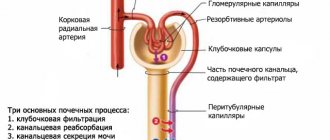
Problems with the genitourinary system can cause great harm to the entire body. Ureterocele disease occurs frequently in women and men, and is most often caused by congenital pathology. The disease is characterized by disruption of the proper functioning of the ureter due to a narrowed canal. With a ureterocele, a cyst-shaped sac appears that resembles a hernia. Urinary retention and inflammatory processes in the kidneys occur.
Classification
In order to prescribe the necessary and most appropriate treatment, it is necessary to accurately determine the type of ureterocele and the exact location of the disease. Adhering to the basic classification, the attending physician records the specific type of disease in the ureter. Based on etiological characteristics, the disease is divided into primary (congenital) and secondary (acquired). The most common is primary ureterocele, which occurs due to abnormal intrauterine development of the ureter. Congenital disease has three degrees of complexity:
- 1st degree. In this case, there is a slight dilatation in the ureter within the vesicular section. The functions of the genitourinary system are normal.
- 2nd degree. The disease makes itself felt, the first symptoms appear as the size of the tumor grows. The pathology affects the functioning of the genitourinary system and kidneys.
- 3rd degree. The bladder becomes significant in size, and kidney dysfunction increases.
Ureteroceles are also classified according to their location. There is unilateral and bilateral (two-sided) disease. According to localization, the pathology can be simple, prolapsing and ectopic. In the first case, the tumor occurs in a normal ureter. With the prolapsing (prolapsed) form in girls, a dark purple formation covered with mucus is noticed in the urethra. Guys experience acute urinary retention. The reason for this is a cyst that has fallen into the prostatic urethra. An ectoscopic appearance occurs when the structure of the ureter is abnormal. A ureterocele prolapses into the urethra, the vestibule of the vagina.
Treatment methods
The choice of treatment tactics depends on the type of pathology and its effect on the functioning of the entire urinary system. In cases where the patient’s condition allows surgical intervention to be avoided, the doctor prescribes conservative therapy:
- courses of antibacterial drugs to suppress the activity of pathological microflora;
- effective treatment of concomitant arterial hypertension;
- relief of symptoms of intoxication;
- vitamin and mineral preparations that replenish the deficiency of certain microelements and increase the body’s resistance and stability;
- diet therapy, with limited consumption of salt, fatty and spicy foods, animal protein; Recommended foods for consumption: vegetables, fruits, cereals, herbs.
In those clinical cases where conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment methods are resorted to:
- Installation of a nephrostomy involves inserting a special tube into the kidney from the back, through which urine will be transported. The operation is performed under X-ray or ultrasound guidance.
- A plastic surgery of the ureteropelvic region, during which the stenotic ureter is expanded at the site of its attachment to the renal pelvis.
- Plastic surgery of different parts of the ureter in case of their narrowing or the presence of other pathological changes.
- Stenting is carried out by inserting a thin plastic tube into the lumen of the ureter through the urethra and bladder.
- Transurethral excision of ureterocele - the intervention is performed through the cavity of the bladder using a special instrument equipped with a mini video camera.
- An operation to replace the ureter with intestinal tissue.
- Neoureterocystoanastomosis - involves the surgical formation of a new ureteral orifice in cases where there is congenital ectopia or a ureterocele has formed that bulges into the cavity of the bladder.
Ureterocele: features in men and women
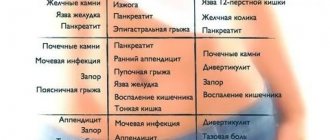
Pathology in the ureters manifests itself differently in women and men. In the female half of the population, the disease is noticed twice as often, especially in childhood. In this case, the cyst prolapses during urination. The formation is dark red in color and covered with mucus. This does not happen every time you go to the toilet; the prolapsed formation is pushed inward on its own. When there are disorders in the genitourinary system in men, the cystic formation penetrates into the prostate area. But this is only in rare cases; most often the disease is accompanied by pain in the lumbar region and urinary retention.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the size of the protrusion. A small ureterocele does not manifest itself in any way or causes nonspecific, mildly expressed symptoms.
Main symptoms:
- pain, discomfort in the lumbar region;
- dysuric phenomena (impaired urination);
- the appearance of blood in the urine.
Urination is impaired due to a reflex reaction.
The most common manifestations of dysuria with ureterocele include:
- involuntary loss of urine;
- frequent bowel movements;
- difficulty urinating, feeling of internal obstruction;
- complete urinary retention (for one day or more).
Dysuria leads to the development of so-called paradoxical ischuria, when the patient simultaneously has incontinence and periodic urinary retention.
If a child suffers from enuresis (urinary incontinence), when diagnosing its cause, it is necessary to exclude ureterocele
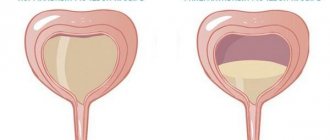
With a significant size of the ureterocele in women and girls, the mucous membrane may prolapse outward in the urethral area. This is due to the fact that the female urethra is much shorter than the male urethra. With this complication, it can be detected by visual examination of the external urethral opening. If the ureterocele completely fills the lumen, the bladder becomes enlarged, pain appears, and urination is severely impaired. Acute urinary retention is possible.
If the disease is not diagnosed in time, the following may occur:
- dilation of the ureter and renal pelvis (hydronephrosis) with deterioration in functioning, and subsequently with loss of viability;
- salt deposition and stone formation in the urinary tract;
- trauma to the tissue of the ureter and bladder.
- inflammatory processes of the urinary system.
Most often, inflammation develops in the bladder (cystitis), urethra (urethritis), and kidney tissue (pyelonephritis). As these complications develop, the clinical picture changes.
Characteristic manifestations:
- constant pulling sensations, lower back pain;
- pain when urinating;
- cloudy urine, pus;
- increased body temperature, sweating, general weakness.
Blood and pus in the urine appear as a result of damage to the mucosa with an increase in the size of the protrusion, as well as with inflammatory complications
When such symptoms appear, it is important not only to diagnose a urinary tract infection, but also to exclude ureterocele as the cause of their development.
Causes of the disease
The clear causes of the disease have not been clarified, and doctors still have disputes regarding the lesions. More often, the pathology is congenital and associated with a narrow orifice of the ureter, and the intramural segment is elongated. This happens when there is a lack of muscle fibers during the formation of the fetus. If the disease is acquired, then it arose as a result of infringement of insoluble elements located inside the ureter segment.
Taking medications that are contraindicated in pregnant women provokes ureterocele disease.
Pathology also occurs due to infection in the mother’s body. A woman who has had rubella, herpes, toxoplasmosis or other viral diseases during pregnancy exposes her child to pathology. Often the ureter succumbs to abnormalities due to drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy. You should carefully monitor your health and maintain your immunity during pregnancy.
Causes
The causes of ureterocele include:
- intrauterine disorders in the development of the distal (lower) part of the fetal ureter, accompanied by a lack of muscle fibers of the walls of the bladder and pathological narrowing of the orifice of the ureter;
- the formation of stone deposits in the kidneys and their movement into the ureter, which leads to blockage of the mouth and expansion of the tube.
When the outlet narrows or becomes blocked, the lower part of the ureter expands and its walls inevitably stretch. Cyst-like cavities form and fill with urine.
We suggest you read: Which doctor treats impotence in men and who to contact
Sometimes their contents may be watery or purulent. Externally they are formed from the mucous membrane of the bladder, and internally from the mucous membrane of the ureter. In the future, these cystic formations can fall into the bladder and even the urethra.
- Ectopic. It is characterized by an opening into the bladder diverticulum or urethra.
- Prolapsing. This is a type in which pathological nodes fall out into the urethra.
- Simple. Cystic formations are located in the cavity of the ureter. Divided into one-sided and two-sided.
The first two types are congenital; in adults, the simple variety is more common. If this anomaly is not treated, serious complications are possible, including kidney failure. Therefore, it is important to start therapy on time.
Doctors still do not have a common opinion about what could be the main reason that contributes to the appearance of ureterocele. However, there is detailed information about exactly what factors can lead to the formation of such a pathology.
So, what can contribute to the development of a ureterocele?
This pathology can be provoked by severe and long-term poisoning with some chemical substances, for example, at work, where you have to breathe harmful fumes of any compounds. The development of such a disease can be greatly influenced by the unfavorable environmental situation in the place of residence, as well as excessive alcohol consumption and nicotine intoxication.
Long-term use of hormonal medications and drugs against tuberculosis increases the risk of ureterocele; in addition, various pathologies that impair the excretion of urine from the body can also pose a danger.
As soon as fluid begins to accumulate in the body, it gradually stagnates and turns into an excellent environment for the proliferation of various pathogenic bacteria, which naturally leads to further formation of pus.
Symptoms
When the pathology is of the first degree, the person does not feel any signs of the disease. The hernia is still small in size and does not cause much harm. At the second stage, dysfunction of the genitourinary system is noticed: urine is slowly and rarely excreted from the body. Ureterocele on the left side is more common than on the right side, so the person feels pain on the left side. They occur due to an increase in cystic formation. If the disease is not treated, it progresses, the tumor greatly increases in size and puts pressure on the bladder. There is a constant desire to urinate. The disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pus appears in urine;
- chronic pyelonephritis or cystitis occurs;
- pain in the lumbar region that accompanies the patient throughout the day;
- fever;
- painful sensations when urinating.
If the mouth of the ureter is completely blocked, then acute hydronephrosis occurs. The person experiences pain that resembles renal colic. In women, when the ureterocele descends into the urethra, urine production stops. When urinating, the hernia may come out. You can straighten it yourself, but this will not solve the problem. It is necessary to urgently contact a specialist for help; surgery may be necessary.
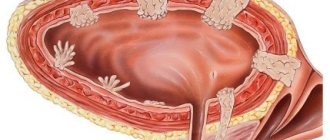
Ureterocele
Ureterocele is a specific disease of the urinary tract, which manifests itself in pathological expansion of the distal (intravesical) part of the ureter. A cyst forms in the affected area and protrudes into the bladder. Over time, unpleasant symptoms develop and begin to intensify: urinary disorders, back pain.
Feature of the disease: the cyst deforms the bladder and can increase over time. The disease affects women more often than men.
For diagnosis, you should contact a urologist; you will need to undergo a series of instrumental examinations. Treatment is predominantly surgical. There are several modern and safe ways to get rid of ureterocele. During the operation, not only the pathological area is removed, but also the normal structure of the ureter is restored.
At CELT you can get a consultation with a urologist.
- Initial consultation – 2,700
- Repeated consultation – 1,800
Make an appointment
Classification
There may be one cyst of the distal ureter. And sometimes a bilateral pathology is observed, when neoplasms are present in both ureters at once.
There are three forms of the disease:
- Simple. The cyst is located in one ureter; no other pathologies of the urinary tract are observed.
- Prolapsing. Occurs only in women. This is a prolapsing cyst that passes through the urethra and is visually noticeable from the outside. In this case, the pathology can be detected visually as purple mucous membrane.
- Ectopic. Located in a pathological ureter, which opens not into the bladder, but into other organs or ends blindly.
In addition, a distinction is made between a primary disease (congenital) and a secondary one (also called acquired).
Causes
The congenital form of the disease most often develops in women. The cause is a narrowing of the orifice of the ureter.
The causes of the acquired disease are more varied:
- formation of a calculus (urinary stone) and its strangulation
- impaired growth of bladder wall tissue
- violation of the outflow of fluid from the excretory system
- stagnation of fluid in the renal pelvis
Congenital and acquired forms are always accompanied by impaired fluid outflow and increased pressure in the ureter. This leads to even greater stretching of its walls, which contributes to the prolapse of the cyst into the bladder. As a rule, there is liquid inside the cyst itself, sometimes purulent contents. Less common are stones or blood.
Despite the fact that the first symptoms seem harmless, ureterocele can lead to the development of dangerous complications. Impaired urine flow from the kidneys increases the risk of infection.
Changes in fluid pressure cause infected urine to enter the kidneys. Chronic infections and pyelonephritis may develop.
If not treated promptly, infectious and inflammatory complications can lead to kidney loss.
Complications and prevention
The most common complication is the development of hydronephrosis, in which fluid accumulates in the renal pelvis. The second most common is ureterocele prolapse. The likelihood of infection and strangulation increases. Pyelonephritis may develop. Ureterocele increases the likelihood of developing urolithiasis. Prolonged course of the disease can lead to chronic renal failure.
Prevention consists, firstly, in timely and complete treatment of infectious and inflammatory diseases of all organs of the genitourinary system. Antibiotic therapy must be carried out under the supervision of a physician until the pathogen is no longer isolated in the tests.
If any unpleasant symptoms from the genitourinary system appear, you should immediately contact a urologist. In the multidisciplinary CELT clinic, you can undergo a full examination and begin treatment for ureterocele.
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7 (495) 788 33 88
Source: https://www.celt.ru/napravlenija/urologija/zabolevanija/ureterocele/
Diagnostics
If the above symptoms are detected, you must consult a doctor and conduct a full urological diagnosis. The doctor prescribes a urine test, which reveals red blood cells, white blood cells and accumulation of pus. By passing a bacterial culture of urine, you can find out the state of the microflora and whether there is an infection in it.
Cystoscopy is used in the diagnostic process, which will accurately indicate a cystic formation.
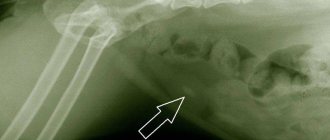
The doctor refers the patient to an ultrasound examination of the kidneys and bladder to confirm the presence of a ureterocele. The procedure will help determine the location of the pathology. Cystography and urography shows an x-ray picture of the neoplasm. Based on the results of the x-ray, the doctor determines defects in the filling of the bladder and an enlarged lower part of the ureter.
Ureterocele in women: causes, symptoms, early diagnosis, treatment methods
The question often arises about what it is - ureterocele in women. A photo of the disease is not included for ethical reasons.
Ureterocele is a disease associated with blocking of the bladder and urinary canal by swollen venous areas and tissue deposits - tumors, cysts.
This phenomenon is often congenital in nature and is considered an anomaly in the development of the genitourinary system.
Surgery for ureterocele in women
As a rule, such a pathology of the urinary tract as a ureterocele is a congenital anomaly; in some cases, a ureterocele is formed due to blockage of the ureter due to urolithiasis.
In both cases, this condition, in the absence of timely medical care, can lead to acute inflammatory processes and chronic diseases of the kidneys and bladder (for example, cystitis, urolithiasis, pyelonephritis). Today, in medical practice, only the surgical method is used to treat ureterocele.
It is important to note that the decision on surgical intervention is made by the attending urologist after a thorough diagnosis.
After the patient is scheduled for surgery, a therapeutic course of antibiotics is administered. This will help minimize the development of inflammatory processes in the postoperative period.
The complexity, volume and scale of surgical intervention depend on the size of the ureterocele and the degree of development of the disease.
Transurethral puncture
If the pathology has not led to the development of pathological irreversible processes in the kidney and bladder, then treatment of ureterocele in women such as transurethral puncture is indicated. Such surgical intervention is usually performed on an outpatient basis, without admitting the patient to a hospital.
The advantage of this method is that no traumatic surgical incisions are made; a medical cystoscope is inserted through the female urethra into the ureter, the ureterocele is cut and the contents are pumped out. The entire procedure takes no more than half an hour, and postoperative recovery proceeds quickly and without serious complications.
Endoscopic electroincision
To remove ureterocele in more advanced stages, surgical intervention is performed in a hospital setting - endoscopic electroincision. This is the most modern method of removal (excision) of a small ureterocele with simultaneous formation of the ureteral orifice. This operation is performed using endoscopic scissors or a halmium laser.
Laparoscopy
One of the frequently used surgical methods in urology is laparoscopy. It is carried out, for example, if, as a result of ureterocele, pathological processes have spread to the kidneys (its functionality is impaired). If the kidney is partially damaged, an upper lobe nephrectomy is performed, and in the case of complete damage, the entire organ is removed.
Open operations
Open abdominal operations on the ureters today are performed quite rarely, since abdominal incisions significantly slow down and complicate rehabilitation.
In addition, to prevent the sutures from coming apart in the ureter, it is necessary to use an inserted internal catheter, which causes a lot of inconvenience for the woman. In the postoperative period, in order to prevent the development of inflammatory processes, an antibacterial course is recommended.
It is important to note that, despite the forms and stages of ureterocele, this pathology has a good prognosis with timely surgical correction.
Folk remedies
Any problems in the genitourinary system can not only greatly worsen the patient’s quality of life, but also provoke many complex diseases that are difficult to treat.
The cyst-shaped pouch that appears with this disease causes constant urinary retention, but the patient may, at the same time, feel frequent urges.
The danger of this disease lies in the fact that it gradually develops, new, more unpleasant symptoms appear, and after a while the patient may feel more pain.
I would immediately like to warn you that this disease is treated only in two main ways, one of which is medicinal, and the second is surgical. The choice of one or another treatment method will naturally depend on the patient’s condition, as well as on what stage of development the ureterocele is at.
As for folk remedies, it is impossible to cure this disease of the genitourinary system with their help; you can only relieve pain and some unpleasant symptoms. Moreover, before using any medicinal herbs for the treatment of ureterocele using folk remedies, you should consult your doctor.
Linden decoction
With the help of such a folk remedy, which has no side effects, you can eliminate pain, pain and constant burning in ureterocele. To prepare a healing infusion, you need to pour linden blossom into a saucepan (two tbsp.
spoons), pour in boiling water (540 ml), then cook the mixture over low heat until it boils, continue cooking for another ten minutes. As soon as the linden decoction is completely ready, cool it, then strain and drink half a glass in the evening.
Freshly squeezed parsley juice
You need to squeeze the juice out of fresh parsley, then dilute it with drinking warm water in a 1:1 ratio. This healing remedy should be consumed three times a day, half a glass. There are many reviews about the treatment of ureterocele in women, and they are all different. Therefore, first of all, you should visit a specialist so that he can prescribe the necessary therapy.
Ureterocele is often diagnosed from birth, but there are also situations of rather late development. The disease progresses, and a tubercle forms on the affected part, which narrows the mouth of the ureter.
A protrusion in the form of a cyst or ball harms the mucous membrane. Ultimately, chronic pyelonephritis is provoked and the excretory function is destroyed.
Pathology can threaten with negative consequences:
- Hydronephrosis (dilation of the collecting system).
- Atrophy. Scars begin to appear on the tissues, and subsequently urine production ceases.
- Bleeding appears.
- Stones may form in the excretory tract.
- Pathology can cause renal failure (salt and water metabolism is disrupted).
- Cystitis, in which pain appears after urination.
- Arterial hypertension. Blood pressure rises and remains at the same level, and it is difficult to treat.
- The disease can cause inflammatory diseases in the kidneys.
Treatment involves complete removal of the organ or its reconstruction. Before performing an operation, it is imperative to carry out a procedure to eliminate pathogenic microbes in the urinary system.
Source: https://FB.ru/article/394855/ureterotsele-u-jenschin-prichinyi-simptomyi-rannyaya-diagnostika-metodyi-lecheniya
Treatment of the disease
Removal of a ureterocele is only possible through surgery. No drugs or traditional medicine can eliminate the disease. The patient can use diuretics if urine diversion is impaired, but this will only temporarily relieve the symptoms. It is important not to delay treatment and consult a doctor. If the disease occurs due to an infectious infection, then antimicrobial therapy is first carried out, and only then surgery is prescribed. The doctor prescribes medications that help eliminate positive and negative bacteria.
During the operation, the doctor makes an incision in the ureter and creates an opening to prevent urine from entering from the bladder. Lately, laser dissection has been in demand because this method is less painful. The duration of the operation is up to 1.5 hours. If the ureterocele also affects the kidney, then the damaged area of the internal organ is removed (nephrectomy).
Treatment of ureterocele
Radical treatment for ureterocele is surgery, which today can be performed in different ways. This depends on the type of ureterocele, size, presence of reflux, preservation of kidney function and inflammatory processes in the genitourinary organs.
If there are no clinical manifestations, reflux, the size of the ureterocele is small (less than 3 cm), dynamic observation is possible.
Open reconstructive plastic surgery is used in cases of large defects with the formation of stones and significant urodynamic disorders.
Open operations are used for both orthotopic and ectopic forms of ureterocele.
Ureterocystoneostomy is the formation of a new ureteric orifice. During the operation, the ureter is cut off from the wall of the bladder, and the excess length is removed, if necessary. Next, a new orifice is formed with the provision of an anti-reflux mechanism.
Endoscopic surgeries for ureterocele
Along with classical operations, endovesical surgical interventions are used, which reduces the percentage of complications in the form of vesicoureteral reflux and is easier to tolerate for patients.
Orthotopic ureterocele
Special optical equipment is inserted transurethrally (through the urethra), and the orifice of the ureter is dissected, thereby restoring adequate urine passage.
If the size of the ureterocele is small and there is no effect on the surrounding tissues, it is possible to perform obliteration of the sac-like protrusion. During cystoscopy, a special substance is introduced into the cavity of the formation, which “glues” the walls, thereby preventing the accumulation of urine.
Ectopic ureterocele
If the ureterocele is combined with doubling of the ureter, which, as a rule, arises from the upper pole of the kidney, when diagnosing atrophic processes, resection of the defective tissues is performed along with the modified ureter.
Note that the upper pole of the kidney, as a rule, is not functional.
If, nevertheless, this part of the kidney functions adequately, a pyelo-pyelostomy is performed.
How can a ureterocele be complicated?
Complications depend on the severity of the urinary passage disorder and the duration of the pathology.
More often, urologists encounter the following consequences:
- hydronephrotic transformation of the kidney with atrophy;
- prolapse of formation through the urethra;
- acute inflammation of the genitourinary tract: cystitis, pyelonephritis, prostatocystitis;
- nephrourolithiasis;
- hematuria;
- persistent nephrogenic hypertension;
- connection of chronic renal failure.
Important
If the size of the ureterocele is significant, it is better to perform surgery, this will help avoid undesirable consequences.
Complications and consequences
If the patient does not seek help in time, the pathology is fraught with serious complications for the bladder and kidneys. Hydronephrosis occurs, in which the pelvis of one or both kidneys dilates. Urolithiasis occurs due to poor flow of bile. Urine sediment that is not excreted from the body forms over time into stones.
In severe cases, kidney atrophy occurs, with scar tissue appearing in place of healthy cells. She is not functioning and is dead. Chronic renal failure appears, which disrupts all functions of the internal organ. It is important to notice the disease in time and consult a doctor. Timely surgical intervention saves the patient’s life. If the ureterocele has formed in a large size and the ureter has burst, then it can be successfully treated with timely treatment.
Complications
Without treatment, the ureterocele enlarges and leads to strangulation of the iliac arteries. As a result, the patient may experience intermittent claudication. When the first symptoms of lameness appear, most patients seek help from a vascular surgeon. Thus, the treatment prescribed is incorrect. In this case, treatment is aimed at eliminating the symptom of the pathology.
Ureterocele can provoke the development of urolithiasis. Urine accumulates in the cavity of the pouch-like protrusion, which over time leads to the formation of stones and stagnation of urinary sediment. In the early stages, the pathology may not manifest itself in any way. The first symptoms appear when the stone begins to irritate the walls of the bladder. The patient may feel severe pain in the lower abdomen. If the mucous membrane is irritated, blood may appear in the urine. Large stones can severely injure the mucous membrane and cause heavy bleeding.
Laparoscopic ureterolithotomy is an effective treatment for stone formation. To perform the operation, the doctor makes 3-4 small incisions in the abdominal cavity, through which he inserts special instruments. During the operation, the doctor opens the lumen of the ureter and removes the stone, and then sutures the walls of the ureter. Ureterolithotomy is performed only if other treatment methods have been ineffective.
Some pathological complications may appear after surgery. Often this complication may be a rupture of the ureter. Rupture occurs if a urethral catheter has not been installed in the bladder. With this complication, the pressure in the bladder increases sharply, which causes a rupture. In this case, the patient experiences sharp and burning pain in the lower abdomen. Body temperature may also rise to 37-38 °C.
Rehabilitation and prevention
The pathology itself does not cause any particular harm to human health and life. The rehabilitation period lasts about 2 weeks. The doctor prescribes antibacterial agents to prevent re-infection. No special diet should be followed; light food is recommended. It is worth giving up alcoholic drinks.
After the operation, a special catheter is placed, with its help it is possible to reduce the pressure in the bladder. It can damage the sutures that are placed on the internal organ. To avoid ruptures at the suture site, a catheter is used. It is worn for 2 weeks, then removed and the stitches are removed. If antibacterial prophylaxis or proper care of the sutures has not been carried out, then suppuration occurs. It is recommended to treat it for a month with ointments.
Since the pathology is often congenital in nature, prevention should be carried out even before the birth, or even conception of the child. It is necessary to cure infectious diseases (herpes, cytomegalovirus and others). A pregnant woman should be careful with chemicals and carefully read the instructions before using medications.
Treatment
If a ureterocele is detected at any age, the only way to get rid of the disease is surgery.
The simplest option is to dissect the ureterocele along its lower edge using a cystoscope. This method is considered optimal due to the ability to avoid sepsis in advance and drain the urinary tract.
For ectopic ureterocele, abdominal surgery is performed, since the size of the cyst is too large for work to be done through optical equipment.
After ureterocele surgery, rehabilitation does not last long. For prevention, it is recommended to visit mineral spas.
Ureterocele of the bladder: what is it and how to treat it in children and women
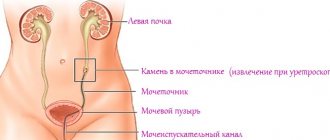
A ureterocele is a hernia-like protrusion of a certain part in the ureter, which provokes improper outflow of urine and is accompanied by an acquired or congenital defect in the orifices of the ureters, narrowing or ectopia.
Description of ureterocele
The first mention of this pathology dates back to 1834, when an anomaly was discovered during an autopsy of a patient, considering it to be a duplication of the bladder. The classification of ureterocele was first made in 1957, but all currently existing pathologies were not specified then. In 1961, it was established that ureterocele most often occurs when the kidneys are doubled.
Loading …
This pathology is also accompanied by ectopia of the mouth of the ureter, its duplication, stones and infection in the organ. The pathology affects patients of any age, the risk of occurrence is 2% among the entire population. Ureterocele appears more often in men than in women. And in children it appears only in one case per 500 newborns.
What forms of ureterocele are there?
Bladder ureterocele can be either acquired or congenital. Depending on the location, there may be an intravesical protrusion in the cavity of the bladder and an extravesical protrusion when the ureter flows into the urethra.
There is currently no single classification of all possible types of ureterocele, but practicing urologists, based on statistics, have identified the following division:
- orthotopic ureterocele of a simple type, which can be either unilateral or bilateral. The ureter dilates and the ureterocele is located in the bladder. The pathology is characterized by a small size, most often it compresses the adjacent ureter if it is doubled;
- ectopic variety - a pathology characterized by entry of the ureter into the urethral canal or in the area of the bladder neck. This is possible with low ectopia of the ureteric orifice. Such a ureterocele is characterized by a large size and compresses the mouth of the main and contralateral ureter.
More on the topic: How is ureteral reimplantation performed?
Based on the degree of development of this pathology, there are 3 degrees of severity of the disease, found in both adults and children:
- the first degree is characterized by slight expansions of the intravesical part of the ureter, there are no functional changes in the kidneys;
- the second degree is characterized by dilation of the ureter, accumulation of excess urine and the occurrence of ureterohydronephrosis;
- third degree, in which ureterohydronephrosis is accompanied by significant impairment of renal function or bladder dysfunction.
Causes of ureterocele
Ureterocele of the ureter occurs with congenital anomalies in the distal part of the ureter, due to which its intramural segment lengthens and a narrowing appears at the mouth.
The reason may also be acquired, due to a blockage of stones or other formations as they pass through the ureteral tube. Most often, it is the mouth that is clogged as the place with the greatest narrowing of the lumen.
When the layered structure of the wall of the lower sections of the ureter is disrupted, its diameter narrows and the pressure increases. The walls are greatly stretched. The expansion forms a cavity in which urine accumulates. The ureterocele can increase in size when filled with urine at regular intervals. As soon as urine is released through the orifice of the ureter, the protrusion decreases.
Pathogenesis
A ureterocele is very small in size and may appear as symptoms with frequent urination. But as soon as its size increases, it protrudes into the ureter and the movement of urine in the body from one of the kidneys is disrupted. The patient experiences problems with deurination, when urine is excreted in small portions at certain intervals.
In women and girls, as the size of the pathology increases, a protrusion into the urethra can be felt from the outside, then urinary retention is acute. For a child, this is fraught with severe pain and pain in the urinary tract.
The danger of this pathology is stagnation of urine due to problems with urination. In the renal pelvis, infection with microbes occurs, pyelonephritis and cystitis develop. Therefore, stones often form, which provokes nephrosclerosis and dysfunction of the renal system.
More on the topic: What are the segments of the ureter?
When the ureters are doubled, several types of such protrusion may appear, but if the ectopia in the orifices is high, then the ureterocele will not form in the main part of the ureter. With ureterocele of the orthotopic type, the ectopia of the orifice is always very low, and there is an absence of the intramural part of the ureter.
With a simple type of ureterocele, localization is noted in one of the corners of Lieto's triangle, while the intramural part remains normal.
What symptoms are characteristic of a ureterocele?
As a rule, this pathology occurs without symptoms, even in children, until the development of pyelonephritis. Its growth is accompanied by complications in the form of pain in the lower back, radiating to the sides, high fever and cloudiness of the urine. The color of the urine also changes, becoming a shade of “meat slop.”
Ureterocele is characterized by infectious diseases of the genitourinary system, sudden frequent urge to urinate, hematuria and pyuria.
If such a protrusion is large and descends into the urethra, the patient suffers from urinary incontinence. In women, this leads to complete retention of urine in the body.
When the outflow of urine from the kidneys is disrupted, acute hydronephrosis develops, and the patient suffers from attacks of pain reminiscent of renal colic.
Diagnostics
Most often, ureterocele is discovered during tests or examination of the patient’s body in connection with relapses of infectious diseases. On a general urine test, red blood cells, pus and white blood cells appear; on bacterial culture, specialists identify the microflora inherent in the infectious disease.
An ultrasound of the bladder reveals a protrusion on the walls of the bladder, which has a round shape with thin walls and fluid inside. Ultrasound of the kidney can show bilateral or unilateral transformation of the organ of the hydronephrotic type.
Only cystography can provide the most informative x-ray picture. With the help of X-ray, vesicoureteral reflux becomes noticeable, as well as defects in the filling of the organ and expansion in the distal ureter.
In order to assess the extent of the problem with the outflow of urine, specialists use excretory urography, when a special contrast agent is injected into the vein.
The mucous membrane of the bladder and the mouth of the ureters can be examined more closely during cystoscopy, when a cystoscope is inserted through the urethral canal.
More on the topic: Why does ureteral spasm occur?
How to treat ureterocele?
This pathology is characterized by obstruction in the ureter of a mechanical type, so elimination of ureterocele is possible only by removal.
For orthotopic excision, transvesical excision has long been used, followed by surgery to eliminate reflux. But if the size of the protrusion is not large, they began to perform endoscopic removal.
During endoscopy, the formation is removed with special surgical scissors or a laser.
During the operation, the wall of the ureterocele is dissected; if there is a stone, it is broken by ureterolithotripsy, then a plastic stage of manipulation is performed aimed at tissue reconstruction.
If the protrusion is large and complicated by ectopia, endoscopic methods become ineffective and then urethrocystoanastomosis is used.
All surgical interventions are performed in parallel with the antibiotic therapy and antiseptic regimen taken. Fluoroquinolone drugs are used to treat emerging pyelonephritis. If the ureter is doubled and part of the parenchyma in the kidneys has atrophied, removal or resection of this part is necessary. If the kidney is completely affected, it is removed.
Ureterocele
Rate this post: Loading…
Source: //onefr.ru/organy/mochetochniki/chto-takoe-ureterotsele-mochevogo-puzyrya.html
Consequences
Ureterocele is often diagnosed from birth, but there are also situations of rather late development. The disease progresses, and a tubercle forms on the affected part, which narrows the mouth of the ureter. A protrusion in the form of a cyst or ball harms the mucous membrane. Ultimately, chronic pyelonephritis is provoked and the excretory function is destroyed. Pathology can threaten with negative consequences:
- Hydronephrosis (dilation of the collecting system).
- Atrophy. Scars begin to appear on the tissues, and subsequently urine production ceases.
- Bleeding appears.
- Stones may form in the excretory tract.
- Pathology can cause renal failure (salt and water metabolism is disrupted).
- Cystitis, in which pain appears after urination.
- Arterial hypertension. Blood pressure rises and remains at the same level, and it is difficult to treat.
- The disease can cause inflammatory diseases in the kidneys.
Treatment involves complete removal of the organ or its reconstruction. Before performing an operation, it is imperative to carry out a procedure to eliminate pathogenic microbes in the urinary system.
What is a ureterocele and how to treat it?
Ureterocele is a transformation of the ureteric orifice, causing the formation of a spherical cystic protrusion, externally similar to a hernia. The disease affects men, women, children, regardless of age.
According to the international classification, it has an ICD-10 code as urological pathology class 14 of urolithiasis. The two-layer structure of the tumor membrane interferes with the outflow of urine.
May lead to complications of urethrohydronephrotic modification, a nonspecific inflammatory process of the kidney.
Diagnosis of pathology includes ultrasound of the urethra, pelvic organs, excretory urography, cystography, cystoscopy, and taking a smear from a woman. Of these, 1% are diagnosed in men, the rest are women. Typically first diagnosed in children, it is characterized by duplication of the ureters.
In urology, the disease has its own designation and classification:
- One-sided.
- Double-sided.
- Simple, located in a healthy ureter.
- Prolapsing, in women it can come out through the urethra in the form of a dark red hernia.
- Prolapsing ureterovesical, in men it spreads to the prostate urinary tract.
- Ectopic, in women it is located in an atypically located ureter, opening into the urethra, the vestibule of the vagina, and the bladder.
In addition, ureterocele is classified into congenital and acquired. The first type is divided into 3 stages:
- the first, in which the intravesical section of the ureter is slightly dilated;
- the second – observed large size of the formation, leads to the formation of ureterohydronephrosis;
- third - in addition to the above symptoms, important disturbances in the functional activity of the bladder are shown.
Symptoms of ureterocele in women
Symptoms of the disease in women are practically no different from the clinical picture of male ureterocele. The most obvious sign is abdominal pain, often spreading to the lower back, possibly followed by fever.
Moreover, women always have problems emptying the bladder. Since the pathology is characterized by an increase in part of its cavity, the volume of urine decreases accordingly, and urine comes out in small portions.
Because of this, the number of urges increases, but women, as a rule, do not feel complete relief after using the toilet.
A woman’s ureterocele may pop out of the system as cystic spheres at the time of bowel movement. You can return them yourself.
This happens quite rarely when the disease has reached the chronic stage. Blood in a woman’s urine is also a characteristic sign of the disease. The biological fluid becomes cloudy and acquires a disgusting odor.
Often illness is the cause of heaviness in the abdomen, kidney colic, frailty, confusion of mind.
Signs of ureterocele in children
In a child, the disease is usually asymptomatic until pyelonephritis develops. When this kidney inflammation occurs, the following signs are diagnosed:
- Cloudy urine.
- Lumbar pain, discomfort.
- Heat.
- Problems with urination.
- Frequent urge.
When the formation descends into the urethra, the activity of the urinary tract valve is disrupted. This phenomenon leads to enuresis.
Treatment of ureterocele
There are some treatment options for patients:
- Endoscopic decompression.
- Replantation of the ureter.
- Heminephrectomy.
In the presence of an infectious infection or obstructive changes in the neck of the urinary organ, it is recommended to perform surgical endoscopy with incision of the formation to open the urinary tract.
Children with ureterocele, who are asymptomatic, are often prescribed antibacterial therapy. In the presence of vesicoureteral reflux, endoscopic correction may be prescribed. Open replantation of the ureter brings optimal therapeutic results. If you look at the photos of surgical episodes, the doctor’s algorithm is quite clear.
Surgery for ureterocele
It is possible to get rid of the disease with the support of the main method - surgical intervention. This effect is carried out in several ways:
- Transurethral puncture. A cystoscope is inserted through the urethra to decompress the diseased part.
- Upper lobe nephrectomy. The operation is indicated for patients with a non-functioning upper part of the kidney. The instrument for intervention is a laparoscopic device.
- Nephrectomy. It is necessary when a cyst causes the kidney to stop working. The ureterocele is dissected, then the cystic growth itself is removed.