Causes
Acute pulpitis is provoked by a variety of irritants.
The main role is played by infections that enter the pulp in different ways:
- descending - the infection comes from the caries cavity in the tooth;
- ascending - the infection penetrates through foci of other diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx;
- hematogenous / lymphogenous - infection occurs in diseases with an acute infectious nature or in sepsis.
In addition, the disease can occur as a result of various dental injuries. Acute pulpitis occurs as a consequence of a wound to the pulp with instruments used by dentists, or when the rules for preparing teeth are not followed.
Also, the cause of the development of pulpitis can be the toxic effects of various chemicals used by dentists.
Routes of pulp infection
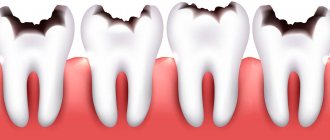
Infection entering the pulp chamber is most often caused by the progression of deep caries. Or its reoccurrence after poor quality treatment. This is the path through the crown of the tooth.
Infection is possible through the apical foramen, that is, through the root of the tooth. The “movement” of bacteria into the pulp chamber through the root opening can be provoked by inflammation or suppuration of tissues adjacent to the teeth: the maxillary sinus, palatine tonsils, gums, dental sockets, periodontal processes and others.
Incomplete or unprofessional cleaning of deep periodontal “pockets” can also cause pulpitis. As well as a general infection of the body, in which bacteria enter the blood and then penetrate the pulp through the blood vessels.
The deeper the periodontal cavities, the greater the risk of pathology
Stages and forms of acute pulpitis
In today's medicine, the following acute forms of pulpitis are distinguished:
- infectious / aseptic pulpitis - by etiology;
- reversible / irreversible pulpitis - according to outcome;
- root / total / coronal pulpitis - by location;
- diffuse / focal - according to morphological and clinical characteristics.
Focal acute pulpitis
Focal acute partial pulpitis represents the initial period of inflammation occurring in the dental pulp. It takes about two days in duration. In this case, the focus is usually located in the zone of the pulp that is closest to the caries cavity.
This form of the disease is characterized by intense pain that occurs suddenly or from any irritation. Its duration always varies, usually up to half an hour. Several hours may pass between attacks of pain. The patient is able to correctly identify the disturbing tooth, since the pain does not spread to other areas.
Diffuse acute pulpitis
Acute diffuse pulpitis represents the second stage of the development of the disease, during which the inflammatory process affects the coronal, and later the root lobes of the pulp. Acute diffuse pulpitis gives the following picture: attacks of pain are longer in duration, and rest periods, on the contrary, are reduced (maximum is about 40 minutes).
Doctors call this form of the disease acute serous pulpitis. At night, the pain persists, but it also bothers you for a long time due to exposure to irritants. In addition, temperature changes cause sharp pain. The pain is not localized, it can be felt in another part of the jaw, in the ear, back of the head, cheekbone, submandibular area, etc.
When the tooth is tapped, pain also appears; upon examination, the doctor reveals deep caries.
Purulent acute pulpitis
Acute diffuse pulpitis after a couple of days is replaced by a purulent stage, or acute purulent pulpitis. This period is accompanied by pain of a pulsating nature, it becomes almost unbearable, almost constant. Painful sensations only occasionally become less severe. Sharp pain occurs when you touch the tooth, as well as when the temperature changes. The purulent stage can last from 2 days to 2 weeks.
Diagnostics
Only a dentist can diagnose the disease after studying the anamnesis, after examining the oral cavity with the help of instruments, electroodontodiagnosis of the disturbing tooth, and radiography.
If acute serous pulpitis occurs, the doctor, upon examination, discovers deep caries. In this case, pain is felt during probing of the bottom area, but it does not occur during tapping of the tooth. If the patient has a purulent form of the disease, then probing, on the contrary, is completely painless, but tapping can cause it.
In addition, thermal test data, as well as the result of radiography of the diseased tooth, help in diagnosing acute pulpitis. In the laboratory, the patient’s blood is additionally examined and the amount of immunoglobulins in the oral fluid is determined.
When diagnosing, it is necessary to distinguish pulpitis from other diseases with a similar history. If there are doubts about making the correct diagnosis, you should consult other specialists.
How to recognize pulpitis? Symptoms and signs of the disease
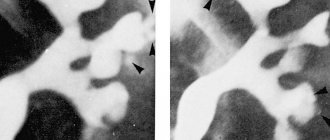
Since an x-ray does not provide a clear picture of pulpitis, it is determined by the type of carious lesion and its location.
Important! Using X-rays, you can only detect caries that has affected at least a third of the hard tissues of the tooth.
Depending on the form, caries appears differently on an x-ray:
- Average caries. There is a darkening localized strictly within the dentin.
- Deep carious lesions. The dark areas on the x-ray communicate with the pulp chamber. Sometimes a slight darkening of the cavity of the neurovascular bundle is visible.
- Secondary caries. X-rays show defects with uneven contours. Light areas are visible next to them. Sometimes the border between the filling and the cavity seems to be “undermined” - this indicates pathological changes in the tissues.
- Wedge-shaped changes. A gap is visible near the neck of the tooth - a wedge-shaped white stripe.
Important! Radiography does not detect cervical, fissure, approximal and caries in the spot stage. These types of pathology are not characterized by significant damage to tooth tissue.
Lesions on the occlusal (chewing) surface are best visible on x-rays. At a certain stage they take on a V-shape.
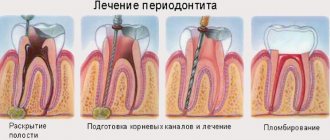
Treatment of acute pulpitis
In the presence of acute pulpitis, treatment is concentrated on preventing inflammatory processes in the pulp, as well as trying to restore its natural functioning.
To relieve the patient of pain, he is prescribed analgesics. If the patient is young, the use of a conservative method in the treatment of aseptic pulpitis allows preserving pulp tissue. The caries area is treated mechanically, and the use of medications is prescribed: non-irritating antibiotics and antiseptics.
An anti-inflammatory medicinal restorative paste is placed at the very bottom of the cavity, and a temporary filling is installed (for a maximum of a week). After this time, if the patient does not report any complaints of pain symptoms, a permanent filling is installed. In certain cases, physiotherapy is prescribed.
If the disease is purulent or serous, then irreversible transformations occur, leading to the loss of the functional performance of the pulp, the result of which is the need for its removal: completely or partially. This procedure is performed under anesthesia. Read more about local anesthesia for dental treatment→
At the same time, partial removal allows you to save the root pulp. They resort to this method of treatment when the disease occurs in multi-rooted teeth, or when the pulp is exposed. The dental cavity is opened with the further elimination of the coronal and ostial pulp, a dentin-stimulating paste is applied, and then the pulp chamber is sealed.
When the pulp is completely eliminated, the root canals are thoroughly treated with medications using instruments, the necrotic pulp is removed, and the tooth is restored with a filling.
Conservative methods
The biological or conservative method of treatment consists of carrying out anti-inflammatory measures, the purpose of which is to stop inflammatory processes without drastic methods. A special paste with a therapeutic effect is applied by the doctor to the bottom of the cleaned carious cavity (the pulp may not be opened, but it can be perforated for the best outflow of exudate).
Medicinal pastes may contain hormonal drugs, antihistamines and antibacterial agents, as well as vitamins and enzymes. Many pastes and proprietary materials used include calcium hydroxide.
Surgical methods
This type of treatment involves complete or partial removal of the pulp.
Most often used:
- The vital extirpation method involves complete excision of the pulp. The operation is performed in one stage under the influence of painkillers.
- The method of devital pulp extirpation is the complete removal of the pulp during its necrosis. The procedure is carried out in 2 stages with the application of arsenic paste or paraformaldehyde.
It doesn’t matter which method of treatment is determined by the doctor, the main thing is compliance with aseptic and antiseptic principles at every stage of the work. To obtain a high-quality result, it is recommended to monitor all stages of treatment using x-rays.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment of acute pulpitis may take from two to fourteen days. It involves stopping inflammation, preserving and restoring the functioning of the pulp. This is often possible with serous pulpitis in young patients. In order to eliminate pain symptoms, the dentist prescribes painkillers. The treatment takes place under local anesthesia. After treating the carious cavity, a special paste is applied to its bottom and a temporary filling is applied. In the normal course of treatment, after 5–6 days it is changed to permanent. With serous-purulent pulpitis, restoration of the pulp is impossible, so it is removed (partially or completely).
Treatment of acute pulpitis has been successfully carried out for several years in the dental department of the CELT clinic.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Complications
In the process of treating inflammatory processes occurring in the pulp, as well as after the end of treatment of pulpitis, complications sometimes arise. Most often they appear due to a violation of the treatment method. However, there are times when complications develop as a result of circumstances beyond the doctor's control.
Below is a list of possible complications:
- The occurrence of pain after a temporary filling has been installed. This usually occurs as a result of excessive pressure of the material on the pulp; re-application of a therapeutic dressing is required.
- Death of cells in gum or bone tissue. Occurs due to improper installation of a temporary dressing with arsenic acid, which gets on the gums. The affected area is washed, the gums are lubricated with iodine tincture. After 2–3 days, you can carefully remove the affected area of tissue.
- The occurrence of acute periodontitis. The pathology develops due to an overdose of the drug during the treatment of pulpitis, as well as as a result of violation of the permissible time for applying the drug. The pulp is removed, and a medicine with an analgesic and antiseptic effect is injected into the canals.
- The occurrence of periodontitis due to poor-quality filling of the canal or incomplete elimination of the affected tissue. This complication is dangerous due to the fact that the patient takes the toothache that occurs after completion of treatment as “normal” and misses time. All this will result in forced tooth extraction.
- Incomplete elimination of the pulp provokes pain, which is a reaction to changes in temperature. Repeated treatment is required, as a result of which the pulp is completely removed.
- Breaking off a dental instrument is quite common. The fragment is removed with tweezers or forceps.
- Perforation of the wall or bottom of the dental canal. The hole is closed with specialized material to prevent the development of inflammation.
Read more about complications of the course and treatment of pulpitis→
Prevention
Prevention of the occurrence of acute pulpitis is the timely detection and subsequent treatment of caries lesions in all teeth, including milk teeth.
To minimize the likelihood of caries formation, you should follow simple rules:
- brush your teeth and tongue twice a day;
- use anti-inflammatory or antibacterial mouth rinses (twice a day);
- after eating, rinse your mouth with slightly warmed boiled water;
- use floss on a systematic basis to clean the spaces between teeth;
- go for a medical examination to the dentist every 6 months;
- stop smoking;
- Eat foods rich in fluoride, calcium and vitamin C.
The health of the body as a whole almost directly depends on the quality of the condition of the teeth in the oral cavity. If a person has unhealthy teeth, it is not only unsightly, but also quite painful for the patient. Toothache is almost impossible to endure.
That is why at a certain stage in the development of dental disease, a person still turns to specialists for help. It is better, of course, when a visit to a doctor occurs at the initial stage of the development of the disease - in this case, there is a high probability of preserving not only the tooth itself, but also the dental tissues.
Do not forget that preventing a disease is easier than treating it in the future. In addition, no artificial tooth can replace a molar, so you need to make every effort to keep your own teeth healthy.
Author: Elena Streletskaya, doctor, especially for Karies.pro