Hydrothorax of the lung is a pathology characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. Due to this feature, this condition is popularly called thoracic dropsy. Hydrothorax cannot be called an independent disease; rather, it can be characterized as a concomitant condition that occurs with other diseases. In this regard, there are certain rules and principles of treatment. It will not be possible to predict the course of therapy and its consequences in advance, since treatment is prescribed individually in each specific case.
The essence of pathology
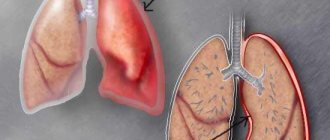
When considering hydrothorax of the lung, one cannot help but pay attention to studying the very essence of this condition. In the human chest there are three special serous sacs, which are intended for each lung separately and for the heart. The pulmonary membrane consists of two layers at once and is called the pleura. The two separate layers are the visceral and parietal pleura. The small slit-like gap between them is called the pleural cavity. In a healthy person, this gap is extremely small and contains 1-2 ml of pleural fluid.
Under certain factors, the amount of fluid in the pleural cavity increases sharply and can reach 1-2 liters. This condition is called hydrothorax of the lung. However, the penetration of other liquids is also possible, and therefore the names change: with the accumulation of blood - hemothorax, lymph - chylothorax, air - pneumothorax.
A characteristic feature of this process is the absence of an inflammatory nature.
Causes
The pleural cavity is the space between the outer and inner layers of the pleura. It contains a small amount of secretion necessary to reduce friction during breathing. Pathology is considered to be an increase in the synthesis of effusion, which is due to the following reasons:
- Glomerulonephritis and renal amyloidosis - pathologies provoke fluid retention in the body, swelling and accumulation of effusion in the pleural cavity. Nephrotic syndrome develops, which is characterized by external and internal swelling of the entire body with subsequent negative consequences.
- Heart failure provokes an increase in blood pressure, against the background of which the fragility and permeability of blood vessels increases. Metabolic processes in the pleural cavity are disrupted.
- Myxedema is the final stage of hypothyroidism, in which there is an acute lack of thyroid hormones, against which the process of absorption and excretion of fluids in the body is disrupted.
- Cirrhosis of the liver - an organ with degenerated tissues cannot cope with its filtration functions.
- Neoplasms in the sternum area, which compress the lungs and provoke fluid effusion into the pleural cavity with the impossibility of its further removal.
- Autoimmune diseases provoke disruption of the lymphatic system, so the effusion is utilized several times slower than it is synthesized.
The causes of pulmonary hydrothorax determine the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Hydrothorax of the lungs in acute form can cause chest injury and damage to the integrity of the pleural membranes. Under the influence of gravity, fluids rush into the lower pleura, putting pressure on the lungs. Lack of resuscitation measures can cost a person’s life.
Pathology is not independent. It accompanies many major diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
Hydrothorax of the lungs in oncology and in trauma has different manifestations and different approaches to treatment.
Features of the appearance of fluid in the pleural cavity
The accumulation of fluid (transudate) in the pleural cavity occurs if the pressure inside the pleural capillaries increases to such an extent that it exceeds the colloid-osmotic plasma pressure. Such conditions cause large amounts of plasma to leak out through the walls of the capillaries. It accumulates in the pleural cavity. The ICD code for hydrothorax of the lung is J94.
An increase in the volume of fluid occurs due to a decrease in the volume of the lung, as a result of which the volume involved in breathing is reduced, and displacement of the internal organs develops.
In adults
Hydrothorax in adults can develop due to various diseases. In this case, there are several forms of development of hydrothorax.
- hemothorax;
- chylothorax.
Hemothorax usually occurs due to injury to the chest. It is known that adults are most susceptible to this type of injury. And this is understandable. Although there are cases in childhood.
Chylothorax is a disease in which lymph accumulates in the pleural cavity. What could cause such an accumulation?
- damage;
- circulation disturbance.
The damage is usually attributed to damage to the lymphatic duct. Mainly in the thoracic region.
The circulation of lymph through the capillaries can also trigger the disease. Since its violation contributes to the accumulation of fluid.
go to top
Localization
This pathological process can occur in several forms, the distinguishing feature being its localization:
- right-sided;
- left-sided hydrothorax of the lung;
- double-sided
The most common occurrence is bilateral hydrothorax. This phenomenon can be explained by the following fact. The presence of an underlying disease causes the accumulation of pleural fluid first in one lung (right or left). The absence of pronounced symptoms most often means the absence of correct treatment, which means that over time a similar process develops in the second lung.
What diseases cause hydrothorax?
Several diseases have been described in medicine that may be accompanied by the accumulation of pleural fluid in the lung. In this case, the main reason is a sharp increase in blood pressure.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. According to medical statistics, in 80% of such cases it is right-sided hydrothorax of the lung that develops.
- Tumors located in the organs and tissues of the chest.
- Chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system or congenital heart defects. The list of such pathologies includes chronic heart failure (known by the abbreviation CHF). With such indicators, blood stagnation occurs in various parts of the body, causing hydrostatic pressure. The result of such changes in the body is often the transition of fluid to the pleural area.
- Chronic kidney diseases (the risk is especially high in those people who suffer from delayed fluid excretion from the body). The accumulation of fluid is explained by a reduced level of oncotic pressure.
- Various mechanical injuries, sternum injuries.
- Malabsorption syndrome.
- Myxedema.
- Pneumonia.
- Anemia.
- Amyloidosis.
- Ovarian fibroids.
Hydrothorax of the lung: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods
Hydrothorax of the lung is a pathology characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity. Due to this feature, this condition is popularly called thoracic dropsy.
Hydrothorax cannot be called an independent disease; rather, it can be characterized as a concomitant condition that occurs with other diseases. In this regard, there are certain rules and principles of treatment.
It will not be possible to predict the course of therapy and its consequences in advance, since treatment is prescribed individually in each specific case.
The essence of pathology
Glucosamine sulfate: instructions for use, analogues and reviews
When considering hydrothorax of the lung, one cannot help but pay attention to studying the very essence of this condition. In the human chest there are three special serous sacs, which are intended for each lung separately and for the heart.
The pulmonary membrane consists of two layers at once and is called the pleura. The two separate layers are the visceral and parietal pleura. The small slit-like gap between them is called the pleural cavity.
In a healthy person, this gap is extremely small and contains 1-2 ml of pleural fluid.
Under certain factors, the amount of fluid in the pleural cavity increases sharply and can reach 1-2 liters. This condition is called hydrothorax of the lung. However, the penetration of other liquids is also possible, and therefore the names change: with the accumulation of blood - hemothorax, lymph - chylothorax, air - pneumothorax.
A characteristic feature of this process is the absence of an inflammatory nature.
Features of the appearance of fluid in the pleural cavity
The accumulation of fluid (transudate) in the pleural cavity occurs if the pressure inside the pleural capillaries increases to such an extent that it exceeds the colloid-osmotic plasma pressure. Such conditions cause large amounts of plasma to leak out through the walls of the capillaries. It accumulates in the pleural cavity. The ICD code for hydrothorax of the lung is J94.
Channel PROGRAMMER'S DIARY The life of a programmer and interesting reviews of everything. so as not to miss new videos.
An increase in the volume of fluid occurs due to a decrease in the volume of the lung, as a result of which the volume involved in breathing is reduced, and displacement of the internal organs develops.
Localization
Vishnevsky Institute in Moscow: services, doctors, address, patient reviews
This pathological process can occur in several forms, the distinguishing feature being its localization:
- right-sided;
- left-sided hydrothorax of the lung;
- double-sided
The most common occurrence is bilateral hydrothorax. This phenomenon can be explained by the following fact. The presence of an underlying disease causes the accumulation of pleural fluid first in one lung (right or left). The absence of pronounced symptoms most often means the absence of correct treatment, which means that over time a similar process develops in the second lung.
What diseases cause hydrothorax?
Several diseases have been described in medicine that may be accompanied by the accumulation of pleural fluid in the lung. In this case, the main reason is a sharp increase in blood pressure.
- Cirrhosis of the liver. According to medical statistics, in 80% of such cases it is right-sided hydrothorax of the lung that develops.
- Tumors located in the organs and tissues of the chest.
- Chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system or congenital heart defects. The list of such pathologies includes chronic heart failure (known by the abbreviation CHF). With such indicators, blood stagnation occurs in various parts of the body, causing hydrostatic pressure. The result of such changes in the body is often the transition of fluid to the pleural area.
- Chronic kidney diseases (the risk is especially high in those people who suffer from delayed fluid excretion from the body). The accumulation of fluid is explained by a reduced level of oncotic pressure.
- Various mechanical injuries, sternum injuries.
- Malabsorption syndrome.
- Myxedema.
- Pneumonia.
- Anemia.
- Amyloidosis.
- Ovarian fibroids.
Types of hydrothorax
In addition to location, cases of hydrothorax may vary in the volume of transudate. There are several options:
- small - this pathology is characterized by a small volume of liquid (up to 150 ml);
- total - characterized by a high content of accumulated liquid;
- encysted.
Field bindweed: photo, description, medicinal properties and contraindications
Depending on the characteristics of the pathology, the clinical picture will differ. In general, the symptoms for all types of hydrothorax are quite similar, but their intensity will vary.
First symptoms
The accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity occurs gradually. This explains the increasing nature of the symptoms. The process can last several days or 2-3 weeks. At the initial stage, a person does not feel pain or discomfort, so going to the hospital is usually postponed.
- One of the first symptoms is a feeling of heaviness in the chest. When standing or sitting, the unpleasant sensation intensifies. The patient's condition can be somewhat alleviated by lying down and precisely on the side where the hydrothorax of the lung is located.
- Frequent shallow breathing. This symptom is explained by a reduction in the working volume of the lung.
- Feeling of lack of air. The patient feels like he can't breathe.
- Blue tint of the skin. This symptom is a consequence of prolonged oxygen starvation.
- Body temperature remains at normal levels or even decreases slightly. This can be explained by the non-inflammatory nature of hydrothorax.
Later symptoms
If pathology is not detected at the initial stage of the process, the amount of transudate in the pleural cavity will increase, and this will intensify the symptoms. The following will appear:
- Fatigue during the day, even with a full night's sleep.
- Increasing shortness of breath. It is observed even at rest.
- Feeling of fullness and pressure in the abdomen and sternum.
- Frequent attacks of nausea, they quite often end in vomiting.
When examining a patient at this stage of pulmonary hydrothorax, the doctor may notice the following signs:
- the spaces between the ribs become smoother or even protrude;
- when breathing, one side of the chest lags behind in movement (this happens if hydrothorax develops only on one side);
- protrusion of the peritoneum in the navel area, change in shape and swelling of the abdominal wall.
To obtain a more accurate picture of the disease, during the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to take different body positions. So, when he sits, the peritoneum hangs down, and if the patient lies on his back, the stomach spreads out and becomes flat. This condition is especially often caused by bilateral hydrothorax of the lungs.
The presence of such symptoms significantly complicates a person’s life, therefore, in addition to all of the above, patients with a similar diagnosis are irritable and suffer from sleep and appetite disorders.
Diagnostics
After visiting the clinic and conducting an initial examination of the patient, the doctor prescribes a series of hardware tests and laboratory tests. It is quite difficult to determine hydrocele of the lung by visual examination alone. The reason for this is the symptoms that are characteristic of many diseases. To identify all associated complications, it is necessary to conduct an examination.
Urine and blood analysis. Laboratory tests of the blood reveal an increased content of carbon dioxide (this feature occurs due to a lack of oxygen in the body).
X-ray. If lung disease is suspected, an x-ray is one of the most effective and reliable diagnostic methods. In the image, the cavities with liquid will be painted in darker shades.
Ultrasound. Ultrasound examination is necessary not only to identify hydrocele, but also to determine its location and size.
CT. With computed tomography it is possible to establish the cause of the pathology.
Puncture. This procedure involves removing a small amount of fluid from the lung to be analyzed in a laboratory. During such a study, doctors are able to identify the chemical composition of the substance and the possible presence of atypical cells in it. This analysis is carried out in case of suspected hydrothorax of the lungs due to oncology.
Basic principles of treatment
The main task of doctors is not to get rid of the transudate, but to eliminate the cause of its appearance, because hydrothorax is only a consequence of the pathological condition of the body.
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=GgR44IINHv0
Pumping out fluid from the pleural cavity whenever it appears is not only a useless, but also a dangerous decision. Each subsequent pumping sharply reduces the amount of protein in the body. If concentration does not have time to recover, then the patient experiences serious complications.
The principle of treatment is based on the characteristics of the underlying disease. The following methods are used to pump out transudate:
- thoracentesis (pleurocentesis) is an operation during which a puncture is made in the chest cavity to gain access to the pleural cavity for the purpose of pumping out transudate;
- puncture with aspiration;
- Bülau drainage (procedure for draining the pleural cavity).
“Arkoxia”: reviews of the drug, instructions for use, composition and analogues, price
It is strictly prohibited to treat hydrothorax of the lung with folk remedies. The wrong choice of treatment can result in serious complications for the patient.
Complications of hydrothorax
The most common complication of pulmonary hydrops is acute respiratory failure. It develops due to severe compression of the lung and is accompanied by pronounced pain in the sternum and shortness of breath even at rest.
In some cases, an infection is added to the pathological condition, leading to damage to the pleural layers (the membranes of the lung). This condition is called pleural empyema.
How to treat hydrothorax of the lungs with medications
Drug treatment is also possible, but it is indicated only in cases where the dropsy is small in size.
If the pathology is associated with heart failure, then patients are often prescribed diuretics to naturally remove transudate from the body. Among the most common medications are “Indapamide”, “Diuretin”, “Diacarb”, “Merkuzal”, “Veroshpiron”.
To reduce protein loss in urine, intravenous infusion of protein drugs is added.
If an infection is detected, the course of treatment for pulmonary hydrothorax must include broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Important aspects of treatment
When treating pulmonary hydrothorax, you must follow all doctor's instructions. So, the speed of recovery is affected by several aspects.
Diet control. Nutrition plays an important role in this pathology. The patient should avoid the following products:
- salty food;
- fried, fatty and smoked foods;
- alcoholic products;
- coffee;
- a large amount of liquid.
In case of complications, it is extremely important to maintain bed rest. In this case, the load on the body will be significantly reduced, and recovery will proceed at a rapid pace.
For the same reason, you need to achieve a stable emotional background. Stressful situations and overexertion must be avoided.
Forecast
In general, thoracic hydrops responds well to treatment, and doctors give an optimistic prognosis. Hydrothorax of the lungs in oncology is a more complex case; here it is important to take into account the degree of spread of the cancerous tumor, the presence or absence of metastases, the age of the patient and his general condition.
However, such indicators are only possible if the pathology was identified in time and doctors prescribed the correct treatment.
Doctors warn: in order to get a lasting effect and prevent re-accumulation of transudate, treatment should not be interrupted immediately after the symptoms have resolved. The course of therapy must be completed.
In this case, the duration of treatment and dosage of all drugs is controlled only by the attending physician.
Otherwise, hydrothorax of the right lung (or left) leads to an increase in the size of the pathological process and provokes inflammatory diseases.
Considering all of the above, we can conclude that this pathology is not as dangerous as it may seem to patients with a similar diagnosis. Chest hydrops can be eliminated quite quickly and effectively by treating the underlying disease. The only exception is those cases when this condition is caused by oncological processes. In this case, long and complex treatment awaits.
Source
Source: //1Ku.ru/zdorove/25151-gidrotoraks-legkogo-prichiny-simptomy-diagnostika-i-metody-lecheniya
Types of hydrothorax
In addition to location, cases of hydrothorax may vary in the volume of transudate. There are several options:
- small - this pathology is characterized by a small volume of liquid (up to 150 ml);
- total - characterized by a high content of accumulated liquid;
- encysted.
Depending on the characteristics of the pathology, the clinical picture will differ. In general, the symptoms for all types of hydrothorax are quite similar, but their intensity will vary.
First symptoms
The accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity occurs gradually. This explains the increasing nature of the symptoms. The process can last several days or 2-3 weeks. At the initial stage, a person does not feel pain or discomfort, so going to the hospital is usually postponed.
- One of the first symptoms is a feeling of heaviness in the chest. When standing or sitting, the unpleasant sensation intensifies. The patient's condition can be somewhat alleviated by lying down and precisely on the side where the hydrothorax of the lung is located.
- Frequent shallow breathing. This symptom is explained by a reduction in the working volume of the lung.
- Feeling of lack of air. The patient feels like he can't breathe.
- Blue tint of the skin. This symptom is a consequence of prolonged oxygen starvation.
- Body temperature remains at normal levels or even decreases slightly. This can be explained by the non-inflammatory nature of hydrothorax.
Hydrothorax
Hydrothorax is the accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers - in the pleural cavity.
The pleural layers cover the lungs and line the inner surface of the chest. Normally, there is only a few milliliters of liquid between them, which acts as a lubricant. If the lungs become inflamed, exudate accumulates between the pleural layers. This is a fluid that is released from small blood vessels. Transudate may also appear in the pleural cavity. It accumulates due to impaired blood and lymph circulation.
Unlike exudate, the formation of transudate is not associated with inflammatory processes. Exudate is characteristic of another disease - pleurisy. In this article we will look at transudate accumulation.
The causes of pulmonary hydrothorax can be different. These are heart failure, kidney disease, liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension, pulmonary embolism, etc.
Hydrothorax also accompanies cancer. Most often it develops in cancer of the lung, pleura, breast, and ovaries. In such cases, fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity due to the appearance of metastases on the pleura, which increase the permeability of blood vessels and impair the outflow of lymph.
Symptoms and signs of hydrothorax
The symptoms of hydrothorax are caused by accumulated fluid squeezing the lungs. Patients are concerned about a feeling of heaviness, pressure in the chest, dry cough, shortness of breath. If a large amount of transudate accumulates in the pleural cavity, the outflow of blood from the neck veins becomes difficult. Then their swelling becomes noticeable.
The classification of hydrothorax is based on the volume and location of the fluid. There are small and large, right-sided and left-sided, total and encysted hydrothorax.
In most cases, hydrothorax covers both pleural cavities, and when it is metastatic, a unilateral lesion is more often observed.
Diagnosis of hydrothorax
An x-ray examination of the chest organs is carried out, which reveals the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity. If tumor hydrothorax is suspected, computed tomography is indicated to identify metastases in the chest organs.
A final diagnosis of hydrothorax can be made only after laboratory examination of fluid in the pleural cavity. To collect it, a pleural puncture is performed. The fluid is sucked out through a small puncture in the chest.
Laboratory analysis shows whether it is an exudate or a transudate.
However, in some cases, laboratory analysis of the fluid cannot determine the cause of hydrothorax, and video thoracoscopy may be recommended to make a final diagnosis. This endoscopic method allows you to examine the pleural cavity and perform a biopsy of the suspicious area.
Treatment of hydrothorax
Minor hydrothorax does not require special treatment. The fluid resolves on its own with successful treatment of the underlying disease.
If there is a significant accumulation of transudate, pleural puncture is used as not only a diagnostic, but also a therapeutic method. Complete removal of fluid is called thoracentesis.
The procedure is performed in an operating room by a thoracic surgeon under local anesthesia.
Treatment of pulmonary hydrothorax with thoracentesis improves the patient's condition, reduces shortness of breath and discomfort. But since hydrothorax is a secondary disease, subsequent treatment should be aimed at the cause of its development.
For persistent hydrothorax, especially of a metastatic nature, video-assisted thoracoscopic pleurodesis can be performed. The surgeon, under the control of an endovideo camera, introduces various agents, often chemical (talc pleurodesis), into the pleural cavity. The procedure causes an adhesive process between the layers of the pleura, which prevents further accumulation of fluid.
The Thoracopulmonology Center of the Oberig Universal Clinic has everything necessary for the diagnosis and treatment of hydrothorax. Pleural puncture, as well as video thoracoscopy, is carried out using modern high-tech equipment.
The Oberig Universal Clinic has its own pathohistological center, where pleural fluid is examined. Accurate diagnosis of the cause of hydrothorax is the basis for the correct treatment strategy for the patient.
Make an appointment with specialists at the Thoracopulmonology Center by calling:
(044) 521 30 03
(099) 521 30 03
(073) 521 30 03
Source: https://oberig.ua/ru/diseases/gidrotoraks/
Later symptoms
If pathology is not detected at the initial stage of the process, the amount of transudate in the pleural cavity will increase, and this will intensify the symptoms. The following will appear:
- Fatigue during the day, even with a full night's sleep.
- Increasing shortness of breath. It is observed even at rest.
- Feeling of fullness and pressure in the abdomen and sternum.
- Frequent attacks of nausea, they quite often end in vomiting.
When examining a patient at this stage of pulmonary hydrothorax, the doctor may notice the following signs:
- the spaces between the ribs become smoother or even protrude;
- when breathing, one side of the chest lags behind in movement (this happens if hydrothorax develops only on one side);
- protrusion of the peritoneum in the navel area, change in shape and swelling of the abdominal wall.
To obtain a more accurate picture of the disease, during the examination, the doctor may ask the patient to take different body positions. So, when he sits, the peritoneum hangs down, and if the patient lies on his back, the stomach spreads out and becomes flat. This condition is especially often caused by bilateral hydrothorax of the lungs.
The presence of such symptoms significantly complicates a person’s life, therefore, in addition to all of the above, patients with a similar diagnosis are irritable and suffer from sleep and appetite disorders.
General clinical manifestations
With the development of hydrothorax, the symptoms are not always pronounced. The following clinical manifestations are possible:
- dyspnea;
- feeling of heaviness in the chest;
- forced body position.
In severe cases, ascites develops. With it, fluid accumulates in the abdominal cavity. If both lungs are affected, the patient's condition is more severe. This syndrome leads to displacement of the mediastinal organs and compression of tissues. In most cases, the symptoms of hydrothorax increase gradually. The main symptom is shortness of breath.
It is associated with impaired lung function. Patients complain of a feeling of lack of air. Gradually breathing becomes more frequent and deeper. This can be detected during a physical examination. If left untreated, bilateral hydrothorax can lead to cyanosis. The reason is the accumulation of carbon dioxide in the blood. This is manifested by cyanosis of the skin.
The bilateral pathological process does not manifest itself as pain. This is different from inflammatory diseases. The affected half of the chest lags behind the healthy half when breathing. This syndrome often causes affected people to adopt a posture with the upper body elevated. There are no symptoms of intoxication such as fever and chills. In severe cases, complications may develop in the form of purulent pleurisy, respiratory failure and ascites.
Diagnostics
After visiting the clinic and conducting an initial examination of the patient, the doctor prescribes a series of hardware tests and laboratory tests. It is quite difficult to determine hydrocele of the lung by visual examination alone. The reason for this is the symptoms that are characteristic of many diseases. To identify all associated complications, it is necessary to conduct an examination.
Urine and blood analysis. Laboratory tests of the blood reveal an increased content of carbon dioxide (this feature occurs due to a lack of oxygen in the body).
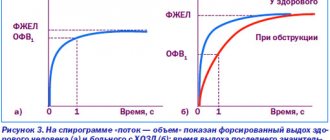
X-ray. If lung disease is suspected, an x-ray is one of the most effective and reliable diagnostic methods. In the image, the cavities with liquid will be painted in darker shades.
Ultrasound. Ultrasound examination is necessary not only to identify hydrocele, but also to determine its location and size.
CT. With computed tomography it is possible to establish the cause of the pathology.
Puncture. This procedure involves removing a small amount of fluid from the lung to be analyzed in a laboratory. During such a study, doctors are able to identify the chemical composition of the substance and the possible presence of atypical cells in it. This analysis is carried out in case of suspected hydrothorax of the lungs due to oncology.
Hydrothorax of the lungs: what is it?
To quickly cure cough, bronchitis, pneumonia and strengthen the immune system, you just need...
The lungs of a healthy person are separated from the abdominal cavity by the pleura - a kind of film. There is a cavity between it and the respiratory organs.
Due to certain factors, liquid may accumulate in this cavity. This condition is called pulmonary hydrothorax.
A small amount of liquid does not manifest itself in any way, but a volume of more than 200 ml causes characteristic symptoms and can also cause a number of complications.
So, pulmonary hydrothorax: what is it, how to recognize the disease and can it be cured?
Types of hydrothorax
The accumulation of fluid in the chest cavity has several forms, which depend on the causes of the disease and the nature of its course.
Hydrothorax is classified according to the location of the lesion:
- Right-handed;
- Left-handed;
- Bilateral.
The left-sided form is very rare; fluid accumulated on the right is slightly more common. Bilateral hydrothorax is the most common.
The paradox is that it becomes such only after alternating damage to both lungs. But this process proceeds quickly and does not cause any special symptoms, so doctors most often encounter a bilateral form of pathology.
Based on the nature of the fluid accumulating in the pleura, there are:
- Hemothorax (the cavity fills with blood);
- Chylothorax (in this case we are talking about lymph).
These varieties depend primarily on the causes of the disease.
Important! Patients of all ages are susceptible to hydrothorax. Its varieties are identical for everyone.
Causes
Hydrothorax is not an independent disease; provoking factors contribute to the development of the disease. As a rule, these are serious diseases in the final stages.
Fluid accumulation occurs:
- In case of problems with the liver and kidneys;
- For oncology;
- With increased blood pressure in the pulmonary artery;
- Due to heart failure.
Pathology is also caused by some “female” diseases, for example, ovarian fibroma.
A special situation arises in patients with liver cirrhosis. Ascitic fluid penetrates from the abdominal cavity under the dome of the diaphragm on the right side. The result is right-sided hydrothorax.
Fluid accumulation occurs in 10% of these patients. However, if cirrhosis is accompanied by heart disease, then the main cause may be in them.
Hepatic hydrothorax is characterized by the accumulation of more than 500 ml of fluid, which is a very large indicator for heart problems.
Symptoms
The intensity of the symptoms of the disease depends entirely on the volume of accumulated fluid. Also, all signs of hydrothorax are combined with symptoms of concomitant diseases.
Main clinical manifestations of the disease:
- Dyspnea. It manifests itself at all stages of the disease, regardless of the amount of fluid. In the early stages, shortness of breath occurs only during physical exertion, but later the patient feels it even at rest.
- The patient is forced to lie on the painful side. With advanced hydrothorax, this position allows the lung on the affected side to open more, which makes breathing easier.
- The precutary sound is dull. Along its upper border you can trace the Dmoiseau line - it allows you to determine the degree of damage.
- Weak trembling on the affected side. With a large amount of liquid it may be completely absent.
- Cyanosis, that is, blue discoloration of the skin. Occurs due to a lack of oxygen due to a reduction in the respiratory function of the lungs.
Pain with hydrothorax is uncharacteristic. They can be observed only in the early stages of the disease, when there is still very little fluid in the pleural cavity.
Diagnostics
Contrary to popular belief, x-rays are not effective in diagnosing hydrothorax. It can only detect large accumulations of liquid, the volume of which exceeds 200 ml.
An x-ray is taken only in advanced cases. The liquid appears in the image as a curved, uniform shading. Moreover, there is a shift of internal organs towards the healthy side.
A more effective way to detect the disease is ultrasound. It allows you to detect a minimal amount of liquid, the volume of which does not exceed 10 ml. However, it is practically not used as an independent diagnosis.
An ultrasound examination is usually ordered to determine the best location for a biopsy.
A biopsy is performed to identify the root cause of the disease, as well as diagnose cancer. The fluid is withdrawn using a long, hollow needle by puncturing the chest. Usually performed under anesthesia, it does not pose a risk to the patient’s health.
To clarify the causes of pulmonary hydrothorax, additional examinations are carried out:
- ECG;
- biochemical studies for protein, hormones, urea;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys.
If diagnosis is difficult, an ultrasound examination of all abdominal organs without exception is performed. In this case, much attention is paid to the thyroid gland.
Treatment
To cope with hydrothorax, you should be cured of the provoking disease.
The therapeutic course depends entirely on the nature of the pathology, the degree of its neglect, as well as the characteristics of the patient’s body. It is impossible to give any general recommendations here; everything depends on the diagnostic results.
During treatment, fluid must be removed from the lungs.
This is done by puncture with a special needle. By puncturing the chest tissue, a needle is inserted into the pleura, after which fluid is pumped out. There is a limitation - no more than one and a half liters can be pumped out at a time.
This therapy is indicated only when a large volume of fluid accumulates. People who suffer from hemophilia should not undergo a puncture.
Important! If there is little liquid, pumping is not performed. In this case, resort to other treatment methods.
A special diet helps reduce the amount of fluid in the pleura:
- Minimum salt;
- Less fluid intake;
- If severe protein loss is observed, albumin administration is prescribed.
This diet is most relevant for heart failure; in other cases, the doctor prescribes an individual diet.
Important! Hydrothorax itself is not particularly dangerous, but the provoking disease can lead to serious health problems. Therefore, you should pay less attention to the fluid in the pleura and focus on treating the underlying disease.
Danger
Fluid in the pleural cavity is not lethal, although it causes some inconvenience in large volumes. Major diseases pose a much greater danger. Remember that hydrothorax is one of the main signs of oncology.
Also, ignoring the disease can lead to:
- Acute form of heart failure;
- Hepatitis;
- Impaired kidney function;
- Heart attack.
Hydrothorax itself causes only acute respiratory failure, and even then in the complete absence of treatment.
Hydrothorax of the lungs indicates problems with the cardiovascular system, kidneys, and liver. It is also one of the signs of cancer.
During the examination, it is recommended to check all organs and systems to identify the underlying pathology. Treatment should also be focused on it, and not on the fact of the presence of fluid in the pleural cavity. Take care of your health!
Source: https://pnevmonii.net/other/gidrotoraks-legkih
Signs and symptoms of hydrothorax
The underlying disease does not affect minor hydrothorax. Total hydrothorax carries certain signs; organ compression of the lung parenchyma and mediastinal area occurs. Transudate accumulates in the following hydrothorax:
- right-sided view;
- double-sided view
Isolated hydrothorax is rare. Fluid accumulation is localized:
- subcutaneous layer;
- abdominal cavity;
- pleural cavity
The clinic appears gradually. Signs of the disease:
- breathing problems;
- chest heaviness;
- breathing problems;
- there is no pain;
- no fever
The reason is the absence of an inflammatory process. Visual signs of hydrothorax are as follows:
- chest damage;
- acrocyanosis;
- specific patient position
The patient takes a semi-sitting position. "Lying on your side" is also a possible position. A dull sound is determined by percussion, vesicular breathing is absent. Displacement of percussion boundaries is a sign of pleural effusion.
Signs of ascites are:
- enlarged belly;
- soft tissue swelling
Respiratory failure is a symptom of people with cirrhosis of the liver. Hepatic hydrothorax is manifested by the following pathologies:
Signs of infection with this disease:
- chest pain;
- hyperthermia;
- sign of encephalopathy
Causative agents of hepatic hydrothorax:
- microorganism;
- stick in the intestines
go to top
Methods for diagnosing hydrothorax
Timely diagnosis is an indicator of quality treatment. The measures usually taken are of the following nature:
- pleural puncture;
- cytological examination;
Purpose of fluoroscopy:
- identifying the presence of exudate;
- establishing fluid volume
Manifestations of hydrothorax:
- dark area;
- oblique upper border;
- pleural sinuses are not identified
The indicator in radiography is the position occupied by the patient. Lying on your side is acceptable. Ultrasound examination is a therapeutic measure used for the disease. Computed tomography allows you to determine the following indicators:
- pathological changes;
- treatment methods
Pleural puncture is an event after detection of the disease. The purpose of this event is as follows:
- definition of inflammation;
- cytological examination;
- sowing
It is not only the surgeon who performs pleural puncture. The procedure is gentle and is carried out using anesthesia. Equipment used for puncture:
- trocar;
- adapter;
- system
The patient's position is a sitting position, the chest tilts. Local anesthetic drug – novocaine. Puncture localization - seventh hypochondrium. Recommendations during the rehabilitation period:
- applying a bandage;
- bed rest
Complications of the pleural cavity:
- impaired blood supply to the brain;
- vascular embolism;
- bleeding;
- compromised lung integrity
The method for diagnosing complications is control x-ray. Diagnostic technique:
- urine pattern examination;
- biochemistry;
- pleural analysis;
- cytological studies;
- samples;
- bacteriological research
Features of punctate:
- increasing protein levels;
- increase in acidity
Diagnosis of hepatic hydrothorax:
- surgical technique;
- thoracoscopy method;
- biopsy method
go to top
Hydrothorax therapy
The leading cause of the disease is identified and therapy is determined. Identifying the underlying disease is important. Treatment of the disease is etiopathogenetic. The progression of the disease is a consequence of improper treatment.
The consequences of the disease are as follows:
- respiratory dysfunction;
- cardiac disorders
Treatment of the patient is as follows:
- proper nutrition;
- lifestyle change
The daily routine should be correct, sleep will be normalized. Excludes:
- stressful situations;
- emotional tension
The diet involves fractional meals; salt and liquid are limited. Conservative treatment includes:
- cardiac glycosides;
- inhibitors;
- diuretics;
Types of diuretics:
- thiazide;
- potassium-sparing;
Diet and bed rest are prescribed in the following situations:
- renal pathology;
- swelling
It is necessary that diuresis is normal. Blood transfusion is a method used to correct the composition of the blood. The albumin solution is poured. The drug Ramipril is used in treatment.
Diuretics are used for a long time as a method of combating fluid accumulation. Treatment methods for hepatic hydrothorax are:
- antibacterial drugs;
- diuretics;
- thoracentesis
If there is no effect of therapy, surgical intervention is necessary. Operative methods:
- shunt placement;
- diaphragmatic closure
It is important to perform a puncture of the pleural cavity, the goal is to reduce the risk of acute complications. Indications for puncture:
- the fluid secretion is not large;
- hemodynamic disorders
Timely detection of the disease is the key to successful treatment. The prognosis is favorable. Complications are possible with this disease. Disease prevention - traditional medicine methods.
Traditional medicine should have a diuretic effect. In this case, parsley tincture is used. Methods for preparing parsley tincture:
- parsley is steamed;
- straining;
- take one tablespoon
Source: https://bolit.info/gidrotoraks-2.html
Basic principles of treatment
The main task of doctors is not to get rid of the transudate, but to eliminate the cause of its appearance, because hydrothorax is only a consequence of the pathological condition of the body.
Pumping out fluid from the pleural cavity whenever it appears is not only a useless, but also a dangerous decision. Each subsequent pumping sharply reduces the amount of protein in the body. If concentration does not have time to recover, then the patient experiences serious complications.
The principle of treatment is based on the characteristics of the underlying disease. The following methods are used to pump out transudate:
- thoracentesis (pleurocentesis) is an operation during which a puncture is made in the chest cavity to gain access to the pleural cavity for the purpose of pumping out transudate;
- puncture with aspiration;
- Bülau drainage (procedure for draining the pleural cavity).
It is strictly prohibited to treat hydrothorax of the lung with folk remedies. The wrong choice of treatment can result in serious complications for the patient.
Treatment of hydrothorax of the lungs with traditional methods
Treatment of hydrothorax with folk remedies is not a panacea and should certainly be discussed with your doctor. Self-resorption of transudate from the pleural cavity is facilitated by treatment of the underlying disease, as well as taking medications that help remove fluid from the body. Diuretic folk remedies include:
- decoction of parsley in milk - pour half a kilogram of parsley with unpasteurized milk and place either on low heat or in the oven; simmer until the broth has reduced by half, but do not boil; take 1-2 tbsp;
- decoction of turnip peels - place 1 cup of turnip peels in a saucepan, pour 3 liters of boiling water, close tightly and simmer in the oven for two hours; take one glass per day;
- onion juice - finely chop two onions, add a little sugar overnight, squeeze out the juice in the morning and take 2 tbsp daily on an empty stomach.
Alternative treatment for underlying diseases is also possible, which again needs to be discussed with your doctor.
Complications of hydrothorax
The most common complication of pulmonary hydrops is acute respiratory failure. It develops due to severe compression of the lung and is accompanied by pronounced pain in the sternum and shortness of breath even at rest.
In some cases, an infection is added to the pathological condition, leading to damage to the pleural layers (the membranes of the lung). This condition is called pleural empyema.
How to treat hydrothorax of the lungs with medications
Drug treatment is also possible, but it is indicated only in cases where the dropsy is small in size.
If the pathology is associated with heart failure, then patients are often prescribed diuretics to naturally remove transudate from the body. Among the most common drugs are Indapamide, Diuretin, Diacarb, Mercuzal, Veroshpiron.
To reduce protein loss in urine, intravenous infusion of protein drugs is added.
If an infection is detected, the course of treatment for pulmonary hydrothorax must include broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Important aspects of treatment
When treating pulmonary hydrothorax, you must follow all doctor's instructions. So, the speed of recovery is affected by several aspects.
Diet control. Nutrition plays an important role in this pathology. The patient should avoid the following products:
- salty food;
- fried, fatty and smoked foods;
- alcoholic products;
- coffee;
- a large amount of liquid.
In case of complications, it is extremely important to maintain bed rest. In this case, the load on the body will be significantly reduced, and recovery will proceed at a rapid pace.
For the same reason, you need to achieve a stable emotional background. Stressful situations and overexertion must be avoided.
Forecast
In general, thoracic hydrops responds well to treatment, and doctors give an optimistic prognosis. Hydrothorax of the lungs in oncology is a more complex case; here it is important to take into account the degree of spread of the cancerous tumor, the presence or absence of metastases, the age of the patient and his general condition.
However, such indicators are only possible if the pathology was identified in time and doctors prescribed the correct treatment.
Doctors warn: in order to get a lasting effect and prevent re-accumulation of transudate, treatment should not be interrupted immediately after the symptoms have resolved. The course of therapy must be completed. In this case, the duration of treatment and dosage of all drugs is controlled only by the attending physician. Otherwise, hydrothorax of the right lung (or left) leads to an increase in the size of the pathological process and provokes inflammatory diseases.
Considering all of the above, we can conclude that this pathology is not as dangerous as it may seem to patients with a similar diagnosis. Chest hydrops can be eliminated quite quickly and effectively by treating the underlying disease. The only exception is those cases when this condition is caused by oncological processes. In this case, long and complex treatment awaits.