Each person's perception of reality is individual. It’s sad, but some people, due to various mental disorders, may lose an adequate perception of reality. A distorted perception of reality occurs. Mental disorders can lead to various manias (obsessive states) and phobias (obsessive fear). Such conditions significantly complicate a person’s life; he is simply “captured” by obsessive thoughts.
The most common obsessive disorder in people is persecution mania. In medicine, this disorder is called “delusion of persecution.” Like various types of delusions, delusions of persecution are considered one of the signs of insanity. With this condition, the reality that the patient sees can be greatly distorted. His world lives by its own laws and everything happens differently in it.
Delusion is a disorder of thinking, due to which a person has false ideas that completely take over his consciousness. Such disorders cannot be corrected from the outside, i.e. it is impossible to explain to the patient the discrepancy between his perception of reality. These ideas are based on false premises, called “crooked logic” in medicine. Delirium can be a symptom of other mental disorders, in particular schizophrenia, or occur as an independent disorder. However, the state of persecution mania has a number of specific differences:
- Adaptation disorder, a person cannot live and work normally in society;
- This condition cannot be corrected from the outside;
- This is a manifestation of illness, and not of a person’s developed imagination;
- There is inventing all sorts of facts about reality.
At its core, persecution mania is paranoia that completely captures a person’s consciousness. Under the influence of this state, a person may refuse to perform usual actions, for example, refusing food, thinking that someone has poisoned it. He may be afraid to move down the street or cross the road, fearing that they want to run him over. It seems to a person that danger awaits him at every step and that attackers are only looking for an opportunity to harm or kill him.
Symptoms of persecution mania
In short, the main symptoms of persecution mania include:
- thoughts of constant persecution and threat to life;
- jealousy;
- mistrust;
- attacks of aggression.
The symptoms of persecutory mania have long been the subject of careful study by psychiatrists. The symptoms of this disease are described in detail in many medical works. The main manifestation of the disorder is the patient’s obsessive feeling that a certain person or group of people is pursuing him with the aim of causing harm - to rob, injure, kill.
Delusions of persecution take on various forms. The patient may only be afraid of one specific aspect of life. If a person can name the time when the persecution began, the activities carried out for this event and the results of sabotage, then there is a high level of systematization of delirium. This indicates a long duration of the obsessive state and its transition from a “delusional mood” to a “delirium of persecution.”
A person develops a growing feeling of anxiety, he constantly expects negative events. At the moment when anxiety becomes constant, they speak of the first appearance of delirium.
Persecution mania develops gradually and the “source” of the threat may change over time. At first, a person may only fear his life partner, considering him the main intruder; then neighbors and other people from the patient’s environment may come under suspicion. More and more people in the patient's imagination become accomplices in a conspiracy against him.
Over time, thinking becomes very detailed; the patient can describe “attempts” down to the smallest detail. At the same time, his stories are destructured, and he can pay equal attention to important and minor facts.
Changes in a person’s personality also occur; he becomes tense, aggressive, suspicious and wary. The patient begins to do things that are unusual for him, and is reluctant to answer questions about the purpose and reason for such behavior.
Quite often, persecution mania is accompanied by “overvalued ideas.” That is, a person can misinterpret events occurring in reality, giving them a perverted interpretation. However, this fact in itself cannot indicate the presence of delusions of persecution; it is alarming only in combination with persecution mania.
How to determine the symptoms of the disease?
Persecution mania has pronounced symptoms. A person who suffers from persecution mania believes that someone is hunting him. The reasons for such a hunt can actually be anything - an individual’s behavior, hair color, clothing, smell, appearance and much more. It should also be understood that such behavior may indicate that such actions can be both real and occur in the human brain. People who have this behavior can behave extremely inappropriately. So, for example, a person suffering from a phobia may react negatively even to how exactly and who pronounces his name, or whether someone laughs at him.
In order to identify and help get rid of such a phobia, it is necessary to learn about the causes of the development of this disease. Usually, the causes of a phobia go deep into a person’s subconscious and only a qualified psychiatrist can correctly diagnose and cure this disease. You should understand that you will not be able to identify such a phobia yourself.
Symptoms of the disease also include:
- constant feeling of being watched;
- the patient believes that he is accused of something and is treated poorly;
- the patient does not trust anyone, he considers himself exceptional and always right;
- a person feels that someone is constantly trying to catch him;
- aggressive behavior.
Treatment of the disease
Unfortunately, despite sufficient study of this disorder, an effective treatment method for persecutory mania is still under development. Existing methods of treating persecutory mania are far from ideal. Also I.P. Pavlov called delusions of persecution a symptom of brain dysfunction. And today the occurrence of this disorder is associated with the pathology of conditioned reflex activity of the brain. And all biological disorders are usually treated with pharmacological methods. However, in paranoid states, electroshock therapy, insulin therapy and similar techniques are ineffective.
Psychotherapeutic methods of treatment also do not produce positive results in the treatment of persecutory mania. The reason is that this condition, as mentioned above, cannot be corrected from the outside. However, this does not mean that patients do not need the help of psychologists and social workers who can help create good conditions for the adaptation of patients in society.
Today, persecution mania based on schizophrenia is treated with psychotropic medications, and if they have a positive effect, rehabilitation procedures are prescribed.
If mania is caused by the abuse of alcoholic beverages or medications, you should immediately stop using them.
Typically, people suffering from paranoia do not seek medical help on their own because they do not recognize the presence of any abnormalities. Close people should persuade such a person to seek medical help.
Description
Delusions of persecution can cause distrust, isolation, self-isolation, and attacks of aggression in the patient. Patients with this form of delusion do not consider themselves unhealthy and lose the ability to critically perceive themselves. Although there have been cases where supposed patients turned out to be right in their suspicions, and they were actually persecuted, therefore the facts presented by them always need to be verified.
Statistical studies conducted in the USA have shown that persecutory delusions are one of the most common types of delusions. As a rule, it is caused by paranoid schizophrenia, but sometimes it is caused by other reasons: alcohol poisoning, so-called. “alcoholic paranoid”[3] is a very dangerous form for the patient and others, due to drug poisoning, delusional disorder, brain damage (senile and atherosclerotic changes, Alzheimer’s disease, etc.)
The disease is treated with medication, is prone to relapse and is undesirable, since it can classify the dissuader as an agent of “enemies.” In especially severe cases, the patient can pose a danger both to himself and to others.
Therapy
Persecutory mania, the symptoms and signs of which must be detected in the early stages of the disease for more effective treatment, can be treated using various methods. The main method of working with patients with persecutory delusions is psychotherapy; sometimes in advanced stages of the disease the patient is prescribed medication.
Electroconvulsive therapy is an effective and safe treatment for many mental disorders, but its use is controversial. The choice of treatment method for persecutory delusions depends on the complex of therapy prescribed only by the attending physician; self-treatment can significantly worsen the patient's condition.
Psychotherapy
The most famous and effective treatment for persecutory delusions is cognitive behavioral psychotherapy. Its course can last from 7 to 20 sessions, depending on the severity of the disorder and the patient’s desire to work with a doctor.
During the sessions, the doctor tries to explain to the patient his incorrect perception of the world around him, which causes a feeling of fear and a sense of persecution and anxiety. As a result of therapy, the patient learns the mechanisms by which his feelings arise and learns to control his feelings.
This is interesting: Creatorrhea - muscle fibers in stool: causes and treatment
There is also a psychoanalytic approach that sees the problem of the emergence of panic, anxiety and fear in a person’s intrapersonal conflicts. To recognize the patient’s internal conflict, the doctor uses the technique of projection and transference, and after identifying the necessary elements of subconscious contradictions, he tries to show them to the patient.
As a result of therapy, the patient develops self-awareness, understanding and the ability to analyze the motives of his actions. In this way he learns to control his emotions and know the source of their occurrence.
Family therapy and art therapy are also effective. These methods are additional, but quite effective for working through your emotions and relationships with people.
Delusion of persecution is a difficult disease for the patient’s loved ones to accept, so family therapy will help establish contact between the patient and his family. Art therapy is a way for the patient to express his emotions through creativity, which is an important additional part of basic psychotherapy.
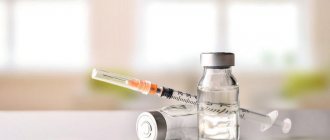
Use of medications
The use of medications during persecutory delusions depends on whether the illness is a consequence of another mental disorder or abnormality. Also, the taking of medications is influenced by the individual characteristics of the patient, the severity of delirium and the adequacy of the patient, so medications are prescribed exclusively by the attending physician.
The most commonly prescribed drugs during the treatment of persecutory delusions and related diseases:
- Phenazepam. The drug is prescribed in the early stages of the disease and helps relieve symptoms such as anxiety, tension and depression.
Phenazepam is a sedative pill that relieves anxiety symptoms associated with persecutory mania.
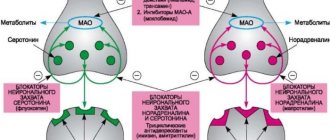
- Alimemazine, thioridazine, quetiapine. These antipsychotics should be used only during acute attacks of panic attacks and anxiety. They perform only the function of suppressing anxiety, without relieving other symptoms. Neuroleptics have side effects such as lethargy, lethargy and hormonal changes.
- Risperpet. The drug is prescribed only for acute forms of schizophrenia and inhibits the active development of symptoms of the disease, eliminates hallucinations, delusional states, increased aggression and depression.
- Clonazepam, oxazepam. The drugs can quickly relieve the patient of anxiety symptoms and are used at the very beginning of treatment. Remedies are not the only drugs prescribed; they are used in combination and in special dosages with other antidepressants, which is associated with the likelihood of the patient becoming dependent on tranquilizers.
- Lithium preparations. Psychotropic lithium drugs are taken during periods of mania. Its action is aimed at reducing impulsivity and aggression, but the effect begins to appear only on the 5th day of administration, so the drug is used as an additional remedy in combination with other medications.
- Cyclodol. The medicine is taken to eliminate the patient’s motor disorders, which often occur during an exacerbation of schizophrenia. Cyclodol is prescribed for the treatment of muscle stiffness, tremors and various spasms.
- Fluoxetine, Zoloft, Prozac. The drugs are classified as antidepressants and are most often prescribed during periods between exacerbations of the disease. Medicines are necessary to improve mood, eliminate sleep problems and generally improve the patient’s psychological state.
Electroconvulsive therapy
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) has at various times been considered a violent, unsafe way to treat mentally ill patients. Despite this, ECT is now considered effective in treating severe mental disorders.
Indications for electroconvulsive therapy are:
- depression (severe forms of the disease, suicide attempts);
- bipolar disorder (a disease with rapidly alternating cycles of depression and mania, psychotic symptoms, suicidal tendencies);
- schizophrenia (acute schizophrenia in combination with severe psychosis, catatonic syndrome (motor disorder)).
Electroconvulsive therapy can be effective in treating persecutory delusions, most often when they are combined with symptoms of schizophrenia.
The mechanism of action of ECT is not fully understood, but the therapy is known to affect components of the central nervous system. After a therapy session, the neurotropic factor of the brain changes, that is, a human protein that acts on certain neurons of the central and peripheral nervous systems, as a result of which its level changes.
Contraindications for electroconvulsive therapy:
- diseases of the field of cardiology (volumetric intracranial processes);
- neurological abnormalities (angina pectoris, heart failure, arterial hypertension, ventricular arrhythmias);
- mental disorders (obsessive-compulsive disorder);
- autonomic failure;
- diabetes;
- metabolic disorders;
- chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- renal failure;
- gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Side effects of electroconvulsive therapy:
- memory loss;
- convulsive attack;
- sinus tachycardia;
- hypertensive attacks;
- headache;
- mania;
- sleep disorder;
- disturbances of consciousness.
Complications and consequences
Persecutory mania, the symptoms and signs of which must be noticed in the early stages of the disease, can lead to negative consequences in the absence of timely treatment:
- the patient loses his sense of reality and cannot distinguish delusional thoughts from healthy ones;
- everything surrounding the patient in its provision becomes potentially dangerous, which is why the patient feels constant anxiety;
- the patient begins to withdraw and try to isolate himself from society, refuses food, suffers from insomnia;
- during periods of exacerbation of delusional thoughts, the patient reacts extremely aggressively to others;
- the patient may resort to suicide attempts.
This is interesting: Acute pain in the knee when walking, flexing and straightening, standing up, going down stairs.
Causes, first aid, treatment Such complications require urgent hospitalization of the patient and strict monitoring of him by medical personnel.