0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.08.13
3 087
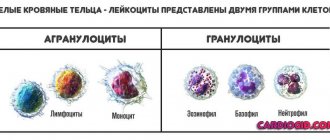
Red blood cells
The composition of blood is formed by its liquid part - plasma, and the formed elements contained in it: leukocytes, erythrocytes and platelets. When examining test results, both the number of formed cells and their size are of interest. And if deviations from the norms of this parameter are detected, further diagnosis will require a repeat study, followed by treatment if the diagnosis is confirmed.
Red blood cells - erythrocytes
What is anisocytosis?
The morphology of erythrocytes is varied and is divided mainly based on the size of the element:
- Microcytes;
- Megalocytes;
- Macrocytes;
- Normocytes.
Altered and normal red blood cells
Normocytes are cells with a size of about 7.1-9 microns. Microcytes measure up to 6.9 microns. Macrocytes are represented by cells with a size of 8 microns. And megalocytes have sizes from 12 microns.
With normal red blood cell counts, the blood contains about 70% of the total number of normocytes. Macro- and microcytes occupy a niche of 15%. If the analysis shows an increase or decrease in the content of one or another type of element, then this is already a sign of developing disorders in the body, and therefore the RDW value also increases. This is called anisocytosis.
An increase in RDW can be recorded during the treatment of anemia, even at the initial stages. The picture changes as soon as the first stage of therapy is completed.
That is, if we explain it in simpler terms, then with anisocytosis the qualitative composition of erythrocytes changes significantly, in which normocytes are replaced by micro- and macrocytes. The main difference between the pathology is expressed in the violation of the correct ratio of different sizes of red blood cells. This deviation is determined by a general blood test (CBC).
Even with minor micro-changes in the composition of the blood, it is necessary to carry out a number of additional diagnostic manipulations of laboratory and hardware type (blood, urine, stool tests, MRI, CT, and so on, depending on which diagnosis needs to be clarified) to exclude more serious diseases. Microcytosis is most often associated with anemia, in which the hemoglobin content in all red blood cells is noticeably reduced. Therefore, it is necessary to periodically monitor the condition, which will exclude more serious diseases.
Anisocytosis of erythrocytes in a blood test (RDW index)
Erythrocyte anisocytosis is a change in the size of red blood cells. Red blood cells can have different diameters. Mature cells with a diameter of 7-8 microns are normal and are called normocytes. In microcytes, the diameter is less than 7 µm, in macrocytes - from 8 µm, in megacytes - from 12 µm. The indicator of erythrocyte anisocytosis is designated in a blood test as RDW. This erythrocyte index is called an indicator of red cell heterogeneity by volume. The abbreviation stands for the width of the distribution of red blood cells.
RDW standard
In healthy people, the number of normal red blood cells in a blood test is at least 70%, macrocytes and microcytes - no more than 15%. For adult men and women, this figure should range from 11.5 to 14.5%.
In children under six months of age, the RDW index should be between 14.9 and 18.7%. Starting from six months, this parameter is close in value to the norm for an adult – 11.6-14.8%.
If the number of small or large red blood cells is higher than normal, the RDW is said to be elevated. Deviations from the norm of this indicator, as a rule, indicate pathological processes in the body.
Classification of anisocytosis
There are four degrees:
- first (minor anisocytosis) – microcytes and macrocytes make up 30-50%;
- second (moderate) – 50-70%;
- third (pronounced) – above 70%;
- fourth (sharply expressed) - almost all red cells have a size different from the normal value.
Depending on the increase in the number of certain forms of red blood cells, there are:
- microcytosis - an increase in the number of small cells;
- macrocytosis – increase in the number of macrocytes;
- mixed - an increase in the number of both small and large cells.
Microcytosis is usually observed in the following conditions:
- iron deficiency anemia;
- in case of lead poisoning;
- thalassemia;
- sideroblastic anemia;
- with anemia associated with chronic bleeding;
- for some malignant diseases.
With anisocytosis, red blood cells of both small and large sizes are present in the blood.
Macrocytosis can be a normal variant or pathological. In the first case, we are talking about anisocytosis of newborns in the first two weeks of life; by two months the condition is normalized. Pathological macrocytosis is due to the following reasons:
- impaired DNA synthesis, which may be associated with the use of certain medications, myelodysplasia, erythroleukemia, folic acid and cobalamin deficiency.
- pathology of red blood cell membrane lipids in liver diseases, alcoholism, hypothyroidism, after removal of the spleen.
In mixed anisocytosis, both microcytes and macrocytes can predominate. In the first case, as a rule, hypochromic anemia occurs. If macrocytes predominate, then the possibility of B12 deficiency or pernicious anemia cannot be excluded.
Reasons for increasing and decreasing RDW
Anisocytosis is an early sign of anemia, the severity of which is determined by its degree. The main reasons for increased RDW in both adults and children are as follows:
- Iron-deficiency anemia.
- Hemolytic anemia.
- Megaloblastic anemia (deficiency of vitamin B12 and folic acid).
- Chronic liver diseases.
- Metastases to the liver.
- Blood transfusions.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome.
- Alcohol addiction.
In addition, RDW can be increased in Alzheimer's disease, hemoglobinopathy, lead poisoning, microspherocytosis, bone marrow metaplasia, and cardiovascular diseases.
During treatment of iron deficiency anemia, the anisodide index increases. This is explained by the appearance in the blood of a large number of young red blood cells, which differ in diameter from mature ones. With effective treatment, RWD returns to normal, but after other indices.
A change in the diameter of red blood cells is considered a diagnostic marker that informs about the risk of developing coronary heart disease.
RDW is almost never low. If you receive such a result, you most likely should retake the analysis. If the indicator is slightly reduced and there are no other changes in blood tests, this result should be considered normal. A reduced RDW has no diagnostic value.
In some pathologies, RDW does not change; the indicator remains normal. This includes the following conditions:
- anemia accompanying chronic diseases;
- β-thalassemia;
- spherocytosis;
- acute aplastic and hemorrhagic anemia;
- sickle cell anemia.
Analysis on RDW
Blood is examined for anisocytosis during a general analysis. The fence is made from a finger. You need to take it on an empty stomach in the morning. The degree of anisocytosis can be determined manually by laboratory assistants. Today, the RDW index is increasingly calculated using modern hematology analyzers, which provide faster and more accurate results. This parameter is determined automatically using a special formula, taking into account other erythrocyte indices.
The analysis is deciphered by the attending physician, and the values of other indicators are taken into account. Thus, in parallel with the assessment of RDW, the erythrocyte index MCV (average erythrocyte volume) is assessed. This is due to the fact that the anidocytosis index may remain normal, but the presence of micro- and macrocytes is a pathology.
The value of the anisocytosis index is necessary for the doctor to interpret the test result and diagnose anemia, including differential diagnosis. Determining the number of red blood cells in the blood and the level of hemoglobin does not give a complete picture, but only indicates the presence of anemia.
Conclusion
If the RDW index in a blood test is higher than normal, this may indicate the development of anemia. Such changes in this case are an early diagnostic sign. It is impossible to judge the state of health based on one blood indicator, such as anisocytosis, since in a number of diseases, including thalassemia, RDW may remain normal. This index is used in medicine as an auxiliary criterion for diagnosing anemia. In this case, it is necessary to consider other erythrocyte indices.
serdec.ru
RDW standard
A normal body produces red blood cells that are almost identical in volume. Moreover, in a healthy adult, normocytes make up about 70% of the total volume of red cells. With anisocytosis, red cells have different shapes and volumes.
RDW analysis allows us to determine the degree of distribution of red blood cells by volume, that is, their heterogeneity. As a person ages, these cells gradually begin to decrease in volume. The same changes occur with anemia.
The following approximate indicators are considered the RDW norm:
- 13% for adults;
- 16.8% for children under six months;
- 13.2% for children six months and older.
Indicators can vary between 1.5-1.9%. If the transcript shows a deviation from the norm, then it is necessary to examine the patient followed by therapy.
RDW standard
Classification of anisocytosis
Anisocytosis is divided primarily according to the severity of the condition.
- The first stage is characterized by slight to moderate anisocytosis. Red blood cells are 30-50% composed of macro- and microcytes.
- The second stage is characterized by average anisocytosis with a content of micro- and macrocytes in the amount of 50-70%
- The third stage is pronounced, severe anisocytosis, in which micro- or macrocytes occupy more than 70% of the total volume of red blood cells. If the index is so elevated, the reasons should be sought in the body itself - from severe anemia to oncology.
- This stage of pathology development is characterized by complete replacement of normocytes with micro- and macrocytes.
Normocytes are also elevated, as are micro-, macro-, and megalocytes. This is evidence of the development of various pathological processes in the body.
This disease is accordingly divided according to the type of cell predominant in the composition of red blood cells:
- Macrocytosis;
- Microcytosis;
- Mixed type anisocytosis, in which macrocytes and microcytes predominate at the same time.
This division allows you to pay attention to specific deviations in the composition of the blood, as well as what pathologies could cause them. The lower the indicator, the more serious the problem.
Anisochromia is a different degree of cell staining during OAC. It can be either the result of a serious pathological process or a normal reaction of the body to changes in the environment.
Platelet anisocytosis
Platelet anisocytosis is a fairly rare disorder, since a change in the normal size of red blood cells is more often observed. The PDW indicator characterizes the level of deviation of the volumes of formed blood particles from the average values, which normally range from 14 to 18%.
In most situations, such a deviation is caused by pathological processes occurring in the body. For example, myelodysplastic syndrome, oncology, parasitic invasion.
The disorder has several characteristic clinical manifestations, including weakness and fatigue, increased heart rate, and excessive pallor of the skin.
Anisocytosis is detected only in a general blood test, which is indicated for both adults and children. The information obtained is usually not enough to detect the root cause, which is why the diagnostic process must include not only laboratory, but also instrumental procedures.
Situations in which the indicator is decreased or increased, as a rule, are eliminated independently during the treatment of the underlying disease - therapy can be conservative, surgical or complex.
Platelet anisocytosis means a change in cell size or shape. This is the presence of formed bodies of various sizes in the blood, which is revealed by studying the frequency of their distribution in the blood.
The concentration of modified cells from 14 to 18% is considered normal. An increase or decrease in values by 1 - 2% is allowed, which is determined by the individual characteristics of each human body.
A larger change in particle diameter may be associated with the following conditions:
- insufficient intake of iron or vitamins;
- the course of oncology, in which metastases reach the bone marrow;
- myelodysplastic syndrome;
- blood transfusion;
- the presence of diseases of an inflammatory or infectious nature, leading to severe intoxication;
- blood transfusion;
- helminthic or parasitic infestation;
- damage to the walls of blood vessels;
- rehabilitation of patients after surgery;
- excision of the spleen;
- long-term use of corticosteroids;
- thrombocytopenia of autoimmune origin.
The anisocytosis index decreases against the background of:
- leukemia;
- aplastic anemia;
- radiation sickness;
- long-term treatment with cytostatics;
- thrombocytopathies;
- splenomegaly;
- septic condition;
- anemia of megaloblastic type;
- storage diseases, such as Niemann-Pick or Gaucher disease;
- hemolytic-uremic syndrome;
- chronic hepatitis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- DIC syndrome.
In a child or adult, a blood transfusion may be a predisposing factor. It is worth noting that in such situations, anisocytosis will be temporary, and a return to normal values will occur independently.
Clinicians distinguish several degrees of severity of the pathological process, which is why there are the following varieties:
- + or minor form - in such situations, no more than 25% of blood cells can be transformed;
- ++ or moderate form - the disease involved 50% of platelets;
- +++ or pronounced form - modified cells predominate in number over healthy ones, their level is increased to 75%;
- ++++ - pronounced or critical form, in such cases all cells undergo replacement.
Depending on the degree of change in formed blood particles, the disorder is divided into:
- microcytosis - platelet size is reduced;
- macrocytosis - the opposite situation is observed (the main parameter will be increased);
- mixed type - characterized by the fact that the content of macrocytes and microcytes reaches at least 50%; in the first case, cells normally have volumes of 8 micrometers and above, and in the second - no more than 6.9 micrometers.
Platelet anisocytosis can be indicated not only by data from a general clinical blood test, but also by some external manifestations. The problem is that the symptoms may be mild or hidden behind the symptoms of the underlying disease. It follows from this that very often the anomaly goes unnoticed by humans.
The clinical picture is presented:
- increased heart rate and shortness of breath - such symptoms appear even at rest;
- fatigue and fatigue - very often these are the most noticeable external signs;
- pallor of the skin, mucous membranes, eyeballs and nail plates;
- constant drowsiness and muscle weakness;
- decreased concentration;
- headaches;
- hypersensitivity of the skin to external irritants;
- hepatosplenomegaly;
- changes in taste preferences;
- emotional instability;
- acrocyanosis - slight bluish discoloration of the skin.
The above signs are observed in both adults and children, often complemented by the clinical picture of the provoking disease. If one or more symptoms appear, you should consult a clinician as soon as possible.
To detect platelet anisocytosis, a laboratory examination of a blood smear is sufficient, but to obtain more detailed information, a general clinical blood test is performed.
During the study, a platelet histogram is compiled - a graphical representation of the quantity and quality of platelets in the material being studied. A hematologist is responsible for interpreting the results, but to find out the etiological factor, you should contact a therapist or family clinician.
Platelet histogram
To establish the cause of the development of the disorder, a comprehensive examination of the body will be required, which begins with the following measures:
- studying the medical history will help to find the main pathological source of transformations;
- collection and analysis of life history - to identify provocateurs not related to the course of any disease;
- assessment of the general appearance of the patient - the specialist pays close attention to the skin;
- percussion and palpation of the abdomen will help determine the presence of hepatosplenomegaly;
- measuring heart rate and blood tone;
- a detailed survey of the patient - to determine the severity of the main clinical manifestations and compile a complete symptomatic picture.
In addition, it is necessary to carry out a number of laboratory and instrumental procedures and consult clinicians from various fields of medicine. This diagnostic program is selected personally for each person.
When platelet anisocytosis is detected in a person, it is necessary to eliminate the provoking disease. For this in some cases it is quite enough:
- change your diet;
- carefully select donors for blood transfusions;
- enrich the menu with products that contain iron and other nutrients;
- take vitamin and mineral complexes.
In other cases, treatment tactics will be purely individual. For example:
- for oncological tumors they resort to surgery, radiation treatment and chemotherapy;
- for thyroid pathologies, hormonal therapy or surgery are used;
- in cases of penetration of pathogenic agents into the body, antibiotics, diet therapy, physiotherapeutic procedures and other conservative methods are necessary.
Recovery is indicated by several factors - improvement in well-being and complete elimination of symptoms, changes in the results of a general clinical blood test.
To prevent the problem from developing, it is enough to follow a few simple rules. Preventive recommendations:
- complete renunciation of addictions;
- complete and balanced nutrition;
- frequent exposure to fresh air;
- constant strengthening of the immune system;
- avoiding physical and emotional stress;
- regular comprehensive preventive examination in a medical institution.
Regardless of whether the volume of formed parts of blood is reduced or increased, the prognosis will be dictated by the etiological source. It is necessary to take into account that each basic disease has a number of its own complications.
medanaliz.pro
Reasons for the development of anisocytosis
Isolated anisocytosis of red blood cells may be present in mild stages of anemia. It can develop in a woman during her period, especially if for one reason or another it is somewhat delayed. There can be many reasons for this condition, both minor and quite serious.
The most common symptom of anisocytosis is:
- Anemia, hypochromia, chlorosis, posthemorrhagic anemia, hyperchromic anemia and so on;
- Lack of vitamin B12;
- Lack of iron;
- Lack of vitamin A;
- Lead poisoning;
- Malignant neoplasms;
- Received blood transfusion.
Lack of iron
In the case of the last point, we can say that this is a passing anisocytosis, which will eliminate itself as soon as the body gets used to the “new” blood and replaces diseased cells with healthy ones. So in this case, you just need to wait time and, if necessary, replenish internal reserves with vitamins, minerals and other useful substances.
Often the state of platelets changes in parallel with pathological changes in erythrocytes.
Causes of microcytosis
An increased content of microcytes is typical for different groups of people at different periods of life. Microcytosis can often be observed after an infectious disease in a child. If the level of such red cells is slightly increased, then it can be easily corrected with the right lifestyle and nutrition.
This is a common condition in infants, since the systems are just returning to normal. Therefore, such conditions can go away on their own without treatment. Also, women often suffer from microanisocytosis during pregnancy and lactation due to hormonal changes in the body and high consumption of nutrients .
In other cases, anisocytosis of this type can be caused by:
- Iron deficiency or microcytic anemia;
- Microspherocytosis;
- Cooley's syndrome or thalassemia;
- Chronic infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- Heavy bleeding;
- Lack of foods with iron in the diet;
- Oncological lesions.
It is important to remember that some diagnoses require not only clarification and lifestyle adjustments, but also serious treatment. Oncological diseases can develop very quickly, and therefore one should not delay diagnosis.
The deterioration of cell characteristics can lead to the deterioration of red blood cell function.
Causes of macrocytosis
Macrocytosis may also indicate the development of anemia. Third-party factors may also influence this sign. Even a lack of nutrients and vitamins in the diet can significantly change blood composition.
But often an increase in the number of macrocytes is caused by such conditions as:
- Heavy bleeding;
- Various types of anemia;
- Bone marrow pathologies;
- Oncological lesions, most often blood;
- Thyroid dysfunction;
- Chronic alcoholism;
- Diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- Taking certain medications.
Macrocytosis
Some diseases are quite serious and require immediate intervention. Often, some pathologies end in death in the absence of adequate therapy.
Mixed type
The mixed type of anisocytosis is manifested by the dominance of macrocytes and microcytes over normocytes. Combined pathology with a predominance of macrocytes is characterized by the presence of an impressive number of abnormally large red blood cells. They are detected in blood smears and have a hyperchromatic structure without clearing in the center. The cells look like ovals with a diameter of about 11-12 microns.
Detected when:
- Vitamin B12 deficiency;
- Folic acid deficiency;
- Hypochromic anemia;
- Pernicious anemia;
- For anemia during pregnancy;
- With dyserythropoiesis;
- With helminthic infestation.
This deviation quite often develops when affected by worms, and therefore it is necessary to identify their presence, as well as determine the type of disease. Only in this case will it be possible to recover from pathogenic organisms.
Anisocytosis rate higher than normal can even be due to a simple change in the environment, due to moving.
Let's understand what macrocytosis is and is it dangerous?
Blood is the most important component of any living organism, which is represented by liquid tissue and consists of plasma and formed bodies (leukocytes, erythrocytes, platelets). The function of the circulatory system is to connect and nourish absolutely all organs of the body, so it is very important to monitor the condition of the blood by conducting regular clinical tests.
Based on the results of a laboratory blood test, a specialist can judge the functional disorders of the body.
Red blood cells with abnormalities
In some cases, red blood cells may be found in human blood, the size of which deviates from the norm (68 microns) up or down. Large red blood cells are called macrocytes, and the process of changing cell size is called macrocytosis.
This condition is a sign of the development of certain types of anemia in the patient, including those caused by a lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid in the body or an increase in the rate of red blood cell formation.
Abnormal platelets
As in the case of red blood cells, platelets have the same condition - the presence in the blood of a large number of immature (and therefore defective) platelets, the size of which is beyond the upper limits of normal. At the same time, the average volume of platelets in the blood increases. This condition has a number of signs:
- fatigue, lack of energy, increased fatigue;
- shortness of breath, respiratory dysfunction;
- increased heart rate (in any condition);
- pallor of the skin, mucous membranes, nails (sometimes the skin may acquire a blue tint).
The presence in the blood of both abnormally large and unnaturally small red blood cells (macrocytes and microcytes) is a condition called anisocytosis. A condition such as anisocytosis has 3 degrees:
- anisocytosis of the first degree - deviation from the norm in the size of the erythrocyte (in one direction or another) is observed in 30-50% of the total number of cells;
- anisocytosis II degree - deviation in 50-70% of cells;
- Anisocytosis III degree - more than 70% of macro- and/or microcytes.
As a rule, such macrocytosis as red blood cells does not manifest itself in any way and is detected only during a clinical blood test, when other diseases are treated.
Causes of macrocytosis of erythrocytes and platelets
Macrocytosis (both red blood cells and platelets) is not a disease, but only a sign of pathological processes occurring in the human body. This condition can be caused by a number of reasons, which can only be determined by a doctor based on test data and a more detailed examination.
The causes of this condition in the case of red blood cells:
- deficiency of vitamin B9 and/or B12;
- anemia caused by blood loss (posthemorrhagic);
- anemia that developed due to the destruction of red blood cells (hemolytic);
- bone marrow pathologies;
- oncological diseases (usually blood cancer);
- functional disorders of the thyroid gland;
- chronic alcoholism;
- diseases of the hematopoietic organs;
- pregnancy;
- use of certain medications.
Causes of platelet macrocytosis:
- accelerated platelet destruction;
- enlarged spleen, hypersplenism;
- diabetes;
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- functional disorders of the thyroid gland;
- some blood diseases;
- Bernard-Soulier macrocytic platelet dystrophy;
- May-Hegglin anomaly (a disease characterized by quantitative and qualitative changes in platelets);
- chronic alcoholism;
- smoking.
What can you do?
Having received the results of the analysis, you should not decipher the data yourself, since only a specialist can make the most accurate diagnosis. When macrocytosis is detected, it is usually recommended to conduct a repeat blood test, and if the data is confirmed, the specialist, based on studying other indicators, determines the possible cause of the pathology and prescribes the necessary treatment.
In the absence of pathological diseases, a person can restore normal blood counts by following some tips:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- adjust your diet;
- carry out blood tests regularly;
- promptly treat diseases that affect the quality of blood cells.
Should I worry?
Of course, deviations from normal blood test values in themselves cause concern for the patient. It should be remembered that macrocytosis in newborns is normal, just as during pregnancy, macrocytosis is not pathological, and, therefore, treatment is not required. Minor fluctuations may be a physiological characteristic of a person, or a consequence of taking certain medications (treatment of other diseases), while a significant excess of normal values is a reason for urgent consultation with a specialist.
It is important that if signs of macrocytosis appear or if this condition is detected during a laboratory blood test, consult a doctor who will identify the true cause of the abnormalities and prescribe the necessary treatment.
What could be the treatment?
Treatment of macrocytosis is prescribed exclusively by the attending physician and, as a rule, is aimed primarily at treating the causes that caused it.
No comments yet
1pokrovi.ru
Analysis on RDW
This analysis is carried out using analyzers. They help to accurately count red blood cells of all sizes and shapes in 1 μl of blood. The sampling is carried out on an empty stomach. The material for the study is taken from a vein.
The average capacity of an erythrocyte is determined automatically, and the deviation in the number of normocytes in relation to macro- and microcytes is calculated. The data is displayed in the form of a histogram. If the percentage of RDW falls within the normal range, then the result is recorded as negative.
If the norm is exceeded, a positive result is indicated. For such cases, the procedure is duplicated in order to identify the causes of abnormal indicators.
Sometimes a false positive result occurs, especially if there are a large number of macrocytes in the blood. These results often occur after surgery or blood transfusion. The redistribution or change in the type of cells itself can change frequently, and in a short time.
Therefore, it may be necessary to process the data using a statistical analysis method. The standard deviation value is calculated using a number of formulas. Previously, the results were obtained manually, but this is an extremely labor-intensive process, and therefore today it has been practically abandoned in favor of computer data analysis.
Mixed platelet anisocytosis. How is pathology detected?
How to determine when platelet anisocytosis is low or high?
To achieve this, modern medicine uses three main methods:
- Hematological analysis, carried out using special equipment, is increasingly used today as a way to determine the status of platelets.
- Counting the number of formed elements on a smear using a 6% EDTA solution.
- Use of phase contrast for platelet counting using a microscope. For counting, a device called a Goryaev chamber is used; concentrated ammonium oxalate 1% is used as the working fluid.
Determination of platelet status is carried out in accordance with the developed instructions.
With a mixed type of change in the size of blood cells, the total number of macro and microcytes in the blood does not rise above 50%. The Price-Jones curve will help identify this. If we talk about mixed anisocytosis, then macrocytes will predominate in the blood. The most common diagnoses are either pernicious anemia or anemia caused by vitamin B12 deficiency.
The normal RDW is an average of fourteen to eighteen percent. An abnormality caused by a decrease or increase in platelet size can be mild to moderate.
Treatment
Treatment of anisocytosis is directly related to the elimination of the cause of its development. Depending on the type of disease, a treatment regimen is prescribed to eliminate influencing factors. In case of iron deficiency anemia, a course of replenishing the deficiency of the substance in the body with the help of medications is required.
Oncological diseases require a more serious approach in the treatment of anisocytosis using hormonal, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and so on.
If a general blood test reflects a change in the volume of normocytes according to the RDW index, then there is a high probability of developing anemia. This is one of the first indicators when making this diagnosis. But only this auxiliary criterion in making a diagnosis will not give an accurate picture of the type of pathology and the patient’s state of health.
Therefore, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnosis and begin treatment of the disease.