What is a disease?
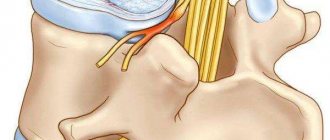
Spondyloarthrosis is a chronic disease that leads to degeneration of the facet joints and is accompanied by similar pathologies. In the later stages of development, bone tissue grows and spondylosis occurs. The disease is protracted and contributes to a gradual narrowing of the spinal canal and intervertebral foramina.
Facet arthropathy, a certain form of osteochondrosis, which is manifested by dystrophic disorders of articular cartilage tissue. When two adjacent vertebrae become inflamed, bilateral spondyloarthrosis occurs, which can subsequently lead to spondylolysis.
Symptoms
In 90%, pathology of the lumbar region develops between the L4-L5 vertebrae. The main symptoms of arthrosis of the facet joints of the spine are:
- difficulty moving in the morning due to low mobility of the lumbar region during sleep,
- back pain when the body remains in one position for a long time,
- crunching in the joints due to the formation of osteophytes,
- radiculitis pain,
- muscle spasms,
- tingling and numbness of the legs,
- difficulty bending and turning the body.
Exercise stress
In addition to pain relief and rehabilitation therapy, the patient is advised to carry out special exercises. The complex is quite simple, which is why they can be done independently.
Gymnastics helps eliminate pain, stretch muscle tissue and make it more elastic. This eliminates muscle spasms and reduces pain.
Gymnastics also helps build muscle mass and creates a powerful protective corset. Strengthening the muscles helps create reliable protection for the intervertebral disc from excessive stress. During the rehabilitation period, it is recommended to carry out additional exercises in the pool, gradually increasing the load.
If you have spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine, gymnastics will make your life much easier. Naturally, it should be gentle. You should definitely do exercises to strengthen and develop flexibility in your back muscles. Try to monitor your posture and body weight. If the weight is too much, you should get rid of it.
Be sure to do hard work. Don't be in the same static position all the time. There is no need to make sudden movements. To eliminate the disease you need to do the following exercises:
- Lying on your back, place your hands behind your head, bend your legs. Next, we close our elbows with each other and return to the starting position.
- Lying in the previous position, bent legs should be pulled to the stomach and clasped with your arms.
- Do the exercise to establish correct posture.
Signs
The first and main signs are pain. First, aching pain, which manifests itself mainly in the morning. Then the pain becomes burning, occurs much more often and becomes more and more difficult to endure. Deterioration in lumbar mobility also indicates the presence of the disease.
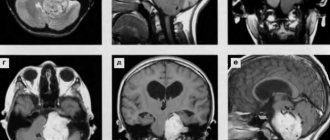
Facet arthropathy accompanies other spinal diseases associated with changes in the facet joints. Even with moderate spondyloarthrosis, significant degenerative changes are noticeable on the MRI picture.
Causes
The main causes of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine are:
- passive lifestyle,
- genetic predisposition,
- heavy load on the lower back,
- improper diet,
- spinal injuries, including microtraumas,
- congenital anomalies associated with degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spinal column,
- diseases leading to the destruction of cartilage tissue (osteochondrosis, scoliosis, kyphosis, etc.),
- excess weight,
- poor posture.
Some sports associated with weight lifting predispose to the development of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system. Weightlifting involves lifting heavy weights, which puts stress on the spine, leading to degeneration of the facet joints.
Age is considered an important factor contributing to the development of pathology. 85% of people over 65 years of age suffer from this disease. This does not mean that younger people are not susceptible to spondyloarthrosis. The younger a person is, the more difficult it is to get rid of pathology.
Orthopedic surgeon, 12 years of experience. Women suffer from facet arthropathy more often than men. This is due to the fact that during menopause, estrogen production in women decreases. This hormone protects bone tissue, and when it is deficient, degenerative processes occur in the spine. Therefore, women over 45-50 years of age are advised to consume more calcium and magnesium to increase bone strength.
HOW IS THE DISEASE DETECTED?
It is important to understand that spondyloarthrosis is a serious disease of the spinal column, which, despite the gradual development and gradual increase in the intensity of the symptomatic picture, very quickly leads to pathological, irreversible processes. This means that further aggravation of the disease can be prevented only by timely contacting a doctor as soon as a person experiences the first back pain.
At the doctor's appointment, the patient is asked about the complaints that bother him. The specialist examines the patient, checks his posture, conducts a series of tests that help identify the intensity of the pain symptom, the amplitude of motor function, in order to determine the stage of development of the degenerative process.
To exclude myelodysplasia (a congenital anomaly in which the spinal cord is underdeveloped) and other pathologies associated with disruption of the condition and functioning of nerve endings in the back, the patient will be referred for consultation to a neurologist and other related specialists.
If the disease has not reached stage 3 of development, it will be difficult to make a diagnosis. To obtain an accurate and detailed picture of the condition of the spinal column and identify the causes of pain and other unpleasant symptoms, a number of instrumental techniques are prescribed.
Diagnosis of pathology includes the following instrumental techniques:
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
- X-ray.
- CT scan.
An additional diagnostic method is electromyography. It involves observing the state of the nerve endings of the spine under the influence of electrical impulses. It is used in cases where there is a suspicion that the roots of the nerve endings of the spine are involved in the degenerative process.
Classification
Facet arthropathy is divided into 4 types, differing in symptoms, treatment methods and diagnostics.
Degenerative
When the facet joints are affected by spondyloarthrosis, degeneration of the vertebral cartilage occurs. The cartilage becomes thinner, the height of the intervertebral space is reduced, and this can lead to subluxation of the articular processes. Flattening of the cartilage reduces its elasticity and leads to disc protrusion.
Ankylosing
It is also called ankylosing spondylitis. This is a chronic pathology that leads to inflammation of the joints of the spine. Prolonged inflammation can lead to impaired mobility of the musculoskeletal system, and in later stages even to paralysis.
Polysegmental
The ridge consists of parts, segments that are susceptible to spondyloarthrosis. With polysegmental facet arthropathy, several segments of the spinal column are affected at once, which expands the area of pain and often complicates the diagnosis of the disease.
Deforming
This type differs from the others in that when large osteophytes (bone growths) appear, displacement of the cartilage tissue may occur. Deforming arthropathy is characterized by protective muscle tension of the paravertebral muscles and deformation of the lumbar region of the spinal column. This type of pathology is irreversible.
Stages
There are 4 stages of facet arthropathy. Let's take a closer look at each of them.
First
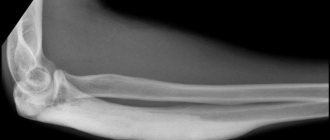
The early stages of arthrosis of the facet joints are not so easy to notice, since the first degree is asymptomatic. There is no pain. On X-ray photographs, only ghostly manifestations of narrowing of the joint spaces can be seen.
Simple preventive procedures in the form of exercise therapy and massage will stop the progression of the disease.
Second
The second stage is characterized by mild aching pain in the lumbar region and stiffness of movement in the morning after sleep. When you spend a long time in a stationary state, pain also occurs, which goes away after performing basic warm-up exercises. The MRI image shows a progressive narrowing of the joint spaces and the beginning of the formation of osteophytes.
It is prohibited to perform therapeutic exercises until the patient gets rid of pain. He is prescribed special medications and only after complete anesthesia is he allowed to do simple gymnastic elements.
Third
At this stage of development, the pain becomes burning in nature. The patient is forced to take a certain body position to relieve pain. The bone tissue begins to grow, forming osteophytes. They put pressure on the nerve endings, and sometimes on the spinal cord. Radiculitis pain appears.
The X-ray image already clearly shows large bone growths and a complete absence of joint space. It is possible to do without surgery in the presence of grade 3-4 lumbar spondyloarthrosis in isolated cases.
Fourth
It is final in the development of arthropathy. It is characterized by unbearable pain in the lumbar region, which can radiate to the hips and legs. With the fourth degree of pathology of the lumbar region, the mobility of this area is completely lost. Ankylosing (fusion) of the intervertebral joints occurs.
Orthopedic doctor, 12 years of experience Spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine must be treated in the initial stages to avoid complete immobilization of the affected area.
Symptoms of the disease and its varieties
The first symptom accompanying spondyloarthrosis is the occurrence of pain in the back. As the disease progresses, limited movement of certain areas of the spine occurs. This leads to discomfort and disrupts the usual rhythm of life.
Doctors divide this spinal disease depending on the part that is affected. There are:
- cervical;
- chest;
- lumbar spondyloarthrosis.
Depending on the rate of development of the disease, it is customary to distinguish stage 1 spondyloarthrosis, which is the initial stage of the disease. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the disease progresses and the development of osteophytes is noted on the affected vertebral region.
There is also a reduction in the intervertebral foramina. This condition is typical for stage 2 of the disease.
Disease of the cervical spine
The main reason for its occurrence can be considered an uncomfortable position while working at the computer.
Often, while working, a person is forced to be in an uncomfortable position. Constant work in an uncomfortable position disrupts posture and leads to a deterioration in the general condition of the body.
A patient suffering from this disease, which affects the cervical spine, complains of periodic or constant pain in the shoulders and neck. Quite often, foci of pain can be concentrated in:
- forearms;
- in the area between the shoulder blades;
- above the shoulder blades;
- hands;
- back of the head area.
The development of the disease leads to an increase in growths of cartilage tissue, which are concentrated near the vertebral joints. This leads to a decrease in the intervertebral distance and irritation of the spinal cord roots.
In turn, this leads to pressure on the artery and thereby disrupts the blood supply to the organs and brain.
Disease of the thoracic spine or dorsarthrosis
Dorsaarthrosis, according to medical statistics, is considered a rare disease. This is due to certain difficulties in diagnosing it. In most cases, the disease affects the joints that are located behind the ribs and therefore difficult to access.
Doctors believe that there are many more cases of spondyloarthrosis of the thoracic spine, but due to the complexity of diagnosis and insufficient development of the disease, it is quite difficult to determine.
The causes of this type of spondyloarthrosis are similar to those for diseases of the cervical spine. Most often, this type of disease develops in older people.
The result can be reduced mobility of the spine, as well as complete damage to blood vessels and nerves.
Disease of the lumbar spine
This type of disease occurs most often in patients compared to other types. A person with lumbar spondyloarthrosis feels the symptoms of the disease already in its early stages. All patients in their complaints describe constant pain of the following nature:
- pain in the hip area;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- pain in the buttocks.
Basically, pain occurs when the body is tilted back or when making rotational movements. Patients also experience pain after a long stay in one position or after sleep. In order for the pain to decrease slightly, after staying in one position, you need to warm up slightly.
Read also: Hand arthritis symptoms and treatment
Types of diagnostics
Before starting treatment for arthrosis of the facet joints of the spine, it is necessary to correctly diagnose it. To begin with, the doctor needs to collect an anamnesis, study the medical history and, taking into account the patient’s complaints, prescribe the following diagnostic procedures.
CT scan
CT scan is an examination performed using X-rays. It differs from radiography in that with x-rays the result comes out in the form of a two-dimensional image, and with computed tomography the image will be three-dimensional. Three-dimensional imaging makes it possible to more accurately determine the location of the disease and the extent of damage to the facet joints and vertebrae.
X-ray
Radiography is the simplest method for diagnosing spondyloarthrosis. It does not provide as accurate results as can be found with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, but it does provide a basic understanding of the disease.
Magnetic resonance imaging
The essence of magnetic resonance imaging is not very different from computer imaging: obtaining data and modeling it based on a three-dimensional image. The MRI procedure uses electromagnetic waves. The doctor is obliged to carefully study the patient’s medical history, since there are many contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging.
Contraindications for spondyloarthrosis
After you have completed the course of treatment, the doctor is obliged to familiarize you with contraindications for spondyloarthrosis. It is necessary to follow all these simple recommendations to prevent the deterioration of your spine. Need to remember:
- hypothermia should be avoided;
- do not make sudden movements or jerks;
- you cannot lift weights;
- You can’t stay in one position for a long time;
- If you have a long trip ahead, use an orthopedic corset.
But do not overuse orthoses and other devices. With prolonged use, patients experience weakening of the trunk muscles, static disorders of the spine, as well as pain. Experts strongly advise doing physical therapy, walking more and paying attention to skiing.
Treatment methods
Provides for the comprehensive use of conservative and physiotherapeutic procedures aimed at relieving pain.
Medication
Anti-inflammatory drugs and chondroprotectors are used for treatment. To relieve pain, the patient is prescribed corticosteroids and analgesics in injections. With the development of neuropathic pain, antiepileptic drugs cannot be avoided, and muscle relaxants are used to relax muscles and normalize tone.
If conservative treatment options are ineffective, the patient is prescribed epidural injections. The purpose of these injections is to relieve pain in inflamed areas. To quickly get rid of pain that cannot be tolerated, novocaine blockades are used. For greater results, you need to undergo simple physiotherapeutic procedures along with taking medications.
Surgical
Surgery cannot be avoided in case of injury or lack of effect from conservative treatment. The following procedures are carried out:
- transpedicular fixation,
- discectomy and laminectomy,
- installing a distractor
- radiofrequency or chemical denervation (pain relief),
- decompression intervention.
Operations are indicated only in the final stages of the disease, but some of them are performed after injury to the spinal column.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are used by those people who do not have the opportunity to engage in therapeutic exercises or swimming. Most often these are elderly patients. Physiotherapeutic procedures strengthen the muscle corset and relieve pain. Such procedures include:
- acupuncture,
- magnetotherapy,
- traction therapy method,
- ultrasound with chondroitin,
- UHF.
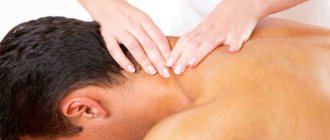
Massage
One of the physiotherapeutic procedures includes massage. It allows you to normalize muscle tone and relax after a hard day. When performing a massage, blood circulation increases, which speeds up metabolism in the affected area, and, accordingly, recovery. The skillful hands of a massage therapist relieve pain for some time.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture (or acupuncture) is a procedure that involves influencing the body by inserting needles into special points on the body.
For spondyloarthrosis, acupuncture can relieve pain, relieve spasms and shorten the period of exacerbation in chronic processes. The beneficial effect of drug and physiotherapeutic treatment is significantly enhanced when supplemented with a course of acupuncture.
Gymnastics
Exercise therapy to strengthen the muscle corset includes isometric gymnastics, which includes exercises that are easy to perform and do not require stress on the muscles without changing length. The simplest example is applying pressure to the couch with the lumbar region of the spine while lying on your back with your knees bent.
Yoga
Yoga therapy helps strengthen back muscles and relieve pain. These are comfortable and sustainable exercises aimed at stretching the spinal column and strengthening the muscles. All this must be done under the supervision of an instructor.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine methods include special ointments, massages, rubbing and compresses, which are easy to make at home. For preparation, various oils, honey, natural salts, hops, etc. are used. Traditional medicine is aimed at short-term relief from pain.
Exercise therapy and exercises
This treatment method is useful not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of deformation of the facet joints. The trainer will determine the correct exercises for a particular patient. You can exercise at home without using equipment, but there are exercises that require lifting light weights to increase the effectiveness of therapy. The workout involves alternately lifting different parts of the body from a position lying on your back or standing on all fours.
Features of pathology detection
Before starting treatment, spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine must be correctly diagnosed. Otherwise, therapy will not only not help, but will also cause harm. That is, you cannot self-medicate here.
So, in order to obtain reliable data about the patient’s condition, the doctor is obliged to collect his anamnesis and take into account complaints. Naturally, an X-ray examination and an MRI will have to be performed. Computed tomography is important in diagnosis. It is also advisable to conduct a neurological examination of the patient. That is, checking reflexes makes it possible to understand whether the spinal cord is damaged, and if so, how much.
If the doctor suspects that there is damage to the nerve endings, he may prescribe an electromyography. A bone scan is performed to determine the extent of hard tissue destruction. After diagnosis, appropriate treatment is prescribed. Spondyloarthrosis of the lumbosacral spine is a difficult disease that requires long-term therapy and a combination of different methods to eliminate the pathology.
Treatment of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine involves the use of a complex of conservative and physiotherapeutic procedures, which are mainly aimed at eliminating the symptoms of the disease. In order to correct physiological defects, surgical intervention is necessary. Although this does not always help.
So, to eliminate pain, the following medications are used: Diclofenac, Ketonal. Moreover, the drugs are used both in the form of tablets and ointments. If the disease is not in an acute form, then the patient has the opportunity to undergo a course of manual therapy. Naturally, all massage methods should be very light and gentle.
As for physiotherapeutic procedures, treatment of spondyloarthrosis of the lumbar spine in this case involves the use of magnetic therapy, phonophoresis, and ionogalvanization (with anesthetics).
Patient prognosis
The treatment and diagnosis of spondyloarthrosis is carried out by a vertebrologist, a neurologist, and in some cases a surgeon. In case of complications caused by the disease, several doctors can treat the patient together.
Prognoses are announced to each patient individually. Their favorability depends on the following factors:
- degree of development of facet arthropathy,
- the degree of damage to the joints passing along the spinal roots,
- whether bone formations put pressure on the spinal cord.
The younger the patient, the easier it is for him to cope with the disease. However, when spondyloarthrosis occurs in adulthood, the likelihood of complications during the development of the disease increases.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine during the treatment of spondyloarthrosis can bring a significant improvement in well-being, eliminating painful sensations. A massage using warming ointments, honey compresses or cupping can bring good results.
Baths with the addition of sea salt help eliminate soreness and reduce inflammation. Apitherapy has also proven itself quite well, since bee stings combine acupuncture and the effects of an anesthetic ointment.
Traditional methods can cause side effects, which is why you need to first consult a doctor and undergo a full examination.
Among the non-traditional recipes, the most effective are the following:
- Healing compress made from infusion of calendula flowers. To prepare it, take 100 g of grass and half a liter of vodka. It is advisable to infuse the product in a dark place for about 14 days. The mixture can then be used to rub the spine, and also as a compress.
- Fir oil is very effective, which can be purchased at every pharmacy. This inexpensive and very good product should be used for rubbing and massage.
- You can prepare a medicinal ointment for yourself from dandelion roots, mint leaves, birch buds and coriander. All ingredients should be taken in equal parts. Pour 6 large spoons of the mixture with a glass of boiling water and leave on low heat for 5 minutes. Next, the resulting product must be mixed with 100 g of vegetable oil or fat (preferably nutria). The ointment should be used at night.
Possible complications and consequences
Pain due to spondyloarthrosis can lead to disability and complete immobility of the spinal column. The following complications may appear in the final stages of the disease:
- low stability of the ridge,
- spondylolisthesis,
- paralysis,
- spinal artery compression.
When the disease spreads to other parts of the spine, the blood supply to the brain may deteriorate, which will lead to ischemic apoplexy. If the disease is not stopped in a timely manner, there is a risk of disability.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of facet arthropathy, it is necessary to exercise in the morning, lead a more active lifestyle and maintain a proper diet. It is advisable for office workers to move more and do a warm-up after every hour of sedentary work.
It would be a good idea to reduce the likelihood of spinal column injury by installing curbs in shower stalls, avoiding walking in poorly lit areas, and eliminating rugs in the bathroom.
Facet arthropathy of the lumbar spine is a complex and unpleasant disease that can significantly limit a person’s mobility and cause a lot of trouble. It is necessary to contact a vertebrologist when the first symptoms appear. If all doctor’s prescriptions are followed correctly, the likelihood of pathology progression will be significantly reduced.
Facet syndrome: what is dangerous and how to treat it
The bones, cartilage, and ligaments in the spine work together to protect the spinal cord, support the weight of the upper body, and facilitate movement. Each component of this complex system depends on the others. Because of this, any, even the most minor, pathology can ultimately lead to chronic pain and difficulties with movement.
Facet syndrome occurs when there is an uneven load on the intervertebral (facet, also known as facet) joints. Typically, this condition occurs as a result of a decrease in the height and volume of the intervertebral disc due to spondyloarthrosis and other degenerative processes. The facet joints become inflamed and can cause pain and stiffness.
Although every part of the spine can be affected by facet syndrome, it most often affects the lumbar region of the spine (lower back). This makes sense since the lower back carries a significant amount of stress from everyday life. Increased load on the facet joints leads to rapid wear of the cartilage, stretching of the joint capsules, the formation of osteophytes and cramping acute pain with any load on the spine. Exacerbation of pain is observed after long periods of inactivity. Patients also complain of a crunching sound when moving.
Treatment is medicinal
Many over-the-counter medications can reduce the inflammation caused by facet syndrome and allow patients to undergo physical therapy and other long-term care programs.
Localized injections of painkillers may also provide long-term relief from discomfort associated with movement. Sometimes these injections have to be done for 6 months.
Muscle relaxants can be used to reduce localized muscle spasms.
After the painful symptoms of facet syndrome have been brought under control with medication, the doctor may refer the patient to exercise therapy to strengthen the lumbar spine and associated muscles.
Stretching exercises aimed at restoring the correct pelvic tilt are very useful; Therefore, special attention should be paid to stretching those muscles that cause excessive anterior pelvic tilt (eg, hip flexors and lumbar extensors).
Stretching should not be limited to just these muscles, because all the muscles associated with the lumbar spine and pelvis can be out of balance, and regular stretching will help restore normal movement in the lumbar spine and pelvis. Stretching done through dynamic postural movements (such as yoga poses) is especially beneficial because it helps restore balance to the muscles of the lumbar spine and pelvis.
Aerobic exercises such as walking or cycling have also worked well for facet syndrome. They need to be done for 20 to 30 minutes a day.
Massage can be beneficial for both short-term and long-term pain relief from facet syndrome. Some evidence suggests that massage, when combined with exercise therapy and physical therapy over a period of a year, may actually reduce the need for pain medications.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy for facet syndrome includes instruction in correct posture and body positioning during daily activities to protect injured joints and reduce painful symptoms.
Cryotherapy, ultrasound therapy, electrophoresis and radiofrequency ablation can help relax the muscles and reduce the clinical manifestations of the disease.
A fixing orthopedic semi-rigid corset for the lower back allows you to maintain the spine in the correct fixed position, preventing displacement of the vertebrae and relieving the spine of part of the load. Ideally, the corset should be selected for the patient by an orthopedic specialist.
Treatment with folk remedies
To reduce blood flow to the affected area and provide temporary pain relief, you can apply an ice pack to the affected area for 10 to 15 minutes.
The essential fatty acids found in fish are an effective supplement for treating back pain. Essential fatty acids are the “building blocks” that make up fats and oils.
Read also: Periarthritis of the shoulder joint
They are essential for muscle recovery and increase the production and activity of anti-inflammatory substances, which help control pain and inflammation in the joints. Therefore, fish must be in the diet of people who have been diagnosed with facet syndrome.
Prevention
Exercise aimed at strengthening the back muscles, losing extra pounds and increasing the flexibility of the body helps reduce the load placed on the spine and prevent facet syndrome.
Buying the right shoes, avoiding too much stress on the spine and maintaining correct posture (even while sleeping, with the help of an orthopedic mattress and pillow) are also effective measures to prevent the development of facet joint disease.