat diagnosis How to treat and prevent gonorrhea of the throat? Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that is sexually transmitted. Gonococcus is the causative agent of this disease; it can also infect the oral cavity. This manifests itself in a pale yellow coating on the mucous membrane of the pharynx. This disease appears as a result of sexual contact with an infected partner, or more precisely, during oral sex. In […]
- Herpes low-grade fever Long-term low-grade fever Low-grade body temperature refers to its fluctuations from 37 to 38 0 C. Long-term low-grade fever occupies a special place in therapeutic practice. Patients whose long-term low-grade fever is the dominant complaint are seen quite often at appointments. To find out the cause of low-grade fever, such patients are subjected to various […]
- Tonsillitis gonorrhea How to treat and prevent gonorrhea of the throat? Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease that is sexually transmitted. Gonococcus is the causative agent of this disease; it can also infect the oral cavity. This manifests itself in a pale yellow coating on the mucous membrane of the pharynx. This disease appears as a result of sexual contact with an infected partner, or more precisely, during oral sex. In […]
- Herpes is caused by bacteria. What should you do if you have anal herpes? Characteristics of the virus The virus that causes herpes is very unstable in the external environment. At room temperature it dies in literally a couple of tens of minutes, and heating to 50 degrees kills it in half an hour. However, at a temperature corresponding to the temperature of the human body, that is, at 37 degrees, he is able to maintain his vitality […]
- Hanging mole or papilloma How to get rid of hanging moles? Reasons for the appearance of hanging nevi on the body What to do with an unusual mole? Dangerous locations Methods of removal Accumulations of pigmented cells on the skin of the body are popularly called moles; in medicine there is a specific term for them - nevi. They appear in large numbers closer to adolescence, and later in life [...]
- Second laparoscopy endometriosis The use of laparoscopy in the treatment of endometriosis. Peculiarities. Contraindications. Contents Endometriosis is a dangerous inflammatory disease, the complications of which later lead to infertility. In order to prevent the development of the disease and its transition to a chronic form, you should immediately consult a doctor when the first signs appear. Endometriosis is characterized by [...]
- Opened ovarian cyst Features of laparoscopy surgery for ovarian cyst Contents IMPORTANT TO KNOW! An effective remedy for CYSTS without surgery and hormones, recommended by Irina Yakovleva! Read more. When diagnosing a woman with an ovarian cyst, it is important to diagnose the disease, which makes it possible to determine the type, nature and structure of the formation. This will depend on [...]
- Mushrooms for chlamydia What are chlamydia and candidiasis? Table of Contents Among fungal diseases, chlamydia and candidiasis are not the last on the list of frequently disturbing people. What it is? This is a lesion of the skin and mucous membrane, which occurs in a short time due to the vigorous activity of Candida microbes, which have a yeast-like form. The most common cause of infection with these fungal […]
How does throat gonorrhea manifest and how to treat it?
Since gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease, should it progress only on the genitals? But no, this is a mistake. Gonococci, that is, the causative agents of gonorrhea, feel great on almost any mucous surface of the human body, including in the throat. This form of the disease is called oropharyngeal gonorrhea, or gonorrhea of the throat. Moreover, it can bring no less unpleasant consequences than in its classic form. What kind of disease is this, how is it transmitted and can it be cured?
Etiology and routes of transmission
Types of throat diseases
Gonorrhea is one of the common infections. The process of becoming infected with gonococcal infection can occur during any form of sexual contact, but the development of gonorrhea in the throat area is characterized by the fact of oral sex.
The causative agent of such a diagnosis as gonorrhea, regardless of its location, is gonococcus. This non-spore-forming pyogenic microorganism is capable of very firmly fixing on the cells of the mucous membranes of the throat, leading to the development of active inflammation in the oral cavity. The pathogen can easily spread throughout the body, including through the lymphogenous route, but the development of an infection such as gonococcal sepsis is rarely diagnosed.
Ways of infection with gonorrhea of the mouth and larynx:
- Oral sex
- Deep kissing, especially when alternating with oral sex (in this case, the sexual partner does not have to be sick with gonorrhea with the infection located in the mouth)
- Through personal hygiene items, dishes (but it is still worth noting that the causative agent of gonococcal infection is not able to survive for a long time in the external environment)
Previous oral gonorrhea does not lead to the formation of immunity in the patient and can be contracted again through unprotected sexual or oral contact with the patient.
Causes
Gonorrhea of the throat occurs more often in women than in men. The reason is that during oral sex, the partner’s genital organ enters much deeper into the oral cavity, thus ensuring more efficient transmission of infection. Moreover, oral sex without a condom is the main route of infection; all other ways of infection entering the body are very rare:
- Kiss . For infection, you need not a simple “smack”, but rather the French version of contact, with deep penetration. By the way, the longer this kiss lasts, the higher the likelihood of contracting gonorrhea in the throat.
- Violation of personal hygiene rules . Infection occurs when using dishes after a carrier of gonococcus. Moreover, if the cutlery has been lying on the table for some time, the danger becomes much lower - microorganisms are poorly adapted to survive in the external environment, and in such conditions they quickly die.
Self-infection is also possible. True, it is very rare. To do this, you need to hold dirty fingers, on which many microbes have accumulated, in your mouth for some time. People who are most at risk are unscrupulous people who like to bite their nails and suck their fingers. Considering that such individuals are very rare, and this method of infection itself is the exception rather than the rule, doctors do not seriously consider this risk.
Infection with gonorrhea of the throat
Gonorrhea of the throat occurs more often in women.
But it is not uncommon among men.
Infection occurs through oral contact.
It can be oral-genital, less often – oral-anal.
Theoretically, infection can occur through rimming or open-mouth kissing.
In practice this happens very rarely.
Because oral and rectal forms of gonorrhea have minimal clinical manifestations.
There are very few allocations.
Not a lot of bacteria are released either.
Therefore, the risk of infection is not high.
Much more often, infection occurs through genital-oral contact.
Most often, gonorrhea affects the pharynx or tonsils.
Less commonly – gums, oral mucosa, larynx.
Infection requires more than just sexual contact.
Predisposing factors are required to allow the infection to penetrate the tissue.
These are any damage to the skin:
- mechanical
- thermal
- chemical
Very often predisposing factors are present.
Because all people from time to time get burned by hot food, eat acidic foods that corrode the mucous membrane.
There are inflammatory processes in the mouth.
All this contributes to infection of the throat with gonorrhea.
Symptoms
Unlike gonorrhea, which develops in the genitals, this variant of the disease rarely occurs without obvious symptoms. According to statistics, only 17-20% of patients encounter the latent form. But there is a subtlety - the signs that manifest themselves are very similar to the symptoms of a sore throat. It is because of this that some patients initially begin the wrong course of treatment, which contributes to the development of gonorrhea and its complications.
If appropriate treatment is not started in time, gonorrhea can become chronic with the development of serious complications. You can learn about the course of the disease and methods of its treatment in men.
Symptoms usually appear 5 days after infection. In this case, the first signs are dryness and burning in the mouth, which is sometimes accompanied by severe itching. After some time, other symptoms appear that are more characteristic of throat gonorrhea:
- hoarseness of voice;
- severe pain in the throat even with complete rest;
- pungent and unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- increased salivation;
- swelling of the lymph nodes (and severe pain may occur when palpating them).
At the same time, areas of inflammation appear on the mucous membranes. They are often covered with a yellowish coating, which misleads patients - they are firmly convinced that they are dealing with purulent tonsillitis.
The sooner a person with such symptoms consults a doctor, the better. The fact is that gonorrhea of the throat is quite difficult to treat due to its resistance to many antibiotics. While the doctor selects the right therapeutic course, the infection can reach the brain, and then the patient will not feel enough.
Smears for throat gonorrhea
Genital forms of gonococcal infection can be detected by microscopy of urethral discharge.
But in the case of gonorrhea of the throat, microscopic examination is not performed.
There are two reasons for this:
- low sensitivity of such a study
- its lack of specificity
Low sensitivity is due to the fact that gonorrhea of the throat is often asymptomatic.
In the foci of infection there is not a large amount of pus or plaque in which bacteria could be found.
There are very few of them, and they do not always fall within the field of view of the microscope.
Low specificity is due to the fact that in the mouth, unlike the urogenital tract, various Neisseria live.
They look exactly like gonococci.
These can be pathogenic microorganisms (meningococci) or saprophytic neisseria.
It is not always possible to distinguish them through a microscope.
To avoid false results and unjustified treatment, diagnosis is confirmed by other methods.
Diagnostics
Detection of the disease in the early stages is the basis for successful treatment and the patient’s well-being in the future. Although the symptoms of the disease are not specific, that is, inherent specifically to gonorrhea of the throat, the doctor can draw the first conclusions based on anamnesis and visual examination of the patient’s mouth and throat. But based on this, it will not be possible to make an accurate diagnosis, so additional measures have to be prescribed:
- microscopic examination of a throat swab;
- seeding the patient’s biomaterial from the pharynx and oral cavity (the most accurate method);
- blood test for antibodies to gonorrhea.
Please note that even with confirmed purulent sore throat, doctors will take smears, including to identify potential gonorrhea. The symptoms of the diseases are very similar, so such an examination will definitely not be superfluous.
Treatment
This infection is very difficult to clear, so you can’t get rid of it with antibiotics alone. Moreover, the choice of specific medications depends both on the stage of the disease and on the characteristics of the gonococcus in each specific case. But whatever one may say, the basis of all therapy is antibacterial drugs:
- Penicillin (costs no more than 100 rubles, although you can find options for more than 1000);
- Bicillin-3 (price - from 10 to 50 rubles);
- Ampicillin (costs about 50 rubles);
- Ketocef (cost about 200 rubles).
Doctors also prescribe Biseptol as an additional remedy (it can cost up to 500 rubles, but there are options for 150), but its effectiveness is questionable. Doctors resort to such remedies if they are allergic to the main medications (they are based on penicillin and its derivatives) necessary for the treatment of gonorrhea of the throat.
Do not forget that any antibiotics are harmful to the body. At a minimum, they disrupt the intestinal microflora. To restore it, doctors prescribe special medications. You should not choose them yourself, since a number of such products can somewhat reduce the effectiveness of antibacterial drugs. In addition, you should take vitamins. Any sexually transmitted disease can be defeated by the body’s own defenses, and without a strong immune system this is simply impossible.
While taking antibiotics, you should rinse your mouth and throat with oak bark, sage, herbal infusions from the pharmacy, and also lubricate the area of the root of the tongue with Lugol (the procedure is unpleasant, but necessary).
By the way, quite a long time ago our ancestors came up with some folk remedies to combat gonorrhea of the throat. They are again associated with rinsing, and sometimes drinking herbal decoctions:
Birch leaves have also worked well, used as a gargle. Just remember that it is impossible to completely defeat this disease using folk methods; they can only be used as auxiliary measures.
Prevention
As with any other sexually transmitted disease, prevention of throat gonorrhea involves careful selection of sexual partners. If you really want to go “extreme”, then don’t forget to use condoms. Particularly dangerous spots are considered to be places where people close to the lumpen class gather, as well as various nightclubs - special caution must be taken there. In addition, do not forget the rules of personal hygiene:
- wash dishes on time;
- try not to dine in dubious establishments with a frankly poor level of sanitation;
- Wash your hands frequently and thoroughly.
Don't forget about strengthening your immune system. To increase the level of your own defenses, you should promptly treat any infectious diseases, monitor your daily routine, and also consume as much vitamin-rich food as possible. Take care of yourself!
You can also find out by watching this video the opinion of a specialist, where he talks about the causes and how gonorrhea develops in the throat.
Clinical picture
The clinical picture of gonorrhea (gonorrhea) of the throat largely coincides with other diseases, so it is important to note some symptoms characteristic of gonorrhea in the throat:
- absence of runny nose and nasal congestion, in contrast to “cold” respiratory diseases;
- bilateral tonsil damage;
- absence of purulent “plugs” characteristic of follicular tonsillitis;
- enlargement of only the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes (in contrast to infectious mononucleosis, in which both axillary and inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged);
- absence of bubbles with serous contents in the throat and oral cavity (unlike herpetic sore throat).
Pathogen
The bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae (gonococcus) is the causative agent of oral gonorrhea. Pathogens, once in the oropharynx, multiply intensively. They affect the tongue, pharynx, tonsils, palate and gums.
The incubation period is short, lasting from 2 to 30 days. Outside the body, bacteria quickly die. They are hypersensitive to cold and heat. The optimal temperature for their development is + 35-55 0 C. In a warm environment, gonococci live for 6 hours. Excessively high temperatures kill them within 5 minutes. Diplococci live in purulent masses for about 24 hours.
Neisseria is instantly destroyed by weak antiseptics. They die when treated with silver nitrate; they are destroyed by antibiotics from the group of penicillin and streptomycin. Bacteria constantly mutate and develop resistance to many antibacterial drugs. Not all antibiotics can fight them, even if they belong to the latest generation of drugs.
Symptoms of gonococcal pharyngitis occur in isolation or in combination with infection of the urogenital apparatus. Against this background, gonorrheal urethritis, proctitis, stomatitis, and arthritis develop. At the same time, the respiratory organs are affected.
Causes and routes of infection
Classic gonorrhea involves the genitourinary organs in the inflammatory process. However, damage to other systems is not excluded. Gonorrheal pharyngitis occurs when Neisseria gonorrhoeae enters the throat.
When a healthy person comes into contact with a sick person or a carrier of gonococci, infectious pathogens are transferred from the lesion (usually from the urogenital organs) to the oral mucosa. The pharynx becomes inflamed after unprotected oral-genital sex. Gonorrhea of the throat is acute and chronic.
Methods of infection
Oral-genital contact without using a condom is the main cause of gonorrheal sore throat.
The infection is transmitted in several ways:
- when performing sexual intercourse (traditional, oral, anal);
- contact household (through hygiene products in common use, bed and underwear, dishes);
- perinatal (when a child comes into contact with infected mucous membranes of the birth canal);
- when kissing (when the oropharynx of the sexual partner is infected with gonorrheal tonsillitis).
Gonococcal infection affects people of all ages. It is diagnosed from birth until old age. The risk of infection is high when there is close contact and hygiene rules are ignored.
Transmission routes
Infection of throat gonorrhea in the vast majority of cases of the disease occurs through oral-genital contact.
It is possible to become infected by kissing someone who has throat gonorrhea, especially if the kiss is accompanied by an active exchange of saliva or the patient has inflammation on the lips.
Gonorrhea of the throat occurs in newborns who became infected while passing through the birth canal of a sick mother (they are also at risk of gonorrheal conjunctivitis of newborns).
In a household way, you can become infected by immediately (gonococcus does not live for a long time in the air) transferring a spoon, lollipop, toothbrush, etc. from mouth to mouth.
Symptoms
The infection affects not only the pharynx, it is localized on the tongue, tonsils, palate, nasal cavity and larynx. The disease is often asymptomatic, or its signs are greatly erased. It is characterized by manifestations of ordinary pharyngitis. Patients suffer from:
- pain syndrome that occurs in the throat;
- discomfort caused by dryness and soreness in the oropharynx;
- cough;
- hoarseness;
- difficulty swallowing;
- elevated temperature;
- drowsiness;
- weaknesses.
Differential diagnosis
The clinical picture of gonorrhea coincides with other diseases:
- Cold. As with gonorrhea, there is pain in the neck area, but in addition there are symptoms associated with a runny nose or nasal congestion. They do not occur with gonococcal bacillus.
- Flu. This disease is infectious in nature and affects the entire body, causing fever, sore throat, and runny nose. Gonorrhea affects only the mouth and respiratory tract.
- Tonsillitis. It manifests itself in inflammation of the tonsils, fever and sore throat. These symptoms include general malaise, nausea and lack of appetite.
- Streptococcal infection. Leads to sore throat, general malaise, rash on the body and larynx.
- Mononucleosis. Gonorrhea of the throat is caused by the herpes virus. Sore throat, fever, fatigue and swollen lymph nodes in teenagers. In adults, an enlargement of the liver and stomach is added.
Sources of infection
In infected people, gonococci are found in exudate from the genitals, saliva, and urine. Gonorrhea of the throat occurs with all types of unprotected intimacy (especially during oral contact). The pathogen is transmitted not only during the act, but also through kissing.
The risk group includes:
- Those who have sex without using protection (condoms). In this case, infection occurs with both a casual and regular partner.
- Children. Babies, passing through the birth canal, receive the mother's microflora. To protect children from infection, Albucid is instilled into their nasal passages and eyes. When doctors know a woman is infected with gonorrhea, they consider performing a caesarean section. Surgery reduces the risk of passing gonorrhea to the baby. Children often become infected with gonococci through contact and household contact. They get the infection from their mothers. If gonorrhea is detected in a woman, her children must be examined.
- Persons with immunodeficiencies. Gonococci affect those who suffer from HIV, AIDS, and congenital immunosuppression. Gonorrhea in the mouth develops in patients who have had organ transplants or bone marrow transplants. Various pathogens easily penetrate the body of people with weakened immune systems, and defense mechanisms cannot cope with their suppression.
Long-lasting inflammation in the oropharynx, untreatable and constantly recurring, indicates that oral gonorrhea or another atypical type of pharyngitis has developed. The exact diagnosis is determined by the doctor based on test results.
Gonococcal pharyngitis - diagnosis
It is impossible to distinguish gonococcal pharyngitis from other throat diseases on your own. Only a doctor makes a diagnosis; he identifies the disease based on test results. If you suspect gonorrhea of the throat, do the following:
- take a smear;
- do sowing;
- carry out PRC (polymerase chain reaction).
The smear sometimes gives false results. When the pathogen enters the mucous membranes in the patient’s body, cellular immunity is activated. Macrophages begin to fight bacteria. They, having absorbed microbes, try to digest them. But they fail to completely destroy gonococci.
PCR analysis of throat gonorrhea
Most often, PCR is used to detect gonococci.
Because this method is highly sensitive and specific.
It rarely gives false results.
A swab is taken from the mouth with a special probe.
It is then placed in a test tube and sent to the laboratory.
There, PCR is performed to identify a specific fragment of gonococcal DNA.
If the result is positive, treatment is prescribed.
A negative result with a probability close to 100% will mean that the person does not have gonorrhea of the throat.
False-positive PCR results are occasionally possible.
They are associated with the discovery of DNA sections of saprophytic Neisseria.