The well-known acetylsalicylic acid is widely used as a means of reducing fever. However, not everyone knows that this medication is often prescribed to patients for the treatment of diseases of the cardiovascular system. In this article we will talk about such a drug as Acecardol tablets. The instructions for use state that this medication contains acetylsalicylic acid. This medicine has been used in cardiological practice for many years and has proven itself well among both doctors and patients. What Acecardol tablets help with can be found in this article.
A full description of the drug, instructions for use, reviews, indications and side effects - all this information is given for informational purposes only and cannot serve as a basis for taking the drug on your own. Self-medication with such a medication can be harmful to health, and therefore it should be taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
Pharmacological features
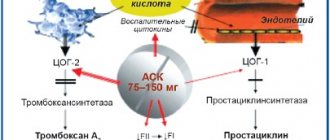
The drug "Acecardol" is a coated acetylsalicylic acid that dissolves directly in the intestines. This is a non-steroidal drug with an anti-inflammatory effect. The mechanism of action of the drug is that the active component causes irreversible inhibition of COX, resulting in suppression and blockade of thromboxane A2 synthesis and platelet aggregation. The effect of the active component lasts for a week, the maximum concentration of the drug is achieved in the blood 15 minutes after administration. During normal functioning of the urinary system, a single dose of the drug is excreted in the urine within 24 to 72 hours.
In addition, high doses of the drug have the ability to anesthetize and relieve fever. Suppression of platelet synthesis allows this medication to be used in the treatment of various cardiovascular diseases.
pharmachologic effect
Acetylsalicylic acid, the active substance of Acecardol, has an antiplatelet effect on the body by inhibiting cyclooxygenase. This leads to suppression of platelet aggregation and blocking of thromboxane synthesis.
Even after using ASA in small dosages, an antiplatelet effect develops and persists for 7 days.
In high dosages, the drug has analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects.
After taking the drug, the maximum plasma concentration of acetylsalicylic acid is reached after 15 minutes. With normal kidney function, a single dose is excreted over 24-72 hours.
Who is the medicine "Acecardol" indicated for?
Instructions for use describe the conditions for which it is recommended to take these tablets.
As a rule, the drug is prescribed for preventive purposes when there is a threat of acute primary and recurrent myocardial infarction, if the patient has risk factors such as diabetes, obesity, arterial hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Indications are also considered unstable angina pectoris, the threat of ischemic stroke (including in transient cerebral circulatory disorders).
The drug "Acecardol" can be prescribed to patients for the prevention of thromboembolism after surgical and invasive interventions on blood vessels, such as coronary and aortovenous bypass surgery, angioplasty of the carotid and coronary arteries.
Indications for use
According to the instructions, Acecardol is indicated for unstable angina, as well as for the prevention of:
- Blockage of the pulmonary artery and its branches by blood clots and deep vein thrombosis;
- Thromboembolism after invasive and surgical interventions on blood vessels;
- Ischemic stroke, including in patients with transient cerebrovascular accident;
- Acute myocardial infarction in the presence of predisposing factors (hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, obesity, arterial hypertension, old age, smoking), as well as repeated myocardial infarction.
Contraindications
Almost all medications have a list of conditions under which they cannot be taken. Acecardol tablets are no exception. The use of this medicine is not recommended for people with conditions such as:
- bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract;
- erosions, gastrointestinal ulcers;
- bronchial asthma in the stage of exacerbation and remission;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- chronic heart failure;
- polyposis of the paranasal sinuses and nose.
It is strictly forbidden to take the medicine "Acecardol", analogues and drugs similar in composition during the period of bearing and breastfeeding a baby. Individual sensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and auxiliary components in the composition of the drug, in particular lactose, can also be considered a contraindication.
Prescribe the medicine with caution in cases of liver dysfunction and during anticoagulant therapy. During proposed surgical interventions, it is also undesirable to take Acecardol tablets. The instructions for use contain information that this medicine should be prescribed with extreme caution to people with kidney disease, since it is excreted through urine.
These tablets are intended for long-term use. High doses of medication may be prescribed as a last resort to reduce high fever.
Contraindications to the use of Acecardol
Even if indicated, Acecardol is not recommended for use in:
- Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- Dissecting aortic aneurysm;
- Erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Acute renal or liver failure;
- Vitamin K deficiency;
- Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura;
- Hemorrhagic diathesis;
- Heart failure;
- Gastrointestinal bleeding;
- Initial hypoprothrombinemia;
- Thrombocytopenia;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.
In addition, Acecardol is not prescribed in the 1st and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy and during lactation , and the use of the drug is unacceptable for children under fifteen years of age if it is used as an antipyretic.
Acecardol is used with caution for hyperuricemia, chronic respiratory diseases, nasal polyposis, and hay fever.
In the 2nd trimester of pregnancy and with simultaneous therapy with methotrexate, the dose of Acecardol should not exceed 15 mg per week.
Reception scheme
How to carry out therapy with the drug "Acecardol"? The instructions for use state that the drug is intended for oral use. Take the tablets before eating and wash them down with a glass of water.
For the prevention of acute myocardial infarction, 100 mg is prescribed daily or 300 mg once every 48 hours. To ensure rapid absorption and achieve the concentration of the active substance in the plasma, the tablets are chewed and then washed down with water.
If the medicine is prescribed to patients with unstable angina or to prevent recurrent heart attack, ischemic stroke or to prevent thromboembolism in the postoperative period, take 100 mg tablets every 24 hours.
To prevent pulmonary embolism and its branches, as well as deep vein thrombosis, it is recommended to take 100 mg tablets once a day or 300 mg every 48 hours.
ACECARDOL: DOSAGE
The tablets should be taken orally, before meals, with plenty of liquid. The drug is intended for long-term use. The duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician.
Prevention for suspected acute myocardial infarction: 100-200 mg/day or 300 mg every other day (the first tablet must be chewed for faster absorption).
Prevention of new-onset acute myocardial infarction in the presence of risk factors: 100 mg/day or 300 mg every other day.
Prevention of recurrent myocardial infarction, unstable angina, prevention of stroke and transient cerebrovascular accident, prevention of thromboembolic complications after surgery or invasive studies: 100-300 mg/day.
Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery and its branches: 100-200 mg/day or 300 mg every other day.
Undesirable effects
Does the drug “Acecardol” (tablets) have a negative effect on the body? Instructions for use and reviews indicate the following possible side effects:
- hematopoietic system: anemia and increased likelihood of bleeding;
- Gastrointestinal tract: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, heartburn, perforated ulcers of the duodenum and stomach, increased activity of liver enzymes;
- immune system: allergic rashes in the form of spots, blisters, urticaria, Quincke's edema and anaphylactic shock;
- from the respiratory system, bronchospasm is possible;
- central nervous system: hearing loss, noise and buzzing in the ears, headache and dizziness.
These are the side effects described in the instructions for use for the drug "Acecardol", however, reviews indicate that these manifestations are rare and, as a rule, the medicine is well tolerated.
Side effects
The use of Acecardol may cause the following side effects:
- Digestive system: nausea, vomiting, heartburn, stomach and duodenal ulcers, abdominal pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, increased activity of liver transaminases;
- Hematopoietic system: increased risk of bleeding, anemia;
- Allergies: skin rash, itching, cardiorespiratory distress syndrome, Quincke's edema, urticaria, swelling of the nasal mucosa, rhinitis, anaphylactic shock;
- Central nervous system: tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness, headache;
- Respiratory system: bronchospasm.
Use of the product during pregnancy
Why can’t you use the drug “Acecardol” during pregnancy and lactation? The answer to this question lies in a simple explanation. Acetylsalicylic acid is considered an undesirable substance in the immature body of a child. Among the many contraindications to the drug "Acecardol", the instructions also include a clause regarding the prohibition of taking the medicine by persons under 18 years of age.
The active substance, reaching its maximum concentration in the blood after administration, is able to penetrate the developing body of the fetus.
Its effect is especially dangerous in high dosages in the first and third trimesters. Taking this medication increases the risk of developmental defects, particularly cleft palate and congenital heart defects.
Acecardol tablets, analogues of this drug, containing the same active ingredient, are prescribed only with an adequate assessment of the risks and benefits of therapy.
Acetylsalicylic acid in a dose of more than 300 mg in the last months of pregnancy negatively affects labor and causes premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus, and also increases the risk of bleeding during childbirth and cesarean sections in the mother and baby.
What does the instructions for use say about the possibility of using Acecardol tablets before childbirth? Analogs and the medicine itself can cause cerebral hemorrhage in a child immediately before birth; premature infants are at particular risk. Therefore, it is better to refuse such therapy.
ACECARDOL
DOSAGE FORM, COMPOSITION AND PACKAGING Tablets, enteric-coated, white or almost white, round, biconvex. Enteric-coated tablets are white or almost white, round, biconvex. PHARMACHOLOGIC EFFECT
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). The mechanism of action of acetylsalicylic acid is based on irreversible inhibition of COX, as a result of which the synthesis of thromboxane A2 is blocked and platelet aggregation is suppressed. It is believed that acetylsalicylic acid has other mechanisms of suppressing platelet aggregation, which expands the scope of its use in various vascular diseases. Acetylsalicylic acid also has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Suction
After oral administration, acetylsalicylic acid is absorbed from the upper small intestine. Cmax in blood plasma is observed on average 3 hours after taking the drug orally.
Metabolism
Acetylsalicylic acid undergoes partial metabolism in the liver with the formation of less active metabolites.
Removal
Excreted by the kidneys, both unchanged and in the form of metabolites; T1/2 of acetylsalicylic acid is about 15 minutes, metabolites - about 3 hours.
INDICATIONS
- prevention of acute myocardial infarction in the presence of risk factors (for example, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, arterial hypertension, obesity, smoking, old age) and recurrent myocardial infarction;
- prevention of recurrent myocardial infarction;
- unstable angina;
- prevention of stroke (including in patients with transient cerebrovascular accident);
— prevention of transient cerebrovascular accident;
- prevention of thromboembolism after operations and invasive interventions on blood vessels (for example, coronary artery bypass grafting, carotid endarterectomy, arteriovenous bypass, carotid angioplasty);
- prevention of deep vein thrombosis and thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery and its branches (for example, with prolonged immobilization as a result of major surgery).
DOSING REGIME
The tablets should be taken orally, before meals, with plenty of liquid. The drug is intended for long-term use. The duration of therapy is determined by the attending physician.
Prevention for suspected acute myocardial infarction: 100-200 mg/day or 300 mg every other day (the first tablet must be chewed for faster absorption).
Prevention of new-onset acute myocardial infarction in the presence of risk factors: 100 mg/day or 300 mg every other day.
Prevention of recurrent myocardial infarction, unstable angina, prevention of stroke and transient cerebrovascular accident, prevention of thromboembolic complications after surgery or invasive studies: 100-300 mg/day.
Prevention of deep vein thrombosis and thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery and its branches: 100-200 mg/day or 300 mg every other day.
SIDE EFFECT
Allergic reactions: urticaria, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic reactions.
From the digestive system: nausea, heartburn, vomiting, abdominal pain, ulcerative lesions of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum (including perforated ones), gastrointestinal bleeding, increased activity of liver enzymes.
From the respiratory system: bronchospasm.
From the hematopoietic system: increased bleeding; rarely - anemia.
From the side of the central nervous system: dizziness, tinnitus.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
— erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- gastrointestinal bleeding;
- hemorrhagic diathesis;
- bronchial asthma induced by the intake of salicylates and NSAIDs, the Fernand-Vidal triad (a combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to ASA);
- combined use with methotrexate at a dose of 15 mg/week. and more;
— I and III trimesters of pregnancy;
- lactation period (breastfeeding);
— age up to 18 years;
- hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and/or other components of the drug;
- hypersensitivity to other NSAIDs.
The drug should be used with caution for gout; hyperuricemia; if there is a history of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract or gastrointestinal bleeding, renal and liver failure, bronchial asthma, chronic respiratory diseases, hay fever, nasal polyposis, allergic reactions to other drugs; in the second trimester of pregnancy; in combination with methotrexate at a dose of less than 15 mg/week; with vitamin K deficiency; deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
The use of salicylates in high doses in the first trimester of pregnancy is associated with an increased incidence of fetal defects (cleft palate, heart defects). In the second trimester of pregnancy, salicylates can be prescribed only taking into account a strict assessment of the expected benefit of therapy for the mother and the potential risk to the fetus.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, salicylates in high doses (more than 300 mg/day) cause inhibition of labor, premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus, increased bleeding in the mother and fetus, and administration immediately before birth can cause intracranial hemorrhages, especially in premature infants. The administration of salicylates (including acetylsalicylic acid) in the third trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated.
Salicylates and their metabolites are excreted in small quantities into breast milk. Accidental intake of salicylates during lactation is not accompanied by the development of adverse reactions in the child and does not require cessation of breastfeeding. However, with long-term use of the drug or when it is prescribed in a high dose, breastfeeding should be stopped immediately.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS
The patient can take the drug after a doctor's prescription.
Acetylsalicylic acid can provoke bronchospasm, as well as cause attacks of bronchial asthma and other hypersensitivity reactions. Risk factors include a history of bronchial asthma, hay fever, nasal polyposis, chronic respiratory diseases, and allergic reactions to other drugs (for example, skin reactions, itching, urticaria).
Acetylsalicylic acid can cause bleeding of varying severity during and after surgery.
The combination of acetylsalicylic acid with anticoagulants, thrombolytics and antiplatelet drugs is accompanied by an increased risk of bleeding.
Acetylsalicylic acid in low doses can provoke the development of gout in predisposed individuals (those with reduced excretion of uric acid).
Combination therapy with acetylsalicylic acid and methotrexate is accompanied by an increased incidence of side effects from the hematopoietic organs.
Acetylsalicylic acid in high doses has a hypoglycemic effect, which must be kept in mind when prescribing it to patients with diabetes mellitus receiving hypoglycemic drugs.
When concomitantly prescribing GCS and salicylates, it should be remembered that during treatment the level of salicylates in the blood is reduced, and after discontinuation of GCS, an overdose of salicylates is possible.
The combination of acetylsalicylic acid with ibuprofen is not recommended, since the latter worsens the beneficial effect of Acecardol on life expectancy.
Exceeding the dose of acetylsalicylic acid is associated with the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Overdose is especially dangerous in elderly patients.
When combining acetylsalicylic acid with alcohol, there is an increased risk of damage to the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and prolongation of bleeding time.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
There is no observed effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
OVERDOSE
Symptoms of moderate overdose: nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness, confusion.
Treatment: reducing the dose of the drug.
Symptoms of severe overdose: fever, hyperventilation, ketoacidosis, respiratory alkalosis, coma, cardiovascular and respiratory failure, severe hypoglycemia.
Treatment: immediate hospitalization in specialized departments for emergency treatment - gastric lavage, determination of acid-base balance, alkaline and forced alkaline diuresis, hemodialysis, administration of solutions, activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy. When carrying out alkaline diuresis, it is necessary to achieve pH values between 7.5 and 8. Forced alkaline diuresis should be carried out when the concentration of salicylates in plasma is more than 500 mg/l (3.6 mmol/l) in adults and 300 mg/l (2.2 mmol/l) in children.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
When used simultaneously, acetylsalicylic acid enhances the effect of the following drugs:
- methotrexate by reducing renal clearance and displacing it from protein binding;
- heparin and indirect anticoagulants due to disruption of platelet function and displacement of indirect anticoagulants from binding with proteins;
- thrombolytic and antiplatelet drugs (ticlopidine);
- digoxin due to a decrease in its renal excretion;
- hypoglycemic agents (insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives) due to the hypoglycemic properties of acetylsalicylic acid itself in high doses and the displacement of sulfonylurea derivatives from binding with proteins;
- valproic acid due to its displacement from binding with proteins.
Acetylsalicylic acid weakens the effect of uricosuric drugs (benzbromarone) due to competitive tubular elimination of uric acid.
By enhancing the elimination of salicylates, systemic corticosteroids weaken their effect.
An additive effect is observed when acetylsalicylic acid is taken simultaneously with alcohol.
CONDITIONS OF VACATION FROM PHARMACIES
The drug is approved for use as a means of OTC.
CONDITIONS AND DURATION OF STORAGE
The drug should be stored out of the reach of children, in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Shelf life: 3 years.
Reviews from doctors and patients
Basically, all reviews about the drug are positive. Doctors note that the tablets are intended to prevent recurrent heart attacks, strokes, and thrombosis after surgery and cope well with their task.
Patients who have undergone therapy claim that if you do not chew the tablet, there is no discomfort in the stomach after taking it. The main thing is just to adhere to the dose recommended by your doctor. Patients also witnessed positive dynamics in the prevention and treatment of blood clots.
Among the reviews, such a positive point as the pricing policy was noted. The tablets are inexpensive and belong to the generally available group of drugs.
Interaction with other medications
When taking the drug itself and analogues of the drug "Acecardol", the indications for which are almost identical, you need to be extremely careful when combining it with other medications, since acetylsalicylic acid can enhance the effect of individual substances that are part of other drugs.
For example, due to the weakening of renal clearance and its displacement from binding with proteins, the effect of Methotrexate tablets is enhanced, which is undesirable when carrying out chemotherapy with this drug.
The main component of the drug "Acecardol" displaces valproic acid from its connection with proteins and thereby increases its effect on the body. It is not advisable to take thrombolytic and antiplatelet drugs and Acecardol tablets at the same time. Reviews from doctors about this combination indicate a negative effect on the human body.
Acetylsalicylic acid enhances the effect of insulin and its derivatives, which must be taken into account by people who monitor sugar levels in the body.
It is strictly forbidden to take Acecardol tablets together with medications containing the substance ibuprofen and its derivatives.
Drug interactions
When used simultaneously, acetylsalicylic acid enhances the effect of the following drugs:
- methotrexate by reducing renal clearance and displacing it from protein binding;
- heparin and indirect anticoagulants due to disruption of platelet function and displacement of indirect anticoagulants from binding with proteins;
- thrombolytic and antiplatelet drugs (ticlopidine);
- digoxin due to a decrease in its renal excretion;
- hypoglycemic agents (insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives) due to the hypoglycemic properties of acetylsalicylic acid itself in high doses and displacing sulfonylurea derivatives from binding with proteins;
- valproic acid by displacing it from bonds with proteins.
Acetylsalicylic acid weakens the effect of uricosuric drugs (benzbromarone) due to competitive tubular elimination of uric acid.
By enhancing the elimination of salicylates, systemic corticosteroids weaken their effect.
An additive effect is observed when acetylsalicylic acid is taken simultaneously with alcohol.
Special instructions for taking Acecardol tablets
The instructions for use, the photo of which is presented in the article, is the original version of the description of the drug from its manufacturers, which is attached to each package. It contains all the data regarding recommended doses, describes the pharmacological action, indications and side effects. And although this medicine is available in pharmacies without a doctor’s prescription, it is not recommended to resort to independent long-term treatment with this medicine. Also, special attention should be paid to a single dose to reduce body temperature, especially for those patients who have problems with the hematopoietic system.
It is strictly forbidden to take the drug "Acecardol" together with alcohol, since such a combination will negatively affect the gastric mucosa and can lead to serious illnesses.
In patients with bronchial asthma, aspirin can cause bronchospasm and provoke an attack of suffocation, therefore, before taking Acecardol tablets, you should evaluate the benefits and risks of the medication.
The drug does not affect concentration, does not cause inhibition or drowsiness, and therefore patients can drive vehicles and perform high-risk work during the treatment period.
special instructions
To avoid complications of the disease or its development, you should familiarize yourself with the rules for taking the drug. Special instructions for the use of Acecardol:
- Acetylsalicylic acid can cause an attack of bronchial asthma, bronchospasms or similar allergic reactions. The tablets should not be used if you have hay fever, chronic forms of respiratory diseases, nasal polyposis, or a history of bronchial asthma. It is not recommended to drink ASA if you have an allergic reaction to other medications (hives, itching, etc.).
- An overdose of an antiplatelet agent can cause gastrointestinal bleeding.
- In people with low uric acid excretion, the drug often provokes gout.
- Acetylsalicylic acid as an inhibitor has an aggregating effect on platelets. It is effective for 2-3 days after starting to take the pills. This reaction increases the likelihood of bleeding during or after surgery.
- During therapy, the patient should be as careful as possible when driving, as well as during activities that require increased attention, concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
- If glucocorticosteroids (GCS) are used together with Acecardol, the effect of salicylates is reduced. If the course of GCS is interrupted, an overdose of ASA may occur.
Article on the topic: Do men go through menopause?
Overdose
Exceeding a single dosage may lead to bleeding in the stomach. Symptoms of overdose include nausea, vomiting, ringing in the ears, cardiovascular and respiratory failure, which can cause the patient to coma. If the dose is greatly exceeded, fever, respiratory alkalosis, ketoacidosis and hyperventilation may develop. In such conditions, it is necessary to adjust the daily and single dose of the drug, and in some cases its abolition and symptomatic treatment. To quickly remove and neutralize the effect of the active component of the drug "Acecardol", emergency therapy is carried out: gastric lavage, hemodialysis, administration of absorbent substances and determination of the acid-base balance for subsequent diuresis.
Storage conditions and release form
How to store the medicine "Acecardol"? Instructions for use and reviews of the drug indicate that no special conditions are required for storing the tablets. It is enough to follow the general recommendations and keep the packages of tablets in a dark and dry place at a temperature not exceeding 25 degrees. Under such conditions, the medicine will retain its medicinal properties for three years.
Acecardol tablets are available in different dosages of the active component: 50, 100 and 300 mg. The main active ingredient is acetylsalicylic acid. The auxiliary components are corn starch, povidone, microcrystalline cellulose, talc, magnesium stearate, lactose, titanium dioxide and castor oil.
The tablets have a round, biconvex shape and are equipped with a coating that dissolves only in the intestines, which prevents unwanted effects on the gastric mucosa.
Release form, composition and packaging
Enteric-coated tablets are white or almost white, round, biconvex.
| 1 tab. | |
| acetylsalicylic acid | 50 mg |
| – » – | 100 mg |
| – » – | 300 mg |
Excipients: povidone, corn starch, lactose, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, talc, cellulose acetate, titanium dioxide, castor oil.
10 pieces. — cellular contour packages (3) — cardboard packs.
Analogues of the drug
What does the instructions for use say about replacing the drug "Acecardol"? Analogs must contain the same active ingredient and have the same effect on the body. Substitutes can be drugs such as Aspirin, Acetylsalicylic acid, Cardi ASA, Thrombo ACC and Aspirin Cardio.
Each of these medications has its own dosage regimen and recommended doses. Analogs, as well as the drug “Acecardol” itself, which consist of acetylsalicylic acid, are not used in pediatrics, have a number of contraindications and prohibitions on combining with other medications.
During therapy, it is imperative to systematically monitor the state of the blood, as well as monitor the presence of blood in the patient’s stool. To do this, it is necessary to periodically conduct clinical tests, the results of which should determine further treatment.
Analogues of the drug according to ATC codes:
ASPIRIN ASPIRIN 1000 CARDIASK UPSARIN UPSA
Before using the drug ACECARDOL, you should consult your doctor. These instructions for use are for informational purposes only. For more complete information, please refer to the manufacturer's instructions.
The drug "Aspirin": instructions
The medicinal properties of this medicine lie in its ability to relieve fever, suppress inflammatory processes and reduce platelet aggregation. Indications for therapy are fever during ARVI and influenza, prevention of heart attack and thrombosis, as well as rheumatic diseases.
Take tablets orally for an analgesic effect at 325, 400, 500 mg, for an antiplatelet effect at 50, 75, 100, 300 and 325 mg.
For fever and pain, adults are recommended to drink the drug in a dosage of 100 mg. Effervescent tablets are dissolved in water and consumed after meals. A single dose should not exceed 1 g of active substance. If the medication is prescribed for the prevention of thrombosis, then its dosage should be 40–325 mg once every 24 hours.
This drug has the same contraindications and side effects as the drug "Acecardol".
The drug "Thrombo ACC": instructions
The medicine called “Thrombo ACC” is identical in action and composition to the medicine “Acecardol”. In appearance, these are round and convex tablets on both sides with a shiny and slightly rough surface. The active substance is acetylsalicylic acid in an amount of 100 mg per tablet. Auxiliary components are lactose, silicon dioxide, triacetin, talc, potato starch, antifoaming silicone agent, methacrylic acid and ethacrylate copolymer.
The medicine is sold in packages of 3 blisters, each of which includes 10 tablets. Recommended doses of the drug are 50-100 mg at a time. However, the doctor may prescribe a higher dosage, taking into account the patient’s condition and the presence of contraindications.
Pregnancy and lactation
The use of salicylates in high doses in the first trimester of pregnancy is associated with an increased incidence of fetal defects (cleft palate, heart defects). In the second trimester of pregnancy, salicylates can be prescribed only taking into account a strict assessment of the expected benefit of therapy for the mother and the potential risk to the fetus.
In the third trimester of pregnancy, salicylates in high doses (more than 300 mg/day) cause inhibition of labor, premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus, increased bleeding in the mother and fetus, and administration immediately before birth can cause intracranial hemorrhages, especially in premature infants. The administration of salicylates (including acetylsalicylic acid) in the third trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated.
Salicylates and their metabolites are excreted in small quantities into breast milk. Accidental intake of salicylates during lactation is not accompanied by the development of adverse reactions in the child and does not require cessation of breastfeeding. However, with long-term use of the drug or when it is prescribed in a high dose, breastfeeding should be stopped immediately.
Medicine "Acetylsalicylic acid": features of use
The peculiarity of this drug is that it does not have an enteric coating, and therefore these tablets strongly irritate the gastric mucosa. This fact makes it impossible to take medication for gastrointestinal ulcers in the acute stage. This medication is contraindicated in children under 15 years of age.
It is recommended to take tablets to prevent thromboembolism, heart attacks and strokes, as well as for rheumatism and infectious and inflammatory diseases. The dosage is selected individually. The official instructions for use contain recommendations regarding the dosage regimen. The dose of the medicine can vary from 40 to 100 mg at a time, but not more than 8 g of active substance per day.