Rupture of the eardrum ranks first in frequency among all middle ear injuries. This damage develops in adults and occurs much less frequently in children. The prognosis of the disease is determined by the degree and nature of damage to the eardrum itself, damage to adjacent tissues, as well as the timeliness of medical care.
Author of the article / Site experts Shulepin Ivan Vladimirovich, traumatologist-orthopedist, highest qualification category
Total work experience over 25 years. In 1994 he graduated from the Moscow Institute of Medical and Social Rehabilitation, in 1997 he completed a residency in the specialty “Traumatology and Orthopedics” at the Central Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after. N.N. Prifova.
Etiology of rupture
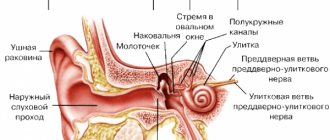
The eardrum is a thin sheet of connective tissue that separates the outer and middle ears. In addition to the barrier function, this organ is directly involved in the transmission of sound - mechanical vibrations of the eardrum are transformed into a signal to deeper structures (stapes and incus) and further to the cerebral cortex.
Serious damage to the eardrum sometimes leads to irreparable consequences - partial or complete loss of hearing.
Rupture of the ear membrane occurs as a result of exposure to a mechanical or chemical factor. The most common situations are:
- purulent otitis – pus accumulating inside the middle ear presses on the eardrum and ruptures it;
- foreign body in an adult – use of foreign objects (hairpin, hairpin, pencil) to clean the external auditory canal;
- foreign body in a child - foreign objects (pebbles, beads, cereals) entering the ear canal;
- barotrauma - sudden changes in atmospheric pressure during takeoff and landing of an aircraft, diving and ascent from the depths of a reservoir;
- mechanical impact due to an explosion, sharp and loud sound;
- combined head injury with damage to the temporal bone and other tissues of the inner and middle ear (road accident, fight, domestic trauma).
Perforation of the eardrum is a serious injury. It is better to consult a doctor with suspicion and rule out such an injury than to ignore the situation and treat its complications.
Structure and functions of the eardrum
The membrane has the following structural features:
- The first layer consists of the epidermis, and is a continuation of the skin present in the auditory canal;
- The second layer has fibrous fibers located in two directions: circular and radial;
- The third layer (inner) consists of the mucous membrane that covers the entire inner ear cavity.
The membrane is 0.10 millimeters thick, but it is very elastic and can withstand pressure and intense sound vibrations.
The functions of the membrane are divided into:
- capturing sound waves for further transmission to the internal auditory organs;
- protective properties, the membrane protects the hearing organs from foreign objects, water and excessive air volume.
The eardrum is located deep in the ear canal between the middle and outer ear. It is stretched and most of it is fixed in the groove of the temple bone. The part of the membrane without fixation consists of epidermal (outside), fibrous (in the middle) and mucous (inside) layers. The shape of the membrane is round in children and oval in adults. It is about five millimeters in diameter and one tenth of a millimeter in thickness.
The eardrum performs a protective function and is involved in conducting sound waves. This organ prevents water, air, microorganisms and various foreign objects from entering the inner cavity of the ear. When the eardrum is damaged, it cannot protect the passage and transmit sound vibrations to the ossicles and other structures of the ear. Thus, ear injuries accompanied by perforation lead to disruption of the protective and sound-conducting functions.
Damage classification
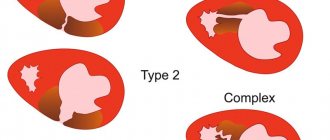
When the otolaryngologist makes a final diagnosis, all the details of the damage to the eardrum are described. The most important:
- area of damage – ¼, ½, and so on from the entire surface of the eardrum;
- degree of rupture - point rupture, perforation, rupture along the entire height, complete tear, etc.;
- the shape of the rupture is slit-like, round, dotted, with uneven edges, etc.
All these nuances are important for the doctor, since this is what determines the further tactics of treating the patient and the possible consequences of the injury.
Lifestyle and home treatment
If you have trouble with your ear, try combining treatment with the following measures, which will protect the eardrum during healing:
- Keep your ears dry during treatment. When swimming, use silicone earplugs or a piece of cotton cloth coated with petroleum jelly;
- Avoid cleaning your ears yourself. Give the eardrum time to heal completely;
- Avoid sharp blowing of your nose. The pressure created by this can lead to damage to the already healing membrane;
- Warm compresses or over-the-counter pain relievers (eg, Paracetamol, Ibuprofen) can be used to relieve pain.
It is not always necessary to consult a specialist for medical advice and diagnosis. For many people diagnosed with a ruptured eardrum, treatment consists only of protecting the injured ear from further damage and preventing possible infections. The self-healing process takes several weeks.
- Keep your ear dry. Whenever you take a bath or shower, insert waterproof silicone earplugs or a cotton ball soaked in petroleum jelly into your outer ear.
- Refrain from cleaning. Do not use any substances or objects to clean your ears, even if they are specifically designed for this purpose. Give your eardrum time to heal completely.
- Don't blow your nose. The pressure created when blowing your nose can damage already injured tissue.
Clinical symptoms
Signs of damage to the integrity of the eardrum depend on the cause of the injury. For example, a rupture of the eardrum from a blow is accompanied by severe pain at the site of its application. In inflammatory processes of the middle ear at the time of pus breakthrough, on the contrary, pain decreases.
The following symptoms indicate a violation of the integrity of this membrane in the ear:
- hearing loss - immediately after a blow or breakthrough of pus, a person feels a decrease in hearing acuity on the side of the damage;
- dizziness and nausea – especially if there is combined damage to the eardrum and vestibular apparatus;
- leakage of pus (during inflammatory processes), blood (combined traumatic damage to the ear and other tissues);
- noise of varying severity in the damaged ear (from moderate to unbearable hum).
All of the above means that you need to contact an otolaryngologist as soon as possible. In case of combined head injury, a medical consultation will act (otolaryngologist, neurosurgeon, neurologist, infectious disease specialist).
Symptoms
The structure of the membrane is fragile, so its rupture is always accompanied by painful sensations, especially at the beginning of the development of pathology.
The main symptoms of a rupture include:
- Severe ear pain;
- Bloody or purulent discharge from the ear canal;
- Bloody discharge, especially after injury;
- Noticeable hearing loss;
- Incessant ringing in the ears;
- Feeling stuffed up.
Painful sensations can pass quickly, but you should not neglect this and let the situation take its course; the pathology can continue to progress, which leads to unpleasant consequences.
General diagnostic principles
In diagnosing damage to the eardrum, an integrated approach is used to select the optimal treatment and prevent the development of negative consequences.
It all starts with interviewing the patient to find out the nature of the injury and all the preceding circumstances. An external examination of the victim allows one to assess the degree and nature of damage to other organs and tissues. For example, with a closed traumatic brain injury with damage to the bones of the skull, a clear liquid (CSF) leaks from the ear and nasal passages. With injuries to the facial skull (including the nasal bones), a characteristic “spectacles symptom” develops (dark circles under the eyes due to hemorrhage).
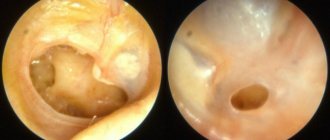
After an external examination, an examination of the ear is required using an otoscope or a conventional visual examination with a mirror and a refractor. Inside the ear, the doctor will be able to see the nature of the damage to the integrity of the eardrum and assess the area of damage. An examination of the nasal passages and oral cavity is also carried out, which makes it possible to assess the patency and integrity of the Eustachian tube and other organs.
Laboratory and instrumental studies include:
- general clinical blood test (demonstrates an inflammatory shift in the blood during otitis media and its complications);
- X-ray examination of the skull bones;
- tomography (computed tomography, positron emission tomography, magnetic resonance imaging) to assess possible damage to the skull bones.
Complex head trauma may require a lumbar puncture and cerebrospinal fluid examination.
Side effects and disadvantages of taking antibiotics
A ruptured eardrum should be treated carefully with antibiotics. Taking these medications may have a number of side effects:
- development of drug resistance;
- the appearance of allergic reactions;
- hearing impairment.
Antibiotic resistance. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics or their overuse leads to the development of drug resistance in bacteria.
Allergy. Like any other medicines, they can cause allergic reactions. We are talking about an allergic rash. Some drugs in this group, such as tetracyclines, can cause allergic photodermatitis, an allergic rash that worsens when the skin is exposed to sunlight. Theoretically, severe forms of allergic reactions, including anaphylactic shock, cannot be ruled out.
Hearing impairment. Some aminoglycoside antibiotics are toxic to the auditory nerve and can cause irreparable damage (ototoxic effects). That is why these antibiotics should be used with caution in cases of hearing loss characteristic of a ruptured eardrum.
A traumatologist can diagnose an injury, and treat it is the specialty of an otolaryngologist.
Damage can only be assessed using a medical device (otoscope). The doctor inserts an ear mirror into the passage, directs the light at the angle he needs, and pulls the auricle up and back to get a good look at the eardrum. This determines the degree of damage, the presence of pus or blood in the ear.
If such an examination is not enough, another examination is performed - audiometry. Using special equipment, the presence of membrane damage, its degree, and how much the patient’s hearing has deteriorated are determined.
Additionally, fluid secreted from the ear is taken for analysis. It is important to analyze its composition for the presence of bacteria and pathogenic microbes.
Maybe
Complications and consequences
The most common complications of eardrum injury are inflammation of the middle and inner ear. A damaged membrane cannot prevent infection from entering. A microbial agent can also penetrate into the cranial fossa - meningitis develops (inflammatory changes in the meninges) or encephalitis (the substance of the brain is involved in the inflammatory process).
The most serious consequence of eardrum injury is deafness, complete or partial. This is observed if the area of damage is significant and the membrane cannot heal completely.
Consequences of injury
Complications caused by a rupture are directly related to how quickly the damage is discovered. The main danger lies in the ability of microorganisms to penetrate deep into the ear, which provokes the development of serious inflammation.
At the initial stage, a person experiences hearing loss. Further, even deeper penetration of the infection is possible. This in turn causes a series of inflammations in the structures of the ear. They are accompanied by human weakness, nausea and vomiting.
With the deepest penetration of the infection, a person develops diseases such as encephalitis and meningitis. In the absence of qualified assistance, the patient may face death or lifelong disability.
The speed with which you contact a doctor determines whether the injury will leave consequences and how serious they will be. The main consequence is that after perforation of the membrane, any microorganisms and infectious agents easily penetrate the ear cavity and cause an even greater inflammatory process.
When infected, labyrinthitis may develop, during which the structures of the inner ear become inflamed. A person with this disease feels sick, vomits, and becomes dizzy. Another consequence is the appearance of neuritis of the auditory nerve, which occurs with unbearable pain. The consequences of a ruptured membrane always include frequently recurring otitis media.
If the damage is severe, which cannot be cured without surgery, there is a risk of remaining with reduced hearing for the rest of your life. If the infection extends beyond the tympanic cavity, the person may develop meningitis (inflammation of the membranes of the brain) or encephalitis (inflammation of the brain structures), and these diseases sometimes cause death. For these reasons, damage should be treated immediately after it occurs.
General principles of treatment
The optimal remedy for a quick and complete recovery is chosen by an otolaryngologist. First aid is provided to the victim himself or the people around him.
First aid
If you suspect a ruptured eardrum, you should contact a medical facility as soon as possible. To maintain relative tightness, the damaged ear should be covered with a cotton swab.
It is strictly forbidden to put any drops into the ear, including antiseptic ones.
Drug treatment
If the damage is small, then no special treatment is required - the eardrum will heal on its own. The doctor may use patches - small paper napkins with a special wound-healing substance that are applied to the site of injury. The napkin is replaced regularly (once every 3-4 days) with a fresh one.
Among systemic medications, the doctor will recommend antibiotics if we are talking about an inflammatory process in the ear. The use of multivitamin complexes has a positive effect on the course of the disease.
Physiotherapy
For better healing, physiotherapeutic procedures are used: exposure to laser or ultraviolet radiation. 5-10 procedures are prescribed, alternating UV irradiation and laser.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is indicated in case of significant damage to the eardrum, when the defect exceeds the size of 2-3 quadrants (quarters) of the membrane. A tympanoplasty operation is performed - filling the defect with an allantoic chicken pouch or an artificial prosthesis. This surgical treatment is performed under general anesthesia.
If the size of the eardrum defect is small (within 1 quadrant), then complete recovery will take 10-14 days. If surgical intervention is required, the recovery time is extended to 3-4 weeks.
Traumatic damage to the eardrum is a condition that requires attention and medical examination, as serious consequences are possible, including complete hearing loss.
What function does the eardrum perform in the body? How dangerous is her breakup?
Treatment for damage to the eardrum
First aid
diclofenac 0.05 g paracetamol 0.5 g 3% After removing the pus, the ENT doctor uses a catheter to infuse the following medications into the ear:
- dioxidine solution (0.5 - 1%) - an antimicrobial drug with a broad spectrum anti-inflammatory effect;
- antimicrobial drops tsipromed (0.3%), which have a wide spectrum of antibacterial action;
- Otofa antibacterial drops (2.6%).
Antibiotic therapy
Based on the nature of their effect on pathogenic microorganisms, antibacterial agents are divided into two groups:
- antibiotics of bacteriostatic action, when used, bacteria do not die, but lose their ability to reproduce;
- Antibacterial antibiotics, the use of which leads to the death of bacteria.
Characteristic
The eardrum is a thin, 0.1 mm thick, three-layer membrane that separates the middle ear from the outer ear, protecting the middle ear cavity from the penetration of foreign bodies and viruses, which, before reaching it, are forced to overcome 2.5 cm through the auditory canal.
At the same time, the membrane is impermeable not only to foreign objects and bacteria, but also to air and liquid. The eardrum also transmits sound vibrations to the inside of the ear. It does this by vibration: sound waves create air vibrations, which are captured by an ultra-thin membrane and begin to vibrate, touching the auditory ossicles located in the middle ear, through which the received information passes further to the inner ear.
When the eardrum ruptures, hearing always deteriorates, and in some cases disappears altogether: viruses and bacteria have a unique opportunity to penetrate the middle ear and, causing inflammation, disrupt its functioning.
Damage to the membrane can be judged by a sharp acute pain in the hearing organs, after which a rumble appears in the ears, and hearing decreases and even disappears.
If the perforation is caused by inflammation of the middle ear, after a short time purulent or clear fluid begins to appear from the ear canal, after which the pain subsides and the amount of fluid begins to decrease. A rupture of the eardrum due to trauma (pierced by a foreign object or damaged due to a sudden change in pressure or noise) causes a bloody discharge.
Methods for diagnosing ear injury
In order not to encounter the problem of violating the integrity of the membrane, it is necessary to perform the following prevention methods:
- Do not swim in dirty waters. Bringing dirt into the ear cavity can disrupt the integrity of the membrane;
- Do not sneeze with your nose closed (this action increases pressure on the membrane, which can lead to its rupture);
- Treat all inflammatory diseases (for example, otitis) in a timely manner;
- Do not swim underwater if you have a runny nose;
- Clean and wash your ears correctly;
- While flying on an airplane, use special headphones or suck on a lollipop;
- Do not stay in noisy places for a long time (do not listen to loud music on headphones);
- Do not use sharp metal objects to clean your ears; this may cause mechanical injury to the ear and membrane;
- If a foreign object gets into your ear, do not try to remove it yourself; you should contact a specialist to remove it.
Compliance with the rules will reduce the likelihood of membrane damage. You should not self-medicate or use medications for other purposes.
A doctor can diagnose a ruptured eardrum by taking into account the patient's or parents' description of the child's behavior. The next stage of the study will be otoscopy, a method widely used in ENT practice. For this purpose, a special device is used that resembles a long elastic tube, at the working end of which there is either a video camera (for modern digital models) connected to a computer, or a simple magnifying glass. The presence of bright light at the time of examination is mandatory.
Sometimes very small holes in the eardrum can be difficult to identify. In such cases, further diagnosis using more complex tests may be required.
- A tympanogram is a test that uses a short burst of air directed against the eardrum.
- An audiogram is a classic hearing test.
Helpful information
Surgery is prescribed for cases where the use of medications does not give the desired result. Surgical interventions are also prescribed for hearing loss and large amounts of membrane damage.
When an infection is introduced into the injured area, the use of surgical intervention can prevent further spread of the infection to the brain.
Myringoplasty
The operation is aimed at restoring the integrity of the eardrum. The procedure is carried out under anesthesia, using a flap of skin, which is taken from the area above the ear, and the damaged areas of the membrane are sutured.
To carry out the operation, special instruments are used, with which the specialist lifts the membrane, and temporary sponges are installed to fix the membrane in the desired position.
A flap of skin is applied to the damage and left until it takes root; after a certain time, the sponges dissolve on their own.
After the operation, the patient must walk with a bandage tampon in the ear canal; to reduce unpleasant symptoms, such as pain, the doctor prescribes painkillers when opening the mouth.
In cases where there is a large violation of the membrane, the specialist sews a flap of skin using special tools with special threads, which dissolve on their own after a certain time.
In some cases, the skin particle does not take root well and requires repeated surgery.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient is prohibited from physical stress and prolonged exposure to cold. Otherwise, complications may arise.
Ossiculoplasty
Surgery is most often used if damage to the tympanic membrane is accompanied by hearing loss. The purpose of the operation is aimed at gradually restoring hearing with the help of special devices.
The operation restores damaged tissues and mucous membranes, and also improves the perception of auditory waves. If the damaged areas cannot be restored, they are completely replaced with prostheses, which are made individually for each patient.
Myringoplasty
In some cases, the skin particle does not take root well and requires repeated surgery.
Ossiculoplasty
In rare cases, after repair of the eardrum, fluid production in the middle ear may develop, requiring ventilation tubes to be inserted. In some people, reinserting the tube does not prevent cholesteatoma and bone inflammation. This condition must be treated surgically, and it is not always possible to preserve hearing.
Perforation (rupture) of the eardrum: treatment, symptoms and consequences
The eardrum, or tympanic membrane as it is also called, is a thin strip of tissue that separates the external auditory canal and the middle ear. When the integrity of this tissue is violated, the eardrum ruptures. This is also called perforation of the eardrum or membrane.
When the eardrum ruptures, a person experiences the following symptoms:
- severe ear pain that may stop suddenly
- hearing loss in the damaged ear
- thin discharge from the ear that may contain blood
- noise or ringing in the ear
- sensation of ear blockage
- dizziness or loss of balance
- nausea
- whistling sound in ear when blowing nose
In this case, the degree of hearing loss depends on the size of the crack in the eardrum.
A ruptured eardrum can occur due to various reasons, including:
Ear infection
Both a single severe infection and several mild infections can lead to a ruptured eardrum.
Otitis media, also known as acute otitis media, occurs when bacteria or viruses cause fluid to accumulate in the middle ear.
Fluid or pus builds up behind the eardrum, creating pressure that can rupture it.
Ear infections can be very painful and lead to hearing problems.
Ear injury
Various injuries can increase the risk of rupture of the eardrum, because it is a very thin strip of tissue that may not withstand damage from impacts, including during sports.
Severe injuries to the ears or head sometimes result in damage to both the middle and inner ear.
Insertion of foreign objects into the ear
The eardrum can be ruptured by inserting objects into the ear, such as cotton swabs, pencils, or thin hair clips.
Children are susceptible to accidental use of such items. If possible, you should avoid exposing your ears to foreign objects.
Loud noise
The danger of rupturing the eardrum also lies in excessively strong sound exposure, for example, during an explosion, acting directly on the ears. Musicians and fans of loud music with headphones are at risk.
Hearing loss and ringing in the ear, also called tinnitus, are observed several hours or days after such exposure.
Barotrauma of the ear
Barotrauma occurs when air or water pressure changes, that is, when one pressure is established in the inner ear, and another in the outer ear.
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the bridge of the nose and throat and equalizes the pressure on both sides of the eardrum. If pressure prevents it from opening, a pressure difference occurs that can cause the eardrum to rupture.
Most often, barotrauma occurs during scuba diving and air travel. When scuba diving, pressure on the ears increases and can damage the eardrum, especially during the dive.
The pressure difference can create a vacuum in the middle ear, causing the eardrum to bulge inward and potentially rupture.
During air travel, a pressure difference occurs in the outer and middle ear. Due to increased pressure, the eardrum stretches and sometimes ruptures.
Treatment methods and home care
If you suspect a ruptured eardrum, you should consult a doctor.
The doctor will examine the inner ear using an instrument called an otoscope. In this way, you can determine the presence of a hole in the eardrum and estimate its size.
Your doctor may also test your hearing, perform a balance test, or blow air into your ear to determine your ear pressure.
A ruptured eardrum often heals on its own within 1-3 months. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, are prescribed to relieve ear pain and fight infections. For moderate pain, a warm ear compress may help.
Your doctor may prescribe antibiotics by mouth or as ear drops to treat inflammation.
If a ruptured eardrum does not heal on its own, a surgical procedure called tympanoplasty may be required.
Recovery
For proper recovery, it is important to keep the ear dry - this will prevent the development of infection.
When showering, it is recommended to use waterproof earplugs or cotton swabs soaked in Vaseline. Swimming and other activities that involve being in the water are best postponed until the eardrum heals.
It is also recommended not to blow your nose if possible. If necessary, you can gently blow your nose by pinching one nostril closed to prevent pressure drop in the ear, as this can slow down the recovery process.
Precautionary measures
Avoid exposing the ears to foreign objects and be careful when cleaning to avoid damaging the eardrum.
Infections that occur must be treated immediately, otherwise the inflammation may intensify and lead to the formation of a crack in the tympanic membrane. Vaccinations, such as influenza or pneumococcal vaccines, can help reduce the risk of ear infections.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), breastfeeding an infant directly until he is 6 months old and continuing to do so for 12 months can reduce his risk of developing various infections, including ear infections.
Quitting smoking, including passive smoking, also reduces the risk of ear inflammation.
The Eustachian tubes must be in the open position so that changes in water or air pressure do not cause barotrauma.
To keep the Eustachian tubes open during air travel and reduce pressure on the ears, it is recommended to do the following:
- swallow more often
- chew gum or suck on a lollipop
- yawn or open your mouth wide
- close your nostrils with your thumb and forefinger and exhale gently while closing your mouth
- use earplugs designed specifically for air travel
If you have nasal congestion, it is recommended to take antihistamines before a flight - they widen the nasal passages.
When scuba diving, you can stabilize your blood pressure by diving slowly, but if you have a cold or allergy symptoms, it is better to avoid this activity altogether. When scuba diving, it is important to follow the instructors' recommendations.
Patients with barotrauma are not advised to dive or fly again until a doctor confirms that it is safe to do so. If ear barotrauma occurs frequently, your doctor may place an ear shunt in the eardrum to keep the eustachian tubes open.
Earplugs, headphones, or other ear protection will help protect your ears from loud noises in loud noise environments, such as concerts, construction sites, or shooting ranges.
If playing sports involves ear injuries, it is recommended to use special protective devices.
conclusions
A ruptured eardrum often heals on its own within a few months.
To prevent the development of infections, it is necessary to keep the ears dry until complete recovery. If symptoms of a ruptured eardrum continue, you should consult a doctor.
In cases where the eardrum is not capable of self-regeneration, surgery may be required to repair it.