When to donate blood after exposure?
By contact we mean non-everyday interaction with an HIV-infected person; the virus is not transmitted by the holy spirit. Today there are many discordant couples, where one partner is infected and the other is healthy; if the woman is not infected, it is possible to have healthy offspring. But an infected mother can give birth to a healthy child if she receives complete preventive therapy. Not a single case of household transmission of the disease in a Russian family has been officially registered; moreover, it is impossible to become infected if you work next to an infected person. The virus is not transmitted through blood in 100% of cases. If you suspect an infection, you should not rush headlong to get tested; antibodies will appear only after two weeks, and may develop much later.
The law provides for anonymous HIV testing; you just need to express your desire for the vial of blood to be marked “anonymous.” If “everything is fair,” then the clinic will ask for the passport of the person donating blood and registration. Anonymity during the initial analysis is a tribute to populism; what’s the point of taking the test anonymously when further treatment is planned if an infection is discovered. They do not register anonymous people with government agencies, and they do not provide free medicines “incognito”. You will have to declassify the name and enter the door under the sign “Center for Treatment and Prevention...”
Registration of a new HIV drug in Russia
In mid-2020, a new drug for HIV was officially registered in the Russian Federation. This is the innovative drug “Genvoya” (cobicistat/tenofovir alafenamide/elvitegravir/emtricitabine, 150/10/150/200 mg). The manufacturer of the drug is the American pharmaceutical company Gilead. Find out more→
When should you tell the truth?
In all medical institutions, wherever an HIV carrier comes, he must declare his status, because the Criminal Code has an article that provides for punishment for concealing information in the event of infection of a third party. Dental treatment, examination with penetration into organs - any invasive manipulation can lead to contact with blood and infection of a medical worker. The doctor will mark the status in the outpatient card and enter it into the electronic medical history so that everyone is warned about following certain measures to prevent the further spread of the immunodeficiency virus.
And this is absolutely true, because there are enough cases of infection of innocent patients with the blood of donors who are not aware of their own HIV status. The law does not require that information about a patient’s HIV-positive status be placed on the title page of a medical record, but it also does not prohibit “secret” marks placed by hospital staff that signal increased vigilance. People are unkind because of lack of education, they shy away from HIV-infected people, however, not only from them, but from cancer patients or those suffering from skin diseases.
Citizens do not understand that there is nothing shameful about HIV status; anyone can accidentally get the virus even with an absolutely righteous life, as 5 years ago three women who were being treated for infertility became infected. Using an innovative technique in a private clinic, they were injected with lymphocytes from a nurse who was unaware of being HIV-positive. This was criminal negligence, but it is precisely such negligence that leads to human tragedies.
Chinese twins
HIV in our society: why even doctors are afraid of infected people
Parents of children with immunodeficiency virus are forced to hide their diagnosis
He Jiankui, a Chinese scientist from the Southern University of Science and Technology in Shenzhen, spoke in mid-November of the birth of twin girls with an altered genome. The genome was edited during embryonic development to protect children from HIV.
The scientist’s task was to “turn off” the CCR5 gene, which is associated with the formation of a protein that allows the virus to enter the cell. He worked with couples in which the men were HIV-positive (and on medications, and therefore not contagious), and the women were HIV-negative. The genome was changed in 16 embryos, of which 11 were used for artificial insemination, and only one woman became pregnant as a result - with twins (the scientist later said that perhaps the second woman also managed to get pregnant). However, both copies of the CCR5 gene were changed in only one of the twins. The second has one copy edited, so that the child may become infected with HIV in the future.
Science_1
Chinese geneticist He Jiankui
Photo: Global Look Press/SC Leung
Author of the quote
About 1% of the population of Northern Europe, including Russia, are immune to HIV from birth.
Life as a myth: why HIV dissidents die
More and more victims of medical conspiracy theories
Scientists have been making attempts to learn how to transfer this immunity from one person to another for a long time. He Jiankui's experiment was based on this idea. But despite the encouraging results, there are many questions about the story of editing the genome of embryos.
First, no article has yet been published in a peer-reviewed scientific journal detailing the work. And the section dedicated to working with children on the website of He’s laboratory at Southern University is not available. And all information about the success of the experiment is based on the scientist’s speech at the International Conference on Genome Editing in Hong Kong and his interview with the Associated Press.
Second, the future risks to children from genome editing are unknown. Meanwhile, “disabling” the CCR5 gene increases the risk of contracting West Nile fever and other viral diseases, and also increases the likelihood of death from influenza. “I believe this can help families and their children. If it causes unwanted side effects or causes harm, I will feel the same pain as them and the responsibility will be mine,” He said in an interview on this matter.
Science_1
Photo: Depositphotos
Due to the lack of evidence of the safety of genome editing, implantation of edited embryos in women is prohibited in most countries. That's why Stanford and Rice University graduate He Jiankui conducted an experiment in China. By the way, he was helped in this by bioengineering professor Michael Dim, whom He met during his studies.
No longer a death sentence: A quarter of Russians with HIV are practically not infectious
By 2020, the proportion of such patients should reach 90%, the Ministry of Health expects.
A significant part of the scientific community condemned the experiment as immoral. “I don’t think there was a medical need for it. The list of diseases [to which the twins' resistance was reduced as a result of the experiment] that was voiced during the discussions is much more concerning,” said David Baltimore, moderator of the conference at which He spoke, Nobel Prize laureate in medicine. Jennifer Doudna, one of the creators of the CRISPR genome editing technology that He allegedly used, also called the experiment unacceptable.
Moreover, the Chinese scientist failed or refused to answer several important questions, including who funded the research and how he ensured that subjects knew about the possible consequences. Scientists were also confused by the fact that data on the start of the experiment were entered into the state register of clinical trials only on November 8, 2020 - almost a year after it began.
However, there are those who welcome the action of the Chinese researcher. For example, Harvard geneticist George Church, who drew attention to the fact that HIV is a growing threat to humanity. And the head of the laboratory of developmental epigenetics of the Institute of Cytology and Genetics of the SB RAS Suren Zakiyan. According to him, if He’s statements are true, “then this is a colossal breakthrough for fundamental science.”
Scientists have discovered ways for influenza and HIV viruses to enter the body
Viruses attack a living cell in a pirate way
What do they look for in blood?
In a blood test, they are not looking for the virus itself, the virus is invisible, they are looking for antibodies produced by the human body to the virus. The order of the analysis is determined by the order of the Ministry of Health, it is unchanged: from a simple screening and exploratory analysis they proceed to a more complex blood test, repeatedly checking the correctness of the result.
Typically, antibodies to the virus begin to be produced from the second week after infection; by the end of the month their level increases significantly and does not fall if left untreated. In nine out of ten infected people, the titer - the amount of antibodies - increases during the first 3 months after the introduction of HIV; only one person will need 3-6 months to start producing antibodies. And only one in two hundred develop antibodies much later.
Therefore, if there is a clear suspicion of infection, when in the first analysis two weeks after the expected time of contact with the blood of an infected person, nothing unnecessary was found, the analysis is repeated after 3 and 6 weeks. You shouldn’t immediately rejoice at the “purity” of the blood, this may be an illusion, but killing yourself and burying yourself is also premature, you need to calmly wait for the result and hope for the best.
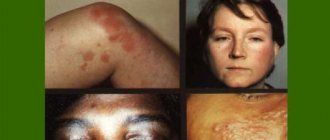
Symptoms
Main signs of HIV
- unreasonable fatigue and lethargy of the whole body;
- constant headaches and migraines;
- sudden weight loss for no apparent reason;
- prolonged diarrhea;
- the appearance and enlargement of lymph nodes throughout the body;
- sweating increases at night;
- body temperature is constantly elevated;
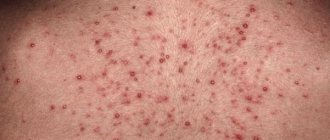
- A rash and redness appear on the body, which causes severe itching.
If a person is suspected of having an immunodeficiency virus, then one of the following diseases will definitely occur
- herpes, which occurs only in people under 50;
- in persons under 60 years of age, Kaposi's sarcoma, which was finally confirmed as a result of the necessary tests;
- pneumonia, lung diseases and disorders of the nervous system;
- brain toxoplasmosis.
What tests are done for HIV?
A standard blood test - enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is not 100% specific, but if it detects antibodies to HIV, then two similar tests are carried out using reagents from other manufacturers. The analysis is done with the same serum obtained by centrifuging the patient's blood. All this is done in a regular laboratory that does not specialize in infectious diseases. If at least one ELISA test detects antibodies to HIV, then the serum is sent to the laboratory of the AIDS center for the second stage of analysis - immunoblotting.
ELISA is a sensitive test, otherwise it would not be used in screening - searching for the virus during mass examinations. But human blood is a very delicate substance; elements can float in the plasma that can give an erroneous positive result even in the absence of a virus. All questions should be resolved by the next stage of research; if the immunoblot is negative, you can breathe out and move on with your life, enjoying yourself and life.
If “neither this nor that” is received in the immunoblot, the patient will be invited for a re-examination in 2-3 weeks to determine the final status. If the immunoblot result is positive, the completed analysis form must be sealed in an envelope, and an infectious disease doctor will issue it with information about what to do next. Life doesn’t end there, you’ll just have to live differently, but that’s also life.
Where to go if HIV is detected?
If HIV infection is detected, you must register with a specialized institution - the Center for the Prevention and Treatment of AIDS. When registering, anonymity is excluded; the entire package of documents is provided. The initial examination is extensive and serious, possible concomitant infections and simply hidden chronic diseases are looked for, all kinds of blood, urine and stool tests are done, consultations with specialists, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and radiography of the lungs are carried out. The entire examination is part of the government guarantee program, free of charge, but very long and uncomfortable.
Dispensary observation is designed to monitor the course of the infectious process - regular examination and provide free treatment if necessary. Everything is exclusively on a voluntary basis, only with the consent of the patient, expressed in writing. The start of treatment is determined by the viral load, which is determined by the number of special blood cells - CD4 lymphocytes, in which the virus lives and multiplies. The lower the number of CD4 lymphocytes, the more virus in the human body.
The observation schedule is determined by the regulatory documents of the Ministry of Health; the attending physician of an HIV-infected person must familiarize the patient with the observation program and even invite him to an appointment, which is not always done. An HIV-infected ordinary person who also sometimes needs to forget about the “sickness”, it is difficult for him to combine work with visiting the Center, especially to manage to undergo examinations and tests without anyone finding out about the problem.
There is a problem?
It is very difficult for uninfected people to understand all the ups and downs of life and the fears of people who suddenly threaten to become outcasts due to the presence of an invisible pathogenic agent in their body. There are always small and big problems with an HIV carrier, no matter how hard he tries to seem independent. No one guarantees that there won’t be a queue in front of the Center’s doctor’s office; moreover, no one promises that acquaintances will not meet on the territory of the medical institution, accidentally “just walking”, who will consider it their duty to notify the “interested party” about the meeting in a suspicious place. place.
No one promises that a “black” mark on the clinic’s outpatient card, placed with good intentions, will not become known to the housemate. The boss may get tired of tolerating the incomprehensible and regular absences of a subordinate on some business, because it is impossible to tell him about the need for examination at the Center. You don’t choose work during a crisis, it chooses you. Yes, and on paper it is written one thing about how it should be in a state medical institution; in real life, visiting the Center is completely different.
In 2020, 100 thousand new patients were registered at the federal AIDS center. All of them were previously observed in regional institutions, but the irregular provision of medicines forced them to go to the capital, where they also provide medicines to only six out of ten patients, but not two or three, as in the regions. The Moscow Center is very reluctant to register those temporarily registered, but even there the queues for examination have grown by an order of magnitude.
How can you help people living with HIV? Only by creating conditions for the patient when, when visiting the clinic, he will have no reason to worry and unnecessary problems, when he will feel “like everyone else,” but at the same time will receive everything he needs.
When should you get tested for HIV infection?
Typically, antibodies to the virus begin to be produced a week after infection, after a month their level increases and does not decrease without treatment. Therefore, ELISA is done two weeks after contact with an HIV patient. In nine out of ten infected people, antibody levels increase in the first 3 months after the virus enters. If infection is clearly suspected and there are no antibodies in the first ELISA, it must be repeated after 3 and 6 weeks. It will take 3–6 months for just one person to start producing antibodies. And only one out of two hundred infected people develop antibodies after six months. Highly professional infectious disease doctors and modern diagnostic equipment at the Medicine 24/7 clinic allow us to identify all the predisposing factors for the development of the disease and create an individual behavioral program in the presence of an infected relative.
Ways to extend life
After contacting a help center, you should not lose contact with other people infected with HIV. Whether it is treated or not, you will have to live with it. And the realization that you are not the only one greatly strengthens the spirit. By communicating with other infected people, you can stay up to date with all new trends in treatment. We need to stick together.
In addition to support, the following ways will help extend your life:
- The main method is, of course, drugs that can suppress the replication of the virus. These are HIV inhibitors, for example: Epivir, Retrovir, Truvada.
- Constant monitoring of health status and timely tests are necessary.
- Awareness. The patient must know how to live with this, how to avoid diseases and maintain immunity. For example, immunomodulators are contraindicated for people infected with HIV.
- Special diet.
- Adequate rest and sleep, no overexertion.
These methods really work and prolong a person’s life for several years and even decades. If you are diagnosed with HIV, life will be different, but it will not end.
Treatment of HIV with modern methods
HIV infection is not yet curable. The patient regularly undergoes PCR and counts the number of immune cells: CD4 T-lymphocytes, or T-helper cells, or T-suppressor cells, or CD8 T-lymphocytes. There should be more than 1400 T helper cells; if there are less than 500 cells, this is immunosuppression. Against this background, five out of a hundred patients may develop AIDS in the next two years. When the number of viruses exceeds a certain level or the number of T-lymphocytes decreases, treatment is prescribed. The effect of HIV treatment is assessed by PCR and T-lymphocyte levels. The best result is the absence of the virus in the blood, but this does not mean a cure. When the number of viruses decreased threefold and T-helpers increased, that’s also good. Gradually, the virus develops resistance to drugs, they are changed to others, but gradually the immunodeficiency worsens, the disease can last almost 30 years. For HIV infection, regular monitoring is necessary for timely treatment. The virus does not show any symptoms for a very long time, but treatment causes many adverse reactions, significantly worsening the quality of life. Refusal of HIV treatment shortens life, bringing AIDS closer. If you suspect a viral infection, it is vital to consult a doctor. Get help from an infectious disease specialist by calling. Anonymity is guaranteed.