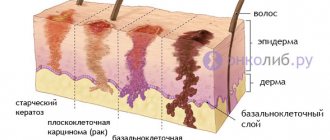
Skin formations are not only a cosmetic defect, but also a signal of an existing disease. Therefore, you should not ignore their appearance. Yellowish plaques, single or multiple, appear on the upper eyelid and are called xanthelasma. Xanthomas protrude on the lower eyelid or other parts of the body. These are benign formations, soft to the touch, with a characteristic color. As a rule, degeneration into malignant does not occur. They are usually diagnosed by a visual examination by a doctor. If necessary, he prescribes additional tests and examinations so as not to confuse them with tumors that pose a threat to health.
What is xanthelasma
The International Classification of Diseases H 02.6 defines xanthelasma as a benign, flat-shaped skin formation. Visualized as a raised plaque on the human skin. They are characterized by a yellow color and absence of pain.
Xanthelasma manifests itself in the form of single or multiple formations. This pathology is one of the signs of skin xanthomatosis, which manifests itself as cholesterol deposits under the skin similar to xanthelasma.
Xanthelasma is classified as a non-life-threatening disease and does not develop into cancer. But, they act as markers of severe atherosclerosis and are a precursor to a heart attack.
The presence of xanthelasma is not only a cosmetic problem, but also a physical one. Therefore, it is important to know what kind of pathology this is and how to get rid of it and the factors that provoked its formation.
Stages of fight and prevention of xanthelasma
The only reliable way to combat xanthelasma is to eliminate it. Only the doctor will decide which method is preferable based on the specific situation. The laser beam is one of the latest achievements of high-tech medicine. Our clinic is equipped with modern equipment, and the procedure for removing xanthelasma of the eyelids is carried out by experienced professionals. Laser removal is characterized by a minimal risk of relapse, high sterility, low likelihood of injury to adjacent skin and the absence of subsequent inflammation. Contraindications for this highly effective procedure include diabetes, pregnancy, and the presence of dangerous tumor processes.
Stages of the fight against xanthelasma:
- preparation - visiting an ophthalmologist, taking tests, choosing a removal method taking into account the indications;
- destruction of education;
- restoration with the implementation of appropriate appointments and follow-up examinations.
As preventive measures, you need to choose those that are aimed at the normal functioning of the body as a whole.
To prevent xanthelasma you should:
- monitor your weight and achieve its optimal value;
- eat wisely, including fruits, vegetables, foods with beneficial properties in your diet, reduce the consumption of flour, fatty foods, and sweets;
- stabilize your drinking regime, drink at least two liters a day;
- lead a healthy lifestyle, eliminate bad habits, stress, regularly give the body adequate physical activity;
- prevent damage to the skin;
- observe personal hygiene standards;
- strengthen immunity;
- systematically undergo preventive examinations.
Causes
The etiology of the appearance of xanthelasma has not been precisely determined to date. The main reason for the appearance is considered to be lipid metabolism disorders, which manifest themselves in the form of:
- Hyperlipidemia. There is a rapid increase in cholesterol levels to abnormal levels.
- Histocytosis. Accompanied by the proliferation of macrophages, which engulf cells of the immune system. As a result, dysfunctions of biochemical processes develop, which also include an abnormal increase in lipid deposits.
In such conditions, cholesterol is deposited on the walls of blood vessels, internal organs and under the skin. Xanthelasma is accompanied by the accumulation of triacylglycerol, which provokes the development of a tumor.
The causes of the occurrence may not only be of a genetic nature, which is associated with disturbances in the structures of lipoproteins. Also, there are a number of pathologies that can provoke the appearance of xanthelasma. The risk of developing skin tumors increases with:
- Obesity of any degree.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Coronary heart disease.
- Diabetes mellitus of any type.
- Thyroid dysfunction.
- Liver or kidney failure.
- Oncological diseases.
Determining the main cause of the disease provides a positive prognosis for a full recovery and getting rid of tumors.
Xanthelasma: causes, treatment, removal, photos and symptoms
Xanthelasma is a benign type of formation that protrudes above the skin level. It has the appearance of yellowish plaques, the focal location is on the eyelids. Xanthelasma is considered a form of xanthoma, mainly observed in older people.
The disease was first described in 1835 by Dr. Ryer. It was named xanthoma in 1869 by Dr. Smith, translated from Greek as “yellow”, characterized by the formation of yellow plaques.
Causes of xanthelasma plaques
The main reason is an imbalance in lipid metabolism - hyperlipidemia, or histiocytosis, which causes cholesterol deposition on the vascular walls, organs and skin.
With histiocytosis, macrophages multiply and devour cells of the immune system, which leads to various biochemical disorders, for example, an abnormal increase in fat deposits.
With hyperlipidemia, cholesterol levels become abnormally high. Cholesterol exhibits two active forms that perform different functions:
- Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) are useful in removing toxins and heavy metals from the body. Triglycerides, which are part of LDL, which form atherosclerotic plaques, are recognized as dangerous substances.
- High-density lipoproteins (HDL) dissolve cholesterol plaques.
With xanthelasma, there is an accumulation of triglycerides, which, when accumulated, form tumors.
What diseases cause xanthelasma? If the disease is caused by genetic pathologies associated with abnormal lipoprotein structures, the disease can develop not only in adults, but in rare cases even in children.
Xanthelasma manifests itself against the background of concomitant diseases:
- Obesity;
- Atherosclerosis:
- Coronary heart disease or peripheral vascular disease;
- Diabetes;
- Lack or excess of thyroid hormones;
- Alcohol consumption;
- Liver and kidney failure - 80% of cholesterol is produced by the liver and only 20% comes from food;
- Malignant neoplasms.
With a secondary cause, the prognosis for full recovery is more favorable with the obligatory fulfillment of certain conditions.
Forms of the disease
- Diffuse flat. The form is characterized by yellow wen with a soft consistency of various irregular shapes with marked boundaries, mainly on the face, neck, and proximal limbs. Develops in most cases in women with liver pathology.
- Tuberous - characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol nodes into large plaques of 1-5 cm, lumpy in shape, capable of rising above the skin level.
The formations have a denser consistency than flat ones, their color is yellowish, varying from yellow to brown. If other types of xanthelasma do not cause discomfort during evolution, the tuberous form is painful. Localized in the buttocks, elbows, fingers. The corneal region and arch of the orbit are especially susceptible to the appearance of xanthoma. - The eruptive form, in which the formation has a red-yellow tint, up to 7 mm in size, covers the surface of the skin in the form of a granular rash or shows a flat appearance, causing itching.
- The disseminated form affects in 50% of cases the oral mucosa, skin of the upper and lower eyelids, larynx, under the eyes, on the lower and upper eyelids, sclera and cornea of the eyes. On the face it can appear in the form of nodular formations of about 3 mm of a red-brown palette. In the skin tissues, many vessels are filled with fatty deposits.
Xanthelasma of the eyelids has an ICD-10 code of H02.6.
Diagnosis of the disease
In 90% of diagnosed cases, xanthelasma develops asymptomatically, manifesting itself only in the presence of a plaque; the eye does not lose mobility and closes. As a rule, such neoplasms do not become inflamed.
As senile xanthelasma grows, it spreads to the eyelids, bridge of the nose, and chin. The plaque creates a general unaesthetic appearance; in special cases, the disease can affect vision and eyelid mobility.
If the disease progresses, removing xanthelasma will become problematic. In the eye area, the vessels are located very close to the surface of the skin. Xanthelasma cells “fuse” with connective tissue, blood vessels and nerves. When removing a plaque, you can easily damage the vascular wall or nerve.
The appearance of xanthelasma as a systemic disease requires an integrated approach to diagnosis, which includes consultation with specialist doctors: ophthalmologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist.
Biochemical blood test (lipidogram) is the most common and effective diagnosis and monitoring of the course of diseases. The accuracy of the results depends on following these rules.
- The test must be taken on an empty stomach 12 hours before blood sampling.
- For three days, you need a diet: exclude fatty and fried foods from your diet.
- Stop taking dietary supplements and antibiotics.
The analysis is taken by drawing blood from a vein.
Lipidogram norms:
Name Lower indicator Upper indicator
| Total cholesterol content | 3.2 mmol/l | 5.2 mmol/l |
| Triglycerides | 0.14 mmol/l | 1.82 mmol/l |
| HDL | From 1 mmol/l |
With xanthelasma, cholesterol and triglyceride levels are exceeded.
A general blood test determines:
- The degree of body resistance;
- The presence of inflammatory processes;
- Hemoglobin level to rule out anemia;
- Blood sugar.
Diascopy - bleeding of the plaque by squeezing the xanthelasma with a spatula; the study is carried out to identify the color of the neoplasm. The mentioned disease is characterized by a yellow color.
Histology. When removing xanthelasma, it is recommended to take a histological analysis to identify pathological changes.
Treatment of xanthoma
The disease can be treated using conservative methods.
- Sequestrants are prescribed to activate the release of bile acids, which leads to a decrease in cholesterol in the blood.
- Statins work by binding to cholesterol-producing enzymes in the liver.
- Hepatoprotectors ensure restoration of liver cell membranes and protect against destruction.
Drug treatment methods are effective for minimal manifestations of xanthelasma. If the xanthoma is extensive, it cannot be cured without surgery; getting rid of xanthelasma is possible only with the help of surgery. This is dangerous, accompanied by negative consequences, and requires healing.
Therefore, plaque removal is prescribed only for the following indications:
- Inflammatory process of any etiology;
- External change in the appearance of xanthelasma: redness, sharp increase, reproduction;
- Very high cholesterol levels.
Let's look at removal methods in more detail.
Surgical removal
This long-standing method was used back in the middle of the 20th century. To remove a xanthoma, no special equipment is required. The main tool is a surgical scalpel.
An incision is made at the site of the tumor, followed by excision of the xanthelasma. Used to remove multiple xanthomas or when a malignant tumor is suspected.
The edges of the wound are cauterized with electric current. Disadvantages of the surgical method:
- The incision requires stitches, which leave scars. As a result, additional cosmetic surgery is required.
- During the operation, due to the close proximity of blood vessels, bleeding occurs, which leads to the formation of postoperative hematomas.
Laser removal
The difference from the surgical method is that the operation takes place under local anesthesia. This method demonstrates a number of advantages:
- Precise localization of the intervention. Laser devices operate using a beam or carbon dioxide. With the latter, the removal of the skin occurs in layers and painlessly, without damaging healthy tissue, exactly at the location of the plaque.
- Laser removal is a bloodless procedure and does not cause hematomas.
- Sterility reduces the degree of manifestation of inflammatory processes and rapid restoration of the skin. After the procedure, the wounded area is covered with a crust, which disappears within seven days.
- Does not leave any traces of intervention on the skin.
- Minimal risk of relapse.
The disadvantages of the method include the price - this is an expensive operation and is performed in a clinic.
There are contraindications for use:
- Diabetes;
- Malignant formation;
- Epilepsy;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Presence of a pacemaker.
Radio wave method
The radio wave method can be used to remove xanthelasma without contact. Excision is achieved due to the ability of the skin to resist the radiation of high-frequency waves; heating the surface leads to its dehydration and dissection. The radio wave is localized at the end of the device, which maximizes the concentration of the process on painful tissues.
How to quickly get rid of the consequences of surgery
To restore smooth eyelid skin without consequences in the form of scars and other irregularities, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Avoid getting moisture into the affected area.
- Treat the wound after removal with castor oil or calendula tincture.
- To dry the skin, use zinc ointment.
- You cannot remove the dried crust until the tissue is completely regenerated, as this will lead to the formation of scars.
- If inflammation occurs, apply Baneocin ointment, and if signs of suppuration appear, use ichthyol ointment.
- If negative consequences occur during the recovery process, consult a doctor.
Prevention of xanthelasma
Preventive measures are aimed at avoiding relapse of the disease; they include both general recommendations for changing lifestyle and nutrition, as well as medicinal maintenance of the body.
- Balanced diet. Aim for a balance of one part fat, one part protein and four parts carbohydrates.
- Macro nutrition. The diet should include vegetables, fruits, fish, poultry, nuts, fresh herbs, legumes, dairy and fermented milk products.
- Limit consumption of fatty and fried foods.
- Control cholesterol levels by taking a lipid profile every six months.
- Maintain an active lifestyle, spend more time in the fresh air and walk.
- Control body weight and prevent obesity.
- When prescribed by a doctor, use statin drugs to normalize cholesterol, such as Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin, Roxera and others.
Relapse of xanthelasma often occurs in people who do not change their previous lifestyle and do not follow recommendations and preventive measures.
Select the city, desired date, click the “find” button and make an appointment without waiting in line:
Source: https://onko.guru/dobro/ksantelazma.html
Forms
Depending on the etiology and characteristic signs, xanthelasmas are classified into several main types.
Table 1. Forms of xanthelasma.
| Diffuse flat | They are visualized as yellow wen with fuzzy contours and a soft consistency. The main location on the body is the skin of the face, neck, and limbs. |
| Tuberose | It is determined by numerous cholesterol nodes that accumulate into lumpy plaques with a diameter of 1 to 5 cm. They have a dense consistency, flat structure, color from yellow to sandy and are painful. Most often the corneal region and the arch of the orbits are affected. |
| Eruptive | Characterized by formations of red-yellow color, size no more than 7 cm, itchy. Visualized as a grain rash or flat plaques. |
| Disseminated | The eyelids, oral mucosa and sclera are affected. Externally it appears as nodular formations of red-brown color with a diameter of no more than 3 mm. |
Treatment of xanthelasmas depends on their form, which is determined based on the results of a full examination in specialized clinics.
What is xanthelasma (xanthoma) of the eyelids: what does it look like, is it dangerous, can it be cured?
09.09.2018
Some people, especially older people, notice the appearance of a lump on the skin near the eyes, resembling a wart or a hanging mole, only yellow in color. This formation is called xanthelasma of the eyelids and is benign. It does not require special treatment, but when it reaches a large size it can cause discomfort. Xanthelasma can be removed by a surgeon.
What is xanthoma
Xanthelasma, or xanthoma, is a benign flat plaque that appears as a result of the accumulation of fat under the skin. Mostly middle-aged women with impaired fat metabolism are affected. There are several types of xanthelasma:
- single;
- multiple – several formations on one or both eyelids;
- manifestation of xanthomatosis - with this disease, such accumulations of fat are located throughout the body.
Many experts consider xanthelasma and xanthomas a sign of severe atherosclerosis with a high risk of heart attack.
Symptoms of education
Xanthelasma of the eyelids is a lump protruding above the skin. It has an oval shape and a yellowish tint. In appearance it resembles a wart. The xanthoma is soft and painless to the touch.
Xanthomas are usually located on both upper eyelids, in their outer corners. Less commonly, xanthelasmas appear on the lower eyelid. Formations can be single or multiple. If there are a lot of them, they merge, forming a bumpy surface.
The clinical picture of xanthelasmas of the eyelids is asymptomatic. They appear suddenly on the unchanged skin of the eyelids. The growth of the formation is slow and does not give the owner any sensations. The size of xanthomas varies from a pea to a large bean.
The location of the tumor close to the edge of the eyelid can cause irritation of the conjunctiva. There is discomfort when blinking, the eye turns red and begins to water. Xanthomas never develop into malignant tumors. The main complaint of patients when such plaques form is the unaesthetic appearance.
How to treat xanthelasma of the eyelids
There are no specific guidelines for which doctor treats eyelid xanthelasma. There is no specific treatment for these neoplasms. It is important to identify the disease that caused their formation and begin its treatment.
Diet
Since in most cases, neoplasms appear against the background of impaired fat metabolism, the patient is prescribed an appropriate diet. It is recommended to exclude foods that contain a lot of cholesterol from your diet:
- fatty meats and fish;
- butter;
- high fat dairy products;
- nuts, seeds;
- alcohol;
- sweets.
The diet should consist of foods that promote the rapid breakdown of fats and cholesterol. These include:
- dairy products;
- cereal dishes;
- vegetables and fruits;
- greenery.
Be sure to drink at least one and a half liters of clean water per day. Periodically, it is allowed to follow a strict plant-based diet - for a month, then switch to a more expanded diet.
Drug therapy
Medicines are prescribed according to the underlying disease.
- For confirmed atherosclerosis, antihyperlipidemic drugs are indicated. Four main groups are used - statins, fibrates, bile acids, cholestyramine. The drugs are prescribed to be taken for a long time, usually throughout life.
- If a person is diagnosed with diabetes, treatment is prescribed depending on its type. For the first type, different types of insulin are prescribed. In the second type, tableted hypoglycemic drugs are indicated.
- For endocrine disorders, hormonal agents are indicated.
Taking medications does not guarantee the complete disappearance of xanthelasma on the eyelids. They decrease somewhat in volume, but persist even during long-term treatment.
Local treatment is carried out at home. It consists of using some ointments and solutions.
- "Solcoderm" is a cauterizing solution that destroys tumor tissue. It must be used to treat eyelids with great care to avoid developing skin burns.
- Zinc-ichthyol ointment. Has a drying and anti-inflammatory effect. Apply to the tumor in the morning and evening, treatment lasts at least 3 weeks.
- Yellow mercury ointment.
Local agents also do not have a significant effect.
Surgical intervention
Radical removal of xanthelasma from the eyelid is performed surgically. There are several ways to do this:
- peeling fat deposits with a scalpel is the most traumatic operation;
- laser removal – the procedure is carried out quickly, does not cause pain, and does not form a scar;
- cauterization with nitrogen - applicable only for small tumors;
- The radio wave method for removing xanthelasmas is possible for hard-to-reach and multiple xanthomas.
The choice of surgical method depends on the location of the plaque, its size and the patient’s wishes.
Watch the video to see how the tumor is removed with a laser:
Folk remedies
For xanthelasmas of the eyelids, treatment with folk remedies is possible, but it is not highly effective.
- To normalize liver function, a rosehip decoction is prescribed. It is prepared as follows: pour 100 grams of berries with a liter of boiling water and let it brew for an hour. Take 50 ml in the morning. Duration of treatment is at least a month.
- Honey dough. Take an egg and a spoonful of honey. Add flour to make a thick dough. Apply as a compress to the eyelid. Leave for 15 minutes, then rinse with water. The procedure is repeated every other day for two weeks.
- Take equal parts of sour cream, salt and honey. Mix and apply to the eyelid for half an hour. Then wash off with cool water. The procedure is repeated every evening for 14 days.
- Bake the onion until soft, then mash with a fork. The paste is applied to a cotton swab and applied to the eyelid for two hours. The procedure is repeated every evening for ten days.
- Cut a piece of aloe leaf and apply it to the affected eyelid for 10 minutes. The procedure is done every evening for a month.
You can use any folk remedies only if you are not allergic to the constituent components.
Symptoms and external manifestations
Xanthelasma refers to pathological conditions that are signs of xanthomatosis. Neoplasms are most often located in the inner corners of the eyes or on the skin under the organs of vision.
Symptoms at an early stage are hidden. As the disease progresses, it becomes visible as a characteristic compaction that protrudes above the skin level. Initially, the tumors do not cause any pain or physical discomfort. Inside they contain fats, microbes, triglycerides, and dead cells.
The external manifestations of xanthelasma are similar to warts or wen and have:
- Not clear, vague boundaries, but shaped like an oval.
- Large base in the form of a leg.
- The size of the tumor varies from 0.5 to 5 cm.
- Soft structure of liquid consistency.
- The color of the new growths varies from lemon yellow to red-brown.
Xanthelasmas develop slowly. At the initial stage there are no manifestations. Hidden symptoms and the absence of negative progression are the main reasons for untimely visits to a dermatologist.
Symptoms
Xanthomas on the skin associated with the accumulation of fats are clinically divided into several options:
- flat;
- intertriginous;
- palmar;
- tendon;
- tuberose;
- flat eruptive.
Sometimes there is a combination of several types.
Flat
The most common type of formation. Xanthomas are asymptomatic and appear on the skin as soft, velvety, flat, polygonal yellow elements. Most often, a flat xanthoma of the eyelids is observed, at the inner corner of the eye. Sometimes they reach gigantic sizes.
Tuberous (lumpy)
These are firm, painless, red-yellow nodules. Lesions on the skin can be multiple and merging. Such xanthomas usually develop in places of friction and pressure, for example, on the extensor surfaces of the knees, elbows, and buttocks. Sometimes they appear on the skin of the cheeks or the bridge of the nose.
Tendon
Slowly enlarging subcutaneous nodules associated with tendon and ligament tissue. These include gouty tophi, affecting the big toe. Such xanthomas most often occur in the extensor area of the upper limbs and in the Achilles tendon.
Eruptive
Eruptive xanthomas on the skin are localized mainly on the buttocks, shoulders, and extensor surfaces of the limbs. Sometimes the mucous membrane of the mouth and face are affected. The lesions are rashes of red-yellow papules on reddened skin. They are accompanied by itching and sensitivity to the touch.
Xanthomas on the palms look like spots; they can appear on other parts of the body. The palmar fold is most often affected by type 3 dyslipoproteinemia.
In patients with normal blood lipid levels, special disseminated and verrucous forms of xanthomatosis occur.
1. Tendon xanthoma 2. Eruptive xanthoma
Disseminated form
The disseminated form of xanthomatosis is observed mainly in adults and looks like multiple red-yellow tubercles and nodules located in the folds of the skin, as well as numerous xanthelasmas on the eyelids. In diffuse xanthomatosis, the skin is affected in the form of yellow plaques under the eyes, on the neck, upper torso, buttocks and in skin folds. In rare cases, the oral cavity is additionally involved.
Verrucous form
Such xanthomas occur primarily in the oral cavity of adults. These are single asymptomatic lesions. They can also be localized on the forearms, limbs, anogenital area, as well as on the walls of the esophagus, making swallowing difficult.
Xanthelasma
A type of xanthoma. Xanthoma is similar in appearance to a yellow subcutaneous formation that appears on the limbs, buttocks and other areas of the skin, and xanthelasma rises above the skin surface, forming a tumor-like formation, primarily around the eyes.
Diagnostics
If the slightest external signs appear on the skin characteristic of xanthelasma, it is necessary to undergo a consultation with a doctor. First of all, you should visit a dermatologist.
By visual examination, the diagnosis is determined at the first appointment. Diascopy is performed, as a result of which, by bleeding the formation, a clear yellow color is determined, confirming xanthelasma.
If xanthelasmas act as a systemic pathology, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out with the involvement of an ophthalmologist and an endocrinologist.
Laboratory diagnostics allows you to accurately determine the degree of progression of the pathology. During the examination, the following is prescribed:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Histological studies.
- Biochemical blood test - lipid profile.
These tests allow you to study lipid metabolism. With their help, the level of cholesterol in the blood serum and lipoproteins is determined. Taking into account the clinical picture, it may be necessary to differentiate the diagnosis from syringoma, malignant tumors and pseudoxanthoma elasticus.
The number of additional hardware and laboratory examinations depends on the underlying pathology that provoked dysfunction of lipid metabolism with the subsequent development of xanthelasma.
Associated conditions
The presence of skin xanthoma in a patient may indicate the possibility of the following diseases and conditions:
- myocardial infarction, aortic valve pathology, as well as pancreatitis;
- large single flat elements sometimes accompany chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, mastocytoma, and ultraviolet ray damage;
- POEMS syndrome (polyneuropathy, organomegaly, pathology of the endocrine glands, skin changes caused by M protein), systemic sarcoidosis and insufficient number of liver bile ducts;
- primary or secondary hyperlipidemia - an increase in fat content in the blood caused by hereditary diseases or atherosclerosis.
Disseminated xanthomatosis affects various internal organs, and patients experience difficulty swallowing, shortness of breath, and blurred vision. The functioning of the central nervous system and musculoskeletal system is disrupted. Such xanthomatosis is often associated with lymphoproliferative diseases and hematological malignancies, such as leukemia. In addition, these patients have an increased likelihood of oral candidiasis, Budd-Chiari syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and Hand-Schuler-Christian disease.
The verrucous form of xanthomatosis accompanies the following diseases:
- lichen planus;
- Paget's disease;
- epidermal nevus;
- discoid lupus erythematosus;
- pemphigus vulgaris;
- dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa;
- chronic graft-versus-host disease;
- actinic keratosis;
- squamous cell carcinoma;
- congenital developmental defects;
- consequences of PUVA therapy with psoralen or radiation treatment;
- period after bone marrow transplantation.
Treatment
Therapy for xanthelasma is not specific. First of all, it involves treating the underlying disease that provoked dysfunction of fat metabolism.
The therapeutic complex involves taking medications, following a therapeutic diet and using traditional medicine. For aesthetic correction, surgical treatment is prescribed.
Drugs
Drug therapy involves taking the following groups of medications:
- Hormonal.
- Lipotropic.
- Hypocholesterolemic.
- Hypoglycemic.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
Medicines for xanthelasma, used to stabilize lipid metabolism, are prescribed according to indications. Most often in medical practice, the use of insulin, thyroidin, lipoic and thioctic acids, clofibrate and diosponin is noted.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is used as an adjuvant therapy for xanthelasma. A high therapeutic effect is shown by the use of herbal medicines from:
- Corn silks.
- Plantain juice.
- Rose hips.
- Immortelle inflorescences.
- Dandelion rhizomes.
The herbal preparations used have a lipotropic effect and a choleretic effect. Therefore, in the presence of pathologies of biliary diseases, their use is unacceptable.
Therapy methods and the choice of drugs are selected taking into account the form and degree of the pathology, as well as the reasons for its development. Treatment of xanthelasma, and, if necessary, its correction, is prescribed by a doctor.
Treatment of xanthelasma
Growths on the eyelids can be treated either in specialized clinics by removal or using traditional methods. It is worth remembering that if you decide to treat xanthelasma yourself, you must agree with your doctor. Basically, traditional treatment tactics will be aimed at improving metabolism and stabilizing fat metabolism (that is, it will be necessary to neutralize lipid disorders in the body). To do this, it is necessary to stabilize the functioning of the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts. In particular, for home treatment of plaques on the eyelids, you can use the following remedies:
- Birch buds. Here 20 g of raw materials must be brewed in one glass of boiling water. The product is infused for 15-20 minutes, after which it is strained. Take this infusion three times a day, two tablespoons.
- Dandelion. A decoction is made from the root of the plant and then a teaspoon of the prepared product is mixed with a glass of water. Take this remedy three times a day.
- Yarrow. To prepare the healing remedy you need to take 2 tbsp. dry plant and pour a glass of boiling water. The product is infused for about an hour and then strained. The entire volume of the infusion should be divided into four parts and consumed during the day before meals.
- Collection of herbs from rose hips, mint and immortelle. Herbs in equal parts (100 g each) are poured with boiling water (700 ml) and boiled over low heat for 1-2 minutes. After this, the broth is infused for another 3 hours. Drink the product four times a day, 150 ml before meals.
Important: it is worth remembering that it is not often possible to remove xanthelasma at home without removal. Treatment of xanthelasma with folk remedies can be effective only at the initial stage of plaque formation, when it is still very small. Thus, it is possible to stop its growth.
Removal
Surgical treatment of xanthelasma is carried out for cosmetic purposes. Removal is carried out in several ways. Their choice is determined solely by the doctor based on clinical indicators.
Surgical method
The main indication for the use of a surgical method to remove xanthelasma is an overhanging skin fold on the eyelid.
Surgical removal is performed by making an incision followed by excision. To avoid bleeding, the edges of the wound are cauterized with electric current.
Laser
Laser removal of xanthelasma is performed under local anesthesia. The operation is low-traumatic, bloodless, painless and has a low probability of infection.
Laser destruction of cutaneous cholesterol plaques is one-stage. Restoration of skin integrity after surgery occurs within a week.
Electrocoagulation
The essence of the operation is the destruction of xanthelasma tissue using electric current. When removing plaques, infiltration or application anesthesia is used. Under its influence, the xanthelasma is excised, followed by cauterization of the base with an electrode.
The postoperative wound heals immediately; after peeling off the crust, a red spot remains on the eyelid for a period of 1.5 weeks.
Radio wave method
Provides contactless removal of xanthelasma using special equipment. The radio wave method of removal involves exposing the skin to high-frequency waves that dehydrate and dissect its surface.
Cryodestruction
Removal of tumors on the eyelid occurs under the influence of liquid nitrogen at ultra-low temperatures. The cell membrane freezes, followed by the development of cryonecrosis. Cryotherapy of xanthelasma has many advantages over other methods of removing cholesterol plaques on the skin of the organs of vision.
Each method of surgical removal of xanthelasmas has its advantages and disadvantages. The presence of direct indications and the absence of contraindications for a certain type of operation guarantees the success of therapy. It also eliminates the development of relapse and complications.
Xanthelasma of the eyelids
Xanthelasma is a deposit of cholesterol in the white blood cells of the skin, causing yellow plaques to form on the skin's surface.
These are the cutaneous manifestations of lipidosis, a condition in which lipids (molecules that occur naturally in the body include fat-soluble vitamin sterols A, D, E, fats, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides and phospholipids) cluster in skin cells and become visible on the surface.
We recommend reading: Yellow spots on eyelids
There are a number of types of xanthelasmas based on various pathologies. However, the original definition remains unchanged.
Causes
To date, the cause of the occurrence is not entirely clear. Often found in older women for no apparent reason.
Normolipidemic formations occur during normal fat metabolism. Doctors suspect that harmless local immune cell disorders are responsible for their development. This form of cholesterol deposition is considered hereditary.
Hyperlipidemic xanthelasmas occur when there are elevated concentrations of fat in the blood. In children and young people, this may be a sign of a fat metabolism disorder. This form occurs in approximately 50% of patients. At the same time, the blood contains more lipoproteins and cholesterol than healthy people.
Risk group
The following are susceptible to developing the disease:
- persons over 40 years of age;
- women, as they are more prone to pathology;
- persons with high blood pressure;
- obese patients;
- smokers;
- persons of Asian and Mediterranean origin.
Symptoms
Neoplasms occur mainly on the inside of the upper and lower eyelids near the nose. They don't cause pain.
Xanthelasmas are whitish-yellow deposits of cholesterol on the eyelids. The formation is difficult to confuse with other growths. Signs:
- rounded;
- color from whitish to yellow;
- flat, soft;
- usually found on both sides;
- often located symmetrically.
Diagnostics
The characteristic appearance and location of the formation allow the ophthalmologist to make a correct diagnosis. During the initial examination, palpation is performed, followed by serological tests.
In approximately 50 percent of victims, xanthelasmas are caused by a fat metabolism disorder. To determine possible changes, your doctor will order a blood test for diagnosis. At the same time, he will pay special attention to laboratory parameters affecting blood fats.
Important indicators:
- total cholesterol level;
- high density lipoprotein;
- low density lipoprotein.
Determination of fasting lipid levels makes it easy to determine whether xanthelasma is a consequence of hyperlipidemia.
If one or all of the fat levels in the blood are elevated, what is called hyperlipoproteinemia often occurs. It appears as part of other diseases such as diabetes, hypothyroidism or liver and kidney diseases. We are talking about the so-called secondary hyperlipoproteinemia. Additional tests will be needed to determine the cause.
Differential diagnosis is carried out to distinguish the growth from a tumor of the appendageal region. It is important to exclude malignancy by taking a piece of tissue for biomicroscopic examination.
Pharmacy drugs
Removal of xanthelasma is possible with medications. Lipotropic drugs are selected:
- Arachiden;
- Lipamide;
- Linetol.
Herbal pharmaceutical products can also remove white spots. Effective use of ointments - yellow-mercury, zinc-ichthyol, Solcoderm
If atherosclerosis is confirmed, the patient is prescribed statins, bile acids, and fibrates. These medications must be taken throughout your life. If hormonal imbalances are detected in women, steroid medications are prescribed.
Medicines are prescribed to support the liver.
Electrocoagulation
While electrolysis is a fairly successful procedure for scar reduction and hair removal, it is not advisable to use it for xanthelasma removal. Most patients claim that the use of electrolysis is ineffective.
Electrolysis is created when electrical currents pass through a solution or liquid made of ions. This chemical decomposition removes the roots using an electrical current.
The main purpose of use is to damage the root. Exposure to electric current has one drawback - a high probability of relapse. Recovery takes 1.5–2 weeks.
Cryodestruction
This is the use of low temperatures to remove diseased or foreign cells and tissues. The procedure involves the use of liquid nitrogen. It damages the microvascular circulation, causing hemorrhagic necrosis and secondary anoxia. In theory, this will kill and damage the abnormal cells.
The problem is that there is resistance to cholesterol-laden cells, causing them to reappear more quickly and more quickly.
Because liquid nitrogen kills nearby healthy cells and cell walls of the growth, xanthelasma attaches to neighboring skin cells. In addition, cryodestruction can lead to hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
Surgical excision
If the white-yellowish deposits do not go away with drug treatment or recur, surgical excision is performed.
When removing xanthelasma using a scalpel, the doctor carefully cuts out the affected area. The skin remains red for a long time. Since xanthelasmas form in close proximity to the eyes, doctors work especially carefully. Sutures are removed seven days after surgery.
If self-absorbable suture material is used, suture removal is not necessary. In addition, doctors recommend giving up alcohol and cigarettes for two weeks after the procedure, because nicotine reduces blood circulation to organs and delays wound healing.
Laser removal
Usually treatment is carried out using a laser device, as the best result is achieved. Short laser pulses remove the top layers of skin and remove xanthelasmas. Using a laser, the doctor treats only the affected area.
This method has the least side effects because, unlike the alternative scalpel method, the laser does little to no damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Folk recipes
The use of folk remedies is recommended in conjunction with medications. Possible ways to remove formation at home:
- Garlic. It has immunomodulatory properties and stimulates the protection of the cardiovascular system. In various tests, 20% of patients had their cholesterol levels reduced when using garlic supplements. Consuming garlic will not get rid of xanthelasma, but it will slow down the growth of plaques. Some recommend rubbing a clove of garlic into the plaques to achieve successful removal of xanthelasma.
- Castor oil has antibacterial properties. Research shows that regular oral consumption of castor oil reduces cholesterol levels. May slow down the downward migration of xanthelasma. Using castor oil to remove xanthelasma may cause adverse effects, castor oil is a monounsaturated fatty acid, a source of ricinoleic acid. High triglyceride levels are one of the reasons for the spread of xanthelasma. Therefore, consume in moderation.
- Honey compress - mix an egg, a spoonful of flour and honey. Apply the product to the formation and leave for a while. Use up to 4 times a day.
- Mix the ground wheat grains with olive oil until it becomes a paste. Apply the mixture for 20 minutes. Rinse off with warm water.
Yellow spots will disappear only with the systematic use of folk remedies. To normalize cholesterol, use propolis tincture. Take the medicine with lunch for several weeks.
Complications
Possible complications include:
- relapse of the disease;
- bleeding from the wound;
- scar formation in place after the suture.
We recommend reading: Red spots under the eyes
Forecast
40% of patients come to the hospital with relapse of the disease after primary surgical excision, 60% after secondary excision. A possible cause may be insufficiently deep excisions.
Prevention
Xanthelasmas that form for no apparent reason cannot be prevented. If formations occur together with another disease, then preventive measures can be taken to prevent relapse of the pathology. Since the accumulation of cholesterol is caused by increased accumulation of fats in the blood, it is possible to avoid the formation of xanthoma or its recurrence by the following:
- Proper nutrition. Eat a balanced and low-fat diet. Eat 5 servings of fruits and vegetables daily; whole grains, legumes and nuts provide plenty of vitamins, nutrients and healthy fats. From 2 fish dishes per week and low-fat dairy products, vegetable fats such as olive oil, a small amount of meat complement the diet. Foods and drinks with a lot of sugar and alcohol negatively affect blood fats. Try to reduce them.
- Physical activity. 30 minutes of exercise a day is enough to prevent fat accumulation. For example, use the stairs instead of the elevator, ride a bicycle instead of a car, or study using any video at home.
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 2 4.50
Source: https://proglazki.ru/bolezni/ksantelazma-vek/
The role of nutrition in treatment
Since the main cause of xanthelasma is dysfunction of lipid metabolism, treatment of neoplasms without correction of the daily menu is impossible.
The role of nutrition in the treatment of xanthelasma is very important. The stabilization of metabolic processes in the body depends on a properly selected diet. Eliminating fatty foods helps maintain cholesterol levels in the body.
Consumption of food products of various groups has an auxiliary effect on lyotropic drugs, which are the basis of drug therapy for xanthelasma.
Diagnosis of xanthomatosis
The doctor studies the state of lipid metabolism to identify primary and secondary hyperlipidemia. Blood tests are used for cholesterol, low- and high-density lipoproteins, and triglycerides. Liver and kidney function tests are performed.
To confirm xanthomatosis of the Achilles tendon, ultrasound and MRI are used. For disseminated xanthomatosis, positron emission computed tomography can be used to identify the severity of the disease and assess the effectiveness of treatment.
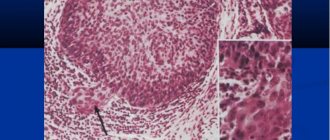
In doubtful cases, a histological examination of tissue obtained from these formations is prescribed. In this case, vacuolated or foamy macrophages are determined - cells that have absorbed fat, which dissolved during processing of the biopsy sample.
Eruptive foci may contain inflammatory infiltrates; verrucous, tendinous and tuberous - connective tissue.
How dangerous is the disease?
Xanthelasmas do not pose a serious threat to health. Neoplasms do not develop into malignant ones. But, a strong proliferation of plaques can provoke the inclusion of blood vessels in their structure.
Subsequently, this threatens the development of serious complications during their removal. This is the only thing that makes xanthelasma dangerous.
Possible complications
Neglect of treatment and non-compliance with medical prescriptions threatens the development of negative consequences. Among them, experts highlight:
- Hypopigmentation.
- Eversion of the century.
- Sagging nasolabial folds.
- Infection of the operated area.
Complications of xanthelasma most often develop in the presence of risk factors. You can avoid their occurrence if you follow all doctor’s prescriptions.
Symptoms of the disease
Formations can appear on any part of the skin and take on a varied appearance. Often, at an early stage they are confused with manifestations of acne, furunculosis and dermatoses of various etiologies. When deposits appear, they may initially be red, and then a yellow solid growth appears. They can be of different sizes and vary in color from white to brown.
xanthelasma in the photo
Depending on the stage of the metabolic disorder, the speed of appearance, appearance and localization depend. Depending on the source of hyperlipidemia, the disease is divided into primary and secondary.
Primary xanthomatosis, in turn, is divided into five types with various disorders of the elements of absorption and breakdown of fats:
- Pathological excess of the norm of triglycerides and chylomicrons in the blood serum. In this case, the appearance of eruptive xanthomas is observed in the area of the joints and buttocks. May appear in children and disappear when consuming foods containing cholesterol is regulated.
- It is observed with high levels of lipoproteins and cholesterol. Deposits appear in the tendon area.
- Beta lipoproteins are found in the blood plasma in combination with increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides. In this case, yellow papules appear in the area of the feet and on the surfaces of the palms.
- With normal cholesterol levels, there is an increased level of triglycerides of reduced viscosity and lipoproteins.
- It is observed with a decrease in the density of chylomicrons and lipoproteins with an increased content of triglycerides.
Summarizing the above reasons, we can conclude that hyperlipidemia can manifest itself depending on various factors, ranging from age, heredity, eating habits and much more.
As for secondary sources, the main factors influencing the course of the disease are the severity and methods of treatment of concomitant chronic pathologies.