Weakness in a muscle group or one individual muscle is called paresis. This condition is caused by certain factors and internal pathologies of systems or organs. There are many reasons for the development.
The disease is not considered independent, since it is a consequence, a reflection of existing pathologies. To eliminate paresis, the main treatment is aimed at identifying and correcting the main cause of the existing disease.
Depending on the location, several groups and forms of paresis are distinguished. Diagnosis requires examination of the entire body.
Attention! If treatment is not treated in a timely manner, serious complications develop, the consequences leading to a complete loss of mobility and disability of the person.
This condition can develop at any age, in both adults and children. However, people in middle and older age are more likely to get sick.
Description
Paresis is a decrease in muscle strength.
This condition is a consequence of various diseases and does not depend on belonging to a particular gender, so we can say that it occurs with equal frequency among both women and men. The age range is also different and depends on the cause of paresis. A decrease in muscle strength leads to a decrease in working capacity and the inability to cope independently in everyday life, therefore the development of paresis is a serious social problem and requires timely provision of medical care.
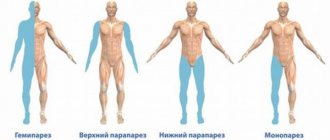
Based on the area of the body in which paresis occurs, it is customary to distinguish the following types:
- monoparesis – symptoms appear on only one arm or leg;
- paraparesis – signs of paresis are present on both parts of the body, which are located symmetrically in relation to each other. With paresis of the arms it is called upper, with paresis of the legs - lower;
- hemiparesis – paresis affects one half of the body;
- tetraparesis - all limbs are affected.
Depending on the level of damage to the nervous system, there are two types of paresis:
- Central (damage is localized at the level of the brain and spinal cord);
- Peripheral (peripheral nerves are damaged).
The main causes of central paresis:
- stroke;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- spinal cord injuries;
- tumors of the brain and spinal cord;
- intervertebral hernia;
- multiple sclerosis;
- amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS);
- cerebral palsy.
Among the causes of peripheral paresis are the following:
- radiculitis;
- demyelinating diseases of the nervous system;
- peripheral nerve injuries;
- compression of nerves, so-called “tunnel syndromes”;
- nerve damage due to connective tissue diseases and vasculitis;
- various poisonings, including alcohol.
Paresis of the oculomotor nerve and abducens nerve: treatment in Moscow
The main method of treatment for paresis of the oculomotor and abducens nerve is the elimination of the disease that caused it. The Yusupov Hospital provides comprehensive treatment for this pathology, which helps eliminate the underlying disease and its consequences. Before prescribing therapy, the patient undergoes a thorough examination, which will help identify the underlying disease and the extent of nerve damage. At the Yusupov Hospital, diagnostics are performed using the latest high-precision equipment, which allows us to determine the cause of the disease even in the most difficult cases. After making a diagnosis and determining the condition of the patient’s body, the doctor draws up the most optimal treatment strategy.
Complex treatment of paresis of the oculomotor and abducens nerve will include drug therapy (drugs are selected depending on the type of underlying disease) and rehabilitation. The course of physiotherapy and rehabilitation is carried out in a specialized center at the Yusupov Hospital, where experienced specialists work in the field of restoring lost functions. Without a course of rehabilitation, paresis of the oculomotor and abducens nerves may resolve within 2-3 months after getting rid of the underlying disease. A rehabilitation course at the Yusupov Hospital allows you to speed up the process of restoring lost functions, contributes to the effective elimination of the consequences of the disease, the patient’s speedy recovery and return to a full life.
You can make an appointment with neurologists, rehabilitation specialists, physiotherapists and other clinic specialists, get information about the work of the neurology clinic, rehabilitation, or clarify other questions of interest by calling the Yusupov Hospital.
Forecast
Paralysis of the arms with timely treatment usually has a favorable prognosis. With the right approach, hand mobility, sensitivity and mobility in the paralyzed hand are gradually restored.
Recovery takes quite a long time - from several months to several years, but the desire and perseverance of the patient himself, as well as the support of loved ones, significantly improves the effect of treatment and promotes a speedy recovery.
Arm paralysis is a serious disorder in the functioning of the body, which not only leads to loss of arm mobility, but also causes a number of psychological problems, so the pathology requires complex treatment and support from others.
- How to treat a pinched nerve in the hand
Causes of limb paresis
The causes of limb paresis include the development of an acute disorder of cerebral or spinal circulation (stroke), including hemorrhage in the brain or spinal cord.
In addition, paresis of the limbs can result from:
- development of brain and spinal cord tumors;
- suffering from brain and spinal cord injuries;
- the occurrence of an abscess (ulcer) of the brain and spinal cord;
- development of inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) or spinal cord (myelitis);
- the presence of demyelinating diseases, accompanied by the breakdown of myelin (a protein that ensures rapid transmission of nerve impulses along the fibers). For example, the presence of multiple sclerosis (a disease accompanied by the formation of many small foci of demyelination in the brain and cerebellum), multiple encephalomyelitis (a disease presumably of infectious origin, with the formation of many foci of demyelination in the brain and cerebellum);
- transfer of poisoning with alcohol, industrial poisons, salts of heavy metals, nerve poisons;
- the presence of immune-inflammatory diseases, for example, Guillain-Barré syndrome, manifested by the absence of reflexes, decreased muscle strength and breathing disorders (weakness of the respiratory muscles);
- identification of myasthenia gravis - a disease characterized by pathological muscle fatigue, while repeated movements increase muscle weakness, which partially or completely disappears after rest;
- the development of botulism, a disease associated with poisoning with botulinum toxin, which is produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Manifestations of this disease include respiratory failure, slurred speech, ptosis (drooping) of the upper eyelid, diarrhea and abdominal pain;
- the occurrence of myopathies - diseases associated with the presence of congenital or acquired metabolic disorders in the muscles;
- detection of epilepsy - a disease characterized by the presence of an epileptogenic focus in the brain, which spontaneously periodically generates an electrical discharge, which disrupts the functioning of the brain;
- the presence of diseases of motor neurons (nerve cells through which muscle movement is ensured): for example, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, spinal muscular atrophy.
Varieties
Clinicians distinguish three types of trigeminal nerve paresis:
- peripheral. This is the type that is diagnosed most often. It can appear in both an adult and a child. The first symptom of peripheral paresis is severe pain behind the ears. As a rule, it appears on one side of the head. If you palpate the muscle structures at this time, you can identify their weakness. The peripheral form of the disease is usually a consequence of the progression of inflammatory processes that provoke swelling of the nerve fiber. As a result, nerve impulses sent by the brain cannot fully pass through the face. In the medical literature, peripheral paralysis is also called Bell's palsy;
- central. This form of the disease is diagnosed somewhat less frequently than the peripheral one. It is very severe and difficult to treat. It can develop in both adults and children. With central paresis, atrophy of the muscle structures on the face is observed, as a result of which everything that is localized below the nose sags. The pathological process does not affect the forehead and visual apparatus. It is noteworthy that as a result of this the patient does not lose his ability to distinguish taste. During palpation, it can be noted that the muscles are under strong tension. Central paresis does not always manifest itself unilaterally. Bilateral damage is also possible. The main reason for the progression of the disease is damage to neurons located in the brain;
- congenital. Trigeminal nerve palsy in newborns is rarely diagnosed. If the pathology is mild or moderate in severity, then doctors prescribe massage and gymnastics for the child. Massage of the facial area will help normalize the functioning of the affected nerve fiber, and also normalize blood circulation in this area. In severe cases, massage is not an effective treatment method, so doctors resort to surgical intervention. Only this method of treatment will restore innervation to the facial area.
Diagnosis of arm paralysis
Diagnosis of arm paralysis is based on the patient's history and examination. With complete paralysis, the upper limb hangs down freely, the elbow joint is extended, and the fingers are bent. There is no motor activity.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe certain tests:
- general blood analysis;
- blood chemistry;
- general urine analysis;
- cerebrospinal fluid examination.
Instrumental diagnostics may include:
- EMG – electromyography – a technique for studying the bioelectric potentials of the neuromuscular system;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- study of the innervation of peripheral nerve fibers.
[35], [36], [37]
Method for differential diagnosis of paresis and paralysis of the quadriceps femoris muscle
The invention relates to medicine, namely to neurology, physical therapy and rehabilitation medicine, and can be used in the timely diagnosis of paresis and paralysis of the quadriceps femoris muscle.
There is a known method for diagnosing paresis of the lower limb, the so-called “Lower Mingazzini-Barre test”, during which, if the patient lying on his stomach bends his legs and tries to hold them at an angle of 45-90°, then on the side of the hemiparesis the leg soon begins to slowly fall. Another option for conducting a test is also possible, in which the patient, lying on his back, bends his legs at the hip and knee joints; if after some time one of the lower limbs begins to fall onto the couch, then paresis is diagnosed on this limb [1].
One of the disadvantages of this method is that the technique allows you to determine the presence of paresis of a group of muscles of the lower limb and does not make it possible to study the condition of a specific muscle separately.
Due to the lack of a comparative analysis of muscle movement before extension and during the moments of extension, abduction and adduction of the limb, there may be false negative diagnostic results and ineffective treatment.
The disadvantages include the lack of quantitative indicators in the method, which reduces the information content of this technique.
There is a known method for assessing the condition of the quadriceps femoris muscle (No. 2058750, class A61B 8/00), according to which ultrasound examination is carried out on a device operating in real time, using sensors with a power of 5-10 MHz. The results are viewed on the display, the image is recorded on thermal paper.
In strictly symmetrical areas, the diseased and healthy limbs are examined in the same mode.
By comparing the most informative indicators of echograms, the thickness of the anterior muscle group in symmetrical areas and (or) the echo density of muscle tissue according to histograms, the difference in these indicators on the diseased and healthy limbs is determined, and the possible result of treatment is predicted based on the magnitude of these indicators.
Using this method, it is known that a decrease in thickness in symmetrical areas of more than 5 mm is considered an unfavorable prognosis and an increase in echo density in symmetrical areas of more than 60% is considered an unfavorable prognosis.
The disadvantage of this known method is that the description of the technique does not indicate the specific location of the ultrasound examination when assessing the condition of the quadriceps femoris muscle.
The method is not intended for diagnosing paresis and paralysis of the quadriceps femoris muscle, since topical pathology can be at different levels that are not specified in the patent.
Also, this method does not allow diagnosing a specific pathology, for example, paresis or paralysis, due to the lack of differential criteria; in connection with the above, treatment can be either useless or ineffective [2].
The objective of the claimed invention is to increase the accuracy of differential diagnosis of paresis and paralysis.
The problem is solved by the fact that according to the method of differential diagnosis of paresis and paralysis of the quadriceps femoris muscle by ultrasound examination of the quadriceps femoris muscle in an extended state, including additional ultrasound in the lower third of the thigh before extension and at the moment of extension of the limb and in the upper third of the thigh at the moments of abduction and adduction of the limb, when visualizing on the screen minimal movements of the three heads of the muscle, in relation to the straight head in the lower third and (or) in the presence of movements of the lateral head in relation to the straight head in the upper third of the thigh, the presence of paresis of the quadriceps femoris muscle is considered proven, and in the absence movements of the heads in the upper and lower thirds of the thigh are diagnosed with paralysis of the quadriceps femoris muscle.
The claimed diagnostic method, based on ultrasound, makes it possible to study individual anatomical variability in real time, makes it possible to visualize the motor activity of the heads of the quadriceps femoris muscle relative to each other and makes it possible to differentiate the phenomena of paresis and paralysis. The undoubted advantage of the claimed diagnostic method is to increase the diagnostic accuracy by indicating the specific motor activity of one or another head of the quadriceps femoris muscle relative to each other. The advantage of the claimed method is also that it is non-invasive and low-traumatic, and has no contraindications. Also, an indisputable advantage of the claimed method is the greater accessibility of ultrasound diagnostics relative to EMG, since EMG is a rather complex and intensive technique. Drawing up a conclusion and recording the results is one of the techniques that facilitates data analysis [3]. Thanks to timely and accurate diagnosis, paresis or paralysis of the quadriceps femoris muscle, it is possible to significantly increase the effectiveness of treatment and reduce its time, and therefore financial costs.
The method is carried out as follows.
To determine the condition of the quadriceps femoris muscle, an ultrasound examination is performed on it using a device operating in real time, using sensors with a power of 5-10 MHz. The results of the study are observed on the display screen, and the image with the corresponding areas of the thigh is recorded on thermal paper.
The examination of the diseased limb is performed in the same manner.
In this case, the sensor is installed in a transverse position along the anterior surface of the thigh in the lower third (in the lower third of the thigh, all four muscles form a common tendon, which is attached to the tibial tuberosity) and the heads of the quadriceps femoris are examined: rectus, medial, lateral and intermediate heads of the quadriceps muscle . Next, the lower limb is extended at the knee joint and the movement of the head of the rectus femoris muscle relative to the other heads is determined. Then the sensor is placed on the upper third of the thigh on the anterior and anterolateral surface. The movement of the direct head in relation to the lateral head is assessed. In the absence of pronounced changes in the movement of the heads of the quadriceps femoris muscle, paralysis of the quadriceps femoris muscle is diagnosed. If minimal movement is detected in the upper and (or) lower third of the thigh, paresis of the quadriceps femoris muscle is diagnosed.
Source: https://edrid.ru/rid/218.016.53b6.html
Forms
Paralysis can be central (spastic) or peripheral (flaccid).
The central form of paralysis occurs due to a malfunction of the motor central nerve cells. With this type of paralysis, deep reflexes intensify, hypertonicity occurs and those reflexes appear that should not normally exist (for example, the Babinsky reflex, Rossolimo, etc.).
The flaccid form of paralysis is a consequence of damage to peripheral motor nerve cells. This paralysis is characterized by a decrease or loss of reflexes, hypotonicity, and atrophy. Sometimes the condition is aggravated by muscle twitching.
Paralysis in most cases occurs due to severe damage to parts of the nervous system. Only sometimes the disease is associated with functional problems. Most often, this is the result of damage to certain areas responsible for movement, which leads to the appearance of:
- monoparalysis or monoparesis (paralysis of one arm);
- paraparalysis or paraparesis (damage to both hands);
- hemiplegia (damages to the arms and legs on the left or right);
- triplegia (damage to three limbs);
- tetraplegia (affects all arms and legs).
In this case, paralysis can affect the entire limb, or only its distal or proximal part.
[22], [23], [24], [25], [26], [27]
Complications
In case of untimely or incomplete therapy, the consequences may be as follows:
- irreversible damage to the nerve fiber;
- improper nerve restoration;
- complete or partial blindness.
What to do?
If you think you have Facial Nerve Paresis
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: a neurologist, an otorhinolaryngologist.
Source
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Causes of arm paralysis
Paralysis of the arms can occur due to injuries, encephalomyelitis, infectious diseases (inflammation of the meninges, tuberculosis, viral encephalitis, polio), metabolic disorders, diseases of the vascular system, cancer, severe poisoning.
Hands can be paralyzed due to congenital or hereditary diseases of the central nervous system.
Among the toxic causes: deficiency of vitamins B1, B6, PP, alcoholic polyneuropathy, poisoning with salts of heavy metals.
In some cases, paralysis occurs after injuries or fractures that damage the motor conduction center.
Paralysis often occurs in mentally ill people.
[6], [7], [8]
Pathogenesis
Paralysis is divided into spastic and peripheral.
- Arm bandages for a fracture: splints and plastic casts for the shoulder joint and hand
With spastic paralysis, the central neurons responsible for the motor functions of the hand are affected, which leads to pathological reflexes, muscle tone, and increased tendon and periosteal reflexes.
In peripheral, peripheral neurons are affected; in this case, tendon and periosteal reflexes are completely absent, muscle tone is weakened.
Most often, paralysis of the arms is associated with peripheral lesions; central paralysis (transient), which is caused by circulatory disorders in the brain due to hypertension or cerebral atherosclerosis, and convulsive epileptic seizures, is extremely rare. Peripheral damage develops due to damage to the nerves of the brachial plexus or the 5th and 6th cervical vertebrae (usually temporary).
If the arm is paralyzed, it is impossible to raise or lower the arm, and the mobility of the elbow joint is limited.
The basis of the pathology, according to experts, is a neurological disorder due to a blow to the neck or shoulder (possibly during exercise, wrestling, falling, etc.).
Paralysis of the upper limbs can develop against the background of tick-borne encephalitis, when paralysis of the cervical muscles, shoulder girdle, and proximal arms occurs during fever.
Treatment of neuropathy
Treatment of neuropathy depends on the reasons that led to its development. Basically, treatment comes down to eliminating the underlying disease. This can be either drug therapy or surgery. At the same time, the symptoms of neuropathy are eliminated, namely the elimination of pain.
Medicines to relieve pain symptoms due to neuropathy
| A drug | Mechanism of action | Mode of application |
| Carbamazepine (trade names Finlepsin, Timonil, Tegretol) | Reduces the intensity of attacks and also prevents new attacks. It is the drug of choice for trigeminal neuropathy. | The frequency of taking the drug per day depends on the form of the drug. Long-acting forms, which last 12 hours, are taken twice a day. If the daily dose is 300 mg, then it is divided into two doses of 150 mg. The usual forms of the drug, which last for 8 hours, are taken 3 times a day. The daily dose of 300 mg is divided into 100 mg three times a day. |
| Gabapentin (trade names Catena, Tebantin, Convalis) | Has a strong analgesic effect. Gabapentin is particularly effective for postherpetic neuropathies. | For postherpetic neuropathy, the drug should be taken according to the following regimen:
|
| Meloxicam (trade names Recox, Amelotex) | Blocks the synthesis of prostaglandins and other pain mediators, thus eliminating pain. Also has an anti-inflammatory effect. | One to two tablets per day, one hour after eating. The maximum daily dose is 15 mg, which is equivalent to two 7.5 mg tablets or one 15 mg tablet. |
| Baclofen (trade name Baclosan) | Relaxes muscles and relieves muscle spasms. Reduces the excitability of nerve fibers, which leads to an analgesic effect. | The drug is taken according to the following regimen:
The optimal therapeutic dose is from 30 to 75 mg per day. |
| Dexketoprofen (trade names Dexalgin, Flamadex) | Has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. | The dose of the drug is set individually based on the severity of the pain syndrome. On average, it is 15–25 mg three times a day. The maximum dose is 75 mg per day. |
In parallel with pain relief, vitamin therapy is carried out, drugs are prescribed that relax muscles and improve blood circulation.
Medicines to treat neuropathy
| A drug | Mechanism of action | Mode of application |
| Milgamma | Contains vitamins B1, B6 and B12, which act as coenzymes in nervous tissue. They reduce the processes of degeneration and destruction of nerve fibers and promote the restoration of nerve fibers. | In the first 10 days, 2 ml of the drug (one ampoule) is injected deep into the muscle once a day. The drug is then administered every other day or two for another 20 days. |
| Neurovitan | Contains vitamins B2, B6, B12, as well as octothiamine (long-acting vitamin B1). Participates in the energy metabolism of nerve fiber. | It is recommended to take 2 tablets twice a day for a month. The maximum daily dose is 4 tablets. |
| Mydocalm | Relaxes muscles, relieving painful spasms. | In the first days, 50 mg twice a day, then 100 mg twice a day. The dose of the drug can be increased to 150 mg three times a day. |
| Bendazole (trade name Dibazol) | Dilates blood vessels and improves blood circulation in nervous tissue. It also relieves muscle spasms, preventing the development of contractures. | In the first 5 days, 50 mg per day. In the next 5 days, 50 mg every other day. The general course of treatment is 10 days. |
| Physostigmine | Improves neuromuscular transmission. | 0.5 ml of a 0.1 percent solution is injected subcutaneously. |
| Biperiden (trade name Akineton) | Relieves muscle tension and eliminates spasms. | It is recommended to administer 5 mg of the drug (1 ml of solution) intramuscularly or intravenously. |
Treatment of diseases causing neuropathy
Endocrine pathologies
Diabetic neuropathy is most often observed in this category of diseases. In order to prevent the progression of neuropathy, it is recommended to maintain glucose levels at certain concentrations. For this purpose, hypoglycemic agents are prescribed.
Antihyperglycemic medications are:
- sulfonylurea drugs – glibenclamide (or maninil), glipizide;
- biguanides – metformin (trade names metfogamma, glucophage);
Symptoms of arm paralysis
The first signs of incipient arm paralysis are a limitation in the amplitude of voluntary movement and the appearance of weakness. Weakness in the limb originates from the wrist, gradually spreading to the proximal muscles. The simplest way to determine increasing paresis is to shake hands.
- Paralysis of the left arm is a common phenomenon that accompanies cerebrovascular disease, cerebral atherosclerosis, and hypertension. In this case, paralysis of the upper limb can occur simultaneously with damage to the lower limb, as well as with paresis of the hypoglossal and facial nerve.
- Paralysis of the right arm can be a consequence of a dislocation of the shoulder joint, damage to the plexus of the shoulder. The patient loses the ability to move the limb to the side and lift it. Movement in the elbow joint is extremely limited or absent altogether.
- Paralysis of the fingers occurs when the nerve in the middle part of the shoulder is damaged. The most common manifestation of finger paralysis is weakness of the hand and lack of motor activity in the phalanges. In some cases, there is a change in the sensitivity of the back of the thumb.
- Partial arm paralysis is a condition where the strength and range of motion in the joints is relatively preserved. To determine partial paralysis, the Barre test is used: the patient is asked to extend his arms in front of him and hold them this way for as long as possible. If paresis or partial paralysis is present, the limbs immediately drop.
- Obstetric arm paralysis is the immobilization of the upper limb in a newly born child. This condition is usually caused by damage to the shoulder or nerve endings during labor.
Degrees
Doctors divide the severity of trigeminal nerve paresis into three degrees:
- light. In this case, the symptoms are mild. A slight distortion of the mouth may occur on the side where the lesion is localized. A sick person must make an effort to frown or close his eyes;
- average. A characteristic symptom is lagophthalmos. A person can practically not move the muscles in the upper part of the face. If you ask him to move his lips or puff out his cheeks, he will not be able to do this;
- heavy. The asymmetry of the face is very pronounced. Characteristic symptoms are that the mouth is severely distorted, the eye on the affected side practically cannot close.