What does a neoplasm look like and why is it dangerous?
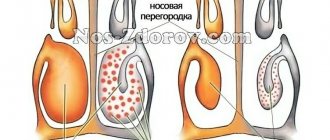
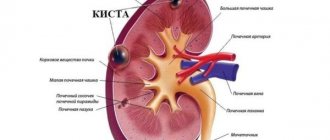
A splenic cyst is a focal process in the parenchyma of the organ. In most cases, round in shape, filled with liquid contents.
Cavity exudate can be of two types:
- hemorrhagic;
- serous.
Statistical data:
- It is observed quite rarely, only 1% of the world's population.
- It affects the working population, on average 35-55 years old.
- Women are more susceptible to developing cysts.
Initially, symptoms of the disease may not appear. As the tumor grows, the corresponding symptoms also increase, up to the development of serious pathologies not only of the organ, but also of the body as a whole.
ICD 10 (international classification of diseases) code D 73.4 is a separate code in the category of spleen diseases.
A small cyst (up to 1 cm), which appears as a result of inflammation, can regress on its own (dissolve) when it is eliminated.
Anatomy of the spleen
The spleen or lien (in Latin) is a lymphoid organ that has a well-defined blood supply network and is involved in the formation of immunity. It is located in the left hypochondrium (IX-XI ribs), between the stomach and the diaphragm.
The size of the spleen can vary from one person to another. The increase or decrease of the organ directly depends on the filling of the blood vessels.
Average sizes of the spleen of an adult:
- length 120 mm;
- width 80 mm;
- thickness 30-40 mm;
- weight up to 200g.
Kinds
According to ICD-10, a cyst in the spleen is classified as a blood disease and is designated as D73.4. Based on the nature of the complexity, doctors distinguish two types of this disease.
If the disease is uncomplicated, it is operable and the patient recovers quickly. If the disease occurs with bleeding, suppuration, with obvious signs of transition to the malignant stage, measures are taken to prevent the occurrence of sepsis and even death. This is a complicated view.
Based on their formation, cysts are divided into true and false:
- True ones arise in the prenatal period. Some of them resolve on their own, and some grow. If there are a lot of brushes, after a while the spleen tissue turns into cystic tissue. This leads to a deterioration in the functioning of the organ.
- False ones appear under the influence of various factors: blows, diseases. They are called acquired.
Cysts are divided into isolated (affects the spleen itself) and non-isolated type, in which other organs are affected.
Cysts up to 1 cm in size are called small, those reaching 3 cm are called medium, those reaching 10 cm are defined as large, up to 25 cm are classified as giant.
Classification of neoplasms lien
Due to the occurrence:
- True or innate. - They are formed in the fetus during intrauterine development. - This is an anomaly in the structural development of the organ. - After the birth of a child, it may disappear without a trace or increase in volume.
- Acquired or false. — They arise as a consequence of previous diseases of the spleen. - These can be inflammatory processes, injuries, surgical interventions and disruption of the blood supply to the organ. - In such processes, the neoplasm itself consists of affected tissues.
- Parasitic. — A cyst in the spleen is formed when the larvae of the parasite infect the organ wall. — The most common hydatid cysts.
By the number of cavities (chambers) of the neoplasm:
- single-chamber;
- multi-chamber.
According to the number of cysts in the organ parenchyma:
- single;
- multiple.
Drug therapy
Treatment without surgery is possible if the diameter of the splenic cyst does not exceed 3 cm. In this case, drug therapy is prescribed, the effect of which is aimed at reducing general symptoms, as well as eliminating the root cause.
It includes:
- antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antipyretics;
- enzymes;
- immunomodulators;
- hepatoprotectors;
- multivitamin complexes.
In addition, the patient’s diet is reviewed and he is prescribed a therapeutic diet. If you have a cyst in the spleen, it is strictly forbidden to self-medicate. Uncontrolled use of drugs will lead to the development of serious pathologies. Therefore, therapeutic agents are selected individually for each case.
Patients diagnosed with a cyst in the spleen undergo an annual follow-up ultrasound examination, which allows them to monitor the condition of the tumor. If it increases in size or pathological growths appear in the structure of the organ, then surgery is prescribed.
Etiology of neoplasms
Spleen cysts can form for many reasons:
- Infectious diseases. — Most often, cavities in the parenchyma of an organ can occur after tuberculosis, typhus, infectious mononucleosis or malaria.
- Impaired blood supply to the organ. - Heart attack.
- Traumatic injuries. — Blunt abdominal trauma, catatrauma, bruises.
- Infection with helminths.
- Developmental defects. — The appearance of anomalies during the formation and formation of the organ.
- Surgical intervention. — Removal of other tumors, puncture of the abscess.
Prognosis and prevention
Small cysts up to 3–5 cm do not pose a threat to health and can resolve on their own over time.
However, dynamic monitoring is necessary; if the size of the cavity increases, surgical intervention will be required. Large cavity formations can be complicated by rupture with subsequent bleeding, suppuration, and the formation of fistulas into the pleural cavity. There is no specific prevention of splenic cysts. It is necessary to avoid abdominal injuries whenever possible and promptly identify and treat other diseases of the abdominal organs. Prevention of parasitic cysts consists of observing sanitary and hygienic standards when in contact with domestic animals and their periodic anthelmintic vaccination.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a neoplasm depend on its size. If the size is small, the patient may not experience symptoms of organ damage.
Neoplasms up to 1-2 cm are asymptomatic.
The growth and increase in the volume of the cavity is usually accompanied by the appearance of symptoms.
Initially, nonspecific symptoms occur:
- nausea;
- heaviness and feeling of discomfort in the left hypochondrium;
- weakness;
- decreased performance;
- periodic pain in the upper abdomen.
As it grows and increases in volume, new signs of the disease appear.
They are associated with stretching of ligaments, the capsule of the organ and compression of atomic formations located nearby:
- Compression of the organs of the digestive system (stomach and part of the intestines): - vomiting, indigestion, cramping pain, bloating, loose stools and constipation.
- Compression of the heart muscle: - pain in the epigastric region and left hypochondrium, radiating to the collarbone, scapula and shoulder on the left
- Problems with the diaphragm: - difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, cough, chest pain.
- Splenomegaly. — When palpating the anterior abdominal wall, you can feel an enlarged spleen (normally the spleen is not detected).
Classification
Spleen cyst includes a wide group of diseases, united by one symptom - the formation of cavities in the spleen that are filled with fluid. About 0.5% - 1% of the total population complains of this disease, especially for people aged from 35 to 55 years. An amazing fact is that in the female half of the population, cysts of this organ are much more common (3-5 times). Most often, this disease is discovered completely by chance during the next examination.
There are several types of disease:
- congenital cyst, also known as true, which is caused by various pathological processes directly during development in the womb;
- a false cyst, also acquired, develops after operations, injuries, and also as complications of serious diseases;
- a parasitic cyst that appears as a result of parasitic microorganisms entering the spleen.
Each type of disease has its own causes of development and, accordingly, treatment. Recently, splenic cysts have often occurred in children. As a rule, it is also detected using ultrasound.
Neoplasm in a child
A spleen cyst in a child is no different in structure from that in an adult. The manifestation of symptoms of the disease is similar in both children and adults.
Neoplasms in newborns are associated with developmental defects in the fetus in the womb.
They can be triggered by a difficult pregnancy:
- the presence of concomitant pathology in the mother (arterial hypertension, kidney disease);
- exposure to toxic substances (alcohol, smoking);
- past diseases (infections and viruses) during pregnancy.
At an older age, the cause may also be the influence of external factors:
- infections;
- injuries;
- surgical interventions;
- long-term use of medications.
A neoplasm detected in the embryo in the early stages (according to ultrasound results) does not yet indicate a final diagnosis. During further screenings it may not be detected.
In children under two years old, small cysts (up to 20mm) can resolve on their own. If complications (symptoms of compression) appear and the size of the tumor increases (according to visual examination methods), surgical intervention is required.
The condition of the baby, if he has an education, depends on his size.
- Small neoplasms behave asymptomatically. — The progression of the process leads to the appearance of painful sensations in the left hypochondrium. — The pain is periodic, spontaneous, against the background of complete health. - But more often they occur after eating.
- Reaching a large size, the cyst puts pressure on neighboring organs and symptoms of compression occur.
In children, these signs are especially pronounced. Such a child can lose a lot of weight and quickly (due to frequent attacks of nausea and vomiting, disorders of food digestion).
The most common complication is abscess formation (suppuration):
- children develop chills;
- increase in body temperature.
In case of such complications, surgical intervention is performed urgently.
Treatment of pathology
The technique directly depends on the size of the formation. Most often, a conservative treatment method is prescribed. The use of folk remedies to complement therapy is also permitted.
It is aimed primarily at relieving the patient’s symptoms. If the cyst increases in size or becomes malignant, surgical intervention is prescribed.
Conservative treatment
This type of therapy takes a comprehensive approach aimed at relieving symptoms. It consists of the following drugs:
- Means for relieving pain. They alleviate the patient’s condition and relieve discomfort caused by the cyst.
- Immunomodulatory. Since this formation affects the spleen, which is responsible for the immune system, it is necessary to help the body maintain its protective function.
- Antibiotics. Prescribed for various inflammations. They also help destroy harmful microorganisms that contribute to the occurrence of various diseases.
- Antihelminthic drugs. They fight various parasites that cause spleen cysts. It is also recommended to use these drugs for preventive purposes.
- Fever relievers. They help alleviate the patient’s condition and relieve the effect of high temperature on the body.
- Vitamin complexes. Prescribed to maintain immunity and improve general condition. These drugs can be used to prevent the occurrence of various diseases.
Types of surgical interventions
This type of intervention allows you to get rid of all types of education. It also helps prevent complications and recurrence of the cyst.
There are several types of surgical treatment. Their choice depends on the type of formation, its size, as well as the condition of the spleen.
Methods of surgical treatment:
- Cyst puncture. It is used when its size is no more than 5 centimeters. The essence of the method is to insert a needle into the formation, pump out fluid from there and inject a special drug that glues the walls of the cyst. After such an intervention, it is necessary to treat the surface of the formation in order to prevent the recurrence of the cyst.
- Husking. During this intervention, the formation is completely removed from the surface of the spleen. In order to prevent bleeding and infection, surgeons use the argon plasma coagulation method. It allows you to seal vessels.
- Removal of part of the spleen. This method is used for deep cyst damage. Usually it is removed along with part of the affected organ.
- Splenectomy. It is used when the formation covers more than 50% of the spleen. Represents the complete removal of the organ itself.
Most often, preference is given to closed operations (laparoscopy). They are carried out very quickly and completely eliminate various risks. Also, after this type of surgery, the patient has almost no scars.
After surgery, the formation is examined for the presence of cancer cells.
Diagnostics
Neoplasms of the spleen, at the initial stages of their development, do not manifest themselves in any way, or nonspecific symptoms appear, characteristic of many diseases of the digestive system. Therefore, they are often detected during routine medical examinations or during the diagnosis of other diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
These methods include:
- Physical examination: - Palpation of the abdomen helps identify painful areas or splenomegaly.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs (ultrasound of the abdominal cavity): - helps to visually see the cyst and assess its size.
- Computed tomography of the abdominal organs. — Performed with the introduction of a contrast agent: it helps to examine in detail the walls of the tumor and its contents.
For differential diagnosis and identification of parasitic cysts, the following are used:
- Cazzoni's allergy test (intradermal injection with echinococcus-containing liquid), information content 90%, is positive for echinococcal cysts.
- Complete blood count - reveals an increase in the number of eosinophils.
- Immunological tests (latex agglutination reaction) are the most modern and informative test, positive in 93.6% of cases.
Which doctor is best to see if you have abdominal pain?
If these pains bother you for a long time, are aching, constant, and are accompanied by periodic digestive disorders, then first you need to visit a therapist.
Only a general practitioner will be able to make a differential diagnosis and refer for the necessary laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, you should contact a surgeon to decide on surgical removal of the cyst.
Diagnosis of splenic cyst.
Splenic cysts are detected in most cases during a clinical examination and routine examination, as well as during a diagnostic search for gastrointestinal diseases during ultrasound examination and computed tomography with bolus contrast.
In the diagnostic algorithm for identifying single splenic cysts, the key issue is to determine the non-parasitic nature of the detected cysts. To resolve this issue, it is necessary to conduct serological studies with parasitic diagnostics for the presence of echinococcosis (Cazzoni reaction and hemagglutination) and alveococcosis (latex agglutination reaction).
Treatment methods
A cyst on the spleen requires treatment and dynamic monitoring of its size.
Therapy includes:
- invasive;
- non-invasive methods.
If there are no symptoms and the cyst is small, surgical intervention is not required. In this case, it can only be detected as a find during a medical examination.
After determining the cause of the neoplasm, dynamic observation is prescribed. Carrying out ultrasound diagnostics a couple of times a year.
Conservative therapy
Treatment without surgery is carried out only if the following factors are present:
- small tumor;
- minor manifestation of symptoms;
- non-parasitic cyst;
- no complications.
Such a cyst must be constantly monitored.
In a child under two years of age, the neoplasm can go away on its own and in this case does not require therapy.
There are no specific medications aimed at resolving spleen tumors. Medicines are used mainly in combination with surgical treatment.
Such drugs are:
- Analgesics (painkillers), to relieve pain (in the presence of abdominal pain).
- Antibiotics - in the complex treatment of abscess (suppuration of a neoplasm), as well as for the prevention of postoperative complications.
- Anthelmintic drugs are prescribed after surgical removal of the cyst to minimize the risk of recurrence.
- Vitamin complexes - to improve immune function.
Surgery
After the appearance or intensification of symptoms, the issue of surgical intervention must be decided.
Indications for tumor removal:
- rupture of the cyst wall and fluid entering the abdominal cavity;
- abscess formation (suppuration) of the cavity;
- bleeding that has begun;
- big sizes;
- multiple splenic cysts.
The choice of surgical treatment tactics is determined by the size of the cyst:
- For small tumors, fluid is punctured from its cavity and drugs are introduced into it to harden the capsule.
- The average size of the cyst is an indication for resection of part of the organ.
- Splenectomy is performed for large cysts and when complications occur (bleeding).
Laparoscopy is a priority method of intervention, as it is less invasive. If it is especially difficult to perform, open surgery (laparotomy) is performed.
The operation algorithm is the same for different types of pathology:
- After surgical access and isolation of the neoplasm, the fluid is first pumped out from the cavity, and then the cyst capsule itself is exfoliated.
- For parasitic cysts, after removing the fluid, special anthelmintic agents are introduced into the cavity.
Possible complications of surgical treatment:
- bleeding;
- abscess formation of the cyst cavity;
- tumor recurrence.
If the intervention is performed incorrectly, the parasitic cyst may rupture. In this case, the echinococcus from the liquid will infect nearby organs, which will lead to re-infection.
Diagnostic methods
There are several research methods that allow you to determine the size of pathologies, identify the sources of occurrence and decide on treatment decisions. An approximate diagnosis is made upon examination of the patient - disproportion of the abdomen and protrusion in the upper left part, palpation of the affected organ.
During instrumental diagnostics, the following procedures are carried out:
- Ultrasound examination is a method in which the presence of an anechoic formation (splenomegaly) is detected and the characteristics of its origin are visually determined;
- multi-slice computed tomography is used to determine the location of the tumor and a detailed determination of the type, as well as when complications are suspected;
- differential diagnosis is carried out to identify pathological processes in the organ;
- laboratory tests are prescribed only for cysts of parasitic origin.
To make a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes examinations:
- Examination by a surgeon to identify symptoms;
- Ultrasound, during which the size, location, and type of cyst are determined;
- To diagnose the characteristics of thickening of the tumor, MSCT (multispiral computed tomography) or CT (spiral computed tomography) is prescribed;
- Blood and urine tests.
The patient's recovery period
The postoperative period is accompanied by bed rest, diet, and administration of medications.
The diet requires the exclusion of fatty and fried foods to reduce the load on the pancreas and liver.
Allowed products (boiled or steamed):
- vegetables;
- lean meat (chicken, turkey);
- fish (low-fat);
- porridge;
- fermented milk products (up to 5% fat content);
- soups with secondary broth.
In the postoperative period, it is also important to conduct a control ultrasound examination to exclude recurrence of the process and timely detection of complications.
Prevention measures
Preventive measures include:
- compliance with the rules of personal hygiene (to avoid infection with helminths);
- undergoing medical examination (for timely detection of the disease).
With timely detection and treatment, the outcome is favorable. Large cysts, if untimely and incorrectly treated, can lead to health-threatening conditions.
Complications
A cyst in the spleen is a rather serious disease that requires constant attention.
If left untreated, the disease leads to the following consequences:
- If the cyst bursts due to an impact or other factors, its contents will enter the abdominal cavity. Without emergency surgery, this will lead to peritonitis, severe intoxication and even death of the patient.
- If the cyst becomes inflamed and suppurates, then an abscess and bacteremia develop.
- An advanced disease without treatment causes bleeding into the cyst cavity, and subsequently into the peritoneum.
Therefore, if you have been diagnosed with a cyst in the spleen, then be sure to follow the doctors’ instructions and take care of your health.