Good day, dear readers!
In today's article we will look at radiculitis, as well as its symptoms, causes, types, diagnosis, treatment with medication and at home, medications, folk remedies and prevention of radiculitis. So…
What is sciatica?
Radiculitis is a pathological condition or symptom that is characterized by back pain.
Other names for the symptom are radiculopathy.
The main cause of radiculitis is osteochondrosis - a disease of the spine, expressed by degenerative-dystrophic damage to the intervertebral discs, and then the tissues of the vertebrae themselves. Other causes include back injuries, intervertebral hernias and other pathologies.
The above reasons contribute to compression or inflammation of the nerve root, which is part of the spinal nerve, which extends beyond the spinal column through the intervertebral foramina, which is why a person with radiculitis feels back pain.
The localization of spinal pain depends on the location where the nerve inflammation occurs; on this basis, sciatica is distinguished between lumbar, thoracic and cervical type. In some cases, the pathology extends to more areas of the spine, which adds additional types of radiculopathy to the classification. In most cases, it is lumbar radiculitis that occurs.
In addition to sharp, sudden pain in the back, symptoms of radiculitis often include stiffness in movement and loss of sensitivity in the inflamed area.
The most common patients with radiculitis are pensioners, professional athletes, as well as people with a sedentary lifestyle - office workers. Moreover, if previously radiculopathy was observed mainly in people after 45 years of age, now this pathology is “younger,” which indicates an increase in “sedentary ways of earning money, for example, at the computer.
Development of radiculitis
To understand the principles of the development of radiculitis, let's deviate a little towards human anatomy, in particular, to the structure of the spine.
The spinal column, or as we usually call it, the spine, is a flexible formation consisting mainly of 33-34 vertebrae. All vertebrae are connected to each other by intervertebral discs, arches, processes and ligaments. The spinal cord runs along the entire spine, between the vertebral bodies, their arches and the processes emanating from the arches. The spinal nodes and roots emerge through the intervertebral foramina located on the sides of each vertebra. Nerve endings emerge from the roots. To make it easier to understand, below you can see a picture showing the structure of the spinal canal.
Now let's move on to consider the issue of the development of radiculitis itself.
With osteochondrosis, destruction of the intervertebral discs occurs, resulting in a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae and direct contact between them. Over time, osteophytes grow on the edges of the vertebral bodies, developing as a result of friction against each other. At the same time, the intervertebral foramina decreases.
As a result of the above processes, osteophytes, when moving, begin to contact the spinal nodes, roots and nerve endings extending from them, pinching them, which is why a person feels acute pain with a return to other parts of the body (leg, shoulder, etc.), numbness and other unpleasant signs of radiculitis. Over time, the roots become inflamed, and signs of radiculitis accompany a person more and more often.
It should be noted that this process of development of radiculitis is superficial, but I think the essence of the pathology is now becoming clearer for many.
Of course, there are cases when, instead of osteochondrosis, pinching of roots and nerve endings occurs due to injuries, intervertebral hernias and other disorders, therefore, for an accurate diagnosis and the correct treatment method, it is best to consult a doctor.
Radiculitis – ICD
ICD-10: M54.1; ICD-9: 729.2.
How does pathology manifest itself?
Symptoms of the acute form of lumbosacral radiculitis are presented in the table.
Table 1. Signs of acute radiculitis:
| Sign | Description |
Bekhterev's symptoms | In the affected area, reflex flexion of the lower limb occurs. The syndrome occurs when a person is sitting or in a horizontal position. |
Symptoms of Neri | Painful sensations intensify with sharp tilts of the head. |
Symptoms of Lasegue | There is excruciating pain in the lower back, buttock and posterior surface of the lower limb. When a person, being in a horizontal position, straightens his leg, the painful sensations intensify. |
Bonnet symptoms | Under the buttock on the affected side, a smoothing of the fold is observed. |
Symptoms of Dejerine | Painful sensations intensify when a person sneezes or coughs. |
Provoking factors
An attack of pathology is provoked by:
- sudden movement of the lower back;
- poisoning of the body;
- viral infection;
- hypothermia;
- physical fatigue.
Causes of radiculitis
The main cause of radiculitis is osteochondrosis, and we discussed how this spinal disease affects the development of radiculopathy in the paragraph “Development of radiculitis.”
Other causes of radiculitis include:
- Herniated discs;
- Spinal injuries;
- Spinal canal stenosis;
- Bone tumors (osteophytes) on the vertebrae;
- Curvature of the spine – kyphosis, scoliosis, lordosis;
- Arthritis;
- Tumors;
- Presence of infection in the body;
- Infectious diseases.
If we talk about the factors that contribute to the development of radiculitis, we can highlight:
Features of treatment of the disease
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a doctor
How to treat sacrolumbar radiculitis?
The patient is recommended:
- observe strict bed rest;
- take medications prescribed by a doctor;
- undergo physical therapy procedures.
When the patient's condition improves, he is prescribed physical therapy exercises.
Drug therapy
The doctor may recommend the use of:
- gels and ointments;
- creams;
- injections;
- chondroprotectors.
Note! Self-medication can cause the condition to worsen.
Application of gels and ointments
When radiculitis worsens, the patient is recommended to use Ortofen, Diclofenac, Ibuprofen or Indomethacin. Less expressive painful sensations are eliminated by more gentle means. The best of them are listed in the table.
Table 2. Recommended gels and ointments:
| A drug | Description | Price |
Apizartron | A combination drug based on bee venom. Has a local irritant effect. Stimulates peripheral nerve endings. | 270-385 rubles. |
Voltaren | Inhibits the biosynthesis of prostaglandins, relieves inflammation, reduces pain. | 226 rubles. |
Camphocin, in the photo an analogue of the drug, Bishofite | A good analgesic, helps relieve inflammation (read more here). | 200-300 rubles. |
Finalgon | It has an irritating and analgesic effect. Has no systemic effects. | 184-302 rubles. |
Application of creams
The patient is prescribed the use of creams based on bee or snake venom. The best creams are presented in the table.
Table 3. The most effective creams:
| Means | Description | Price |
Larkspur | Has anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect. | 120 rub. |
Viprosal | It has an analgesic, absorbable and anti-inflammatory effect. | 196 rub. |
Alvipsal, or its analogue, Salvisar | It has an anti-inflammatory, local irritant and analgesic effect. | From 150 rub. |
Vipratox or its analogue, Dimexide | A good analgesic, it stimulates the sensitive nerve endings of the skin and improves tissue trophism. | 180-200 rub. |
Virapin, or its analogue, 911 | An effective analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug. | 130-150 rub. |
Mellivenone, or its analogue, Indovazin | Contains chloroform and bee venom. | 250-300 rub. |
These remedies help improve blood circulation in the area of damaged vertebrae.
Note! Many of these creams have contraindications.
Application of injections
If the patient complains of very severe pain, he is prescribed injections. The most effective medicines are presented in the table.
Table 4. The best drugs for injection:
| A drug | Description |
Mydocalm | Centrally acting muscle relaxant. The mechanism of action of the drug has not been fully established. |
Lidocaine | A good anesthetic used for superficial anesthesia. |
Meloxicam | Prescribed for acute painful muscle spasms, or for chronic spasticity of spinal and cerebral origin. |
Siralud | Prescribed for very acute pain. |
Novocaine | A local anesthetic drug with a slight anesthetic effect and a wide range of therapeutic effects. |
Trimekain | The medicine promotes the rapid onset of spinal and epidural anesthesia. |
Note! These drugs are not intended to treat sciatica. They are used for temporary relief of symptoms.
The use of chondroprotectors
How to treat sacrolumbar radiculitis?
Often the patient is prescribed chondroprotectors. Medicines in this group promote the restoration of cartilage tissue and stop further progression of the pathology. The most effective drugs in this group are presented in the table.
Table 5. Recommended chondroprotectors:
| Medicine | Description | Price |
Artron flex | The drug is recommended for diseases of the joints and spine that are associated with damage to connective tissue. | 2900-3110 rub. |
Alflutop | It has a chondroprotective, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effect. | 1000-1200 rub. |
Hyaluron | It is a source of chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid. Recommended as a dietary supplement. | 800-990 rub. |
Rumalon | Has a bright protective effect. Reduces the activity of most enzymes that have a destructive effect on the cartilaginous surface of the joint. | 1139 rub. |
Why does the disease occur?
Naturally, many are tormented by the question: where and why does sciatica begin? After all, as you know, forewarned is forearmed, and in the future you can simply prevent aggravation. In medicine, radiculitis is not considered a separate disease, although this is not a mistake. In general, this is an advanced symptom. To understand the mechanics of the disease, you need to understand anatomy.
From a school biology course, any person knows that the spinal cord is located in the spine. Thousands of nerve endings emerge from it, which together ensure normal coordination and movement of the body. As soon as one of the endings or their group is damaged, an inflammatory process occurs - radiculitis, which is also accompanied by pain.
Doctors say that in 90% of cases the cause of exacerbation is osteochondrosis. We are talking about dystrophic changes in the spine. They also arise due to constant sitting, a sedentary lifestyle, incorrect posture, and improper distribution of physical activity. It is possible and even necessary to treat the disease; it is possible to minimize the development and even restore the original state of the spine. But if the disease is started, then at some point it becomes simply irreversible and causes a lot of side symptoms, including radiculitis.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
How to treat lumbosacral radiculitis in order to get back on your feet as soon as possible? Physiotherapeutic procedures have a beneficial effect on the patient’s body. The most effective methods of treatment are presented in the table.
Table 6. Best physical therapy methods:
| Methodology | Description |
Use of ultraviolet | The procedure is carried out in the subacute stage. |
Electrophoresis | Medicines such as Adrenaline, Phenol and Dicaine are used. |
Ultrasound therapy | Powerful analgesics are used. Depending on the form of the pathology, the treatment regimen can be pulsed or continuous. |
Diadynamic currents | Electrodes placed in areas of damaged nerve endings activate the nerves that have been affected by sciatica. |
Note! Sometimes physical therapy gives better results than drug treatment.
Prevention of radiculitis
Prevention of radiculitis includes compliance with the following recommendations:
- Sleep on a flat surface; if possible, buy an orthopedic mattress, just choose it by weight;
- Try to move more, do exercises in the morning;
- Swim, swimming is an excellent preventive action against spinal diseases;
- Give preference in your diet to foods enriched with vitamins and minerals, and do not forget to control the amount of salt you consume;
- Avoid lifting heavy weights, remember, health is more valuable than money, and if you do heavy physical work, think about whether you might need a special support corset;
- Avoid stress, or learn to control your emotions;
- Do not let various diseases take their course, especially those of the musculoskeletal system;
- Avoid hypothermia;
- Control your weight, extra pounds are the enemy of all organs and systems;
- Watch your posture, especially when studying, sedentary work, or spending a long time at the computer;
- Limit your consumption of fatty, fried and smoked foods, as well as coffee and strong tea;
- Pay attention to additional intake of vitamins and microelements, especially B vitamins.
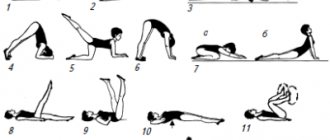
Performing physical therapy exercises
The main goal of therapeutic exercises is to restore mobility of the lumbar spine. Instructions for performing the most effective exercise therapy exercises are presented in the tablet.
Table 7. We treat lumbosacral radiculitis with exercises:
| Exercise | Description |
Back stretch | Take a horizontal position, face up, bend your lower limbs at the knees. Grab your knees with your hands. Round and arch your back several times. Execution time: 1-2 minutes. The recommended number of approaches is 2. |
"Cat" | Get on all fours. As you inhale, tilt your head and arch your back like a cat. As you exhale, throw your head back and arch your back. This exercise helps improve mobility of the entire spine. Execution time is 30-60 seconds. The recommended number of approaches is 3. |
"Boat" | Lie face down on a hard surface. Straighten all limbs and simultaneously raise them as much as possible. Hold the boat position for 10-15 seconds. This exercise helps strengthen the muscle corset. The recommended number of approaches is 4. |
Therapeutic exercises for lumbosacral radiculitis should be performed daily. The pace of classes is slow. If pain occurs during exercise, you need to stop doing gymnastics and consult a doctor.
Using Natural Remedies
Treatment with folk remedies for lumbosacral radiculitis is not the main method of therapeutic intervention. Natural remedies can only be used after an attack of radiculitis has subsided. The most effective recipes are presented in the table.
Table 8. use of folk remedies:
| Means | How to cook | How to use |
Cheremsha | Fill a 3-liter jar with wild garlic and fill it to the top with vodka. Leave in the dark for 30 days, filter, and refrigerate. | The tincture is used to rub the sore spot. The procedure is done at night. Course duration is 7-10 days. |
Ledum | The plant is used to make ointment. Place 2 tablespoons of raw materials in a large saucepan. Add 5 tablespoons of vegetable oil. Heat the mixture over low heat, without waiting for it to boil. Leave for 10 hours, filter. | The ointment is used to rub into the affected area. The pain goes away within 5 days. |
Sheep's wool | A small piece of cloth is soaked in salt water. Then the wool needs to be dried. To prepare a compress, it is best to use sea salt. | The compress is fixed on the sore spot with a scarf or towel. |
The roots of cinquefoil | Pour 1 tsp. cinquefoil roots 200 ml of liquid just removed from the stove. Boil in a steam bath for 30 minutes. leave for 12 hours, filter. | The infusion is used to rub the sore spot. Number of procedures: 5-7. |
Annual pepper | Grind 2 pods of the plant, pour in 300 ml of ammonia. Leave the mixture in the dark for 14 days. | The tincture is used to rub the sore spot. Number of procedures - up to 10. |