Free consultation with a doctor by phone
Surgeon appointments are available daily by appointment!!!
LLC "Your Doctor"
Chat with the doctor
Addresses of medical centers in Moscow (unified reference) +7 (495) 255-45-59
Make an appointment at the clinic Discount on services Promotions
- +7 (495) 255-45-59
- Surgical centers in Moscow
- Every day from 9.00 to 20.00
- call me back
You can make an appointment with our operators by calling +7 (495) 255-45-59
Prices for services Clinic address Make an appointment Call a surgeon to your home Pediatric surgeon Ligation
You can make an appointment with a surgeon by calling +7 or filling out the online form. Our operators will select the clinic closest to you and make an appointment at a time convenient for you. Clinics are located throughout Moscow and operate seven days a week and holidays. Surgeon appointments are by appointment!!!
Surgeon at home
Surgeon in Maryino
Bedsores
Keratoma removal
Phlegmon of the foot refers to diffuse purulent-inflammatory or necrotic processes. The pathological process develops in the tissue of the lower limb in the interfascial spaces.
In contrast to an abscess, when the focus of suppuration is surrounded by a rather dense capsule separating healthy tissue from the abscess. Phlegmon is distinguished by the absence of such a boundary. The pathological process spreads freely through the interfascial spaces and can cover a significant part of the lower limb.
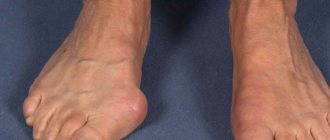
Phlegmon of the foot
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for Joint Treatment: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to heal your joints by taking every day...
Read more "
One of the dangerous surgical pathologies of the lower extremities is phlegmon of the foot, which in advanced cases can lead to amputation of the leg and even threaten the patient’s life. This pathology is manifested by a complex of characteristic symptoms, is successfully diagnosed and effectively treated, usually surgically. But the main condition is early diagnosis of the disease. According to statistics, of all the types of this pathology, the most common is phlegmon of the fingers and toes.
What is phlegmon of the foot
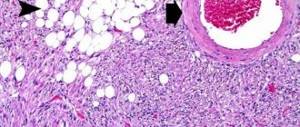
This is one of the types of damage to the soft tissues of the foot, in which a diffuse inflammatory process develops. It affects the skin, subcutaneous fat, fascia and interfascial spaces. As a result of inflammation, a huge amount of exudate and pus is formed, which are localized in a certain part of the foot or occupy its entire volume.
Phlegmon of the foot is literally a “pillow” of pus, which is located under the skin and, in most situations, can be easily identified visually and palpated.
The onset of the inflammatory process is provoked by the entry of various pathogens into the soft tissues of the foot. Consequently, phlegmon always has an infectious origin, which further determines the tactics of therapy. The most common pathogens include streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
They can end up in the soft tissues of the foot, coming from outside through open wounds, which becomes the most common route of infection. But there is another way: through the blood and lymphatic vessels (hematogenously and lymphogenously), that is, from other foci of infection in the body. This happens if the patient has concomitant chronic diseases, significant weakening of the immune system, sluggish or active infectious pathologies.
Of the most important reasons that lead to the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the tissues of the foot, the following can be noted:
- wounds of various types (cuts, stabs, especially gunshots);
- the presence of a foreign body in the structures of the foot;
- scratches and abrasions;
- constant foot injury from narrow shoes and the presence of chronic inflamed calluses;
- advanced state of other purulent foci on the foot.
In some way, the impact of certain provoking factors can determine several types of phlegmon of the foot.
Classification
Depending on where on the foot the infection occurred and how quickly it spread through the blood vessels, soft tissues and spaces between the muscle fascia, foot phlegmon is classified:
- According to the characteristics of the course - acute and chronic.
- By location - phlegmon of the fingers, sole, arch, supraheel zone, entire foot.
- According to the depth of localization - superficial and deep.
Each type of pathology has certain characteristic features. Thus, the acute type of the disease is the most common, manifested by a full set of clinical signs. In a chronic course, the symptoms are more erased, which somewhat complicates diagnosis and causes the patient to see a doctor late. A chronic course can develop if the acute form of phlegmon is incompletely cured or the patient has changes in immunity.
Regarding the localization of purulent masses, approximately the same frequency of phlegmons is observed in both the fingers and other areas of the foot. Moreover, the purulent focus can move along the interstitial spaces, expand to other areas, cover the entire foot and rise along the ankle joint to the lower leg area.
Superficial phlegmon, like acute phlegmon, is characterized by a clear clinical picture and is easy to diagnose; with this type of pathology, the effect of conservative therapy (if prescribed) is clearly visible. Deep phlegmons are often neglected, as they lead to a late visit of the patient to the surgeon and, in addition, cause diagnostic difficulties.
Symptoms
In the acute form, all pathological symptoms are most pronounced, and their intensity increases over 1-2 days or even several hours. First, the patient begins to feel pain in the foot, which intensifies when putting on familiar shoes. Walking becomes difficult, the flexion and extension of the fingers, the raising and lowering of the foot, and its movements in the ankle joint are somewhat limited.
Then there is an increase in the volume of the foot due to swelling and increasing accumulation of exudative and purulent masses in the subcutaneous space. At the same time, the patient begins to feel heat in the foot and visually notices hyperemia of the skin (redness), sometimes a local “bulging” of the reddened skin is visible. Hyperemia is combined with a characteristic shine that occurs due to stretching of the dermal structures by edema. It is noteworthy that the boundaries of hyperemia appear diffuse, blurry and do not have clearly defined boundaries. This sign is very important for differential diagnosis and helps to distinguish cellulitis from another disease caused by streptococcus, called erysipelas of the foot.
The further the disease progresses, the more the foot increases in volume, the more its contours smooth out, the toes swell, the more painful and intense the pain syndrome becomes.
Regional lymph nodes (popliteal, inguinal) begin to respond to the presence of infection in the structures of the foot and its spread throughout the lower limb. Most often this happens to the popliteal lymph nodes, which increase in size and become easily palpable and painful. In severe cases, the skin over them turns red, and pink or red stripes appear from the foot along the entire shin, which indicate the development of lymphangitis (inflammation of the lymphatic vessels).
The same banned issue for which Ernst fired Malakhov!
Joints and cartilage will be cured in 14 days with the help of ordinary...
Simultaneously with the development of local signs of phlegmon on the left or right foot, general symptoms appear, which are combined into the concept of intoxication syndrome. It manifests itself as follows:
- fever, or increased body temperature, which with phlegmon of the foot can reach 39-40 degrees;
- Strong headache;
- a sharp deterioration in health, severe weakness, malaise, lack of appetite;
- characteristic laboratory signs (in a clinical blood test there is an increase in the number of leukocytes, a shift towards young leukocyte forms, an increase in ESR).
It is important that when the very first pathological symptoms appear, the patient goes to a clinic or hospital. The later this happens, the more complications that threaten the health and life of the patient may develop in the future.
Diagnostics
At the appointment, the doctor clarifies the patient’s complaints, the fact of a previous foot injury, the patient’s state of health and the presence of concomitant diseases. The last point is very important, since some chronic pathologies, for example, diabetes, have a very negative effect on the course of the inflammatory process in the soft tissues of the foot, reduce the effectiveness of therapy, delay recovery or even make it impossible.
Then the doctor examines and palpates (feels) the foot, specifying the extent of hyperemia and swelling, points of greatest pain, and the presence of fluctuations. The last symptom, namely fluctuation, is a feeling under the fingers of liquid transfusion under the skin or its vibration, and if you lightly tap on one edge of the phlegmon, then after a split second the shock will be felt at the other end of the lesion. However, this symptom is not specific to phlegmon; it also occurs with an abscess (a cavity in the soft tissues filled with pus, but with clear boundaries due to the presence of a dense capsule).
At the same time, the doctor checks the functionality of the foot joints, damage to regional lymph nodes, and measures the patient’s body temperature. If necessary, he prescribes a clinical and biochemical blood test. The results obtained in the laboratory and during a clinical examination are used for the differential diagnosis of phlegmon, that is, to exclude such pathologies and to make a final diagnosis.
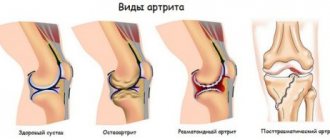
As a rule, phlegmon of the foot is differentiated from the following diseases:
- abscess;
- tenosynovitis (inflammation of the tendon bed);
- purulent arthritis;
- osteomyelitis (inflammation of the periosteum of the foot bones).
Principles of treatment
The type of phlegmon, the severity of the purulent process, and the general condition of the patient determine the doctor’s tactics. In mild cases (localized on the toes or dorsum of the foot), treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis using loading doses of antibacterial drugs. But, as practice shows, in the vast majority of cases, patients require surgical treatment.
The general principles of therapy are:
- ensure the outflow of purulent contents, for which the cavity is opened;
- stop the spread of infection, cleanse tissues of necrotic masses;
- create conditions for successful healing and normalization of foot functions.
The surgical operation is performed under spinal anesthesia, against the background of intensive antibacterial and detoxification therapy. In each case, individual tissue incisions are used, the course of the operation is also specific, which is determined by the location, size of the phlegmon and the presence of purulent leaks in other areas of the foot or leg.
The postoperative period also varies in duration and consists of a course of antibiotics, painkillers, and the mandatory use of a plantar splint for 4-5 days. At the next, outpatient stage, the speed of recovery will depend on good nutrition and vitamin therapy. A light massage after removal of stitches, physiotherapy, and feasible therapeutic exercises are also recommended.
Phlegmon of the foot is considered a dangerous surgical pathology due to the possibility of infection spreading throughout the body (sepsis) and, in severe cases, amputation of part of the lower limb. However, with timely surgical care, the prognosis for the patient’s life and health is always favorable.
Add a comment
My spina.ru © 2012—2019. Copying of materials is possible only with a link to this site. ATTENTION! All information on this site is for reference or popular information only. Diagnosis and prescription of medications require knowledge of the medical history and examination by a physician. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you consult a doctor regarding treatment and diagnosis, and not self-medicate. User AgreementAdvertisers
Causes
Basically, the pathology develops against the background of an increase in glucose concentration and a decrease in sensitivity.
Additionally, the following factors influence:
- insufficient control over sugar levels;
- damage to blood vessels and arteries of the foot;
- bites of wild animals;
- wearing uncomfortable, traumatic shoes;
- regular appearance of calluses, cracks, scratches on the skin of the extremities;
- failure to seek help in a timely manner.
If phlegmon occurs due to diabetes mellitus, tissue nutrition deteriorates, which over time leads to cell death. Due to metabolic disorders, the problem can be complicated by signs of atherosclerosis, which manifests itself in the form of clogging of blood vessels and arteries.
Treatment of ankle ligaments in case of damage
During walking and standing, the highest load falls on the ankle joint. It is the one that accounts for the most ligament damage compared to other joints. The ligaments not only strengthen, but also fix the ankle joint. They are able to connect the bones of the feet and legs together with tendons, fascia and muscles into a single whole.
When a strong traumatic force is applied to the joint apparatus, damage occurs.
Why injuries and tears to the ligaments of these joints occur, and what their treatment is, you will learn in the material.
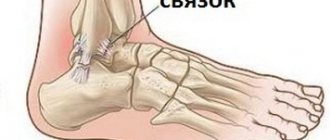
Ankle ligaments and their structure
The shape of the ankle joints is block-shaped, and in terms of movement they are uniaxial. This joint is formed from three bones:
- lower ends of the tibia;
- ram;
- fibular
The joint undergoes dorsal and plantar flexion and extension around the frontal axis. The joint capsule of the ankle can be strengthened through three groups of ligaments.
The collateral (lateral) tendons of the ankle joint are divided into internal (medial) and external (lateral).
In the vast majority of cases, injuries and damage to the ankle joints are directly related to the external ligaments. And each ligament is formed by connective tissue cords. They are made on the basis of individual fibers, which are collected in bundles of different sizes.
The lateral ligaments fan out into a large number of strong bundles. They are attached at the upper end to the ankles - medial and lateral. The external ligament includes three bundles:
- talofibular ligament (anterior);
- the middle bundle, which is formed by the calcaneofibular ligament;
- talofibular (posterior) ligament.
The internal ligament has a more complex structure and has two layers:
- interior;
- surface.
The superficial layer has a wide triangular shape and forms the deltoid ligament. And the inner layer has an anterior and posterior talofibular bundle.
The last group of ligaments serves as a connection between the fibular and tibial ligaments in front and behind.
Classification and mechanisms of ankle ligament injuries
Injuries to the ankle ligaments are very common and are divided into the following categories:
- sprain, when damage occurs, but the integrity of the fibers is not compromised;
- rupture - such an injury is associated with complete or severe damage to the anatomical integrity of the ligaments, accompanied by dysfunction of the ligaments;
- ligament tear (partial rupture of fibers), in which the function of the joint is preserved almost entirely.
Treatment often depends on the type of injury.
In case of severe injuries of the ankle joint, in addition to the ligaments, other components are often damaged:
- tendons;
- fascia;
- muscles;
- bones;
- vessels;
- nerve fibers.
The degree of damage to the injury depends on the magnitude of the traumatic effect, as well as the strength of the tissues and their ability to withstand certain loads. Depending on the type of fabric, the exposure time varies:
- bones - 800 kilograms per square centimeter;
- vessels – 13–15 kg, respectively;
- muscles – 4–5 kg;
- tendons – 645 kg.
The overall resistance of the body increases greatly when the traumatic force affects not only the ligaments themselves, but also the combined tissues.
The elasticity and tension of tissues depends on the strength of the joints. Depending on the severity of the damage, the following types of injuries occur:
- stretch marks;
- fractures;
- deformation;
- gap
Risks of ankle ligament damage
The ankle joint begins to be subjected to heavy loads from the moment a person assumes a horizontal position. Loads increase significantly during running and walking.
The following factors pose a strong risk of developing certain injuries to the ankle joint:
- strong motor activity;
- excess weight;
- leg overload;
- congenital malformations of joints and feet;
- uncomfortable and tight shoes;
- constant hypothermia of the feet.
All this contributes to functional insufficiency of the feet. The muscular-ligamentous apparatus weakens, the elasticity of the ligaments decreases, and blood circulation is impaired. Accordingly, the risks of injury to the foot and ankle joint increase.
And this type of ligament damage, such as a tear, can, in addition to the listed reasons, develop due to the initial instability of the ankle joint and due to a change in its configuration. Very often, the causes of tearing are arthrosis and inflammatory changes against the background of previous infectious diseases, injuries and metabolic disorders.
Main symptoms of a torn ankle
Depending on the severity of the ligament damage, symptoms may vary. The treatment that will be prescribed by the doctor also depends on this. If the ankle ligament injury was minor, the damage will be very mild. The patient feels minor pain, which does not bother him in a calm state, but appears when moving. Swelling appears at the site of joint damage.
With a moderate degree of damage, a partial tear of the ankle ligaments occurs. The patient feels aching and sharp pain that intensifies when moving the legs, swelling or redness appears at the site of injury, and sometimes the temperature in this area rises.
A severe degree of tear of the joint ligaments is characterized by a large hematoma and severe swelling, the pain is severe and can cause dizziness, and sometimes there is loss of creation. A person cannot step on a limb or even move it.
Damage to ankle ligaments: treatment
If the ankle injury is minor, such as a sprain, treatment can be done on an outpatient basis. To begin with, an 8-shaped fixing cruciform bandage should be applied to the joint.
After this, cold is applied to the injury site. The ice should be finely chopped and placed in a rubber heating pad and a plastic bag. Then containers with ice should be wrapped in thick cloth and a towel and applied to the joint for an average of half an hour with breaks of an average of 5-10 minutes. After 2 days, the cold should be replaced with thermal procedures, for example, paraffin applications and ozokerite. Exercise therapy and physiotherapeutic treatment are also practiced.
The method of treatment is chosen by the doctor himself, it depends on the severity and extent of the joint injury. If there was a complete rupture of the ankle ligaments or combined injuries, the patient is prescribed inpatient treatment.
If the patient suffers from severe pain, he is given painkillers, and if hemarthrosis is present, he is punctured and the blood is removed, and a plaster cast is applied to the leg, which partially covers the feet and legs.
Further treatment is aimed at achieving the following results:
- removal of edema;
- resorption of hematoma;
- restoration of joint function.
Treatment methods include massage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy. The physical therapy course includes the following periods:
- immobilization period - take a lying position and move your fingers;
- period after immobilization - during this time, practice active movements in the water, bend and straighten your soles, make slow circular movements with your feet;
- recovery period - perform weight and resistance exercises, roll balls and sticks. You can walk up the stairs.
The time frame for treatment and restoration of damaged ligaments is approximate and different for each age group.
Treatment of torn ligaments
Treatment of a torn ankle ligament should begin with complete immobilization. Often there may be a suspicion of bone injury, so an X-ray examination should be carried out.
The best treatment option is to apply a plaster cast to the injury site. Naturally, it is difficult to find plaster at home, so the joint can be immobilized using a homemade splint:
- take a board and bandage it to your shin;
- the board should partially cover the ankle and reach the knee.
If symptoms are mild, apply a pressure bandage:
- the fastening coil goes around the bottom of the leg;
- The 8-shaped turn should go to the foot itself.
A cold compress placed after an injury can prevent major swelling and hematoma.
If the pain is too severe, treatment includes taking the following medications:
- Renalgan (injections);
- Analgin (injections);
- Ketanov (injections);
- Nicoflex (ointment);
- Finalgon;
- Fastum gel;
- Diclak gel.
Treatment with ointments helps achieve the following results:
- relieve swelling;
- relieve pain;
- improve blood circulation in the ankle joint;
- inflammation resolves.
The ointments are rubbed in very carefully and in thin layers.
Treatment with folk remedies
Treatment of the disease using folk remedies consists of using various lotions, compresses and baths. Here are some recipes:
- lotions based on onions and kitchen salt - grind two onions together with the skin in a meat grinder or in a blender. Mix the resulting mixture with a spoonful of salt and fold it between several layers of gauze and apply to the damaged area;
- vodka compress - it helps to relieve swelling at the site of joint damage within 24 hours. To prepare it, moisten a few layers of gauze with vodka and place it on the injury site. It is covered with polyethylene on top and then with cotton wool. Next, such a compress should be wrapped in a woolen cloth and left for 8 hours;
- recipe based on vodka, garlic and vinegar - mix 120 ml of vodka with 500 ml of vinegar based on apples or wine. Chop 10 peeled garlic cloves and mix with the rest of the ingredients. Place the mixture in a dark place and leave for three weeks. Then strain it, add eucalyptus oil and you can use it for treatment.
As you can see, treatment of damaged ankle ligaments is carried out using different methods, which are prescribed by the doctor in each individual case. Its success depends on the correct choice of treatment method.
Classification
Phlegmon can be primary (arising as a result of the direct introduction of microorganisms) or secondary (developed during the transition of inflammation from surrounding tissues), acute or chronic, superficial or deep, progressive or limited. Depending on the nature of tissue destruction, serous, purulent, necrotic and putrefactive forms of phlegmon are distinguished. Taking into account the localization, phlegmons are divided into subcutaneous, intermuscular, subfascial, retroperitoneal, interorgan, phlegmons of mediastinal tissue, phlegmons of the neck, hand, and foot. If purulent inflammation develops in the cellular spaces around an organ, its name is formed from the Latin name for inflammation of this organ and the prefix “para”, meaning “near” or “around”. Examples: inflammation of the tissue around the kidney - paranephritis, inflammation of the tissue around the rectum - paraproctitis, inflammation of the tissue in the pelvic area (next to the uterus) - parametritis. With a rapid course, phlegmon can go beyond one anatomical area and spread to neighboring ones, simultaneously affecting, for example , buttock area, thigh and perineum or hand and forearm.