What is hepatic porphyria
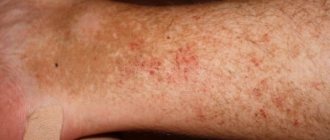
If a violation of the normal content of porphins occurs in the liver, this is hepatic porphyria. This disease is a type of genetic pathology of the liver, where hemoglobin (red blood cells) begins to be synthesized incorrectly. As shown in the picture, the disease and its symptoms can be seen with your own eyes.
It is worth noting that chronic hepatitis gradually turns over the years into cirrhosis, and after a few years into cutaneous porphyria.
Causes
This disease most often has a hereditary form, or the patient may have a predisposition to developing the disease.
However, if an increased amount of porphyrins is detected during a study of urine or red blood cells, this indicates an acquired disease, which cannot be classified as porphyria..
Hemoglobin biosynthesis has eight enzymatic steps, and the problem of each of them can cause disease.
The disease can manifest itself:
- in people who abuse alcohol;
- recently suffered from hepatitis;
- in those who were in direct contact with poisons of the hepatotoxic group;
- for those who have uninterrupted contact with gasoline during work, for example, drivers.
Non-hereditary causes include:
- release of heavy metal fumes;
- long-term use of esterogen, barbiturate, griseofulvin drugs;
- excess iron in the blood and liver;
- pathological changes in the liver, regardless of stage;
- lipid peroxidation.
This video will tell you in detail how the disease develops at the biochemical level.
Classification
There are several classifications of porphyria depending on various characteristics. The basis of the modern classification is the division into hepatic and erythropoietic porphyrias, depending on the location of defects in porphyrin synthesis.
Erythropoietic porphyria includes:
- Gunther's disease, or congenital erythropoietic porphyria, uroporphyria;
- protoporphyria – manifest and latent form;
- erythropoietic coproporphyria.
Hepatic forms include the following:
- acute intermittent porphyria, or pyrroloporphyria, dominant porphyria of the Swedish type - manifest and latent forms;
- protocoproporphyria – varigate with different course options;
- late cutaneous or urocoproporphyria, congenital or acquired;
- hereditary coproporphyria.
There are also unclassified options:
- hepatoerythropoietic;
- hepatic with lightpox syndrome;
- unclassified hepatic;
- a condition accompanied by symptoms of porphyrin metabolism disorders and hemorrhagic syndrome.
Types and symptoms
Like many other diseases, porphyria can be acute or chronic, but the types of this disease are radically different. Let's look at the types of hepatic porphyria and the symptoms of each.
Acute intermittent porphyria
It manifests itself in the form of damage to the central and peripheral nervous system, pain periodically occurs in the stomach, then it instantly changes location in different areas of the abdomen. An epileptiform seizure, hallucination, delusion may begin, and the patient may paralyze the respiratory muscles. The disease worsens during pregnancy, during the birth of the baby, taking many medications (for example, tranquilizers), and surgery. As soon as the exacerbation stage is completed, remission occurs, normal functioning of the body will return. Urine (urine) analysis will help diagnose the disease. To normalize the condition, in addition to taking medications, it is worth undergoing a course of massage and therapeutic exercises.
Hereditary hepatic coproporphyria
If we take into account the symptoms, it can be compared to acute intermittent porphyria. But what distinguishes these diseases is that the neurological symptoms are not so pronounced. The most common symptom is sharp pain in the stomach. Mental deterioration, high blood pressure and tachycardia are observed.
Coproprotoporphyria
The largest percentage of patients were found in South Africa. It is noteworthy that all patients had white skin color. Symptoms manifest themselves in the form of skin rashes, kidney failure, and severe neurological disorders.
Chester form of the disease
It was first discovered among local residents of a small town in Great Britain, from which the name of this form of the disease comes. All people then were united by genealogical kinship. In terms of its symptoms, this form is similar to acute intermittent porphyria, but the consequences are more complex and dangerous. Sometimes patients experienced renal failure.
Urocoproporphyria
This is another type of disease development. As a rule, it can be found more often in the CIS countries. Skin symptoms stand out significantly, which manifests itself in the form of an increase in the percentage of sensitivity to minor mechanical injuries and solar radiation, while pigmentation is disturbed and blisters appear. They are localized on the back of the hands and on the head. The prognosis will be more than positive if treatment is started on time. But the patient must also give up alcohol. In many patients, the liver becomes enlarged and its functioning is significantly impaired. The percentage of porphyrins in feces is always increased.
Important! If the patient has taken a little alcoholic drink, the excretion of excess porphyrins with bile is suspended. They are instantly deposited on the skin and excreted in urine. As a result, the percentage of uroporphyrins and coproporphyrins instantly rises in it.
The main symptoms of the disease, which cover all types of porphyria:
- pigmentation, blisters, hypertrichosis begin to appear on the head, face, hands;
- nails become deformed and destroyed;
- blood pressure rises sharply;
- hemoglobin in the blood decreases below 110 g per liter;
- cutting pain in the stomach area;
- polyneuritis;
- paresthesia;
- psychosis;
- coma;
- functional and organic changes in the liver;
- the bladder decreases in volume and its function is impaired;
- the skin begins to swell and turn red;
- a rash appears;
- disease of the central nervous system;
- a skin sensitivity disorder characterized by numbness.
Complications
The most severe complications of intermittent porphyria are caused by polyneuropathy. With paralysis of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, acute respiratory failure occurs, requiring artificial ventilation. If the muscles of the pharynx are weak, some food may enter the respiratory tract and cause aspiration pneumonia. In paralyzed limbs, blood flow slows down, which creates favorable conditions for thrombus formation. Rarer complications of porphyria are associated with increased production of antidiuretic hormone. These are cerebral edema and rhabdomyolysis (destruction of skeletal muscles). Rhabdomyolysis releases myoglobin and potassium from damaged muscle cells, which can lead to acute kidney failure and life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias.
Diagnostics
Those suffering from the disease should have abnormal results as a result of research in laboratories. To diagnose acute porphyria, the patient needs to be tested for the percentage of delta-aminolevulinic acids and porphobilinogens in the urine. To diagnose a patient with cutaneous porphyria, he is sent to measure the percentage of porphyrin in the blood plasma. The doctor may order other laboratory tests, for example, measuring the quality of enzymes in red blood cells.
Important! Any additional research is carried out only when there is a reason for it. For example, the result of one analysis turned out to be suspiciously bad or, conversely, too good.
Acute porphyria is suspected in all patients who present with:
- painful sensations in the abdominal area;
- mental disorders;
- peripheral nervousness and characteristic changes in urine color.
To confirm or refute the diagnosis, professional research is carried out:
- laboratory tests of urine for the content of porphobilinogens (in case of illness, its percentage increases);
- The activity of porphobilinogen deaminase and a mutation in the same gene are determined.
The acute intermittent form, in addition, should be distinguished from toxic type polyneuritis during lead poisoning, as well as from post-influenza infectious-allergic syndromes of Guillain Barré, as well as from diphtheria polyneuropathies.
To exclude kidney disease, the absorption spectrum of porphyrins is also assessed using fluorescence spectroscopy.
We present you a video that describes the three main symptoms that indicate a porphyria attack.
Epidemiology
Acute intermittent porphyria appears to be the most common form of genetic porphyria. It is most common in the Scandinavian countries (Lapland) and Great Britain, although it is also found among many other ethnic groups. Its prevalence in Europe is 1-2: 100,000, and specifically in Finland - 2.4: 100,000. The frequency of reduced porphobilinogen deaminase activity (including both patients and latent carriers of the defect) in Finland reaches 1:500. Clinical manifestations of the disease occur after puberty and are more often observed in women.
Treatment
To date, no methods have been developed to completely cure a person from porphyria. Therefore, the main goal of treatment is to eliminate the symptoms of the disease.
- The main way to reduce the negative manifestations of the disease is to protect the body from direct sunlight. This is why the disease is often compared to vampirism; patients must apply special creams with a high percentage of SPF factor to their skin.
- It is necessary to completely avoid taking certain medications: these are tranquilizers, Analgin and Sulfonamides.
- If the pain is quite severe and a person cannot cope with it, he is prescribed the narcotic drug Aminazine.
- If high blood pressure is characteristic of the disease, appropriate therapy is prescribed. Basically, all doctors choose the drug Inderal.
- To reduce the percentage of porphyrin concentrations in the blood, intravenous drips with glucose solution are prescribed.
- In addition, to reduce the percentage of porphyrins, the effective medicinal components of delagil are used. Its active substances carry out the connection of porphyrins, as a result they are excreted naturally.
- Sometimes many doctors opt for complex treatment of the disease with delagil and riboxin.
- Patients with porphyria must undergo vitamin therapy: they take folic and nicotinic acid, riboflavins, and retinol.
In addition, for hepatic porphyria the following is prescribed:
- Hepatoprotector Cholestyramine,
- Flavonol,
- active substances Hematin,
- group of chingimin drugs.
This video will tell you interesting facts about porphyria. For example, why is this disease called vampire disease or Dracula syndrome.
Alas, to date no prophylactic complex has been invented that will prevent the development of the disease. But all doctors recommend quitting smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages, applying special products to protect from direct sunlight, and eating food that is rich in vitamins (especially group B).