The human body serves as a tasty morsel for various parasites: roundworms, pinworms, echinococci, Giardia, etc. strive to penetrate it. The last of these parasites deserve special attention, since it is very easy to become infected with Giardia, and the consequences of infection can be very serious. Giardia causes a number of unpleasant symptoms in adults: it can be abdominal pain, appetite disturbances, diarrhea, allergies, etc. Treatment of giardiasis must begin immediately as soon as you learn about the diagnosis. So, today we will talk about the symptoms and treatment of Giardia in adults.
What is giardiasis
Giardiasis is a protozoal invasion that occurs predominantly with damage to the small intestine and is accompanied in some patients by allergic and neurological symptoms. Giardiasis is a protozoal invasion that occurs primarily with damage to the small intestine and is accompanied by allergic and neurological symptoms in some patients
Giardiasis is widespread among rats, mice, rabbits, dogs, cats and other animal species. The source of infection for humans is a person who secretes Giardia cysts, and possibly some species of animals with which humans often come into contact (dogs, cattle, pigs, etc.). The leading role as a source of invasion belongs to humans. Mature invasive Giardia cysts are excreted in feces.
Cyst discharge during giardiasis is intermittent and wave-like and begins 9–22 days after infection. The number of viable cysts excreted in feces can reach 23 million per 1 g, and on average it is 1.8 million per 1 g. In experiments on volunteers, it was established that the entry of 1 to 10 Giardia cysts into the human digestive tract can lead to the development of invasion in 10–30% of people.
Methods for diagnosing giardiasis
Modern medicine offers several examination methods if there is a suspicion of intestinal infection with parasites.
Stool examinations
A scatological examination involves taking stool and searching for Giardia cysts in it using a microscope. If infection occurs, the cysts, in most cases, are detected immediately. However, it also happens that a specific portion of feces in an infected person may not have traces of Giardia, so it is advisable to carry out several samples of material (4 - 5) with an interval of one week.
Examination of intestinal contents
Duodenal endoscopy allows you to obtain a more adequate picture of the patient’s intestinal condition. To confirm the diagnosis, a small amount of contents is taken from the cavity of the small intestine with a special probe and examined under a microscope. Experts assure that the most effective method of duodenal examination is to collect the contents of the duodenum using a vacuum method using a three-channel probe.
Blood test
Serological tests for the presence of specific antibodies in blood serum are an excellent method for diagnosing giardiasis. GSA 65 antibodies can be detected in the sample as early as two weeks after infection. Today, the serological research method is one of the most effective in diagnosing parasitic infestations. In addition, it is much easier to tolerate by patients than duodenal examination.
Giardia entering the human body
As a rule, infection occurs in cases where Giardia cysts enter the body with food (for example, vegetables, fruits, berries), drinking water, and also when hygiene rules are not observed (unwashed hands, flies). Giardia persists in the environment its ability to infect for quite a long time - in soil about 3 weeks, and in drinking water up to 3 months. According to some studies, cysts are found even in sea water (viability for about 1.5 months) and in dairy products (up to 3.5 months). After Giardia has penetrated the stomach in one way or another, their further fate depends on the general state of the immune system person and the number of cysts ingested: the weaker the immune system and the greater the number of cysts, the higher the likelihood of developing giardiasis.
In accordance with the characteristics of parasites’ penetration into the body, the following pathways are distinguished:
- aquatic – infection occurs when using insufficiently purified water taken from the tap, as well as when water from an open reservoir enters the body; Contact-household - accumulation of pathogens occurs directly on household items in the form of clothing, dishes, toys and others;
- food - a variety of food products act as sources of infection. Giardiasis especially often occurs after eating foods that have not undergone appropriate heat treatment (fruits, vegetables, berries).
Routes of infection
Giardia has significant resistance. Depending on the temperature of the environment in which they are located, they can remain viable for up to 70 days in water and almost a month in feces.
Let's look at ways of infection and spread of the disease.
The first and most common route of infection is the so-called Contact-Household, the pathogen is able to enter your body through dirty hands, clothes, dishes, toys, that is, if the rules of personal hygiene are not followed.
The second most popular factor is the water factor, something that many people neglect so much; when drinking poorly or insufficiently purified water for household needs, for example, when washing fruits, vegetables or dishes, you have a high risk of contracting giardiasis. An untreated liter of wastewater contains more than a thousand cysts. In addition to all this, domestic animals that can carry cysts using their fur can be distributors.
About 75% of children have this disease. Adults are almost not bothered by this disease, due to the presence of a strong immune system that can fight off some diseases of the digestive system.
People who have a habit of biting their nails have the greatest chance of becoming infected.
What does lamblia look like?
The parasite can exist in two forms: vegetative and cystic.
- Vegetative (mobile) form . It is a drop-shaped unicellular organism with 4 pairs of flagella and a special attachment disk. The parasite needs flagella to move through the small intestine, and the disc helps tightly attach to the intestinal wall;
- cystic (immobile) form . Serves as an adaptation of lamblia to unfavorable conditions. If the parasite fails to attach to the right place, it enters the large intestine. Conditions in the large intestine are not suitable for the life of the protozoan; lamblia turns into a round cyst.
In this form, the parasite enters the environment with feces. Giardia in the form of a cyst can exist for a long time, wait for suitable environmental conditions, and when exposed to such conditions, it can again turn into a vegetative form.
Diagnostics
There are several basic medical ways to detect giardiasis in adults, for example:
- Fecal analysis, due to the incubation period, may not be able to determine the presence of parasites the first time, so the analysis is carried out twice with an interval of a week or a week and a half.
- Interotest is almost similar to the first method. The test involves swallowing a gelatin capsule with a piece of string inside. When it enters the stomach, the capsule will dissolve, and Giardia should cling to the same rope and come out along with the feces. Using a microscopic examination, the presence of parasites is determined.
- A biopsy test involves removing a small piece of tissue from the stomach wall to examine for the presence of cysts.
How can you become infected with Giardia?
Giardia in the environment is present in an inactive form, in the form of so-called cysts, which live outside the human body for about 3 months. Once in the gastrointestinal tract, they can multiply by pair division, in those places where a lot of them accumulate. How does giardiasis become infected in adults and children? How is giardiasis transmitted? Poor personal hygiene, through dirty hands, that is, by the oral-fecal route; eating unwashed fruits, vegetables, salads; it is possible to become infected through sexual contact if hygiene rules are not followed; using unboiled water, even spring water contains Giardia cysts; the presence of a large number of flies in the premises; they are the main carriers and sources of infection with giardiasis.
Infection with giardiasis is more often observed in childhood, so the incidence among children reaches 70 percent. It is believed that giardiasis in adults occurs three times less frequently than in children, since the strengthened immune system of the adult population is more likely to have resistance to various parasitic infestations in the digestive system.
However, often with giardiasis in adults, the symptoms may be blurred, and the person does not seek a thorough medical examination, mistaking some signs of giardiasis for other disorders of the digestive system or exacerbation of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Diet for the treatment of giardiasis
A special diet for giardiasis in adults, which consists of various foods and supplements, helps reduce the severity of giardiasis, as well as slow down the growth and reproduction of giardia, and strengthen the resistance of the mucous wall of the small intestine.
These goals can be achieved by eating healthy foods that are high in fiber and low in fat. These foods include whole grain breads, cereals, rice and pasta, as well as lean meats and fish, eggs, fruits and vegetables. You should not consume spicy foods, dairy products, citrus fruits, alcohol, or caffeinated drinks for two to three days after symptoms disappear.
Limited consumption of such foods reduces the amount of sugars available in the intestinal lumen, which may reduce the influx of water into the lumen and reduce the severity of diarrhea.
Reducing your fat intake will help reduce the severity of nausea and diarrhea, as well as reduce steatorrhea (fat in the stool). Often with giardiasis, lactase production in the small intestine is reduced, leading to lactose intolerance and subsequent diarrhea. Therefore, minimizing consumption
Dairy products containing lactose can reduce diarrhea, pain and bloating, as well as associated infections. Eating foods containing probiotics, such as kefir and yoghurt, helps improve microflora. This increases the protective properties of the intestinal mucosa and improves local immunity.
Signs of giardiasis in adults
With giardiasis in adults, the symptoms resemble diseases of the biliary tract and liver, and the full absorption of essential nutrients is reduced, leading to general malaise. The symptoms of this disease depend on the location of the parasites in the body and the duration of damage to the body by these protozoa. With giardiasis, a decrease in appetite may be observed
After cysts enter the gastrointestinal tract, an adult may remain only a giardia carrier, without the characteristic symptoms of the disease, but when the proliferation of giardia is massive, giardiasis manifests itself with clinical symptoms of the following diseases:
- cholecystitis, biliary dyskinesia;
- enteritis, duodenitis, enterocolitis, duodenal dyskinesia;
- allergic reactions - the occurrence of bronchial asthma and allergic cough, bronchitis, atopic dermatitis is often associated with the presence of giardiasis in a person;
- depression - Giardia, in the process of life, releases a lot of toxins that have a depressing effect on the human nervous system, causing inexplicable depression, sadness, and apathy;
- If an adult or child is diagnosed with vegetative-vascular dystonia, it is necessary to be examined for the presence of giardiasis, since the signs of giardiasis in adults and children in the chronic stage are similar to this symptom complex.
Giardia can cause apathy and depression
Considering the above, symptoms of giardiasis in adults may be as follows:
- weight loss as a result of decreased appetite, nausea;
- dyspepsia, constipation alternates with diarrhea, possibly foamy stools;
- soreness, bloating, increased abdominal rumbling, sometimes sharp severe pain in the gastrointestinal tract, heartburn, belching;
- mild pain in the navel area, in the right hypochondrium;
- increased swelling, increased sweating;
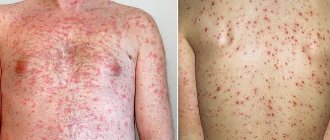
- pallor, dry skin, yellowness and flaking of the skin, formation of jams in the corners of the mouth, cracked lips;
- unmotivated fatigue, weakness, irritability, anxiety, dizziness, headaches; nervous disorders, tics, insomnia, restless dreams.
Symptoms
Many experts call this disease the “Parasite of Melancholy and Sadness”, which is why the disease in some cases manifests itself as tearfulness, irritability and decreased mood. But as mentioned earlier, diagnosing the presence of the disease is quite difficult due to the lack of obvious symptoms; this “hidden” period lasts up to almost four weeks.
But if you suddenly notice that the signals given below have begun to appear for no reason, you should think about visiting an infectious disease doctor; in addition, you can be consulted by a gastroenterologist.
Symptoms that will help identify giardiasis in adults:
- lack of appetite or sudden weight loss;
- dry or pale skin, rash. Sometimes “variegated skin” is observed, characterized by uneven redness of different areas with a yellow tint;
- nervous disorders, insomnia, strange dreams;
- excessive aggression, irritability, anxiety;
- a feeling of bitterness in the mouth;
- frequent constipation, sharply replaced by diarrhea;
- prostration;
- pain in the navel area;
- fever;
- vomit.
Symptoms such as anemia, palpitations, joint pain, dizziness, inflammation of the eyelids, fever sometimes occur with giardiasis and disappear only after treatment is completed.
Intestinal symptoms of chronic giardiasis in adults
With chronic giardiasis, pathologies can develop in the biliary tract, which provokes stagnation of bile and creates all the conditions for the penetration of intestinal bacteria into the gallbladder and bile ducts. Against the background of such changes, cholecystitis develops.
While living in the human body, pests release toxic substances into the blood, causing intoxication. Small flagellated pests, localized in the intestines, contribute to the disruption of the absorption of nutrients and the transportation of digested food to the lower intestines. Stagnation of chyme causes the development of rotting processes, which entails vegetative failure. A sick person quickly gets tired and feels constantly unwell.
There are cases when autonomic disorders in giardiasis, which occurs in an acute form, have more pronounced symptoms than lesions of the gastrointestinal tract. A person has been trying to overcome autonomic dystonia for a long period, but the treatment is ineffective and the symptoms, on the contrary, become intense.
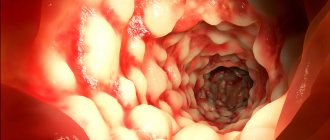
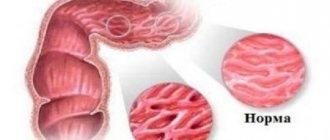
Signs of gastrointestinal lesions during giardiasis, which occurs in a chronic form, appear as a result of mechanical damage to the intestinal mucosa. Giardia is attached by means of a special device in the form of a disk to the villi of the mucous membrane of the small intestine, which provokes inflammatory processes. The main signs of the intestinal form of giardiasis are dyspepsia, abdominal pain
That is why the main signs of the intestinal form of giardiasis are dyspeptic disorders and abdominal pain. Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract include nausea, vomiting, flatulence, constipation, followed by diarrhea. The patient complains of frequent belching and a bitter taste in the mouth. Abdominal pain occurs in the navel area. Their intensity can vary - from cramping to stabbing and stretching. Sometimes the pain that occurs with appendicitis can be disturbing. With a chronic infection, abdominal pain is combined with signs of inflammation of the gallbladder and bile ducts. Against the background of massive invasion, intoxication develops, which most often affects the condition of the skin. In children, it becomes pale, and a jaundiced tint appears in the neck, armpits and sides of the abdomen. The skin on the palms turns red and peels severely.
In babies, giardiasis causes a rash on the neck, shoulders, back and chest. With an advanced infection of a parasitic type, hair loss and the appearance of cracks and swelling in the corners of the lips may occur. In children, skin manifestations of giardiasis occur with pronounced symptoms. Quincke's edema can become a serious complication. Lack of vitamins and iron in the body also has a detrimental effect on the condition of the skin.
How is giardiasis treated in women?
To confirm helminthic infestation, the patient must have feces and blood tested. If infectious agents are found during the examination of these biomaterials, deworming is carried out.
Treatment of giardiasis includes several stages:
- preparation for the removal of parasites;
- deworming and elimination of disease symptoms;
- normalization of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and correction of immunity.
To speed up the recovery process during the treatment period, it is advisable for women (especially pregnant women) to follow a diet.
This will create unsuitable conditions for parasites and reduce the load on the intestines. Also, during antiparasitic therapy it is necessary to drink antihistamines and enterosorbents. When prescribing antihelminthic drugs, the doctor takes into account the individual characteristics of the patient, symptoms of helminthiasis, age and the presence of concomitant diseases. However, pregnant women are prohibited from taking most of these medications, as they are very toxic. In this case, they can use folk remedies (garlic, onion, wormwood, pumpkin seed).
After drug deworming, restorative treatment is carried out. Its main task is to strengthen weakened immunity.
Many women are interested in the question: is it possible to get pregnant when there is lamblia in the body? With this type of helminthiasis, this is only possible if parasitic microorganisms have not infested the genitourinary system. In healthy women, the course of giardiasis is the same as in men.
But it is better not to delay the treatment of this disease, as complications such as infectious-toxic shock can sometimes develop.
At the same time, against the background of a long chronic course of helminthiasis, anemia develops due to impaired absorption of vitamins.
Giardiasis in acute form in adults
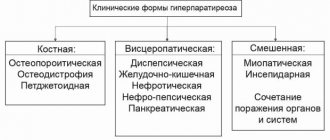
Symptoms of giardiasis can vary. Their intensity depends on how massive the invasion is and on the general health of the patient. Mostly, signs of gastrointestinal disorder are observed. The duration of the incubation period is 7-20 days. A common symptom of giardiasis is gastrointestinal syndrome. Giardia inhabits the small intestine, which provokes a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract. In the acute course of the disease, pain, nausea, belching, flatulence, and poor appetite occur in the navel area. The pain may be aching or cramping in nature. Against the background of an invasion, a person may experience diarrhea. At the beginning of the disease, the stool will have a watery consistency, but over time it will become greasy and semi-formed. The duration of the acute phase is a week, after which the disease becomes subacute and then chronic.
The main signs of the intestinal form of giardiasis include: pain in the epigastric region; pain around the navel; nausea; vomit; belching; heartburn; steatorrhea; lack of appetite; diarrhea followed by constipation.
The hepatobiliary form occurs in many cases in adults. It is characterized by the following symptoms: pain in the right side; bitter taste in the mouth; belching; pain on palpation of the liver; yellowness of the skin and itching; irritability; general malaise; dark circles under the eyes; allergic skin rash; cracks on the lips.
Prevention
At increased risk are women carrying a fetus, who should more carefully observe hygiene rules, namely, not swim in natural bodies of water (open), where the water is stagnant and in public pools.
After all, it is in these places that the simplest parasitic microorganisms are most often found. In addition, raw water should always be boiled before use and all hygiene rules should be carefully observed. In this case, it is necessary to regularly destroy cockroaches and flies.
If one of the family members has suffered from helminthiasis, then all objects with which he came into contact, as well as his towels, bedding and underwear, must be boiled for 5 minutes.
Thus, for preventive purposes, women should carefully observe the rules of hygiene. At the same time, once a year it is advisable to undergo a complete examination of the body for the presence of parasites.
Giardiasis often has a hidden course and does not manifest itself with specific symptoms. However, it is possible to identify the disease; the main thing is to be attentive to your health, and if suspicious symptoms appear, consult a doctor. There are different methods for diagnosing protozoal infection, which will be described below.
Symptoms of lambiasis in children
Parasitic infection with flagellated protozoa of the Giardia intestinalis type is a common disease, which, according to various sources, affects up to 30% of children - newborns, infants, preschoolers, schoolchildren and adolescents. Such an invasion can manifest itself in different ways: rash, intestinal upset, dysfunction of internal organs and – the main thing is general intoxication of the body. And although giardiasis in a child is relatively safe, it can lead to exacerbation of chronic diseases. The transition of the invasion itself to the latent stage also poses a danger. Therefore, parents should know exactly how Giardia appears in children, symptoms and treatment, and prevention of the disease.
In approximately half of the cases, the presence of parasites in the body is practically not manifested in any way. Minor ailments experienced by the child are attributed by parents to other reasons.
The disease in children most often occurs in an acute form, the main symptoms of which are the following:
- diarrhea. Diarrhea is the most common symptom of the disease. The nature of feces with giardiasis changes, the feces become liquid, with an unpleasant odor, mixed with mucus, usually yellow. Sometimes diarrhea alternates with constipation;
- indigestion . Intestinal function is disrupted, gas formation increases, and bloating occurs. Nausea and vomiting are symptoms characteristic of the acute form of the disease; they rarely occur in the chronic form;
- abdominal pain. Increased gas production, flatulence, and improper bowel function lead to spasms and pain around the navel and in the stomach area;
With giardiasis, a child may experience an increase in temperature
- temperature increase. A slight increase in temperature is possible when Giardia first enters the child’s body. It is typical for the acute form of giardiasis and is combined with intoxication and deterioration of the baby’s general condition;
- loss of appetite . Against the background of a general deterioration in the condition, the toddler’s appetite also changes. With an asymptomatic course, there may be no changes in appetite;
- malabsorption. Intestinal dysfunction and frequent loose stools lead to decreased absorption of nutrients in the intestines. The baby does not receive enough nutrients, vitamins and minerals and begins to lose weight;
Skin changes . A lack of vitamins manifests itself in skin symptoms, the skin becomes dry, pockets appear in the corners of the mouth, and cracks appear on the lips. Sometimes there is an increase in pigmentation, marbled skin pattern;
- deterioration in health . All this leads to a deterioration in the baby’s general condition; the baby becomes irritable, capricious, and gets tired quickly. If giardiasis is not recognized for a long time and the correct treatment is not prescribed, chronic malaise leads to a lag in the physical development of children;
Due to giardiasis, children may experience allergic reactions
- allergic reactions . Giardia multiplies in the child's body and produces toxins that are absorbed into the blood. Toxins suppress the functioning of the immune system and provoke the development of various allergic reactions, atopic dermatitis. Why do allergies and cough occur with giardiasis in children? Giardia lives only in the intestines and does not get into the lungs, so why is coughing considered one of the signs of giardiasis? Cough serves as a response to the introduction of toxins and is often allergic in nature. And reduced immunity with giardiasis provokes the development of chronic bronchitis;
- neurological disorders . Constant intoxication and vitamin deficiency lead to nervous system disorders. In addition to irritability and anxiety, there are nervous tics, hand tremors, and teeth grinding at night.
Giardiasis during pregnancy
Giardiasis during pregnancy is a fairly common phenomenon. During this period, hormonal disorders occur, which can cause increased sensitivity to various types of microorganisms. We also should not overlook the weakening of the functionality of the immune system.
How does the disease progress in pregnant women?
In the acute form of the disease, signs of gastroenteritis appear - an inflammatory disease of the stomach and intestines. Frequent, loose, profuse stools appear with an unpleasant odor, but do not contain impurities (mucus, blood). There is bloating and pain in the abdomen, decreased appetite, nausea and vomiting. Sometimes the body temperature rises to 38-38.5°C, and a pinpoint rash appears on the body.
In the chronic form of the disease, the expectant mother is worried about constant bloating, unstable stools (constipation alternating with diarrhea), abdominal pain, severe weakness, dizziness and headaches, nausea, allergic reactions (food allergies, skin rashes and others).
The chronic form of giardiasis in pregnant women is often accompanied by neurological symptoms (headache, mild dizziness, nausea and vomitus), as well as signs of general intoxication.
However, the disease can be asymptomatic, or the expectant mother regards its signs as manifestations of toxicosis. Therefore, he does not consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Does the disease affect pregnancy?
Definitely, it affects because giardiasis can worsen the course of pregnancy. A woman, in addition to toxicosis and other unpleasant but usual conditions for pregnancy, will be bothered by symptoms that sometimes resemble severe intoxication.
The effect on the fetus is also noticeable. Giardia in the intestines interferes with the normal absorption of nutrients into the blood, so the unborn child and the mother herself lack vitamins and other useful elements. Also, these parasites reduce the number of red blood cells in the blood, which leads to insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus. All this can lead to the development of various intrauterine pathologies.
What are the dangers of infection during pregnancy?
Giardia itself is not able to penetrate the placenta and infect the fetus, but the disease adversely affects the course of pregnancy and the condition of the fetus. Since the waste products of Giardia and the decay of dead individuals enter the blood, worsening the mother’s well-being and increasing the manifestations of toxicosis.
In addition, the fetus does not receive enough nutrients due to impaired digestion, as well as the absorption of vitamins, minerals, proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Giardiasis can lead to the development of one of the most serious complications of pregnancy: chronic placental insufficiency. In this case, the functions of the placenta are disrupted:
- delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus;
- hormone production;
- excretion of fetal waste products;
- protection against the penetration of toxins and infections from the mother’s body to the fetus.
When placental insufficiency develops early in pregnancy (before 16 weeks), the likelihood of miscarriage is high.
If the condition occurs late in pregnancy (after 16 weeks), normal fetal development is often disrupted. As a result, a child may be born with intrauterine growth retardation (low weight and/or height), with immature organs and systems. There is also a high risk of premature birth.
However, if changes in the placenta are not pronounced, then compensatory mechanisms are triggered, so a full-term and healthy baby is born.
Giardia, during its existence in the host’s body, releases toxic waste products into the blood, which provokes an allergic reaction. The disease in pregnant women entails certain consequences. Among them:
- Secondary fermentopathy and intestinal dysbiosis. Parasitic infection contributes to the suppression of healthy microflora. As a result, the mother’s body does not receive vital substances. This leads to impaired fetal development.
- Intoxication of the body. Chronic giardiasis causes liver dysfunction and severe allergies. A baby can also suffer from all these pathologies.
- Neurosis. Against the background of massive invasion, problems with the nervous system are observed.
Giardiasis, like other parasitic infections, can cause disturbances in fetal development. A pregnant woman needs to take these risks into account and follow all preventive measures. If you are unable to protect your body from this disease, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Treatment of giardiasis in pregnant women and breastfeeding
If the disease is asymptomatic, the expectant mother is in good health and the fetus is developing, it is recommended to refrain from treating giardiasis during pregnancy.
In other cases, the decision to use drugs to combat Giardia is made individually, since traditional drugs (Tinidazole, Macmiror and others) are contraindicated for use in the first three months of pregnancy.
However, there is a drug that can be used regardless of the stage of pregnancy: Enterofuril, since studies have not revealed its negative effects on the fetus. It is also prescribed for the period of breastfeeding.
Enterofuril is somewhat less effective against Giardia than all other recommended drugs. But if you follow the treatment regimen, dosage and diet, it is possible to eliminate parasites from the body.
In addition, Enterofuril has two advantages:
- It is not absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, minimizing the risk of allergic reactions.
- Does not disrupt normal intestinal microflora.
However, in the early stages of pregnancy (up to 12 weeks), Enterofuril is recommended to be prescribed with caution: when the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the risk of negative effects on the fetus.
Hygiene in the treatment of giardiasis
There is no vaccine for giardiasis, and the immunity that is developed after an illness is not very stable. Therefore, the risk of reinvasion remains high. Therefore, hygiene measures to prevent re-infection are very important.
Activities are carried out not only during the course of treatment, but constantly throughout life, since there is always a danger of contracting one or another parasitic or infectious disease transmitted through nutrition and household contact.
The basis of hygiene is the following rules:
- timely washing of hands after using the toilet and before eating;
- neutralization of drinking water by boiling;
- periodic cleaning of premises and change of underwear and bed linen;
- Washing raw fruits and vegetables before eating is important.
How to treat giardiasis
The question of how to treat giardiasis requires an integrated approach, but the main remedy is antiparasitic drugs. However, they have a high level of toxicity and allergenicity, so it is worth preparing the body before taking them and restoring them after.
In this regard, all treatment is divided into 3 stages:
- preparatory _ This stage lasts 2 weeks and includes: elimination of symptoms of intoxication; restoration of intestinal enzyme activity; taking medications that improve bile flow, enzymes, antiallergic drugs, sorbents; boosting immunity; diet;
- taking antiparasitic drugs. The duration of this stage is no more than 10 days due to the toxic effect of the drugs - this therapy includes taking antiprotozoal drugs, sorbents, as well as antihistamine therapy, which is aimed against sensitization of the body to etiotropic drugs;
- restoring the body and increasing immunity . This is the longest stage. Includes taking vitamins, probiotics, enzymes, as well as a diet that is aimed at restoring intestinal motility. At the same stage and with chronic giardiasis, treatment with folk remedies is allowed.
It is worth noting that specific drugs against Giardia have a number of contraindications: blood diseases; renal, liver failure; organic diseases of the central nervous system; pregnancy; lactation; allergies. It should be noted that drugs against Giardia have a number of contraindications
Side effects include: dyspeptic disorders: nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, salivation; pain in the abdomen; bowel dysfunction; metallic taste in the mouth; violation of taste perception; allergic reactions.
Nervous system disorders: headaches, dizziness; poor sleep, nervousness; impaired coordination of movements; convulsions; hearing loss; loss of consciousness.
Locally: pain in the vagina, copious odorless discharge; fungal infections of the genital organs; polyuria; brick-colored urine may be produced. Some medications are strictly prohibited for children.
Treatment of giardiasis disease
Treatment should be carried out in a comprehensive manner and in several stages.
It is best to start treatment during an exacerbation, since during this period it is best to monitor its effectiveness.
The first stage lasts no more than a week and a half and includes:
Following a strict diet based on eating food that maintains an acidic environment, which is very unfavorable for the development of parasites.
In turn, you should give up flour products, sweets, soda, and fatty foods, due to the fact that all this greatly irritates the gastrointestinal tract.
The diet should be followed in order to worsen reproduction, improve the flow of bile, and remove disturbing signs of giardiasis in adults
The second stage is based on the use of antiparasitic drugs:
- Metronidazole 400 milligrams three times a day for ten days.
- Fazizhin Half a tablet (0.5 grams) four times a day. Albendazole 0.4 grams once a day for five days.
- Macmiror 30 milligrams per kilogram of your weight in two doses.
- Furazolidone 2-3 tablets after meals for ten days.
- Ornidazole 3 tablets before bed or one tablet every 12 hours three times a week.
Folk remedies include: tincture of walnuts, carrot and birch sap. Treatment with onions, garlic, red pepper, etc. is also perfect, but they should not be abused, because spicy foods cause stomach irritation.
All these products do an excellent job of creating unfavorable conditions for reproduction.
Consequences of Giardia parasitism in the body
Giardia parasitism in the human small intestine is accompanied by a number of pathological effects:
- the introduction of Giardia into the mucous membrane of the small intestine causes the development of inflammation in it, which is the result of the toxic effects of the parasite's waste products. As a result of inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, the tissues of the small intestine are damaged, which leads to impaired absorption and insufficient enzyme activity;
Giardiasis negatively affects human immunity
- the binding of bile acids is disrupted, which causes skin itching, impaired intestinal motility, biliary dyskinesia and the development of a chronic inflammatory process in the biliary system;
- the synthesis of secretory immunoglobulin A decreases, which leads to chronic inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract;
- the prolonged vital activity of lamblia and the effect of their metabolites on the body forms a syndrome of chronic endogenous intoxication and secondary immune deficiency.
Treatment
Giardia parasitizes the human small intestine. Its usual place of residence is in the duodenum. There they block the normal flow of bile and thereby create good conditions for their development.
The sizes of Giardia are very small and are measured in microns. The average growth rate is 20 microns. It is simply impossible to see them with the naked eye. The disease is detected by clinical symptoms.
Attention! Giardiasis takes a long time to cure. The recovery period lasts 14 days. These days for the patient are associated with a strict diet and adherence to a diet.
To restore the intestinal microflora, the patient takes products containing bifidobacteria. He is also prescribed some of the enzymes, enterosorbents and antispasmodics.
Treatment with the classical method involves the use of medications:
- Metronidazole, although common, has become resistant to Giardia;
- Tinidazole, despite its effectiveness, has side effects of nausea and dizziness;
- Tiberal is a fairly successful drug in the fight against Giardia.
In the human gastrointestinal tract, Giardia may appear next to Candida, a fungal infection. This union of pests leads to dysbiosis, causing not only nausea and vomiting, but also constipation when excreting feces.
Why is Giardia dangerous in adults? Find out about the symptoms of Giardia in the liver here.
Find out how to treat Giardia in children and adults from the article:
Diet of the sick person During the treatment period, you can eat the following foods:
- a large amount of proteins reduces the growth rate of parasites;
- give up sweets;
- introduce dietary fiber into the diet;
- consume bran in large quantities, as well as porridge, fish from low-fat varieties, marmalade and marshmallows are useful;
- curdled milk, kefir and buckwheat porridge will help reduce the symptoms of the disease.
Nosology puts taboos on the following list: smoked meats, spicy marinades, fatty fish, sweets and chicken eggs.
Intoxication syndrome prompts the attending physician to prescribe medications that strengthen the immune system and reduce allergies.
Success in treatment is achieved with drugs that block the vital activity of Giardia. Enterosorbents, if you follow the regime of their use, neutralize parasite toxins.
A good outcome of treatment is achieved by an optimal relationship between the immune system, gastrointestinal tract and gall bladder. Good liver function and proper bile secretion into the small intestine reliably blocks the development of parasites.
The helminthologist recommends using immunostimulants and vitamins along with classical drugs.
Medical treatment
Akrikhin is considered the basic drug. Doctors have different methods of using this drug in their arsenal. The duration of treatment varies from 3 to 8 days. Mixed forms of the disease require the administration of furazolidone. At the age of 16 years, the therapeutic dose is 0.1 g.
When the doctor sees symptoms indicating chronic giardiasis, the advanced disease is treated by adding erythromycin to furazolidone in a volume of 1 IU (million international units).
Infectious disease specialists from Europe prescribe aminoquinoline to such patients. Take for 5 days, daily dose - 0.15 g. This drug has no side effects when used.
When the patient is in the hospital, he can be treated with a pathogenetic method called “autohemotherapy.” At the same time, vitamins are prescribed and plasma is infused.
Choleretic medications improve the flow of bile into the small intestine, as they relieve spasms of the biliary tract.
The use of classical medicine preparations does not at all interfere with the simultaneous use of folk remedies made on the basis of: horseradish, tansy, yarrow, cloves, wormwood, pepper, seaweed, ginger and chamomile.
Giardia can be easily eliminated using folk remedies. During the period of recovery of the body, it is appropriate to use choleretic and astringent herbs. But even the traditional method should be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Prevention of giardiasis
To prevent the development of this disease, you should follow simple rules:
- The main thing in the prevention of giardiasis is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene. Wash your hands with soap after coming from the street and before eating, no matter how trivial it may sound, and tirelessly repeat this to your children. Towels for adults and children must be separate;
- fresh vegetables and fruits must also be sanitized before eating;
- drink only boiled water. Even tap water can be contaminated with parasites due to a poor filtration system. And boiling kills Giardia in almost 100% of cases;
The main thing in the prevention of giardiasis is compliance with the rules of personal hygiene.
- get rid of the bad habit of biting your nails. Children should be monitored so that they do not put their fingers, toys, or various garbage in their mouths on the street;
- Boost your immunity and eat a balanced diet. Limit easily digestible carbohydrates in your diet and introduce foods that normalize intestinal function: vegetables, fruits, cereals; pay special attention to pets. Be sure to give them anthelmintic therapy.
Giardiasis is a disease in which the body does not develop lasting immunity. Therefore, you can become infected with it again. But its course, like its treatment, is quite long. Be alert: if any doubtful signs appear, consult a doctor so as not to delay treatment.
Correct prevention of pathology
Medicines or vaccines will not prevent giardia infection.
But common sense and basic precautions can help minimize the likelihood that you will become infected with a parasite or become a carrier of infection:
- Wash your hands with soap after using the toilet, before eating, after coughing or sneezing, after contact with any animals, after gardening, etc.
- Avoid ingesting contaminated water or water from any natural sources that may be potentially contaminated. This is especially true for water from open sources, such as rivers and lakes, where Giardia most often lives. Avoid getting water into your mouth when swimming in ponds or pools. Be sure to boil water for at least 1 minute, the quality of which you doubt. If boiling is not possible, you should add 0.5 ml of 2% iodine solution for each liter of water, and at least an hour should pass before drinking it.
- Avoid eating foods that may be contaminated. This applies, first of all, to raw vegetables and fruits, which must be thoroughly washed before consumption in uncontaminated water.
- Avoid introducing fecal residue during sex. It must be safe. For these cases, it is necessary to use condoms as a barrier against infection.
- Clean and disinfect surfaces that have come into contact with animal or human feces.
What is Giardia?
From the point of view of traditional biology, Giardia is a genus of flagellated protists from the order Diplomonadidae. This is a collective term that defines all representatives of its kind. This is not a type of helminth, although they are often put together and called worms. The direct causative agent of human giardiasis is intestinal lamblia, which parasitizes the upper parts of the small intestine. Here the parasite transforms from a cyst into a vegetative form in an active state. Giardia are very viable microorganisms that remain active in the environment for a long period of time. So in water and soil they can exist from three months to three weeks, respectively. However, not every person becomes ill with giardiasis during infection. For the appearance of the disease, two criteria are decisive:
- Number of cysts caught. In other words, the higher the concentration of cysts in the intestines, the higher the likelihood of infection.
- The state of immunity at the time of parasite implantation. If the body's resistance is at the proper level, the disease may not occur.
Animals are believed to play an important role in maintaining Giardia present in the environment. In the West, giardiasis has the popular name “beaver fever,” which is translated from English as “beaver fever.” This is because, in addition to cows, rodents, dogs and many other animals, beavers are considered one of the main vectors.
Giardia in adults multiplies extremely quickly in the body, filling the entire small intestine. Is there a specific chain of infection for giardiasis? It all starts with the fact that products with microscopic cysts come into view. After ingestion, they are sent from the aggressive acidic environment of the stomach to the alkaline part of the small intestine. Under favorable conditions, the outer shell of the cyst undergoes lysis and a new vegetative form appears.
Giardia attaches to the villi of the small intestine and feeds on everything that should have entered the bloodstream: amino acids, beneficial macro and microelements, antioxidants, broken down fats, vitamins, etc. Meanwhile, the human body “starves”, does not receive enough necessary substances and feels a lack of vital energy: the process of enzyme formation is disrupted, and there is a malfunction in the functioning of all organs and systems.
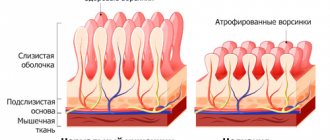
Initially, all changes are purely functional in nature, but as the disease progresses, organic disorders are recorded. The villi on which Giardia parasitize soon atrophy, and destruction of the cells of the gastric mucosa is observed. In the future, even after removing the parasites, it is almost impossible to restore normal function of the small intestine. After destroying the flora of the small intestine, Giardia moves along the gastrointestinal tract to more distant sections. Instead of useful substances and essential amino acids, toxic waste products of parasites enter the bloodstream. This leads to general intoxication and increased allergic status of the patient.
Not all opinions regarding the harm caused by Giardia are clear among experts. Many believe that they cannot in any way affect the health of the liver, disrupt the flow of bile and cause cholecystitis. The main evidence is the inability to move them along the bile ducts, since there they immediately die. But it is claimed that they interfere with the treatment of cholecystitis. There are also erroneous opinions (myths) among people, one of the main ones is that Giardia lives in the liver.
Manifestations of chronic giardiasis
Sometimes protozoal infection occurs without an acute stage. This is due to the fact that parasites have learned to shed immunity factors (antigens) that fight them.
More often, the disease begins in the acute phase, but in the absence of quality therapy, after 4–12 weeks it becomes chronic. That is, chronic giardiasis occurs as a result of prolonged parasitism of pathogenic microorganisms in the small intestine. Then the following changes appear in the body:
- Digestive disorders, absorption of lactose, vitamins, micro- and macroelements, proteins, lipids, carbohydrates. This is due to the fact that Giardia repeatedly damages the inner lining of the jejunum. As a result, the mucous membrane does not have time to renew itself and immature cells are formed that cannot produce certain enzymes.
- Allergic reactions, dysfunction of the central nervous system, as well as the liver. These conditions arise due to increased permeability of the inner lining of the jejunum and the penetration of toxins (harmful substances released by living or dead individuals) into the bloodstream.
- Pain occurs as a result of irritation of receptors in the jejunum.
- Giardia suppresses the immune system.
With the prolonged presence of Giardia in the body, pain appears on the right under the ribs, around the navel or along the entire front wall of the abdomen. Many patients complain of girdling pain, the intensity of which ranges from mild aching to sharp and paroxysmal.
In addition, stool disorders are observed when diarrhea alternates with constipation. As a rule, feces are greasy, have a characteristic shine, and are difficult to flush from the toilet.
An adult may experience flatulence, nausea, vomiting, and decreased appetite. Younger patients experience bruxism (teeth grinding) at night. This symptom occurs when there is a large number of Giardia in the jejunum, which are activated at night.
With chronic giardiasis, allergies develop:
- blisters, spots on the skin;
- itching in areas of the rash;
- inflammatory damage to the edges of the eyelids;
- food allergies;
- runny nose of allergic origin;
- atopic dermatitis;
- asthma, etc.
Children develop more slowly physically due to frequent digestive disorders, as well as impaired absorption of nutrients.
Giardiasis: features of the disease
Giardiasis is a parasitic disease caused by single-celled organisms - Giardia. When many people hear the word “parasite,” they imagine worms—pinworms or roundworms—that parasitize the human body. But Giardia are completely different parasites; they belong to the protozoa. The body of Giardia consists of only one cell, which is a full-fledged organism capable of movement, nutrition and reproduction.
Giardia can exist in two forms that transform into one another - active and inactive. The active form is called trophozyote. In this form, the protozoa can be found in the small intestine of a person, where they reproduce, feed and thereby harm him. The trophozyote has a slightly elongated body shape at one end, resembling a pear in outline. On the body of Giardia there are flagella and a sucker, which it needs for movement, nutrition and attachment to the surface of the intestine.
Important! In conditions outside the human intestine, trophozoites quickly die. Therefore, stool analysis for giardiasis is carried out within half an hour after collection. After an hour, active forms of parasites will no longer be detectable in it.
The inactive form of protozoa is cysts. They have an oval body shape and a dense shell that protects lamblia from negative external factors. Thanks to its presence, cysts can remain viable in the external environment for about 4 months. Trophozoites that detach from the wall of the small intestine and enter the large intestine, where the conditions for their residence are unfavorable, turn into cysts. Cysts are released with the feces of a sick person, and they also enter the oral cavity and provoke infection with giardiasis.
When a person swallows cysts, they move through the digestive tract. Once in the stomach, they, being moderately resistant to acids, do not die under the influence of hydrochloric acid as part of the gastric secretion, and move on.
Note: with an increased level of gastric acidity, the likelihood of contracting giardiasis is reduced. At low levels, the risk of developing giardiasis increases.
Once in the duodenum, the cysts turn into trophozoites - active forms of parasites. Here they feed and reproduce. Giardia reproduces asexually: one cell divides into two. This process occurs very quickly, the number of Giardia in the intestines doubles every 20 minutes.
We recommend that you find out the signs of intestinal polyposis.
We advise you to read why gastric xanthoma is dangerous.
How do adults become infected with giardiasis?
Infection with parasites occurs when their inactive forms enter the body. This can happen in several ways:
- household;
- water;
- food.
One of the main causes of giardiasis is neglect of personal hygiene rules. With unwashed hands, cysts land on household items, dishes, and are then swallowed by a person. Giardia cysts may be present on the fur of pets, especially those that walk outside.
Poorly washed fruits and vegetables and food products that have not undergone proper heat treatment can become a source of infection. Giardia cysts may also be present in tap water, since regular chlorination does not kill them. This is why it is dangerous to drink raw water. Water in reservoirs can also cause the development of parasitic diseases, so during summer swimming you need to make sure that it does not get into your mouth. It is not safe to use it for domestic purposes.
Signs of Giardia infection in adults
Since Giardia parasitizes the small intestine, the main manifestations of acute giardiasis are associated with the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. But extraintestinal symptoms may also occur. They indicate chronic giardiasis in adults.
The acute period of the disease occurs with symptoms similar to an intestinal infection. A person has:
- pain in the navel and right hypochondrium (their intensity increases after eating fatty foods);
- decreased appetite, frequent nausea;
- belching with an unpleasant odor;
- feeling of quick satiety while eating;
- frequent and loose stools (foamy, but without mucus or streaks of blood);
- increased gas formation, bloating.
The above symptoms can be observed for 6-7 days, after which the disease enters the chronic stage with muted symptoms. In the chronic course of the disease, in addition to intestinal symptoms, other syndromes appear that have varying degrees of manifestation:
- skin: pale skin, uneven shade, keratosis on the arms and legs, nodular rash on the neck;
- allergic: attacks of bronchial asthma, skin itching, eczema, blepharitis;
- malabsorption syndrome (impaired absorption of nutrients): anemia, lack of vitamins and minerals, weight loss;
- neuropsychiatric: headaches, sleep problems;
- intoxication: general malaise, increased body temperature, fatigue.