What's happened
Paraovarian cystic formation is always a benign tumor. The formation of a growth is observed during intrauterine development. However, the pathological process has nothing to do with genetic or hereditary factors. Tumor growth occurs at a slow pace
Most often, the disease is diagnosed in women aged 20 to 35 years. Cases have been recorded in which the disease was detected in teenage girls.
The cyst is localized on the side wall of the uterus under the fallopian tube. Pathology makes itself felt when the tumor reaches four centimeters in size. There have also been cases when the cyst formed to a size of more than 20 centimeters and filled the entire abdominal cavity.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
This condition caused deformation of the uterine body and compression of nearby organs. There is also a blockage of blood flow in the vessels, as a result of which tissue necrosis, sepsis or suppuration begins to develop.
Of particular danger is the rupture of a large tumor.
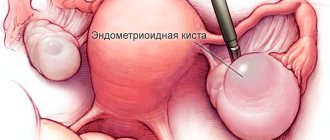
Paraovarian ovarian cyst: what is it?
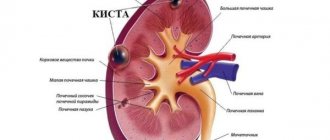
Synonyms for paraovarian cyst are intraligamentary or paratubar cyst, which is due to the specificity of its localization. The formation is located in the interligamentous space (between the leaves) of the broad ligament of the uterus. An enlarged oviduct runs along the upper pole of the cyst; the lower pole of the cyst is in contact with the ovary. The paraovarian cyst owes its origin to the ovarian appendage (paraophoron or paraovary), which experienced some developmental disturbances during embryogenesis. In an adult woman, the paraophoron is in a rudimentary state.
The cyst capsule is thin (no more than 1–2 mm), transparent and lined with flat and columnar epithelial cells. The contents of the formation are represented by liquid with a high concentration of protein. The intraligamentary cyst has a round or ovoid shape and always consists of one chamber. The formation of the fallopian tube's own and mesenteric vessels is supplied with blood. Large cysts have a stalk consisting of the broad uterine ligament, the ovarian ligament, and sometimes the oviduct.
Important
Paraovarian cysts grow very slowly, but can reach gigantic sizes (25 – 35 cm, in rare cases the size of a baby’s head).
Features of paratubar cyst:
- slow growth;
- lack of tendency to malignancy;
- the increase in size is due to the accumulation of fluid in its cavity;
- lack of hormonal activity (remains during menopause);
- asymptomatic (mostly).
Classification
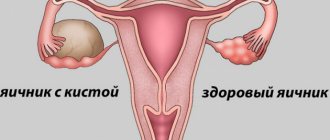
In 90 percent of cases, a cyst is diagnosed affecting one ovary, but sometimes a cyst can form simultaneously on both organs.
A cystic neoplasm of the left ovary is much more common than a paraovarian cyst on the right. But, according to most gynecologists, in most cases the tumor affects the right organ. This is explained by a more intensive supply of blood fluid to this particular appendage.
Due to the structural features of the reproductive structure, the growth located on the right side has the greatest tendency to form a stalk and increase in size, which also contributes to the more frequent occurrence of negative consequences.
The tumor on the left is characterized by less pronounced symptoms, since the growth is pedunculated in rare cases and is characterized by slow growth.
Paraovarian tumor is classified into two types.
Movable
In its structure it has a thin leg and walls. Prone to rapid displacement and twisting of the leg, especially when making sudden movements.
motionless
Has a wide base. The leg is usually absent. Such neoplasms pose less of a health hazard, but have a predisposition to spread to the tissues of the uterine body, gonads and tubes.
Features of right-sided education
The paraovarian cyst on the right is formed from the epididymis. It is localized between the fallopian tube and the gonad, has a smooth outer shell and a round shape. Its internal contents include proteins and mucin.
Such a cyst grows due to the stretching of its own walls under the pressure of the internal contents. It has a thin capsule consisting of epithelial cells. The maximum diameter usually does not exceed 15 cm.
Many women are interested in what a right-sided paraovarian ovarian cyst is. First of all, it should be noted that this is a benign formation that cannot develop into cancer. On the other hand, there is a risk of torsion of his leg. That is why timely contact with a gynecologist plays an important role in preventing the development of complications of the pathology.
The formation, localized on the right ovary, sometimes grows into the tissue of the uterus. Increasing in size, it compresses nearby organs. In addition, the right-sided tumor increases in size relatively quickly, since it is better supplied with blood (compared to a similar foreign inclusion of the left appendage).
The paraovarian cyst on the right, in contrast to a similar formation on the other side, is more likely to rupture. In most cases it has a leg. This differentiates it from a similar neoplasm of the left appendage, which, as a rule, has a wide base. A large paraovarian cyst of the right ovary often gives a pronounced clinical picture.
Causes
The likelihood of developing a cystic formation increases with:
- early puberty;
- frequent abortions;
- diseases the endocrine system, in particular this applies to diseases of the thyroid gland;
- chronic inflammation
- pain of the menstrual cycle;
- mild inflammatory processes affecting the genitourinary system, infections of origin, which can be provoked by sexually transmitted pathogens;
- long-term use of hormonal drugs without prescription by a specialist;
- excess weight or sudden loss of body weight as a result of an incorrectly chosen diet;
- increased physical activity, as a result of fatigue or psycho-emotional state;
- exposure to ultraviolet rays during improper physiotherapy sessions.
According to the majority of gynecologists, the main provoking factor contributing to the appearance of a paraovarian cyst is considered to be a violation of tissue differentiation in the paraophoron at the moment when the genitourinary system begins to form in the embryo.
When the paraophoron has no excretory ducts, the contents of a liquid consistency begin to accumulate inside. As a result, against the background of this condition, a cystic neoplasm begins to form.
The paraophoron is a rudimentary organ of the embryo, which has in its structure ducts and closed tubules extending from them. Its main function in the process of intrauterine development is to participate in the formation of organs. After their complete formation, the significance of the paraophoron is completely lost.
Symptoms
In most cases, paraovarian cysts develop without showing any signs, which is why they are discovered by chance during the next routine ultrasound examination.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Echosigns of adenomyosis
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
If the formations are large, the clinical picture will be as follows:
- The pathological process is accompanied by pulling and aching painful sensations. If you change your body position or add additional load, they will intensify. Sometimes pain can affect the lumbar region from the location of the affected organ. This condition has nothing to do with the menstrual cycle.
- There are rare or, conversely, frequent urges to movement .
- urinate appears due to compression of the bladder by a cystic tumor.
- The abdomen increases in volume.
- The menstrual is disrupted .
- pregnancy arise as a result of pressure from the cyst on the fallopian tubes.
If the pathological process becomes severe due to the development of complications, then this condition will manifest itself:
- sharp pain syndrome of cutting nature in the lower abdomen;
- tachycardia;
- increased sweating;
- increased temperature ;
- surges in blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- dizziness leading to fainting.
If one or more signs occur, you must immediately seek medical help, since this condition is life-threatening for the patient.
Complications with paraovarian cyst
Usually the disease does not make itself felt. Most often, discomfort in the lower abdomen occurs with increased physical activity, sudden changes in body position, while staying in a solarium or in the sun.
The following complications may occur:
- Torsion of the cyst stalk. The uterine ligaments, nerve and vascular endings are compressed. As a result, necrosis of the cystic formation begins, and the woman’s general condition worsens. Spasmodic pain in the abdomen appears, which is difficult to relieve by taking analgesics, a feeling of strong pressure in the front of the abdomen, gases accumulate, tachycardia begins, pressure drops, sweat appears, the skin turns pale;
- Cyst suppuration. Caused by infection in the microflora. There is a high temperature, severe abdominal pain, vomiting;
- Cyst rupture. The most serious condition, as it can lead to heavy internal bleeding, severe pain, loss of consciousness, painful shock and death.
All of the above types of complications are dangerous to health and require immediate intervention by a surgeon.
Diagnostics
If the cystic capsule is large, then detecting the pathology will not be difficult. The specialist will detect the presence of a neoplasm during a two-handed gynecological examination.
In cases where the cyst is small and has just begun to develop, in order to detect it, an additional diagnostic examination is prescribed.
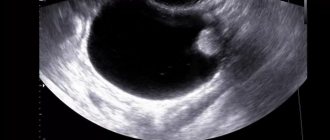
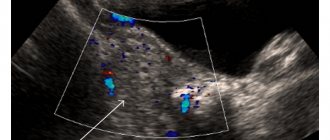
Ultrasonography
An ultrasound of the peritoneal cavity is performed. This method makes it possible to confirm or refute suspicions.
If an image of a cavity structure with thin walls is displayed on the monitor screen, the location of which is the surface above the ovary, then this indicates the presence of a pathological process.
Laparoscopic method
Diagnostic laparoscopy is performed in more severe cases, when it becomes necessary to differentiate an ovarian mass from a tumor. To carry out the procedure, a puncture is made in the abdominal cavity through which a telescopic tube is inserted.
It is with its help that the tumor cavity is examined and a biopsy of a fragment of pathological tissue is taken. Such measures make it possible to determine whether it is a cyst or a tumor.
If necessary, a specialist may prescribe magnetic resonance imaging.
Therapeutic approach
After receiving the results of the diagnostic examination, a decision is made on the choice of method for removing the cystic formation. It is worth immediately noting that treatment without surgery is not provided in this case.
If the tumor is small in size, then wait-and-see tactics are used. In this case, the patient should be constantly under the supervision of a gynecologist to assess changes in the course of the pathological process.
For large paraovarian cysts, surgical intervention is always prescribed. Any operation is planned and requires preliminary preparation. To do this, the woman must be admitted to the hospital several days before the procedure to undergo a full examination.
A prerequisite is to pass:
- electrocardiography;
- fluorography.
It is also necessary to undergo urine and blood tests.
Two techniques are used to remove a cystic tumor.
Laparoscopy
This operation is used when the size of the cyst is no more than three centimeters. The procedure is minimally invasive. To carry it out, special equipment is used. Removal of the cyst is carried out as carefully as possible so as not to injure the ovarian tissue.
The laparoscopic method involves several small incisions through which all manipulations are performed. After the intervention, there are practically no traces left on the body.
The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The duration of the rehabilitation period is no more than five days.
Laparotomy
Prescribed for cystic formations larger than 3 centimeters. To reach the cystic growth, an incision is made along the line on the abdomen. The operation is traumatic. The possibility of damage to healthy tissue cannot be ruled out.
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Do I need to remove an ovarian cyst if it doesn’t bother me?
- Olga Vladimirovna Khazova
- December 4, 2020
The recovery period occurs for at least 10 days. Everything will depend on the patient’s condition.
The choice of surgical intervention is carried out individually for each case. In this case, it is important to take into account such indicators as size, localization and degree of the pathological process.
After surgical treatment, antibiotic treatment is always carried out.
Treatment of paraovarian ovarian cyst
Important
A paraovarian cyst is subject to mandatory surgical intervention. The use of traditional methods and conservative treatment can provoke the growth of a cyst or the development of its complications.
Formations of small diameter (up to 4 cm) can be left under the dynamic supervision of a gynecologist with an annual ultrasound examination. Large cysts are removed, especially at the planning stage of gestation.
The operation is performed laparoscopically, during which the anterior layer of the broad uterine ligament is dissected, the cyst is separated from the surrounding tissues and enucleated. Afterwards, sanitation of the small pelvis, hemostasis and layer-by-layer suturing of the wound are carried out. During surgical intervention, the uterine appendages are preserved; after enucleation of the formation, the deformed tube returns to its previous size and shape. Laparotomy access is carried out in case of contraindications to laparoscopy, gigantic size of the cyst and in case of its complicated course. It is possible to perform a targeted puncture of the formation, remove its contents and inject alcohol into the cystic cavity, causing its obliteration.
Complications
The paraovarian cyst itself does not pose a threat to life, since it has no predisposition to malignancy of the process. The main thing is to identify the disease in a timely manner and constantly monitor it.
Such neoplasms do not affect conception. But if the growth grows to a large size, compression of the fallopian tubes occurs, against which the risk of developing obstruction increases significantly.
With a large cyst, some complications are possible.
Suppuration
The cause of this condition is the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the cavity. The cyst begins to fester, which is accompanied by nausea, weakness, pain in the abdomen, and increased temperature.
Leg torsion
It can occur if you suddenly change your body position or apply additional physical stress to the body. The pain that occurs with this condition cannot be eliminated with medications. In this case, there is a need for emergency hospitalization of the patient.
Gap
This is a rather life-threatening process, which is characterized by the penetration of contents into the peritoneum and the development of inflammation. Also requires prompt medical assistance.
Prevention
Among the main preventive measures to prevent the formation of a paraovarian cyst are:
- timely treatment of diseases of the genitourinary system of infectious and inflammatory origin;
- constant monitoring of hormonal levels;
- regular gynecological examination;
- infrequent visits to the sauna or steam bath;
- absence of promiscuity .