What is diffuse external otitis?
The diagnosis of external diffuse otitis is made in the presence of inflammation of unlimited localization in the area of the external auditory canal. The pathological process covers the auricle, external meatus up to the eardrum.
If both ears are involved in the inflammatory process, then bilateral external diffuse otitis is diagnosed. In cases where the infection affects only one ear, the patient is diagnosed with left-sided or right-sided diffuse otitis media. In all three cases, the same treatment is prescribed.
Clinical picture of external diffuse otitis
The disease begins with itching in the ear, which turns into a pain syndrome, characterized by sharp pain in the ear on the affected side, aggravated by chewing, talking, or pressing on the tragus. Patients note the appearance of congestion in the ear, decreased hearing, headache, sometimes increased body temperature, general weakness, malaise, and tenderness of the lymph nodes on the affected side.
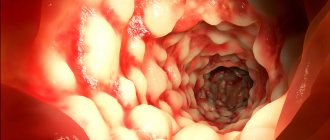
During endoscopic examination, hyperemia and swelling of the skin of the external auditory canal, its narrowing into the flesh until complete obstruction, and sometimes purulent discharge from the ear are observed. Lymph nodes in the parotid region and neck become enlarged and painful on palpation.
A general blood test reveals moderate leukocytosis with a shift of the leukocyte formula to the left and an increase in ESR.
Treatment of diffuse external otitis involves relieving pain and sanitizing the external auditory canal. To eliminate ear pain, analgesics and complex preparations for oral administration are used.
In the presence of copious discharge, a bacteriological examination is indicated to identify the pathogen and the possibility of effective treatment.
The external auditory canal is washed daily with warm antiseptic solutions; in case of profuse purulent discharge, the external ear is toileted using a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide. After toileting the ear, ointment turundas or ear drops are used, depending on the type of pathogen and the stage of the inflammatory process.
In the presence of general symptoms and hyperthermia, bed rest and the prescription of antibacterial drugs orally or by injection are indicated. Also, such patients are indicated for ILBI/UFO therapy for a speedy recovery.
After normalizing body temperature and reducing swelling of the skin of the external auditory canal, physiotherapeutic procedures are indicated - endoural exposure to the red spectrum of a laser and infrared exposure to the parotid area. The use of physiotherapeutic techniques in the treatment of diffuse external otitis accelerates the healing process and normalizes metabolic processes in the tissues of the outer ear.
All procedures, including endoscopic examination, bacteriological examination, lavage of the external auditory canal, laser therapy and ILBI/UFOB can be performed at the ENT CLINIC in Chertanovo, where there are all conditions for a full diagnosis and treatment of patients with pathology of the external ear.
Prevention of diffuse external otitis involves proper and regular toileting of the outer ear using serolitics, avoiding the use of cotton swabs and other items for cleaning the ears, and in-ear headphones.
When planning a summer vacation at the sea and other bodies of water, undergo a preventive examination with an ENT doctor and enjoy your vacation without any problems!
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health. Don't delay treatment, call right now.
Otitis of the external ear in chronic and acute form
Based on the nature and duration of the disease, there are two types of external otitis: acute and chronic. There are more patients diagnosed with acute diffuse external otitis, its symptoms are more pronounced, and with timely treatment the prognosis is favorable, the patient recovers completely.
The chronic form of otitis is characterized by periods of remission, ending with relapses (exacerbations), during which the patient's condition worsens.
In some people, the symptoms of the disease are mild, so they do not undergo treatment; in others, their performance decreases, their appetite and quality of sleep deteriorate.
Symptoms and diagnosis of local (limited) external otitis
The symptoms of local otitis externa differ from the signs of the diffuse form of this disease. In the local form of otitis externa, the symptoms are similar to those of a regular skin boil, that is, it begins with severe itching in the ear canal, which then turns into pain due to compression of the nerve receptors. The larger the boil, the stronger the pain, since the inflammatory formation in the hearing aid is limited to the walls of the auricle.
Painful sensations often spread to the temple, the back of the head, the jaw, and sometimes involve the half of the skull where the boil has formed in the ear. Due to severe pain during chewing movements, a person often refuses to eat, and increased discomfort at night prevents him from sleeping. When a boil completely blocks the ear canal, a person’s hearing decreases sharply.
The initial diagnosis occurs through conventional otoscopy and palpation. The latter helps to determine the location of the boil. When pain occurs when pressing on the tragus of the ear, we can talk about the location of the abscess on the anterior wall of the ear canal.
Pain on palpation of the area behind the ear indicates the location of the boil on the posterior upper wall. Pain on palpation of the lower jaw indicates an inflamed lower wall of the auricle.
In case of hearing loss, the attending physician resorts to audiometry and a tuning fork to determine the degree of pathology, the conductive type of hearing loss. It is also necessary to carry out bacteriological culture of purulent discharge from the ear in order to determine the causative agent of the boil, to differentiate local otitis from other types of disease: mastoiditis, mumps, eczema of the ear canal, which differ in treatment methods.
Causes and risk factors
In most cases, diffuse otitis externa develops due to an infection that has entered the ear tissue through microtrauma. The most common causative agents of the disease: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococci, staphylococci, candida or aspergillus fungi.
Diffuse external otitis may develop for other reasons that are non-infectious (allergy, irritation). Improper ear care is the most common cause leading to diffuse otitis media.
Doctors refer to gross violations of ear hygiene as:
- the system does not have a procedure for cleaning the ears (washing with liquid detergent);
- the external auditory canal is unnecessarily often cleaned using cotton swabs;
- earwax is removed with sharp objects (matches, toothpicks), and there is a high probability of injury to the soft tissues of the ear;
- removing earwax, they penetrate deeply into the ear canal.
One of the factors causing the disease is considered to be insufficient and excessive secretion of earwax; this relates to the individual characteristics of a person. Sulfur lubricant is essential to protect the ear from infection. If there is a lack of it, bacteria (fungi, viruses) are not removed from the ear cavity in a timely manner, which leads to the spread of infection and inflammation. With excessive secretion, a cerumen plug is formed, which prevents the normal cleaning of the ear canal from pathogens.
There are other, no less serious, reasons related to the state of human health. Diffuse otitis media can be caused by:
- decreased general immunity;
- inflammation of the skin (boils, carbuncles);
- mumps;
- eczema;
- seborrhea;
- psoriasis;
- otitis media of the middle ear.
With a weakened immune system, otitis externa can develop against the background of influenza or ARVI, or any dermatological disease. Diffuse otitis often affects people with diabetes.
Diagnosis and treatment of external diffuse otitis
When visiting a doctor, patients complain of severe pain, pressure, a feeling of congestion, and tinnitus. A visual examination reveals redness, discharge of pus, and an increase in pain when pressed.
Otoscopic examination shows swelling and inflammation of the eardrum.
Important! When the process is started, blockage of the ear canal and microcracks are diagnosed, which becomes the cause of the development of conductive hearing loss.
Otitis without ear pain can cause hearing loss if the disease is not detected in a timely manner.
Accurate symptoms are sufficient to diagnose the disease. In some cases, more serious research methods are required, so the patient is prescribed:
- tympanometry;
- CT;
- otoscopy;
- otomicroscopy;
- acoustic reflectometry.
Otitis of the external ear, accompanied by a fungal infection, will require microbiological analyzes of sulfur secretions. If it is necessary to determine: otitis media or cerumen plug, the patient undergoes an otoscopy. The acidic environment of earwax protects the ear canal from bacteria. When moisture gets in, the wax swells and closes the narrow opening in the ear. Constant compression of the tympanic septum and a humid environment lead to the development of otitis media.
Some symptoms are similar to other diseases, so it is unsafe to carry out independent treatment, which can cause serious complications.
Important! Treatment of external otitis should be carried out only after careful diagnosis and establishment of the correct diagnosis.
Primary therapy comes down to cleaning out the pus and prescribing anti-inflammatory and antibacterial medications. When a fungal infection is detected, antifungal drugs of various spectrums of action are used.
Treatment of acute diffuse external otitis is performed only in a medical institution. The patient is prescribed the following topical medications:
- Burov's fluid;
- yellow mercury ointment;
- hormonal therapy;
- analgesics – to relieve pain;
- antihistamines - for allergic manifestations.
In case of purulent inflammation, it is strictly forbidden to warm the ears, as well as use drops and turunds. Local treatment consists of the doctor washing the ears with antiseptic solutions for otitis media.
For a quick recovery, you should clean the sink and ear canal from accumulation of wax every day with special sticks soaked in a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
Treatment of acute otitis at home is carried out in combination with traditional therapy. Ear candles are one of the painless methods. After using them, pain is relieved, traffic jams are removed, and hearing is restored.
If symptoms appear and treatment of external otitis is carried out in a timely manner, improvement occurs after 2-3 days; complete recovery will require 7-10 days.
Symptoms of the disease
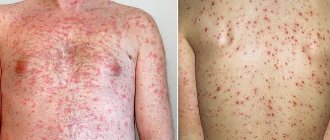
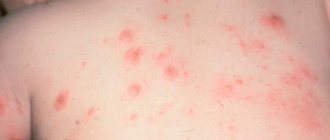
Any inflammation is accompanied by swelling, so the first signs of diffuse otitis are hyperemia (redness) of the tissues lining the ear canal, and their swelling and swelling. Following this, pain of varying intensity and localization appears, itching, hearing is noticeably reduced due to congestion of the ear canal, and purulent exudate is released.
By the nature of the pain one can judge the stage of the disease and its nature:
- at the initial stage of diffuse otitis, painful sensations occur when touching the affected area, with light pressure on the tragus;
- at the stage when purulent compartments appear, the pain becomes regular, independent of tactile contacts;
- With the further development of the inflammatory process, the pain intensifies when chewing food, this often leads to loss of appetite and weight loss.
See also
Medicinal properties and contraindications of aloe in the ear for otitis media
Read
The patient's temperature does not rise above 37-37.5 °C. Complicated acute diffuse otitis is characterized by rashes in the form of hemorrhagic vesicles filled with liquid, interspersed with pus and blood, and a putrid odor. The chronic course of the disease is characterized by the presence of mild symptoms, the mucous tissue of the auditory tube becomes denser, and infiltration of the eardrum is observed. Some patients have enlarged lymph nodes (ear, submandibular) and aching headaches.
Clinical manifestations of the disease
With the development of a pathological process, the first signs are a feeling of fullness inside the ear canal, a feeling of itching, and a local increase in temperature.
Subsequently, a gradually increasing pain syndrome occurs, radiating to the temple and head area. As you eat, the pain becomes more pronounced. Often this pathology is accompanied by weakness, poor health, and lack of appetite.
Additional signs of the development of the disease are:
- Deterioration in the quality of sound perception, this is due to the resulting swelling of the mucous membrane and tissues of the inflamed ear canal, as a result of which it narrows and the lumen decreases.
- Production of serous fluid, and in the next stage, purulent contents in the area of the external auditory apparatus.
- The submandibular lymph nodes increase in size.
The average duration of development of the pathological process is about 14 days. After which there is a significant improvement in the condition, unpleasant symptoms are eliminated, and the recovery stage begins.
In some situations, the clinical manifestations of this form of the disease may be subtle, and the disease may even go unnoticed by the person.
And only after the pathological process has passed into the chronic stage, intensely expressed symptoms appear. During the chronic inflammatory process, scars and adhesions begin to form, which can provoke a decrease in the lumen and progressive hearing loss.
Therefore, it is important to be attentive to the slightest signs of discomfort or other symptoms. This will prevent the disease from becoming chronic.
Diagnostic methods
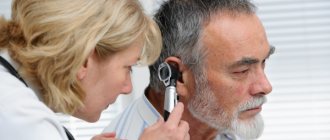
When making a diagnosis, the otolaryngologist listens to the patient’s complaints, first conducts a visual examination, then otoscopy - a detailed study of the hearing organ using a special instrument. First, the healthy ear is examined, then the diseased one.
At the next stage, a comparative assessment is carried out, during which the following parameters are determined:
- intensity of hyperemia;
- amount of edema;
- the presence of defects in the auricle or neoplasms;
- volume of discharged exudate, its nature.
In case of a complicated course of the disease, the patient may be prescribed additional examinations: otomicroscopy, otoscopy, computed tomography, tympanometry, acoustic reflectometry. If the inflammation is caused by a fungus, the sulfur secretions are sent to the laboratory for microbiological examination.
Diagnostics
Defining the disease is not difficult. The diagnosis is made based on the patient's complaints and examination by an otolaryngologist of the pathological focus.
The doctor performs an otoscopy - an instrumental examination of the hearing organs.
If one ear is affected, then the study begins with a healthy organ, and then a comparative description is made. The study evaluates:
- degree of mucosal hyperemia;
- severity of swelling;
- type of auricle, presence of tumors or defects;
- quantity and nature of exudate.
Palpation is also carried out, the degree of soft tissue infiltration and the degree of pain are determined. Lymph nodes are palpated.
Diffuse otitis media requires careful differential diagnosis. The examination is carried out after thorough sanitation of the ear canal. It is necessary to exclude acute inflammation of the middle ear, viral or fungal otitis media.
Laboratory methods include culture and determination of the type of microflora and its sensitivity to antibiotics.
Treatment of the disease
The basis of treatment for diffuse otitis is medications. As an addition to them there is herbal medicine, physiotherapy and folk recipes. The goal of therapy is to eliminate the source of infection, relieve symptoms, and improve quality of life.
Medication methods
The patient is prescribed topical medications: drops, solutions, creams, ointments. Purpose of their use:
- stop the inflammatory process;
- relieve swelling;
- eliminate itching.
Local agents have antibacterial, vasoconstrictor, analgesic, and regenerating properties. Ear drops are the most convenient form of topical medications. Their advantages include rapid penetration into the source of inflammation and relief of symptoms in a short time.
When treating diffuse otitis, use:
- Anauran;
- Garazon;
- Otipax;
- Sofradex;
- Polydexa.
Before instilling the medicine, the ear canal is cleaned of dried crusts and exudate.
Antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate pathogenic flora. The following drugs are popular among ENT doctors:
- Amoxicillin;
- Cefazolin;
- Oxacillin;
- Augmentin;
- Ampicillin.
Antibiotics are taken for a full course; withdrawal can lead to relapse and the disease becoming chronic.
Operation
Surgery is required if pus has accumulated inside the eardrum and does not rupture on its own. The doctor, in order to relieve pain and improve access of medicine to the source of inflammation, makes a puncture in the eardrum. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe a procedure for blowing out the auditory tube.
Traditional treatment
Natural components included in folk recipes increase the effectiveness of drug therapy.
Geranium
It is not difficult to grow geranium on a windowsill; its leaves and flowers contain active substances that have antibacterial properties. To treat diffuse otitis, you need freshly picked, young leaves.
Before inserting the leaf plate into the ear cavity, it is crumpled and twisted into a wick shape. The procedure is carried out daily. It is repeated 2 to 3 times a day. The therapeutic effect is observed if the effect of the medicinal substances of geranium lasts at least 30 minutes.
Aloe and Kalanchoe
Everyone knows about the beneficial properties of these plants. The course of treatment for Kalanchoe otitis is 10 days. 3 to 4 procedures are performed daily. Take Kalanchoe leaves, grind them into a pulp, transfer it to a gauze napkin, roll it up and put it in the sore ear, remove it after 40 minutes. Before using aloe juice for medicinal purposes, the leaf is cut and placed on the refrigerator shelf for 2 days. A tampon is rolled out of gauze, moistened in freshly squeezed juice, and the turunda is inserted into the ear canal.
Onions and cumin
The onion head must be baked in the oven until soft. During heat treatment, the shape of the fruit should be preserved. Using a sharp knife, cut off the top of the onion and carefully remove the pulp from the central part of the head.
See also
Causes, symptoms and treatment of secretory otitis in children and adults
Read
Take cumin (seeds) - 10 pieces, mix with chopped onion, fill the head with the resulting mixture. Cover the onion stuffed with cumin with the cut top and place in the oven for half an hour. After cooling, squeeze the juice out of it. Use it as drops. Instill 3 drops into the sore ear at a time. Treat in this way for at least 10 days.
Mint
Mint tincture helps with otitis media. It is prepared from fresh leaves, take 40 grams, pour a glass of high-quality vodka, and put it in a dark place for a week. The finished product is filtered and used as ear drops. You can instill 3 drops into the ear 3 times a day.
Garlic oil
The base can be olive or vegetable oil. During the cooking process, take 1 part of it and 1 part of chopped garlic. The mixture is placed in a dark glass container with an airtight lid and stored in a dark place for 10 days.
Before use, filter the garlic oil, drop it into the sore ear (warm only), and store it in the refrigerator. You can moisten the turunda in it and insert it into the ear canal, change it every 3 hours.
Birch buds
The antimicrobial properties of birch buds are used for diffuse otitis media. A vodka tincture is prepared from them in a ratio of 1:10 – kidneys – 1 part, vodka – 10. The medicine is ready in 14 days. Before carrying out the treatment procedure, a portion of birch tincture is heated, a cotton pad is moistened in it and, to warm up, is inserted into the sore ear. When the cotton wool cools down, it is removed. Treatment lasts at least 2 weeks. Relief occurs by the end of the first week.
Possible consequences
Pain always accompanies diffuse otitis media, so during illness a person’s mental and physical performance and memory deteriorate. Due to increased pain during chewing, appetite disappears. This leads to weakened immunity and the development of other diseases: stenosis, myringitis, necrosis of epithelial tissues.
In the chronic form of otitis externa, the ear canal narrows, which can lead to hearing loss. A child with hearing impairment has problems with school, and adults begin to have professional problems.
Operation
Surgical intervention is indicated in the presence of a large volume of exudate, intense pain, rupture (perforation) of the eardrum, a sharp decrease in hearing, and high fever.
Contraindications:
- exacerbation of another disease;
- obstruction of the eustachian tube;
- signs of sepsis.
Types of modern operations: radical, myringotomy, myringoplasty. After any operation, the patient requires a rehabilitation period.
Causes
The key reason for the development of inflammatory processes in the external auditory canal is bacterial flora. The prerequisites for its occurrence are a decrease in the barrier function of the skin and general immunity. Why might this happen?
The external auditory canal contains an acidic environment, which is formed due to the wax secreted by the ear glands. It is this that protects the hearing organ from external penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the auditory canal. However, when water enters or continually cleans the ear, the pH level in the ear canal changes, which creates conditions for the development of opportunistic bacteria.
Most often, diffuse otitis is provoked by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, pneumococci, Moraxella, Haemophilus influenzae, Candida fungus, etc. Provocateurs of a decrease in general and local immunity can be:
- ear injuries;
- improper ear hygiene;
- hyperhidrosis;
- bad habits;
- water getting into the ear;
- allergic reactions;
- regular stress;
- infections (tonsillitis, sinusitis);
- endocrine disorders.
ENT disease is called swimmers' disease, since the main cause of its occurrence is the leaching of the acidic environment from the ear.