Good day, dear readers! Skin cancer has become increasingly common in recent years.
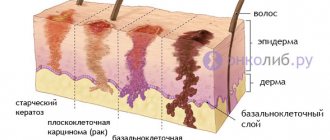
Particularly common is basal cell carcinoma - a predominantly harmless neoplasm that occurs on the face (on the eyelids, in particular), in facial folds and on the scalp.
Basalioma on the head is dangerous because it is not noticed immediately, especially if it is hidden by hair.
When scratching, the sick person will certainly injure it, which is why the tumor can grow faster and turn malignant. Let's study this type of skin oncology in more detail.
What is basalioma?
First, let's figure out what it is - basal cell carcinoma? This is a tumor of the skin, which received its name because of its location. It develops in the superficial layer of the dermis - the basal layer.
Basalioma is diagnosed in 80% of all cases, so it is considered to be the most common skin oncology.
Often the tumor does not metastasize, which is important. This means that it does not spread to nearby lymph nodes and tissues. It grows slowly, over several years or even decades.
Basalioma can be:
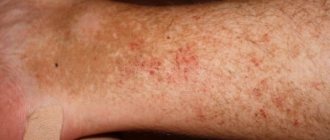
After removal it often reappears. Superficial oncology resembles a round or oval-shaped spot, the color of which varies from pink to red. It is very difficult to notice such a defect in the scalp.
While combing, a person will constantly injure it. Because of this, skin oncology can turn malignant and become life-threatening.
What factors lead to basalioma?
Those who:
- often exposed to the sun;
- exposed to ionizing radiation;
- is often exposed to high temperatures;
- comes into contact with carcinogenic substances;
- has a congenital predisposition;
- smokes or drinks alcohol.
The disease often develops in people over 50 years of age. Both women and men are at risk, and in equal percentages.
Types of basal cell carcinoma on the scalp
Below you see a list of types of skin oncology, as well as the main symptoms by which they can be diagnosed:
Flat - a plaque-type defect with clear roll-like edges that are slightly raised above the surface of the rest of the skin;
Nodular - a defect of pink color and round shape, bloody discharge often comes out of it;
Superficial - a pink spot, slightly protruding, with a shiny surface (this is the most benign variety of all listed).
Danger of basal cell carcinoma
If you have had to deal with scalp cancer, then you will probably be interested in the question: how dangerous is it? Basalioma does not metastasize (does not spread), therefore it is considered safe. It is not transmitted from person to person, except perhaps by inheritance.
Despite this, it is not considered absolutely safe. Basal cell carcinoma can significantly destroy nearby tissues located underneath it, especially muscle tissue.
After wearing this skin defect for a long time and removing it, a deep crater may remain. Fortunately, it will not be visible in the hair, but at this point the hair will stop growing completely.
Basalioma on the head is noticed after it affects the nerve endings and bones. In this case, a strong obsessive pain appears that is difficult to ignore.
This skin cancer can grow in breadth, which can damage a large area of healthy tissue around it.
Symptoms
With basalioma of the skin of the nose, the clinical picture directly depends on the stage of oncological pathology. At first, the disease does not manifest itself, except for a small visible defect. The tumor can often be mistaken for eczema, pimple, herpes, and other harmless formations. As it develops, the surface of the basal cell carcinoma begins to ulcerate and bleed, and also grow in depth and width. Gradually, a cushion with “pearly” bubbles forms around the neoplasm, or the basal cell carcinoma has the appearance of a pearlescent spot.
Painful sensations, as a rule, occur already at the fourth stage of basal cell carcinoma, when it grows into cartilage and bone. When the facial nerve is destroyed, paralysis develops and problems with facial expressions begin.
The absence of any obvious signs at the initial stage of development is not a reason to postpone a visit to the doctor. Having advanced the disease to the fourth stage, it is very difficult to cope with it and its consequences.
Treatment methods for basal cell carcinoma on the head
The diagnosis can only be confirmed in a hospital after a cellular laboratory test. The treating specialist can prescribe several methods for treating the tumors that you see in the photo:
- surgical removal;
- radiation therapy;
- drug treatment;
- combination of techniques;
- cryodestruction;
- laser therapy.
Which method is better? A doctor can answer this question after studying the individual characteristics of the development of the disease. For example, in the early stages, basal cell carcinoma is best treated with radiation therapy. Let's take a closer look at the feasibility of using each of the above methods:
Surgical removal is effective if the tumor is small and not located in a hard-to-reach place. No surgical treatment is complete without a long period of rehabilitation.
The risk of relapse in the case of basal cell carcinoma is quite high, so the tumor is additionally treated with liquid nitrogen.
Combining different techniques is considered the most effective. Initially, the skin defect is irradiated and then surgically removed.
The medicinal method consists in the fact that certain drugs at the cellular level suppress the activity of cancer cells and thereby inhibit tumor growth. This method is used only if the oncological defect is located in a hard-to-reach place.
Cryodestruction - cauterization of the defect with liquid nitrogen. After cauterization, the tumor dies and literally falls off. Of course, a scar will remain in its place, but this is better than a growing tumor. This is a modern method that can be used on various areas of the head.
Diagnostic methods
Patients often seek help in the last stages of the malignant process, so upon examination the doctor sees several ulcers, nodules, and bleeding elements. When you try to remove a particle of the epidermis, blood is released. Under a dermatoscope, basalioma on the nose looks like a tumor that is abundantly supplied with blood and infiltrates into adjacent tissues. Laboratory methods include a general blood test and biochemical study. Patients also take samples for tumor markers, which determine the presence of atypical tissue growth. This method is necessary to confirm or refute the tumor process in the patient’s body.
Invasive methods
To determine the type of basal cell carcinoma and the extent of tumor spread, you need to do a biopsy. Using a special instrument, part of the pathogenic focus is pinched off and sent for examination. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia as it is quite painful. Next, the material is sent for histological and cytological examination.
Prevention of basal cell carcinoma
Skin cancer can be prevented by following simple rules:
- protect scars on the skin from mechanical damage;
- protect your head from prolonged exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation;
- try to have less contact with hazardous chemicals;
- Be sure to examine and treat long-term non-healing ulcers;
- do not allow the epidermis on the head to become excessively dry, maintain hygiene.
That's all. Now you know what basal cell carcinoma looks like on the scalp, how it is treated, and what consequences can occur if it is not treated.
You can share what you read on social networks with friends, and if you subscribe to site updates, you will receive notifications of new publications by email. Good health to you, see you again!
Author of the article: Anna Derbeneva (dermatologist)
Publication date: 09-09-2016
Basalioma is a tumor formed from the basal cells of the dermis. Belongs to the group of skin cancer. Basalioma is malignant in nature. It develops only on the surface of the skin of the face and on the head. Despite its malignant nature, basal cell carcinoma does not metastasize. The disease is easy to treat.
Classification
Based on the international classification of basal cell carcinomas, there are three main types of skin cancer:
- Fibron-epithelial;
- Scleroderma;
- Surface.
Tumors can be:
- single - the disease is characterized by one focus, which is sometimes difficult to notice, especially if it is basal cell carcinoma of the scalp;
- multiple basal cell carcinomas - diagnosed in the presence of a large number of foci of the disease.
Tumors can be located on absolutely any part of the human body: back, chest, forehead, and even affect the legs. In most cases, basalioma is localized on the skin of the face and head. When the disease is localized on the scalp, multiple and single basal cell carcinomas, the presence of which is difficult to notice under the hair, are often diagnosed in the later stages of development.
We recommend reading Treatment of fibroids with folk remedies - recipes that helped without surgery
The following main types of basal cell carcinoma are distinguished:
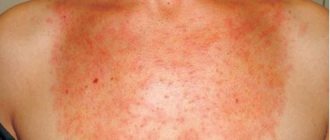
- Superficial basalioma - this form appears in the form of a plaque with a diameter of up to 3 cm. They usually have a red-brown color and a large number of small vessels. On the surface, a flat plaque has crusts that can be eroded, but despite this, the superficial form of the tumor is favorable.
- Warty (papillary) - this form appears in the form of a nodule that rises above the skin. This type of tumor is not characterized by superficial growth.
- Pigmented basal cell carcinomas - such tumors are presented in the form of a pigment containing melanin, which accounts for its dark color and similarity to another form of malignant tumors - melanoma.
- Cicatricial atrophic basal cell carcinoma (scleroderma-like) - this type looks like a scar, which is localized under the skin level. During development, the tumor may alternate between scarring and erosion, as a result of which the patient experiences fresh erosions and tumor scars. Gradually, the neoplasm grows and affects neighboring areas of the skin, and scars form in the middle.
- Ulcerative basaliomas (or nodular-ulcerative) - such tumors pose a serious threat, as they rapidly destroy the soft tissues that surround the tumor. Most often, ulcerative basaliomas are located on the corners of the eyes and on the eyelids, so the disease is often called basalioma of the eyelid or basalioma of the eye. The tumor can also occur on the scalp and in the nasolabial folds.
- Solid basalioma (nodular) - this form of the disease is located in the same areas of the skin as the previous type, but is distinguished by the growth of skin formations outward, and not deep into the skin layers. Externally, this tumor form of basalioma resembles half a ball protruding above the skin and has a yellowish or light pink color, with raised edges. Solid basal cell carcinoma of the skin of the back is most often observed, but it can also occur on other areas of the skin. Due to the dark pigmentation, when diagnosing this tumor, it must be differentiated from other tumors and other skin lesions, in particular from melanoma.
- Adenoid basalioma - cells of this form are characterized by the creation of structures similar to glands and tubes, which is why the neoplasm takes on an openwork appearance. This is a recurrent tumor, which is characterized by the presence of colloidal mucoid content in the lumens of the structures. Often occurs together with the solid form of the disease.
- Warty basal cell carcinomas are often mistaken for ordinary warts, as they appear as dense nodules growing out of the skin. The positive quality of such a neoplasm is that it does not grow into healthy tissues of the body.
Nodular forms of basalioma are diagnosed most often and are characterized by the appearance of a small red nodule on the surface of the skin. During development, the nodule may ulcerate, resulting in the formation of depressions covered with a crust on the surface.
The nodular form of basalioma is usually localized on the eyelids and facial skin. If a patient has basal cell carcinoma of the lower eyelid, it can pose a serious threat to the organs of vision, therefore, if you suspect the presence of this disease, you must be examined by a doctor. When basal cell carcinoma forms, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment methods directly depend on its type and location.
Characteristics of the disease
Skin basal cell carcinoma (basal cell carcinoma) looks like open sores on the surface of the skin. Recently, it has been diagnosed in 80% of patients over 50 years of age. It is very rare in young people and children. Men are more susceptible to this disease than women.
The disease develops only on the dermis of any area of the skin. Usually located on areas of the nose, around the eye - in the area of the upper or lower eyelid, ear, forehead, scalp, temporal region. It is found on the cheek, on the skin of the neck, upper lip, on the shoulder, on the arm, in the back area. It is most often found on the face - up to 90% of all cases. In other cases, it is fixed on the leg or arm and body.
Basalioma is a malignant tumor. A neoplasm develops without the presence of a capsule and a specific membrane. Malignant cells immediately penetrate the tissue, causing the destruction of healthy structures. Germination occurs both in depth and in width, which is accompanied by expansion of the affected area. Penetrating into the depths, the node can affect the tissue of subcutaneous fatty tissue. There is a direct connection between the width of the node and the germination in depth - the wider the area of the outer part of the neoplasm, the deeper the skin layer is affected.
Causes of the disease
The reasons that cause the development of a malignant neoplasm are not yet known to doctors. Scientists have identified a number of factors that can provoke the formation of basal cell carcinoma. Reasons include:
- Prolonged exposure to direct sunlight.
- Tanning in a solarium for an extended period.
- In people with fair skin, basal cell carcinoma develops more often.
- Skin prone to sunburn and freckles.
- Interaction with industrial arsenic compounds associated with professional activities.
- Drinking water with high levels of heavy metals and arsenic.
- Exposure to the body of various carcinogenic elements - from soot, bitumen, paraffin wax, tar with resin and other petroleum products.
- Inhalation of substances after combustion of oil shale.
- Disturbances in the functioning of the immune system.
- A gene disease associated with a mutation of the chromosomal series - albinism.
- The presence of a virus in the body - xeroderma pigmentosum.
- Gorlin-Goltz syndrome.
- Exposure of the skin to ionizing radiation.
- Chemical burns, scars and skin ulcers.
- Old age is considered an important factor in the development of basal cell carcinoma.
- Precancerous diseases - cutaneous horn, leukopenia, actinic keratosis and others.
Doctors recommend treating precancerous formations on the skin - this will prevent the formation of basal cell carcinoma and other dangerous nodules - melanoma or squamous cell skin cancer. Older people should be examined by a dermatologist annually.
Causes of basal cell carcinoma
The exact causes of basal cell carcinoma are not known today.
The exact reasons for the development of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma are not known. It is believed that there is a genetic predisposition to this type of cancer. In addition, the development of basal cell carcinoma is promoted by immunodeficiency states and prolonged exposure to sunlight. People with fair skin, blond hair and blue eyes (Celtic type), as well as albinos, are more susceptible to developing a tumor. Other predisposing factors for tumor development include:
- Prolonged contact with carcinogens (phenols, aromatic amines, nitrosamines, pesticides, arsenic)
- Exposure to ionizing radiation
- Long-term use of drugs that suppress the immune system
Types of disease
Doctors classify the disease according to the external structure with the growth of the tumor and according to the internal structure. Practitioners usually use a classification based on appearance and height. The internal structure is of more interest to histologists. Histological examination data is used for the scientific study of this disease.
According to the appearance and growth of the tumor, varieties are distinguished:
- The nodular-ulcerative type of neoplasm occurs in the eyelid area, on the eye - in the inner corners, on the nose and on the cheek between the folds. At the initial stage, basal cell carcinoma looks like a small nodule above the skin. The color of the nodule is any shade of red and pink. The surface covering the nodule is very thin. It grows slowly. With the growth process, the diseased area becomes covered with ulcers with an internal depression filled with a sebaceous substance with a crust. Gradually the nodal shape becomes deformed. There is a noticeable accumulation of blood capillaries around. The edge of the tumor takes the form of a pearl-colored roller. As the tumor grows, it destroys adjacent layers of skin.
- The solid (nodular or large-nodular) form is formed according to the same principle as the nodular-ulcerative one. The nodular form differs from the previous one in that it grows above the surface of the epidermis in the form of a regular semicircle, slowly increasing in size. The color is light pink or yellow. Blood capillaries can be traced under the node.
- The perforating appearance occurs in areas subject to systematic trauma. Outwardly it resembles nodular-ulcerative, but the degree of ulcerative damage is higher. The entire surface is covered with a thin crust, leaving a small area at the edges not covered with ulcers, and with the presence of blood vessels. The growth rate is high.
- Warty basalioma grows above the skin and looks like cauliflower. It looks like a multiple tumor formed from semicircular nodules. The neoplasm is lighter in color than the skin, without ulcer formation. Blood vessels are not visible. The knot has a very dense consistency.
- The pigmented, or flat, scar form may have a brown or black tint, similar to a mole. The tumor circumference has a specific rim of small formations, similar to a necklace. During the growth process, the center becomes covered with ulcers and is filled with purulent mucus. Gradually, the diseased area heals, leaving a scar. As a result, a dark spot appears with scars inside.
- The scleroderma-like form resembles a nodule with a dense, pale consistency that protrudes above the surface of the skin. A sclerosing tumor forms a plaque with a thin, pale skin crust with clearly visible blood capillaries. Sometimes ulcerations within the plaque may be observed.
- The superficial form develops as a flat plaque with shades of red or pink. There are small nodules along the edges of the neoplasm, forming a pearly fence. The tumor grows slowly - for many years without disturbing the person.
- Cylindroma, or Spiegler's tumor, occurs on the head - in the hairy area. Composed of many dense formations in the shape of a semicircle, developing above the skin. The color of the tumor is purple-pink. The sizes range from 10 mm to 100 mm.
- The adenoid form is formed in the area of the tonsils. Resembles tissue from glandular epithelium, consists of many cyst-like nodules. The cells are filled with basophilic substance.
Histology distinguishes the following types: superficial multicentric, sclerodermal and fibrous-epithelial basalioma.
Skin basalioma: treatment and removal of basal cell cancer in Odessa | Medical house Odrex
Basalioma is a malignant skin tumor that forms from the epidermis. Moreover, the tumor cells are identical to the cells of the basal layer of the skin, which is why they received this name. Basalioma tends to return - from time to time, a seemingly cured disease manifests itself again.
This disease is mainly observed in people over 40 years of age. In children or adolescents, such a diagnosis is quite rare.
They may only have a congenital form of basalioma - the so-called Gorlin-Goltz syndrome - which is not a single tumor focus, but many neoplasms “scattered” throughout the body in combination with malformations of the skeleton, endocrine and nervous systems, as well as the eyes .
Fact. Women's skin is thinner than men's. Accordingly, the risk of developing pathology in our protective layer of the body is much higher. The age factor also plays a significant role: the renewal of skin cells slows down over time: in newborns, these processes occur every 72 hours, and in people from 16 to 35 years old - approximately once a month.
This disease is the most common among all malignant epithelial tumors - it accounts for about 70-75% of the total number of skin cancers. Basalioma progresses slowly.
But, if you do not operate on it in time, then literally in a couple of years it can increase to 10 cm or more. Capable of growing into surrounding undamaged tissue.
At the same time, it practically does not lead to metastasis.
Symptoms of skin basal cell carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma is localized either on the face or neck or on the scalp in the form of a dense formation - the so-called papule, averaging 2-5 mm in size with a convex or flat surface. When basal cell carcinoma forms, the pain syndrome is pronounced.
First, a kind of pimple appears on the body. It grows painlessly, becomes covered with a crust, and if the crust is removed, a depression remains, which heals again over time. A dense circle of small granular components gathers around the tumor. Subsequently, the nodules merge with each other, and ulceration begins in the central part of the tumor.
At first, the papule is pink or beige. And it practically does not bring any discomfort to the patient. But over time it increases in size and becomes covered with a bleeding film.
And under this keratinized layer the process of ulceration begins. The papule develops into a flat plaque of much larger size - up to 10 cm. The surface of such a layer on the skin peels off.
It can also take the form of a mushroom-shaped nodule or ulcer that penetrates into adjacent tissues and even affects the bones.
Causes of basal cell skin cancer
- Excessive exposure to sunlight, light-skinned people are especially vulnerable in this regard;
- Staying in a high temperature zone;
- Radioactive exposure;
- Contact with carcinogens, dyes, resins and oils, petroleum products and arsenic;
- Regular damage to the same area of skin - and as a result - the constant occurrence of scars and burns;
- Taking immunosuppressants.
Fact. The composition of the dust in the rooms where we are is approximately 70% layers of dead skin cells. Our body sheds 30 thousand keratinized scales in a minute. And throughout its entire existence, the human body produces an average of 18 kg of skin. And it manages to update itself up to 1000 times.
The following types of basalioma are distinguished:
- Nodular-ulcerative - the compaction reaches a large size and an ulcer forms in it; the outlines of the tumor become blurred. Localized at the nasolabial fold, in the eyelid area or in the inner corner of the eye;
- Large nodular (nodular form of basal cell skin cancer) - looks like a single node that protrudes above the skin, with a vascular network passing through it. The node does not grow deeper into the skin layer, but from the outside;
- In the form of warts - resembles spherical seals that spread on the surface of the skin like cauliflower and do not grow into the surrounding tissues;
- In the form of pigments - the center and edges of the tumor contain high pigmentation;
- With scars - scarring occurs in the center of the pathogenic focus, while the edges still remain ulcerated;
- Flat basal cell carcinoma is a flat formation from pink to purple in color that does not grow into the deep layers of the dermis;
- Spiegler's tumor - reddish or bluish nodules up to 10 cm, penetrated by dilated blood vessels, located on the scalp;
- “Penetrating” form - quite quickly destroys surrounding tissues, appears in places where the skin is regularly injured;
- Sclerodermiform basal cell carcinoma is a pale nodule that gradually compresses and takes the form of a flat, rough plaque with a clearly visible contour and may contain ulcers.
Fact. The elasticity of the skin depends on the sufficient content of protein in the connective fibers of bones and tendons.
As the body ages, it is lost as collagen cells absorb heavy metals.
The older a person is, the more collagen cells straighten, which in youth are in the body in a twisted form and thereby provide the outer covering with the necessary tension.
Where can you get timely help?
At the Odrex Medical House, a dermatovenerologist or oncodermatologist will always give you the necessary recommendations for the treatment of basal cell skin cancer and tell you what to do to prevent the development of the disease and the onset of its complications. Here you will undergo the necessary diagnostic examination and prescribe an individually suitable therapy for you.
Fact. The functional purpose of the skin varies: it is also a protective function; and respiratory; removal of fluid; heat exchange (in the internal environment of the body, a temperature of up to 37 degrees is considered acceptable for life). In addition, the skin serves for touch, absorption of nutrients, and is capable of self-cleaning from dirt and self-healing.
Differential diagnosis of basalioma
Basal cell skin cancer is so clear that it is noticeable even upon visual examination. But in order to finally make sure of the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe the patient a cellular examination of a smear taken from areas subject to erosion.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma
The main treatment for basal cell skin cancer is surgical excision. Since the tumor does not metastasize, its local excision is quite convenient from a medical point of view - the surgeon eliminates the tumor without affecting adjacent tissues.
Question answer
Of course, the disease itself proceeds relatively smoothly, since it does not metastasize. Basically, complications are associated with the destruction of surrounding tissues. And with such a development of pathology, when the membranes of the ears, eyes and even the brain literally disintegrate, a fatal outcome is possible.
The prognosis of basal cell skin cancer depends on at what stage of the disease you see a doctor. A tumor that has grown more than 20 mm is considered difficult to treat. She is capable of relapse.
If the tumor-like formation has not yet penetrated into the subcutaneous cellular layer and its area is less than 20 mm, then basal cell carcinoma is curable in almost 95% of cases.
However, from an aesthetic point of view, the disease still leaves cosmetic flaws.
Fact. On every square cm of skin there are 100 sweat glands, a similar number of blood vessels and more than 150 nerve roots. There are also sebaceous glands on the skin: on the stripe of the forehead - the sides of the nose - the chin; under the scalp; in the chest area and between the shoulder blades, their number can reach from 400 to 900 glandular bases per square meter. cm.
Initially, after a person receives a wound, the blood clots, platelets are activated and a fibrin (protein clot) is formed. Then the affected area of the skin becomes inflamed, and this lasts up to a week.
The wound healing process is aided by blood cells, lymphocytes, macrophages and neutrophils, which fight infection that has entered the subcutaneous layer and remove the remnants of destroyed tissue connections. Then comes the proliferative phase - the phase of formation of new connective tissue, epidermal cells and blood plexuses.
Exudate is released from the wound during the healing process - this liquid helps restore the skin, but at the same time it saturates the infection. This means that the wound may reopen.
Source: //Odrex.ua/treatment/bazalioma/
Signs of disease formation
When a malignant tumor forms on a skin area, it constantly increases in size. Sometimes basal cell carcinomas larger than 100 mm are recorded. Symptoms of the pathology in the early stages of formation are not pronounced - a small bubble of a pinkish-gray hue appears on the skin. On palpation, it feels like a dense formation covered with a crust on top.
Sometimes, with basal cell carcinoma, an erosive area may be observed that extends deep into the skin layer. Signs of this pathology include the presence of central ulcerations. If the crust separates from the nodule, blood discharge from the areas of ulceration is noticeable. There is a border of transparent bubbles around the affected area. The lesion constantly moves into the epidermal layer, and the surface layer begins to peel off.
The disease occurs in two forms - it can grow above the dermis or move inside. Plaques of different sizes gradually form above the skin. Pathologies developing inside can destroy bone structures.
Stages of disease development
The disease is divided into five stages during its development:
- Stage zero is characterized by the formation of a cancer cell in the body, but without signs of nevus formation.
- At stage 1, a superficial spot up to 20 mm develops.
- At stage 2, the nevus begins to grow to 50 mm.
- Stage 3 is characterized by growth into the depths of the dermis and ulceration on the surface.
- Stage 4 is determined by the large size of the tumor, the presence of multiple ulcerations and destruction of the bone structure.
Also, doctors sometimes use another classification:
- The initial stage (t1n0m0) is similar in characteristics to the zero and first stages - this means that the tumor does not exceed 20 mm without the presence of ulcerations.
- Advanced stage (t2n0m0) – there are initial signs of ulceration formation, the dimensions do not exceed 50 mm.
- The terminal stage is characterized by large sizes and deep penetration into the skin.
Skin cancer stages
Establishing the stage of the disease is necessary for planning treatment tactics.
For this purpose, an X-ray examination of the chest organs and additional methods are performed, such as: ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs and regional lymph nodes; X-ray of bones or computed tomography of the affected area (for primary advanced tumor processes and metastatic forms of the tumor).
- stage 0 preinvasive carcinoma (carcinoma in situ);
- Stage I tumor up to 2 cm in greatest dimension;
- Stage II tumor is more than 2 cm in greatest dimension;
- Stage III tumor with invasion into deep extradermal structures (muscles, bones, cartilage, jaw and orbit) or a single metastasis in the lymph nodes measuring no more than 3 cm;
- Stage IV tumor of any size with metastasis in a lymph node measuring more than 3 cm, multiple metastases, including in other organs (lungs, liver, bones)
Possible complications of pathology
This neoplasm does not form metastatic shoots and develops in one area of the skin. But basal cell carcinoma can cause side effects that lead to failure of some organs. There are examples of deaths. This is due to the deep germination of malignant cells.
The formation of a node in the auricle, eye, and brain tissue provokes dysfunction - decreased hearing and vision, nervous disorders. Basal carcinoma spreads deep into the bone, causing destruction. Formation in the finger area can lead to complete destruction. Multifocal oncology is dangerous due to multiple lesions of the body, which complicates the treatment and diagnosis of the disease. Several outbreaks can make it difficult to identify the most dangerous area that threatens human life. A person can die from the growth of cells in the brain tissue.
Diagnosis of skin basal cell carcinoma
To make a final diagnosis, it is necessary to identify tumor cells. For this purpose, the patient may be prescribed the following diagnostic procedures:
- Scraping dead skin flakes. It is carried out if there is dead tissue on the walls of the neoplasm.
- Smear-imprint. Indicated if there is access to the bottom of the tumor, which happens in ulcerative forms of the disease.
- Biopsy. It is carried out if other diagnostic methods have failed or if the surface of the tumor is not changed.
In addition, if necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional examination methods (x-ray, CT, MRI, ultrasound).
Diagnosis of pathology
Basal cell carcinoma often has a similar course to melanoma. It differs from melanoma in the internal structure of the cells and the absence of metastatic germs. At the first sign of suspicious formations, you should consult a doctor. Only a doctor can distinguish and recognize a benign formation from a dangerous type for human life.
To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to undergo an examination using laboratory and instrumental methods. Diagnostics includes the following methods:
- The doctor performs a physical examination and takes a medical history.
- Dermatoscopy will reveal the structure of the tumor - dermoscopic methods are often insufficient to make a diagnosis.
- The patient will need to undergo a general blood and urine test to identify abnormalities in the body.
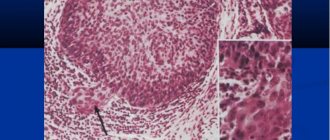
- Histology studies the internal structure of the nodule - a small area of the diseased area will be required.
- Cytology identifies specific pathogens by examining a smear or scraping.
- Ultrasound with CT and radiography will be required if the formation grows deep into the bones and cartilage.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis, a biopsy of the affected tissue is used.
Often diagnosing basal cell carcinoma does not cause any difficulties for the doctor. To confirm the diagnosis, a biopsy may be necessary - a histological examination of a tissue sample. In addition, to diagnose basal cell carcinoma, a dermatologist can use a skin examination using a special lamp (Wood's lamp). To do this, a special cream is applied to previously prepared areas of the skin, after which these areas are illuminated with a Wood lamp in a dark room.
In addition, to diagnose basal cell carcinoma, dermatoscopy is used - examination of the skin using a special device - a dermatoscope.
Treatment
To treat basal cell carcinoma, removal is carried out using different methods. The formation of a tumor on the surface of the dermis can be removed using several methods. Treatment consists of surgical and conservative methods. Conservative therapy consists of gamma ray irradiation, chemotherapy, medicinal ointments and lotions. Surgical excision is possible using several techniques.
Removal surgery is used for large formations with deep growth into the dermis under local anesthesia. Therefore, after excision of the diseased area, the patient is sent home. Removal is possible using the following methods:
- The use of a laser allows you to remove a hard-to-reach tumor with minimal damage to healthy tissue. A small scar remains and there is no risk of wound infection. When using a laser, the possibility of relapse is minimized.
- Cryodestruction involves freezing the tumor with liquid nitrogen, which leads to the death and destruction of malignant cells. Performed using anesthesia. Recommended for use by women due to the invisible scar.
- Treatment of pathology with gamma ray irradiation begins when it cannot be removed by other means. Several courses are prescribed until it disappears completely.
- The electrocoagulation method uses high-frequency current discharge. Point cauterization of the diseased area is carried out with minimal damage.
- Chemotherapy uses ointments of antitumor drugs - 5-fluorouracil, Imiquimod, Methotrexate or Colhamine. The product is applied to the sore spot and after a while the malignant cells die. Doctors consider this method to be gentle, because... does not cause massive damage to healthy cells.
- Photodynamic therapy involves exposing the tumor to flashes of light with the internal injection of a photosensitizing substance. After PDT, a small scar remains. It also allows you to remove hard-to-reach tumors.
Sometimes combined treatment is used - several methods are used simultaneously. This is used to treat complex pathologies located deep in the dermis.
Which method to use will become clear after receiving all the necessary examination results. The age and degree of damage to the area is also taken into account.
Disease prognosis
The prognosis for the pathology is favorable. The survival rate with adequate treatment exceeds 90%. People with cured forms of basal cell carcinoma at an early stage live on average up to 10 years or more.
In medical practice, there are cases of a new nodule appearing in the same place, which requires repeated therapy. To prevent relapse, it is recommended to be regularly examined by a doctor after treatment. Sometimes the patient is prescribed a special diet. A balanced diet helps support the body and boost the immune system.
Basalioma of the scalp is one of the most common skin cancers. Basalioma appears at an intermediate stage, when a benign neoplasm transforms into a malignant one. This disease is diagnosed in most cases in people whose age has exceeded 50 years. Most often, the skin disease affects exposed areas of the head (nose, temples, nasolabial folds, upper lip, corners of the eyes), but the disease can also be localized in the scalp.
Symptoms
In the case of basal cell carcinoma, symptoms and signs depend on the form of the disease. The tumor may look like:
- plaque;
- nodule;
- ulcer.
In the early stages of development, basaliomas look like complexes of dark red cells. Along the periphery of the neoplasm there are prismatic cells consisting of cytoplasm and prismatic nuclei.
During development, it appears in the form of a small nodule of dull white or pink-yellow color, which protrudes above the surface of the skin. When a patient has multiple basalioma, these nodules can merge, forming a mesh. It is worth noting that in the center of the resulting plaque, individual nodules may disappear or form a dense ridge along the periphery of the tumor.
We recommend reading Neuroblastoma in children - what is it, survival, treatment
During development, a tumor can manifest itself in one of two possible conditions:
- In the center of the tumor, erosion is formed, characterized by an ulcer or an uneven bottom. Gradually, the ulcer will grow both in area and in depth, destroying all the tissues surrounding it, in particular bone, cartilage and soft tissue. In this case, the patient will feel sharp pain.
- The tumor may not cause ulceration, but the skin over the tumor will have the appearance of a thin film. In some cases, there is a protrusion of the tumor above the skin, and it looks like a “cauliflower” with a wide or narrow base.
If you experience symptoms indicating the occurrence of basal cell carcinoma, you must be examined by a doctor. Further treatment of the tumor and the prognosis for the patient depend on the timeliness of diagnosis.
Types of basalioma and its symptoms
There are several forms of this pathological disease:
- Flat basal cell carcinoma. A plaque-like shiny new formation appears on the skin, which is slightly raised above the skin and has clear outlines. The pathology progresses very slowly.
- Nodular form. This form is considered the most common. It is characterized by the appearance of a pink tumor on the skin, which has a small depression in its center. The patient may periodically notice minor bleeding from this depression. Once the tumor appears on the head, it does not cause discomfort or other inconvenience. As the disease progresses, the patient notices that the surface of the nodular tumor becomes thinner and a small ulcer appears that bleeds. When the wound heals, you can notice how the pathogenic node has increased in size. In addition to growing in width, basal cell carcinoma also spreads deeper.
- Superficial basalioma. Pink spots appear on the head, which have a shiny surface. In most cases, this tumor is not localized on the head. Over time, the tumor increases the extent of its damage.
Removal of basal cell carcinoma of the scalp | | Medic Help
Treatment, removal of skin basalioma
What are basal cell carcinomas?
Skin basal cell carcinoma (basal cell epithelioma) is an epidermal tumor prone to malignancy. This neoplasm has locally destructive (destructive) growth and develops from the epidermis or skin appendages. There are practically no metastases.
What do basaliomas look like?
As a rule, skin basalioma is a single hemispherical node with a diameter of 1-2 cm with a crater-shaped depression in the center. Most often appears on exposed skin. Favorite localization is the face and head. Most often, basal cell carcinoma occurs on the nose, basal cell carcinoma of the eyelid, and on the skin near the eyes.
Basalioma of the head, or more precisely, of the scalp, is also not uncommon. Appears in the form of a small nodule or several merging small nodules of dense consistency, pinkish, pinkish-yellow or gray in color. The skin over them becomes thinner, acquiring a matte or pearlescent hue.
The nodules gradually enlarge and can form a fairly large nodule, often with a depression in the center. Then, if basalioma is not treated, skin ulceration occurs. An ulcer is formed that increases in length and depth with an uneven funnel-shaped bottom covered with grayish-pink crusts.
The edges of the ulcer are dense, raised, and a so-called pearl ridge is formed. Sometimes skin basal cell carcinoma grows over the surface, forming papillomatous growths. In the superficial form, small flat, clearly demarcated plaques of a reddish color appear on the skin, almost not raised, usually multiple.
With this form, basal cell carcinomas grow very slowly, sometimes for years. Over time, they begin to peel off and may ulcerate.
If basal cell carcinoma is left untreated, it grows to a very large (over 10 cm) size and appears as a mushroom-shaped node protruding above the surface of the skin or a deep ulcer that destroys the underlying muscle tissue and even bones.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma is mandatory, as it is one of the most unfavorable benign skin tumors.
There are several types of basal cell carcinomas:
Nodular - a round, pink tumor that rises above the surface of the skin and bleeds easily when traumatized. There may be a depression in the center of the formation.
Flat - looks like a plaque with raised roll-like edges.
Superficial - a pinkish spot with roller-like edges and a shiny surface, usually multiple. Appears more often on the body.
The main causes of cutaneous basal cell carcinoma are currently considered to be:
- Prolonged ultraviolet irradiation (in the sun or in a solarium) Prolonged thermal exposure Radioactive radiation Occupational hazards (contact with arsenic, tar, tar, soot, dyes, oils).
But we must remember that no one is immune from the appearance of neoplasms. Therefore, if spots or nodules of unknown origin appear on the skin, you should consult a doctor.
Why is basal cell carcinoma dangerous?
This tumor occupies a borderline position between malignant and benign neoplasms. In this regard, there are also dangers associated with its appearance:
- It can become malignant, causing rapid growth and destruction of surrounding tissues. Theoretically, it can metastasize. Quite often it recurs even after radical removal. Even with slow growth, it can destroy the underlying tissues (muscles, bones).
How to treat basalioma?
Treatment for basal cell carcinoma is its removal. First of all, you need to choose a clinic where to remove basal cell carcinoma.
Self-medication is extremely dangerous, as it can lead to malignancy and metastasis of the tumor. To remove basal cell carcinoma, it is necessary to remove the tumor within healthy tissue.
Surgical removal of basal cell carcinoma is possible provided the tumor is small in size and there is sufficient tissue to close the defect. At an advanced stage, combined treatment is used: irradiation of the tumor and its excision.
Treatment of basal cell carcinoma is more effective the earlier it is started.
How to choose a clinic?
The clinic must have not only a therapeutic, but also a surgical license, since removal of basal cell carcinoma is a surgical intervention.
To carry out surgical interventions in accordance with the rules of the SES, the clinic must have an equipped operating room, equipped with a special sterilizer, ultraviolet air irradiator, etc.
There must be a dermato-oncologist surgeon on staff, since basal cell carcinoma can only be removed by a specialist with a surgical specialty and knowledge in the field of dermato-oncology.
It is desirable that the clinic has the opportunity to send the removed material for histological examination to confirm the diagnosis.
The clinic staff must have not only professionalism, but also a friendly and attentive attitude towards patients. After all, any operation is stressful, and it is easier to survive it in a cozy, comfortable atmosphere.
TsDAKH GBUZ SKKOD satisfies all of the above requirements.
How is the procedure performed?
The most effective treatment for basal cell carcinomas is their surgical removal.
Surgical removal of basal cell carcinoma is performed under local anesthesia. The neoplasm is excised within healthy tissue.
Then, a neat cosmetic suture is applied, which is removed 4-6 days after the operation. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, which means you can leave the clinic immediately after the procedure.
When removing basal cell carcinoma on the scalp, it is not necessary to shave the hair.
In our Center, removal of all benign skin tumors is performed by a dermato-oncologist surgeon with more than 5 years of experience in oncology. Operations are performed in a specially equipped operating room.
It is possible to send the removed material for histological examination to the laboratory.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are many reasons why basal cell carcinomas can appear on the head. The main influencing factors include:
- Genetic predisposition to this disease. If one of your close relatives has been diagnosed with skin basal cell carcinoma, the risk of developing the pathology increases significantly.
- Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays. If the skin is constantly exposed to ultraviolet radiation, cells change at a structural level, which leads to changes in DNA molecules. Thus, a favorable atmosphere is created for the development of tumor tumors.
- Prolonged contact with substances harmful to the body.
- Problems in the functioning of the body's natural protective functions (weak immunity).
- Actinic keratosis. Seborrheic skin disease, which is not viral in nature. A yellow or brown spot initially appears on the patient's skin, which can be compared to a freckle. There can be many such spots on the face. Over time, pigment spots become darker, and their structure also changes - they become hard. Initially, a small spot begins to grow and can increase to a size of 2 cm. The top layer of the new growth becomes covered with a crust, which is characterized by cracking. If the integrity of such a spot is violated, a person notices that the neoplasm begins to bleed.
When basal cell carcinoma forms on the open part of the head, its presence is difficult to miss. But if the tumor is localized on the scalp, then not everyone can detect it immediately, since initially there are no obvious signs of its appearance.
Although the tumor rarely metastasizes, it is recommended to remove it. This fact is explained by the fact that neoplasms tend to grow. It is not uncommon for people who have had basal cell carcinoma removed to have a small depression left at its location after surgery.
Basalioma that appears on the head can still threaten the patient’s life, all for the same reason - the growth of the tumor into bone and muscle tissue with their subsequent destruction.
Where can you get timely help?
At the Odrex Medical House, a dermatovenerologist or oncodermatologist will always give you the necessary recommendations for the treatment of basal cell skin cancer and tell you what to do to prevent the development of the disease and the onset of its complications. Here you will undergo the necessary diagnostic examination and prescribe an individually suitable therapy for you.
Fact. The functional purpose of the skin varies: it is also a protective function; and respiratory; removal of fluid; heat exchange (in the internal environment of the body, a temperature of up to 37 degrees is considered acceptable for life). In addition, the skin serves for touch, absorption of nutrients, and is capable of self-cleaning from dirt and self-healing.
Treatment methods for basal cell carcinoma
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor, in addition to a visual examination and the presence of patient complaints, must conduct a number of required studies. With their help, it is possible to confirm or refute the fact that it is basal cell carcinoma that has formed on the head, and not a spot of another etiology.
It is impossible to independently try to find out whether a tumor is benign or malignant, since such an analysis is done in a laboratory setting. Both self-diagnosis and self-medication for basal cell carcinoma of the head are not acceptable. In folk medicine there are many recipes that, according to traditional healers, will help cope with the problem. It is worth understanding that traditional medicine can also be very effective, but also dangerous. Therefore, before deciding to try one of the recommended traditional methods of treatment, the patient should consult with his or her doctor. There is a possibility that the doctor himself will give recommendations regarding which traditional medicine methods are worth trying.
As many years of practice have shown, treatment of basal cell carcinoma with folk remedies does not give the desired results. For this reason, their use can only be acceptable in combination with the main therapeutic course.