- Backache
- Shoulder pain
- Redness of the skin at the site of the lesion
- Pain in the affected area
- Swelling in the affected area
- Bruising
- Pain when trying to bend your fingers
- Inability to bend the leg
- Ankle dysfunction
- Crunch when injured
- Bruise at the site of a tendon rupture
- Impaired muscle mobility
- Impaired grasping function
- Inability to move the lower leg
- Recession of the muscle
- Patellar displacement
Tendon rupture is a traumatic injury to these anatomical elements. Most often, a tendon rupture occurs in the leg, since this is where the greatest load falls. A tendon rupture occurs when there is traumatic injury to the connective tissue portion of the muscles that attach to bones and muscles.
- Causes of breakups
- Varieties
- General symptoms
- Achilles tendon rupture
- Symptoms
- Treatment
- Treatment
Anatomical structure of the hand
The brush consists of sections:
- wrist;
- metacarpus;
- fingers.
Each finger on the hand consists of three phalanges. The joints that will interest us most are the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints. The proximal interphalangeal joint is formed between the 1st and 2nd phalanges of the fingers, and is the first joint on the finger from the palm. The distal interphalangeal joint is located between the 2-3 phalanges, this joint is located near the tip of the finger.
There are two surfaces of the hand: palmar and dorsal. Bending of the fingers is carried out in the direction of the palmar surface: if we clench our fingers into a fist, we bend them. The flexor muscles are responsible for flexion; the flexor tendons of the fingers are located on the palmar surface of the hand. Extension of the fingers is the reverse process: if we look at the open palm, the fingers are in an extended position.
The extensor muscles are responsible for extension; their tendons are located on the dorsum of the hand. They are more susceptible to traumatic factors, so their rupture occurs more often than the rupture of the finger flexor tendons.
Peculiarities of applying a primary suture to the flexor pollicis longus tendon
The tendon of the flexor pollicis longus runs on the hand in the thickness of the muscles. It is enclosed throughout its entire length in a synovial sheath, which is looser than the sheaths of the other fingers. If the tendon of the long flexor pollicis is damaged at the level of the metacarpophalangeal joint, it is difficult to find the central end in the thickness of the Shepag muscles and a significant widening of the wound or an additional incision is often required. It is also difficult to pass the tendon through the fibrous canal at the level of the metacarpophalangeal joint. In addition, when operating in this area, it is always necessary to anticipate the danger of damage to the sensory and motor branches of the median nerve (see Fig. 27). Still, the results of suture and plasty of the flexor pollicis longus tendon are better than on adjacent fingers.
Rice. 122. “Critical zone” for the suture of the finger flexor tendons (shaded).
Rice. 123. Diagram of the transfixation technique for suturing the flexor tendons. a - according to Pugachev; b - according to Verdan; c, d, e - according to Bstekh.
Primary suture of the flexor tendons on the palm. Here the flexor tendons of the II-III-IV fingers, surrounded for 1.5-2 cm by loose peritendineum, pass outside the synovial sheaths. The results of their recovery are more favorable. Injuries to the flexor tendons in this area are often multiple and complicated by injury to the digital nerves.
Suture of the digital flexor tendons in the area of the synovial sheaths in the “critical zone” is difficult and gives worse results (Fig. 122). Each surgeon has the right to decide the question of feathering, delayed suture and flexor tendoplasty in the area of tendon sheaths in practice in accordance with his experience and specific conditions. According to the opinion of most modern surgeons, a primary tendon suture throughout the “critical zone” can only be used under ideal conditions: a clean wound with smooth edges without complications of bone damage and without a skin defect and no later than 6 hours from the moment of damage.
Rice. 124. Scheme of transosseous fixation of the central (a) and peripheral end (b) of the deep flexor tendon.
The principle is briefly summarized as follows. When tendons are injured in the “critical zone,” only the flexor digitorum profundus is restored to integrity. The central end of the superficial flexor tendon is sutured to the deep one, proximal to the tendon suture, outside the tendon sheath area. This detail not only helps maintain finger strength, but also maintains muscle balance. Most surgeons (N.M. Vodyanov, 1973; Beeleb, 1956; Veran, 1960) use the transfixation technique with “supporting” sutures to suture the flexor tendons in the tendon sheath area (Fig. 123). With this method, after excision of the wound, the area of damage to the tendon sheath expands in the proximal and distal directions, but, as far as possible, the retaining annular and cruciate ligaments are preserved. If the central end of the tendon is not found in the wound, then an additional incision is made in the palm, from which it is brought out into the wound towards the distal end.
In the area of the palmar wound, under the control of the eye, the central end of the deep flexor through the skin, the palmar aponeurosis and the superficial flexor is pierced with a stainless needle and fixed to the periosteum of the metacarpal bone in the corresponding interosseous space. With this method, the tension force of the muscles is removed, and the abutting ends of the tendon on the finger can not be sutured or only adapting sutures can be applied to the peritenonium, then the ligamentous apparatus of the tendon sheath is restored using the method of S. I. Degtyareva (1970) or another method. To avoid adhesions, partial excision of the tendon sheath is recommended at the level of damage within 0.5-1 cm. The operation ends with careful hemostasis and a blind suture of the wound; immobilization of the hand with a simulated dorsal plaster splint.
The duration of immobilization depends on the period of tendon regeneration and on the consolidation of the fracture in case of combined injuries. The needles fixing the tendon are removed after 3 weeks. If the deep flexor tendon is damaged at the level of the distal interphalangeal joint, fixation of the central end to the distal phalanx with a transosseous removable suture is indicated (V.S. Dedushkin, 1976; Fig. 124). The postoperative management of patients with damage to the tendons of the hand is very responsible. Special works are devoted to this issue (N.V. Kornilov et al., 1975, etc.) - Of course, it is necessary to carry out postoperative treatment under the direct supervision of the operating surgeon together with a physiotherapist and a physiotherapist according to a developed, but always individualized scheme.
Active movements are allowed only after removal of the fixing needles and blocking threads - no earlier than 3 weeks. Active movements in the distal interphalangeal joints are carried out with sparing fixation of the middle phalanx (V.I. Rozov, 1952). On average, patients are discharged to work after 1.5 - 2 months. Removable, lightening or hanging sutures interfere with blood circulation to a lesser extent and are simpler than intra-barrel sutures, therefore several of their variants have already been developed and the improvement of parts continues both here and abroad. Conditions for emergency intervention are always less favorable than planned surgery by a qualified surgeon in a calm environment. Therefore, the indications for the primary suture within the synovial-aponeurotic zone are narrowed in favor of delayed suture and early tendoplasty.
How does a finger tendon rupture occur?
The mechanism by which a rupture occurs is different: excessive load on it with excessive stretching and subsequent rupture, or a sharp strong blow directly to the tendon. In addition, in some diseases, tendon fibers tend to become thinner, and then they rupture with minimal load or spontaneously.
Tendon ruptures occur:
- open;
- closed (subcutaneous);
- complete (with separation of a bone fragment);
- incomplete (without bone damage).
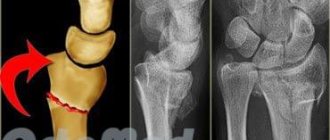
In addition, the gap can form at various levels: in the area of the distal or proximal interphalangeal joints, as well as at the level of the metacarpus and wrist. However, the most common injury occurs at the level of the distal interphalangeal joint (where the tendon fibers attach to the tip of the finger).
What happens when a tendon ruptures?
Symptoms of injury are quite specific. Usually, after a strong blow, pain and swelling of the finger occur, then characteristic deformities develop. When a rupture occurs at the level of the distal interphalangeal joint with bone damage, a so-called “hammer finger” occurs. In this case, the tip of the finger seems to hang down, and its extension is impossible. If there is no treatment, this type of deformation may progress to the next.
A “swan neck” is formed. This deformity occurs when there is excessive pulling force on other tendon bundles located at the proximal interphalangeal joint and relaxation of the palmar aponeurosis. If the rupture occurs at the level of the proximal interphalangeal joint, then, with prolonged absence of treatment, a “loop-shaped” deformation of the finger occurs: the finger cannot be straightened in this joint, and deviation to the side also develops.
Important! These deformities can form after a fairly long period of time from the onset of pain and swelling. Long after the injury, it will be more difficult to restore finger mobility. Therefore, delay in this situation can lead to complications; it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Diagnosis of damage to the extensor muscles of the fingers is relatively easy and is carried out by a surgeon in the presence of characteristic deformities and the very fact of injury. It should be remembered that due to the work of the hand’s own muscles, extension in these joints can be maintained. Therefore, the doctor must be attentive and vigilant in order to promptly exclude concomitant injuries and prevent possible complications.
To do this, it is necessary to take an x-ray of the hand in two projections. In addition, if the rupture occurs spontaneously, it is necessary to conduct a number of other diagnostic studies (identifying inflammatory and other markers in a blood test) to identify the cause of thinning of the tendon bundles.
Signs of an ankle injury
We have already described the general signs of such injuries, so let’s figure out what happens in the leg when the joint is displaced and the ligaments are injured. With an internal twist of the leg, the entire weight of the human body suddenly shifts to the outer part of the foot, while the reflexes do not have the opportunity to work correctly, because they direct their action to regain lost balance. This creates critical tension on the outside of the ankle, where the tendons connecting the bone are located. As a result, when the maximum load is generated, the ligaments do not have time to adjust and are injured. The degree of damage depends entirely on the duration of the load and its maximum weight. At lower values of these indicators, minor injuries are formed; larger values accompany the formation of much more serious injuries.
Treatment options: what methods and techniques are used?
Treatment of ruptures of the extensor tendon of the fingers can be carried out with or without surgery.
Conservative treatment involves applying a plaster splint for at least 6 weeks. Fixation of the finger is carried out either in the “writing” position or in the position of excessive extension. This depends on the level of the tear and whether there is bone damage. In addition, a plaster cast can only be applied for fresh tears.
You should know! Conservative treatment, which involves applying a cast, is only possible for certain types of tendon ruptures. In each specific case, the question of the possibility of such treatment is decided by the attending physician.
However, most often the treatment of such injuries is surgical. It is important to know that surgery in the area of the distal interphalangeal joint has a slightly worse prognosis. This is due to the fact that the blood supply to the distal parts of the finger is carried out by smaller vessels and is easily disrupted, and the tendon fibers gradually become thinner.
When sutures are applied to thin fibers, they may not withstand the load and come apart. In addition, the operation involves applying a tourniquet to the hand for better visualization of the surgical wound, which to some extent also impairs the blood supply to the finger. As a result, tissues grow less well and complications may occur more often. However, surgery is considered the most effective and relatively quick treatment method if all requirements and precautions are met.
The main indications for surgery are:
- stale breaks;
- damage to surrounding tissues;
- wound suppuration;
- ineffectiveness of previously performed conservative treatment.
The operation may consist of several stages. In case of severe inflammation and suppuration of the wound, it is necessary to carry out sanitation of the wound: remove non-viable tissue, wash the wound and reduce the inflammatory reaction. If the ends of the tendon are difficult to bring into the wound, they resort to widening its edges and removing the ends using special tools. Only after this can you resort to tendoplasty - restoring the integrity of the tendon bundle. Tendoplasty is carried out in conditions of a calm wound and subsided inflammation.
The operation may include several components: applying a tendon suture, internal splinting, suturing the capsule of the damaged joint, suturing the bone.
A tendon suture is a special type of suture in which the surgeon brings together and connects the ends of a torn tendon in a special way and restores its integrity. The importance of this stage is due to the special load on the tendon fibers.
This suture is used for pronounced and long-standing ruptures, when matching the ends is difficult, and precise fixation is necessary for complete fusion of all fibers. Sutures can sometimes erupt, but more often this happens with inflammatory diseases, as well as if the wound has festered, or the immobilization with plaster has not been carried out for a long enough time.
In addition to the application of a tendon suture, internal splinting is characterized by the removal of a thread-holder through the skin and its fixation on a button or to a gauze ball. Thus, the load on the tendon is reduced, and the likelihood of sutures cutting through becomes less.
Important! Additional incisions are made in accordance with the anatomical structure and location of skin folds. Incorrect incision can subsequently lead to complications in the form of additional deformities. In addition, incisions that cross skin folds are more difficult to heal and slow down the recovery and rehabilitation process.
What to do after surgery?
The postoperative period is accompanied by immobilization of the hand with plaster or wires passed through the bone for a period of at least 4 weeks. This is necessary for complete fusion of the sutures and prevention of complications. If tendon integrity has not yet been restored and the cast has been removed before 4 weeks or is broken, the toe will return to the corresponding deformity position and a re-cast or reoperation will be required.
Rehabilitation after removal of the cast consists of active and passive gymnastics. This helps restore tendon function and prevents the development of contractures (immobility in the joint). In addition, hydrotherapy and heat therapy are used. It is very useful to perform various household manipulations.
You can wash small items in warm water, play musical instruments, do modeling or knitting. Return to professional activity is possible after 8 weeks of rehabilitation. In each specific case, the question of the need for exercise is decided by the attending physician and the exercise therapy doctor.
In conclusion, it should be noted that rupture of the extensor tendon of the fingers is a fairly important problem in modern traumatology. Injuries occur in everyday life and, if not treated correctly, can lead to loss of hand function.
The success of treatment largely depends on the duration and severity of the injury - extensive and stale injuries worsen the further prognosis even if the stages of the operation are performed correctly. In addition, performing an operation requires sufficient qualifications of a surgeon, so these operations are performed routinely in specialized departments of hospitals.
In trauma practice, hand injuries are the most common; 30% of the total number of patients consult doctors with hand injuries. This is due to the fact that a person performs almost all types of work with the help of his hands. There are frequent cases of damage and rupture of the extensor tendons of the fingers. Due to the special anatomical structure, minimal amount of fat and muscle tissue, at first glance, a not deep cut can not only damage the skin, but also reach the tendons.
The hand is conventionally divided into three sections:
- Wrist – consists of 8 small bones arranged in two rows. These bones are located in different planes, due to this, an anatomical depression is formed on the inner surface of the palm, a groove where the tendons of the finger flexor muscles are located.
- Metacarpus – formed by 5 short tubular bones (corresponding to the number of fingers).
- Finger bones - 4 out of 5 fingers consist of three phalanges, the longest (proximal) is closer to the metacarpus, then comes the middle one, and the nail or distal phalanx ends the finger. The thumb is an exception, having only two phalanges, excluding the middle one.
33 different muscles are involved in providing motor functions of the hand, most of which originate in the forearm, then muscle fibers form tendons, ligaments that cross the surface of the palm, joints, located on the inside of the fingers.
There are no muscles on the outside of the palm. The inner side has three muscle groups, their names correspond to the group of fingers whose movements they provide:
- muscles of the thumb;
- little finger muscle complex;
- middle muscle group.
Extension movements are possible thanks to the tendons located on the outer surface of the hand; flexion is provided by those located on the inside of the palm.
According to statistics, ruptures and injuries of the extensor tendons are more common.
Classification of tendon ruptures
An important factor in classifying hand injuries is the time elapsed from the moment of injury to the time of contacting a traumatologist. Fresh injuries are those that are less than three days old; after this time, stale injuries are diagnosed. Old injuries include hand injuries that occurred more than 21 days ago.
The number of damaged flexor and extensor tendons of the fingers also affects the determination of the injury class; the following are possible:
- isolated rupture (the integrity of one of the fibers is broken);
- multiple (rupture of several tendons);
- combined (various types of tissues are involved - nerve endings, blood vessels, ligaments, tendons).
A subcutaneous tendon rupture is classified as a closed injury; if there are cuts to the skin, it is classified as an open injury.
Depending on the factor that caused the violation of the integrity of the tendon, the acute or degenerative form of the injury is determined. Acute becomes a consequence of cuts, bites, degenerative occurs due to wear (degeneration) of fibers during constant, same type of physical activity or due to diseases that cause changes in the structure of tissues.
Features of Achilles tendon injury
The Achilles tendon is the most powerful in the human body, so it is quite difficult to rupture because it requires considerable force. In addition, its location prevents rupture - it is located in a special channel containing liquid to reduce friction.
Damage to this anatomical element can be of several types:
- open, which most often occur as a result of an industrial injury, for example, a leg injury in the Achilles tendon area with metal shavings, glass, etc.;
- closed, usually found in athletes after unsuccessful jumps or due to high-speed mechanical impacts;
- direct, resulting from a direct blow to the area of the Achilles tendon, and indirect, resulting from severe tension or stretching of the calf muscle.
In case of injury, the tendon can either completely rupture or tear, and depending on this, two types of pathology are distinguished: complete and partial rupture.
There is also such a variety of this damage as professional. This pathology is a degenerative injury to the Achilles tendon in the leg over a long period of time due to regular stress on it. Dancers and athletes (including acrobats) are susceptible to this disease.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this pathology are as follows:
- sharp pain in the leg (directly at the site of injury);
- upon inspection, a depression is noted above the damaged area;
- the defect can be felt by palpation;
- ankle function is impaired;
- there is a positive Thompson effect - when pressing on the calf, there is no reflex flexion of the foot.
Features of the treatment of this pathology
It should be said that conservative treatment of this type of traumatic injury is possible only if you consult a doctor in a timely manner. The doctor can apply a plaster splint only in the first hours after the rupture - in the future, surgical restoration of the integrity of the ligament is required.
In addition, surgery is indicated when there is an open rupture of the Achilles tendon and when the injury is very serious.
Note that conservative treatment through immobilization is used extremely rarely today, and the reason for this is that during the period of immobilization the joint completely loses its mobility and it is almost impossible to develop it after that. In the case of surgical restoration of the ligaments, the joint retains mobility, which allows the person to return to their usual lifestyle and continue their activities.
Diagnostics
Primary diagnosis is associated with determining the nature of the injury; the survey conducted by the doctor at the emergency room is aimed not only at identifying and identifying the traumatic object, it is important to know the associated factors. Unfortunately, many patients are injured while intoxicated, which is a contraindication to the use of many medications, including some painkillers.
Having collected a thorough history, the specialist proceeds to a visual examination and palpation of the patient.
The so-called hammertoe shape of the finger is the result of a fall on the hands with straightened fingers or a wound caused by a sharp object. In this case, it is visually noticeable that the finger is slightly bent at the joint located between the middle and nail phalanx (proximal interphalangeal joint). With the cutting nature of the condition, partial separation of the distal phalanx is possible.
If the victim's finger(s) are bent in all phalanges, we can talk about damage to the hand on the outside and damage to the wrist. Open wound surfaces leave no doubt; in cases of closed injuries, the doctor makes a diagnosis, determines the location of the rupture, based on visible symptoms.
A proximally bent finger is described as a boutonniere deformity. In this case, it is clear to the doctor that the rupture occurred in the central part of the tendons, the lateral ones are not affected. From instrumental studies, it is recommended to take an x-ray of the finger from several angles.
If the cause of the rupture of the tendons of the hand is destructive processes in the body, additional tests are prescribed to determine the cause and nature of the inflammatory process.
Ruptures of wrist extensors and flexors
Although the Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body, there are others that are also commonly injured. In particular, the most common type of industrial injuries are ruptures of the tendons of the finger (finger phalanges) on the hand, as well as flexors and extensors of the hand. Damage can be either complete or partial, while lesions of both the extensor and flexor of the hand and fingers are equally common, which is why a person has a dysfunction of grasping function.
The extensor tendons are located in the area from the middle third of the forearm to the nail phalanges and are responsible for the ability to straighten the fingers; they pass under the skin of the hand and are attached directly to the bones of the hand.
Most often, such traumatic injuries are open, when the ends of torn ligaments are visible in the wound - this is the main criterion for diagnosing this injury. Also, with this type of injury, the position of the fingers is indicative - they are in an extended state, and the person experiences pain when trying to bend them.
The main diagnostic sign of this injury is the sensation upon palpation of a triangular-shaped bone fragment that protrudes in the proximal part. General symptoms are also present: pain, swelling, redness and dysfunction.
Treatment
Treatment of this pathology can be either conservative or surgical. Conservative involves applying an immobilizing bandage for several months (6–8 weeks). If there is an open wound surface, surgical treatment is recommended, consisting of pre-treatment of the wound and the application of a special tendon suture. For chronic traumatic injuries, the injured tendon is excised and replaced with a graft.
Treatment options
When choosing a treatment method, the decisive factors are the class of injury and the speed at which the victim seeks medical help.
Surgery can be avoided in cases of early, closed, isolated, incomplete ruptures. Conservative treatment methods are used. Immobilization and symptomatic drug therapy are carried out. After the splint (plaster) is removed, rehabilitation procedures are prescribed.
In combination with medication, treatment with folk remedies is possible; for tendon tendinitis, curcumin has a good effect; it is used as a seasoning in cooking. This remedy leads to a reduction in swelling and pain. An anti-inflammatory and restorative remedy is a decoction of bird cherry berries (one tablespoon is poured into 250 ml of boiling water), drink several sips throughout the day.
A mixture of crushed ginger root and sarsaparilla is steamed with a glass of boiling water, drink 2 tsp. every 6 hours, the infusion has a beneficial effect on inflammation of the tendons; it can be used during the rehabilitation period after a rupture of the extensor finger. The use of traditional medicine must be agreed with the attending physician; uncontrolled use of medicinal herbs can lead to complications.
In other cases, surgery is indicated. The sooner the operation is performed, the more positive the prognosis for the restoration of motor functions of the upper limb.
The operation is aimed at:
- connecting broken sections of fibers;
- fixation of the tendon fiber when separating it from the site of anatomical attachment;
- according to indications, the wound surface is sanitized, necrotic tissue areas are removed (for wounds with a large area of damage);
- fixation or removal of bone fragments;
- internal splinting;
- Work is underway to stitch up and restore the capsule of the damaged finger joint.
To avoid postoperative ruptures and complications, a splint made of polymer materials or a plaster cast is applied. The duration of wearing the fixing bandage is 4 weeks or more. With early removal of immobilization agents, tendon sutures may be cut, scars that have not yet formed may be ruptured, and pathological flexion of the fingers will resume.
In the future, the patient does not require constant medical supervision and is transferred to a day hospital regime.
Rehabilitation after injury
To restore full function after a rupture of the tendon(s) on the finger, strict adherence to the prescriptions of a rehabilitation doctor is required. The specialist selects a set of physical therapy exercises, prescribes massage, and coordinates the use of restorative medications with the attending physician.
You can begin to develop your fingers after surgery only after the inflammation of the tendons has completely resolved. In cases where anti-inflammatory drugs were prescribed during the postoperative period, recovery of the finger tendons occurs more slowly.
Good results in developing fingers can be achieved by performing a simple exercise of clenching the hand into a fist and then opening the palm, fixing each position for 10-30 seconds. The exercise should be performed without jerking, slowly, and repeat approaches as often as possible.
Tendon injuries are a common problem, especially with open injuries. Closed injuries are less likely to affect tendons. Moreover, even a minor injury to a finger can lead to injury to the tendons, since they are located very close to the skin.
Rehabilitation
In all cases, after tendon ruptures, patients are prescribed rehabilitation aimed at restoring functions lost by joints and ligaments. Rehabilitation includes physical therapy, massage, dosed stress on the joints, as well as various thermal procedures.
The prognosis in most cases is favorable - a person can make a full recovery. And only with complex injuries is there a possibility of residual effects, manifested in the form of limited mobility in the affected joints. Recovery usually takes up to six months, but it all depends on the severity of the injury.
What to do?
If you think you have a tendon rupture
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: orthopedist-traumatologist, surgeon.
Source
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
Establishing diagnosis
In the presence of open wounds, diagnosis is not difficult. The nature and extent of damage can be determined during a visual inspection. If the tendons are torn, their ends can be seen with the naked eye. With closed injuries, diagnosis is somewhat complicated and requires the use of additional methods. Ultrasound diagnostics is mainly used to confirm the diagnosis.
The main signs of a tendon rupture are:
- Inability to bend the injured finger, lack of motor activity.
- Deep wound on the palm or wrist.
It is impossible to heal the tendons without surgery; restoration of the flexor tendons of the fingers
. This is because the muscles will contract, thereby preventing the tendon from constantly touching.
Operation
carried out in the following cases:
- Open injury.
- Tendon rupture (open or subcutaneous).
- Presence of old damage.
Thanks to the capabilities of modern surgery, restoration of hand tendons
can be carried out with virtually no restrictions, even for pregnant women and small children.
General principles of treatment
In the case of an injury such as a rupture of the quadriceps femoris tendon, or in the case of injuries to the tendons of the shoulder girdle, the treatment of this pathology will be the same. It consists of providing first aid - immobilization of the injured limb, general anesthesia (painkillers) and transporting the victim to the hospital.
After examination by a doctor, either conservative treatment is prescribed, as in cases with injuries to the flexor or extensor tendons of the phalanges, or surgical treatment, as in the case of such a pathology as rupture of the tendons of the quadriceps femoris muscle.
Surgical treatment consists of the surgeon stitching the torn tendons together, and sometimes, in the presence of open injuries, performing preliminary surgical treatment of the wounds. In this case, fusion occurs no earlier than two months after the operation, but a person can regain working capacity in 3–4 months - it all depends on the complexity of the injury.
How is recovery going?
It is better to begin tissue restoration measures immediately, in the first few days after injury. Restoring finger tendons after rupture
requires qualified assistance using microsurgery techniques. Thanks to the use of an operating microscope and high-precision methods during the operation, the following is achieved:
- Minimal invasiveness of the intervention.
- Minimal risk of complications.
- The possibility of restoring a damaged nerve.
- Achieving optimal fixation and reliable tissue connection.
The timing of the operation is very important. The sooner after the injury it is carried out, the greater the likelihood of a complete recovery. Otherwise, degenerative changes develop, overcoming which will require more serious intervention and hand surgery.
If the tendon is torn from the bone, it is fixed in the right place and a suture is applied. Afterwards, the limb must be immobilized so that the tissues have the opportunity to grow together in the correct position. Usually a splint is used for this. If the tear is incomplete, fixation of the limb without surgery may be effective. The main condition is sufficient tension of the tendon in a fixed state.
Postoperative recovery period
Rehabilitation includes several points:
- Elimination of movement of the affected area (a plaster cast is used for this).
- Physiotherapy course.
- Therapeutic gymnastics with a gradual increase in load.
Exercises are necessary to normalize blood circulation in the hand, tone the muscles, develop hand movements, and restore motor skills. Only if all points of the recovery plan are followed will mobility and all functions be fully restored.
The operation can be performed in a modern clinic of the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow. Making an appointment and any required information is available by phone or on the clinic’s website.
The indication for tendon suturing (tenorrhaphy) is its complete closed or open damage or dissection of more than 2/3 of the diameter of its trunk.
The primary tendon suture is applied during the first 24 hours after an open injury, simultaneously with PSO of the wound. A secondary suture is performed in case of significant contamination of the wound, crushing of tissues, formation of defects, or late seeking of medical help by the victim, after the wound has healed (2-4 weeks after the injury). The two-stage treatment tactics prevent the occurrence of purulent inflammation of the wound and melting of the tendon.
Treatment of tendon injuries of the hands and fingers
First aid for cut tendons consists of treating the wound, applying an aseptic bandage, fixing the damaged organ with a splint, and administering anti-tetanus serum.
Treatment of cut tendons of the hand and fingers is carried out in a hospital setting. A primary tendon suture is applied to the wound. When applying a primary suture, the surgeon must carefully restore the tendon bed in order to recreate the sliding apparatus, since the final outcome of the operation largely depends on this. If the wound is contaminated or lacerated, it is not recommended to place a primary suture on the torn tendon. In such cases, they treat it and wait for it to heal. A suture is placed on the damaged tendon only after one and a half to two months. For injuries on the palm, the best option is a removable suture made with nylon, nylon or thin metal thread. For old wounds, the tendon is excised and replaced with a tendon graft. To restore the functions of the damaged limb, therapeutic exercises are prescribed; it should be carried out from the first days after surgery until complete recovery. Physiotherapy is used at the same time.
How to Simply Recommend
Why the medicine does not work The key to successful treatment is, of course, following all the doctor’s recommendations and informing him of all significant changes during therapy. However, a specialist can talk as much as he wants about the regimen and duration of taking the drug, but most patients will still violate these rules. Read more
Tendon suturing technique
The tendon is sutured on a bloodless limb after applying a tourniquet. During surgical access, the skin must not be cut perpendicular to the fold lines. The tissues are cut layer by layer with a sharp scalpel, avoiding their blunt separation. Perform all elements of PCP of the wound; non-viable tissue is excised, the surface of the wound is washed, and if necessary, osteosynthesis is performed, sutures are placed on nerves and blood vessels, and skin defects are replaced.
The proximal end of the damaged tendon is often displaced a considerable distance from the wound as a result of muscle contraction. To find it, it is necessary to make additional incisions with the obligatory preservation of the integrity of the annular ligaments.
After this, both ends of the damaged tendon are brought into the wound and sutured using an atraumatic needle with a non-absorbable thread.
Methods of tendon sutures: 1- according to Bunnell; 2 - according to Tajima; 3 - by Pulvertaft
Tendon damage
A tendon injury is a common injury in which the integrity of the tendons is compromised due to a cut or tear. Due to their wide prevalence, open injuries to the tendons of the hand and fingers are of greatest clinical importance. A distinctive feature of such injuries is the lack of independent fusion, caused by muscle contraction and the formation of significant diastasis between the separated tendon fragments. Without treatment, the outcome is loss of function of the corresponding muscles, impaired movement and, as a consequence, limitation or loss of ability to work.
Tendon injuries can be single or multiple. Combinations with other injuries of the same anatomical zone are possible: extensive wounds with soft tissue defects, fractures of the bones of the hand and fingers, etc. Concomitant damage to other organs and anatomical segments is less common, including fractures of the bones of the limbs and torso, injuries to the chest , TBI, blunt abdominal trauma. Traumatologists treat tendon injuries.
Requirements for the technique of suturing tendons in synovial sheaths
- the seam must be strong and not cut between the longitudinal elastic fibers. To do this, the tendon is stitched diagonally several times, as Bunnell suggests, or a loop is cast according to the Tajima method;
- the surface of the stitched tendon should be smooth and not form thickenings or irregularities that could impede or completely block the movement of the tendons in the narrow channel as it slides between the walls of the annular ligaments. To prevent these complications, additional microsurgical adapting sutures are applied to the edges of the tendon, smoothing out the protrusions that often form between its edges after tying the threads. Another technical complication is the formation of an “accordion” (corrugation) after excessively tightening the ends of the thread. Such a tuberous surface of the tendon prevents its free movement through the opening of the annular ligament. In addition, stitching tendons of different diameters can lead to the formation of protrusions on its surface. Suture using the Pulvertaft method smoothes the transition from thick tendon to thin tendon;
- After suturing the tendon, its length should not change. Shortening or lengthening leads to limitation of movements;
- the suture material must be biologically inert relative to nearby tissues, not cause an inflammatory reaction and not contribute to the formation of scars;
- the tendon suture should not disrupt its blood supply. Therefore, the number of punctures should be the minimum necessary to ensure a durable anastomosis;
- mandatory restoration of the synovial sheath, annular ligaments and skin is necessary to prevent fusion of the tendon with nearby tissues and ensure its effective sliding;
- early mobilization after
In the field of practical traumatology, various types of mechanical injuries to the hands are classified as injuries that are especially often received by victims.
Not least in this category are tendon ruptures in the fingers. This trend is due to the specific structure of the hands.
The fingers are deprived of the natural protection represented by muscle tissue; the movements of the hands are carried out by connective tissues, namely the extensors and flexors of the fingers.
The severity of the injuries and the need for treatment is determined by the type of injury.
In mild cases, conservative therapy and rehabilitation measures are sufficient; in more severe situations, surgical intervention is necessary.
Help for deep cuts on legs
Cuts on the legs are distinguished by the degree of tissue damage.
They will be shallow and complex, with damage to the skin, muscle fibers, tendons, and blood vessels. Unlike closed wounds, in which the skin remains intact and bones and tissues are damaged, cuts on the legs are always open.
Use search Are you having a problem? Enter “Symptom” or “Name of the disease” into the form, press Enter and you will find out all the treatment for this problem or disease.
↑
Cuts on the legs with a blade occur as a result of shaving with a blunt instrument.
Without delving into the causes of cuts, let's consider what to do:
- You need to understand the severity of the injury, then the wound is washed and not touched with your hands.
- If you don’t have anything at hand, you can wash the wound with soap, preferably not household soap, but baby soap, and blot it with a clean cloth. The purpose of this treatment is to stop the bleeding, so the leg is placed so that the cut is as high as possible.
- The cut is compressed. After a few minutes the bleeding stops.
- Treated with an antiseptic.
- The bandage is changed daily, and after 2-3 days it can be removed.
↑
First aid
Cuts occur due to careless handling of sharp objects. Wounds are characterized by smooth edges and profuse bleeding, which washes away dirt and germs in the first minutes. More often than not, the wounds heal well.
Recommendations for anyone suffering from cut wounds:
- The victim must take a body position in which the injured part is in a calm, relaxed state;
- Do not touch fabrics with bare hands to avoid infection;
- Immediately after a cut, care must be taken to ensure that the wound is protected from the effects of microorganisms; to do this, cover it with a sterile cloth or wrap it with a bandage; in the absence of sterile material, use dry cloth, preferably ironed or disinfected;
- Stop bleeding; if the wound is deep, when choosing between stopping the bleeding and the risk of infection, they always give priority to preventing blood loss, we are talking about preserving the life of the victim;
- If it is deep, medications are not used without prescribing treatment or consulting a doctor, they interfere with the necessary procedures;
- Foreign bodies are removed by a doctor; independent removal leads to heavy bleeding, which can lead to death; The leg is fixed until examined by a doctor;
- First aid should be provided within the first 6 hours.
Minimal damage can provoke tetanus, so preventive vaccination should not be neglected.
All wounds, except minor scratches, should be treated by a doctor to prevent infection.
↑
Foot swelling
After a cut on the left or right leg, can the foot swell? This is a dangerous symptom of the inflammatory process. It is called felon caused by purulent accumulations.
Accompanied by felon:
- High temperature;
- Twitching in the area of the cut;
- Edema;
- Limited movements.
The disease develops rapidly. Pus penetrates inside.
If you detect at least one of the signs of panaritium, you must urgently consult a surgeon. Lack of treatment causes tissue death and sepsis. Timely assistance will save the patient from surgical intervention.
↑
Description
Depending on the characteristics of the anatomical location, the tendons of the hands, which ensure their mobility, are called flexors and extensors. The first ones are located on the palmar surface of the hand, the second ones are on its back side.
In addition to other classification options, flexors are also divided into two main types - superficial and deep. The tendons are supported by the proximal and distal phalanges of the fingers. The fibers cross the interphalangeal joint and attach to the subsequent joint.
The hands are deprived of natural protection in the form of fatty tissue and muscle layer, and therefore, when receiving mechanical injuries or lesions caused by various types of diseases, the tendons that perform flexion and extensor functions and are located in the proximal or distal direction are damaged.
According to the nature of the damage received, as well as the addition of additional signs, which include trauma to the skin, tendon ruptures are divided into open and closed. The treatment methods required to restore the integrity of the tendons are selected according to the characteristics of the injury.
Causes
Damage to the tendons on the fingers can be a consequence of various reasons, the characteristic features of which are the specific nature of the injury. According to this classification option, hand injuries can be divided into two main types:
- Traumatic. Ruptures of the tendons of the fingers can be a consequence of the influence of factors such as injury from sharp objects, stretching of a finger during active sports, or excessive physical activity. Both open and closed injuries to the extensor tendons are possible.
- Degenerative - dystrophic. Violation of the integrity of the tissues of the fingers according to this type is a consequence of diseases leading to damage to the tendons.
To draw up an appropriate treatment plan for the fingers, determining the cause of the injury is mandatory.
Forms
Depending on the location of the injuries to the fingers, ruptures are divided into several main types:
- Multiple. Violation of the integrity of several fibers, damage to the central bundle of the extensor tendons.
- Combined. This type includes open tendon injuries at various levels, implying a violation of the integrity of the skin and ligaments.
- Isolated. Damage to an individual tendon of the finger.
The nature and severity of the injury received are determined by the characteristics of its receipt. It should be noted that the most common cause of ruptures of tendons located on the surface is palmar subluxation of the distal phalanx.
Characteristic symptoms
A rupture of the ligaments of a finger, regardless of its characteristics, is accompanied by severe painful sensations. Other signs may vary somewhat depending on what types of ligaments were injured:
- Violation of the integrity of the flexors is accompanied by a decrease in the corresponding ability, the fingers assume an excessively extended state.
- Damage to the extensors is characterized by the inability to straighten the fingers.
It should be noted that even with isolated injuries, the motor functions of the entire arm are impaired. For example, with injuries to the first finger, the area of pain can spread to other segments of the hand.
Treatment methods
The treatment regimen for tendon ruptures on the finger is selected according to the nature, severity of the injury, as well as how long ago it was received. For minor injuries, a measure such as finger immobilization, that is, the use of fixing bandages, is sufficient. In more severe cases, surgical intervention is necessary, the main task of which is to restore the integrity of the tissues using radical methods.
Medication
Drug treatment is mandatory for all types of ligament ruptures in the finger. First of all, it is necessary to use anesthetic drugs that will help relieve pain and eliminate discomfort. Taking medications of this group must be carried out until the expressed pain disappears.
In open forms of tendon ruptures on the fingers, it is necessary to prevent tissue infection and the development of inflammatory processes. For this purpose, antibiotics and agents with anti-inflammatory properties are used. The choice of drugs is carried out individually, according to the characteristics of the clinical case.
Folk
Safe but effective methods of alternative medicine will help to cope with inflammatory processes and painful sensations when ligaments of the fingers are torn. The following recipes are most effective:
It should be remembered that it is possible to achieve positive results with the help of alternative medicine only if you use them regularly and over a sufficiently long period of time.
Physiotherapy
In order to speed up the healing process after a tendon rupture, it is necessary to use physiotherapy methods, the therapeutic effect of which helps eliminate pain, relieve inflammation, and stimulate regenerative processes. Frequently used methods include laser therapy, physiotherapy, paraffin baths, and mud therapy.
Therapeutic exercises
To restore the motor abilities of a limb after a ligament rupture, it is necessary to regularly perform therapeutic exercises that help develop the damaged tendons. To get positive results, it is enough to perform simple but very effective elements of gymnastics for the fingers:
- Alternate squeezing and unclenching of hands.
- Connecting the brushes into a lock.
- Make circular movements with the brush.
Operational
Surgical intervention is necessary against the background of significant damage to the ligamentous apparatus. Treatment of this kind includes the following manipulations:
- Connection of damaged fibers.
- If the fiber has been separated from the anatomical attachment site, its fixation is necessary.
- Elimination of foci of infection and inflammation, if any are identified.
- Applying internal splints to the damaged finger.
After surgery, the patient is recommended to follow preventive measures for a certain period of time to prevent recurrent tissue damage. Such measures include wearing a plaster cast, which is subsequently replaced with an elastic one.
Tendon sprain and rupture
- Causes
- Types
- Kinds
- Achilles tendon
- Flexors
- Therapy
Tendons connect muscle tissue to bones.
They ensure normal motor activity of the limbs. Tendon stretching or rupture causes a lot of discomfort to a person.
Such an injury not only limits the patient’s movement, but can also have other, rather unpleasant consequences.
If a person’s tendon fibers are sufficiently developed and trained, he will very quickly be able to cope with the consequences of damage. Until the age of 15, tendons grow and develop, and then the process of strengthening them begins. To avoid sprains and tears in the future, you need to actively engage in sports at a young age from 15 to 25 years.
Causes
A tendon is a connective tissue that is a natural extension of a muscle. With the help of such fibers, muscles are tightly attached to bones. Doctors distinguish several types of tendons, namely:
- Short and long;
- Cord-shaped, lamellar, round;
- Wide, narrow.
Most tendons are distributed in the area of the lower extremities - in the foot, pelvis, and under the knee. Some fibers experience little stress, while others are constantly stretched and are at greater risk of injury.
When stretched, the connective tissue of the tendon increases slightly. This occurs by breaking some of the fibers in the large bundle. If the injury is very serious, the doctor may diagnose a tendon rupture. Why this happens, we will consider further.
The thing is that the tendons on the leg can stretch, but only in a certain direction, and to certain limits. For example, the popliteal fibers are designed to flex and extend the leg. If this fabric receives a large load, along with torques, stretching or tearing may occur.
The main causes of tendon injury include:
- Bad fall, slipping on ice;
- Dislocation of a limb;
- Excessive exercise in the gym.
Doctors say that with age, connective tissue fibers become less strong, so the risk group for limb injuries includes not only athletes and bodybuilders, but also older people.
Types
Foot ligament rupture
With the development of inflammatory disease of the tendons, their elasticity decreases significantly, the fibers become less elastic. If your doctor has diagnosed you with tendonitis or paratenonitis, you must take care of the ligaments, since the development of these pathologies significantly increases the risk of sprain.
Tendinitis is inflammation of the tendons. Occurs if the muscles of the limbs constantly experience severe overload.
Often this pathology affects athletes who work too hard in the gym and lift a lot of weight. Tendinitis can also develop as a complication from rheumatism or an infectious disease.
With this pathology, the tendon fibers become less strong, making them easier to stretch or tear.
Parathenotitis is a disease in which the tissue around the tendon becomes inflamed. This disease can develop against the background of frequent but minor hemorrhages into the tissue, which gradually accumulate.
This leads to swelling and hardening of the tendon. On palpation, the patient feels painful discomfort.
Most often, parathenotitis affects the lower extremities and is localized in the lower leg or heel area.
To treat inflammation of the tendons, the doctor may prescribe a course of physical therapy, as well as taking antibacterial drugs. Strengthening therapy will help protect inflamed fibers from sprains and tears.
Kinds
Types of Sprains
Most often, the tendon is damaged as a result of injury. You can make a careless sudden movement, lift too much weight, and weakened connective tissue fibers will stretch or even tear. Athletes often suffer from such injuries, but injury can also occur at home.
Doctors distinguish several types of sprains of varying severity:
- First degree. It stretches only a few fibers in the ligament, the rest of the connective tissue remains intact. This injury is accompanied by minor pain in the area of injury. Some swelling may occur. The course of treatment, as a rule, lasts no more than 7-10 days.
- Second degree. The tendon is not completely torn, but most of the connective fibers are damaged. The patient feels pain, the joint becomes almost motionless. You can often see a bruise on the surface of the skin. It will take about 1 month to treat such an injury.
- Third degree. All fibers in the tendon are torn. As a result of such an injury, the joint becomes unstable, motor activity is impaired, and the person feels very severe pain. The affected limb swells and bruising is visible on the skin. A torn bundle of fibers must be restored within 40-50 days. If the injury is complex, the doctor may prescribe surgery.
The injury of the first degree of severity passes without any consequences. More complex injuries can lead to the formation of small nodules at the site of the connective tissue rupture, which will often become inflamed and cause pain.
A sprained or torn ligament should be treated under strict medical supervision. If the nerve endings do not heal properly, the sensitivity of the limb will be impaired, and the patient will often feel a tingling sensation in the injured area.
Achilles tendon
Achilles ligament
The Achilles tendon is located at the back of the foot. It is believed that this ligament is very strong and elastic, but, nevertheless, the risk of injury is very high.
The thing is that such fibers are very often subjected to heavy loads. A person can strain their Achilles tendon as a result of a bad jump, spinning their foot, or falling.
Most often it goes to the area of the distal connection, located in the heel area.
An Achilles tendon rupture is a very serious injury that can be safely classified as grade 3 of severity. Typically, the fibers rupture after a strong blow to the tendon.
You may suddenly turn your foot incorrectly while jogging, or jump unsuccessfully from a height and twist your ankle. The victim immediately feels severe pain, a blood spot forms under the skin, and the foot swells.
Directly at the site of tendon rupture, the skin and muscles visually fall inward. The movement of the foot is limited, so the patient cannot stand on his toes.
To fully restore the victim’s motor activity, you need to urgently consult a doctor. He will conduct an examination, make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment. Your doctor will likely immediately apply a splint or cast to your foot to limit its movement.
In some severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Today, ligament injuries are less and less treated by immobilization. The thing is that during the time necessary for normal fusion of fibers, the joint completely loses mobility, and it is very difficult to restore it later.
Surgical repair of the tendon allows the patient to recover faster and return to normal life.
Flexors
In addition to the Achilles tendon, small tendons of the fingers and flexors of the hand are at risk of injury. Most often, these types of fibers suffer from damage in production. If the flexor ligaments are damaged, the person cannot fully clench the hand into a fist or grasp something in the hand.
Connective tissue injury can be either open or closed. When trying to bend the fingers, the victim will feel severe pain. Additional symptoms of a torn or sprained flexor muscle in the hand or finger may include swelling, redness, and loss of movement.
Depending on the severity of such an injury, the doctor may prescribe surgery or conservative treatment, which involves wearing a special immobilizing bandage for 1-2 months.
A special surgical operation can effectively repair an open rupture of the tendon of the hand or finger. The doctor will pre-treat the wound and then apply a special tendon suture.
If the injury is old and untreated, the motor activity of the hand can be restored by replacing the damaged ligament with an implant.
Therapy
Location of tendons in the foot
If the doctor has diagnosed you with a grade 1 tendon injury, you can safely limit yourself to treatment at home. To do this, just follow the following recommendations:
- Wear a special orthopedic bandage that will fix the joint in one position.
- For several days after the injury, try not to put stress on the tendon. It's better to spend this time in bed.
- Ice compresses will help relieve pain. You can use them every 15-20 minutes until the unpleasant symptom completely disappears.
- Treat the damaged area of skin with special medicinal ointments.
If the injury is severe, the doctor first immobilizes the joint and prescribes painkillers. The patient will have to undergo a long course of treatment and rehabilitation in a hospital. Prolonged immobilization of the joint leads to disruption of its basic functions.
To restore mobility to the limbs, you need to perform therapeutic exercises, massage, and attend physiotherapy. Remember that the fused tendon is still very weakened, so you need to load it gradually.
The rehabilitation process after a serious injury can take from 6 months to several years.
Source: //pro-md.pp.ua/legs/travmy/rastyazhenie/suhozhiliy/