Osteosclerosis is a condition—a symptom of many diseases—that involves hardening of one or more areas of bone. As a result, the bone loses its elasticity, and under normal loads, a fracture can occur precisely in the areas of osteosclerosis.
Osteosclerosis of bones does not show itself for a long time, while the process goes deeper and deeper and can lead to immobilization of the limb, the development of tumors, and pathological fractures. The disease is detected using radiography, and based on its results, orthopedists or traumatologists prescribe treatment: either conservative or surgical.
About osteosclerosis
Only an attentive doctor who takes an x-ray for another disease can determine its presence at the very beginning. However, this rarely happens. You can suspect osteosclerosis (subchondral, that is, on the connective tissue) with osteoarthritis, because these two diseases often go together.
Also, osteosclerosis is often combined with the following diseases:
- Melorheostosis;
- Osteoporosis;
- Osteopoikilosis;
- Chronic idiopathic myelofibriosis.
Modern clinics are increasingly offering genetic studies that can determine predisposition to a particular disease. Such studies provide a high degree of accuracy in assessing the risk of disease. At the same time, the danger of osteosclerosis cannot be underestimated, since it can lead to paralysis and even malignant tumors, that is, cancer.
However, osteosclerosis also happens not pathological, but physiological, which appears during the growth of the skeleton in children. In this case, it is detected in the growth zones, but then, as a rule, it goes away on its own. But the pathological one occurs already in adulthood.
The likelihood of developing osteosclerosis is relatively high because it is the second most common bone disease after osteoporosis. Diagnosis and treatment plan are prescribed by a traumatologist and orthopedist.
How does the disease manifest itself?
Usually the symptoms are subtle, so a person is not in a hurry to see a doctor. When applying, patients usually complain of high fatigue when walking, as well as pain in the limbs. In some cases, deformities may occur and pathological fractures may also occur.
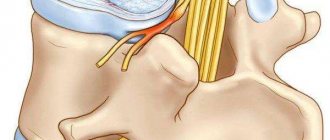
It should be noted that at first there are no pronounced symptoms when such a disease appears in the spine, but osteosclerosis often causes the appearance of osteophytes, the development of which can lead to a number of extremely unpleasant pain syndromes and neurological disorders.
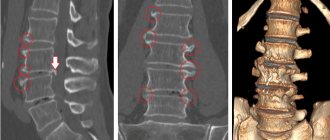
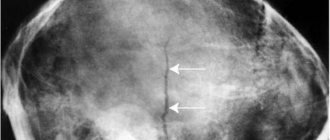
Osteosclerosis on x-ray
- On an x-ray with osteosclerosis, shadows of the bone are visible against the background of the surrounding soft tissues;
- The spongy substance inside the bone acquires a finely looped structure (looks like many small loops);
- The internal contour of the bone becomes uneven;
- The medullary canal becomes narrower or even disappears completely.
Foci of osteosclerosis of the spine, knee, and hip joints look like many evenly distributed light spots. This is piebald osteosclerosis. With it, the cortical layer does not become thinner, but the inner one turns into spongy and loose. There is also even osteoporosis. With it, osteosclerotic lesions look transparent. In the spongy substance, trabeculae, that is, plates and septa, are visually visible.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I consult for osteosclerosis?
If you have complaints, you should start with a therapist. Most likely, he will write out a referral to a surgeon or traumatologist. The treatment of the disease is carried out by an orthopedic doctor, who may request consultations with a surgeon, infectious disease specialist, traumatologist and oncologist, if necessary. If necessary, a sample may be taken for a biopsy (for cancer testing). Densitometry helps determine the mineral density of bone tissue.
X-ray image of osteosclerosis
Stories from our readers! I want to tell my story about how I cured osteochondrosis and hernia. Finally, I was able to overcome this unbearable pain in my lower back. I lead an active lifestyle, live and enjoy every moment! A few months ago I got a cramp at the dacha; a sharp pain in my lower back didn’t allow me to move, I couldn’t even walk. The doctor at the hospital diagnosed osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, herniated discs L3-L4. He prescribed some medications, but they did not help, the pain was unbearable. They called an ambulance, they put a blockade and hinted at an operation, I kept thinking about this, that I would turn out to be a burden for the family... Everything changed when my daughter gave me an article to read on the Internet. You can’t imagine how grateful I am to her for this. This article literally pulled me out of my wheelchair. In recent months I have started to move more; in the spring and summer I go to the dacha every day. Who wants to live a long and energetic life without osteochondrosis,
To identify osteosclerosis of the endplates, the patient is examined in the hospital by a vertebrologist, arthrologist, or orthopedist. Doctors identify complaints, collect anamnesis, conduct examination and palpation. Subchondral sclerosis of the vertebral bodies can be reliably diagnosed by densitometry. These are special test studies that confirm increased bone density. To differentiate and confirm the diagnosis of endplate sclerosis, a number of instrumental examinations are prescribed:
- x-ray,
- Ultrasound,
- CT,
- MRI,
- tests that reveal density.
Causes of osteosclerosis
In many cases, systemic osteosclerosis develops due to a genetic predisposition to it. However, there are other reasons - for example, the presence of an infectious disease. It often occurs with tertiary syphilis and bone tuberculosis.
The genetic factor, as well as the load on a particular organ, will help determine where exactly osteosclerosis will develop:
- In the spine;
- In the hip joint;
- In the rib;
- In the shoulder joint;
- In the knee joint;
- In the calcaneus;
- In the femur.
If a person knows about the predisposition, he has a better chance of taking an X-ray on time and stopping the progress of the disease at the initial stage, before it leads to dire consequences.
An increased risk of developing osteosclerosis appears:
- For Albers-Schönberg disease, fluorosis, saturnism, tumors of the breast, prostate and bronchi;
- If you have other diseases of the joints and bones;
- With low changes in hormone levels during menopause or simply with aging;
- With very serious stress on the joints;
- In case of joint injury;
- With excessive weight, obesity;
- In case of poisoning with heavy metals and chemical components;
- If there is inflammation in the body;
- For benign and malignant neoplasms;
- For fractures of a certain part of the body;
- With improper nutrition (absorption of large amounts of junk food);
- For metabolic disorders (metabolism);
- With dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- For marble disease, osteopoikilia and melorheostosis.
Clinical picture
Subchondral osteosclerosis ranks second in popularity among diseases of bone structures.
It can be both an independent pathology and act as a sign of other serious abnormalities: neoplasms, infections, genetic abnormalities and intoxication of the body.
The disease affects bone and cartilage tissue when there is an imbalance between the internal functioning of the body, which is responsible for the destruction and formation of bone structures.
A feature of the course of osteosclerosis is the absence of severe symptoms. The condition of the affected bone structures can only be assessed by x-ray. The lesions may be uniform or patchy in appearance.
The inner layer of the bone becomes more loose, and light defects are visible in the transparent bone pattern. The size of the bone and its geometric parameters remain unchanged. In the international classification of the disease, ICD-10 is assigned the code M85.8 and Q77.4.
Changes in the hip joint with osteosclerosis
Types of osteosclerosis
In addition to dividing osteosclerosis into forms (pathological and physiological, which appears during bone growth), it is also subdivided on other grounds.
By the number and volume of affected bones:
- Focal;
- Local;
- Common;
- Systemic.
Accordingly, focal osteosclerosis affects the smallest area of tissue, and systemic osteosclerosis affects the entire body. With local, we are usually talking about an injury superimposed on the disease in a certain area of the body, and with widespread, the pathology occurs in several bones at the same time.
The causes of osteosclerosis are:
- physiological (bone structures stop growing, and then the growth zones are damaged; usually occurs in children and adolescents);
- idiopathic (due to disruption of the correct process of bone development);
- post-traumatic (due to dislocations, cracks, fractures);
- reactive (as a reaction to a neoplasm, for example, a tumor, as well as in cases where nutrients do not enter the bone in the required volume);
- toxic (due to poisoning by chemicals or heavy metals).
Determining the causes of osteosclerosis helps to correctly prescribe a course of treatment. It will vary depending on the specific reason. For example, in case of toxic poisoning, it will be necessary to detoxify the body, in case of injury, it will be necessary to treat the injury, and so on.
Symptoms of the disease
Regardless of what form of the disease occurs and what localization, pain will be present in the clinical picture. At the initial stage of development, the pain will be periodic and appear only with increased physical activity. As the pathological process worsens, the pain syndrome will become chronic.
Thus, osteosclerosis of the heel bone and foot will be characterized as follows:
- curvature of the foot;
- deformation of the phalanges of the fingers;
- fatigue in the legs even with little physical activity;
- foot pain;
- flat feet;
- motor dysfunction.
It should be noted that this form of pathology occurs most often in children. Surgical treatment is used extremely rarely; conservative methods are quite effective.
Osteosclerosis of the hip joint will be characterized by the following clinical picture:
- pain in the pelvic area, which only intensifies when walking;
- as the pathological process worsens, the pain in the hip will become chronic;
- limited mobility;
- lameness.
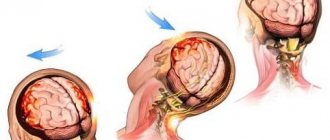
The development of this form of pathology is especially dangerous, since there is a high risk of neck fracture and the onset of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Such complications lead to disability, and death cannot be ruled out.
Spinal lesions are usually a complication after other diseases of the musculoskeletal system. In this case, there are no specific symptoms, the clinic of the underlying disease will manifest itself.
The danger of this type of pathology is that the discs become too fragile and a compression fracture can occur even after minor physical impact. Subchondral osteosclerosis of the spine more often than other forms leads to human disability.
In some localizations, the disease can be asymptomatic for a long time - when the ilium or shoulder joint is affected.
The clinical picture of this disease as a whole is nonspecific, so if you have joint pain, you should immediately seek medical help and not self-medicate. Treatment with folk remedies, in this case, is inappropriate.
Analyzes
In addition to X-rays, if osteosclerosis is suspected, computed tomography and MRI are used. Ultrasound may also be needed. Genetic testing is expensive, so it is done by those who can afford it. They are good because they allow you to determine with a high degree of accuracy whether there is a predisposition to osteosclerosis.
They also do an analysis of the biochemical composition of blood, urine, and, ideally, tumor markers, because this disease relatively often leads to oncology.
Treatment of osteosclerosis
Treatment of osteosclerosis with folk remedies is impossible; the use of modern medicine is necessary. The basis is injections with glucosamine and chondroitin, which restore bone and cartilage tissue. You need to prepare that the course of treatment will be long - from a quarter of a year to six months.
The administration of drugs is stopped when the doctor sees visible changes on the x-ray indicating that the disease has subsided.
Anti-inflammatory painkillers (hormonal and non-hormonal) are also used. Normalization of bone tissue function is accelerated by physiotherapy, which includes mud therapy, massage, ultrasound, magnetotherapy and electropheresis with medications selected by a doctor.
Therapeutic exercise serves as a complementary aid to the body with osteosclerosis. The load is increased gradually, and various types of exercise equipment are used during the recovery process. Recovery is accelerated by a proper diet with a minimum of fatty, fried foods and refined sugar.
Braces and bandages protect against injury, which will significantly complicate the course of the disease. A bandage is also necessary when increasing physical activity during treatment. And healthy, full sleep helps tissue change more quickly towards normal.
Main symptoms and diagnostic methods
Symptoms of osteosclerosis depend on the stage of its development:
- At the first stage, discomfort and unusual sensations appear.
- At the second stage, there is a feeling of stiffness in movements. It becomes difficult to carry out daily activities.
- At the last stage, if treatment is not started in time, complications may arise.
In order not to miss the chance to be cured, it is important to recognize the pathology in time. To do this, a number of diagnostic measures are carried out:
- First of all, this is an x-ray. With osteosclerosis, the image of the spine will have many dark spots - these are compactions of the bone tissue.
- MRI and CT.
- General, detailed and biochemical blood test.
Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes treatment.
Prognosis for osteosclerosis
In a large percentage of cases, a complete cure of osteosclerosis is possible, but if the problem has affected the joints and/or spine, then it can only be stopped and the patient relieved of pain, as well as further complications. You will have to constantly adhere to a certain lifestyle. A complete cure requires a bone marrow transplant. In some cases, splenectomy or red blood cell transfusion is used (if anemia develops due to illness).
If the disease is not treated in time, changes in the shape of the skeleton, paresis of the facial nerve, anemia, permanent injuries and even cancer are possible. In the worst situation, a person can become disabled or even die.
Damage to the hip joint
Osteosclerosis, which occurs as a result of coxarthrosis, causes significant trouble. People complain of severe pain that does not subside even with rest. Regular spasms are fraught with the development of excessive lameness. The condition is dangerous due to the high probability of a fracture of the femoral neck, or necrosis of the head of its bone. Circumstances result in disability or death. If discomfort persists, it is important to undergo examination to prevent the risk of complications.
Prevention
Osteosclerosis is easier to prevent than to treat it. Therefore, those who are at risk (genetic predisposition, heavy workload, living in a poor environment, excess weight) should take a number of measures to protect themselves from the disease.
- Limit the amount of alcohol you drink;
- Sleep on a hard-soft mattress;
- Make sure your posture is correct;
- Do not overload the joints;
- If you have excess weight, get rid of it;
- Do physical education.
Physical education is good because it improves blood circulation, and good blood circulation contributes to the normal functioning of tissues and reduces the likelihood of developing