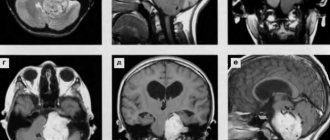
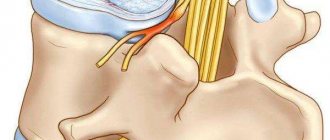
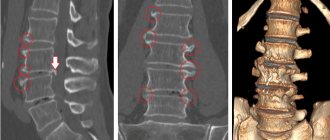
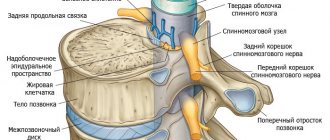
How does spondylosis of the lumbar spine occur?
Spondylosis deformans has classic symptoms similar to injuries, osteochondrosis and herniated intervertebral discs. If damage occurs to the nerve endings of the spinal column, problems arise with the limbs and correct movement. It is important to identify the pathology in the early stages so that conservative treatment has an effect and spinal cord damage does not occur. Spondylosis is associated with dystrophic changes in the intervertebral discs. When connective tissue weakens, thinning of the ligamentous apparatus occurs. The result is an increased risk of injury.
Over time, osteophytes form at the site of damage - bone growths that gradually grow inside the fibrous ring of the articular discs and in the thickness of the intervertebral ligaments. The most common spondylosis occurs in the lumbosacral spine. Due to the growth of osteophytes, the articular processes cannot cope with the task of shock absorption, which leads to severe pain. Also, the appearance of pathology is significantly influenced by the patient’s lifestyle.
How to recognize a lesion in the thoracic spine?
We also recommend reading: Deforming spondylosis of the lumbar spine
It is worth noting that, due to its anatomical and functional features, spondylosis of the thoracic spinal column is the least common. Why?
The fact is that the thoracic region is the least mobile, which makes it somewhat protected from dynamic and static overloads. But, nevertheless, sometimes this part of the spine is also affected.
A feature of thoracic spondylosis is the long asymptomatic course of the disease. The processes of osteophyte proliferation can already be very common, while there are no symptoms or signs of the disease.
Signs of damage to the thoracic vertebrae appear when the nerves that exit the thoracic region (intercostal nerves) are involved in the pathological process. They innervate the anterior chest and abdominal walls, the posterior and lateral surfaces of the chest. Accordingly, the signs of damage to these nerves have the same localization.
Symptoms of thoracic spondylosis:
- thoracago - acute, sudden, short-term pain along the affected intercostal nerve in the form of a lumbago; patients often confuse thoracago with pain in the heart;
- Thoracalgia - constant pain in the chest, which sometimes intensifies in paroxysms, often has a girdling character, one-sided localization, intensifies during sudden movements, coughing, deep inspiration;
- shallow breathing due to fear of increased pain;
- the pain may resemble angina attacks (pseudoangina);
- muscle tension in the upper and middle back;
- numbness, a crawling sensation in certain areas of the chest and abdominal wall (very rare);
- pain in the stomach, liver, pancreas.
The main symptoms are various chest pains
You can suspect spondylosis based on the symptoms described above. But an accurate diagnosis can only be established with the help of additional examinations: x-rays of the thoracic spine, MRI and CT.
Causes of spondylosis
The main provoking factor is premature aging and wear and tear of the patient’s body. With age, destructive processes occur in the skeletal system associated with wear and thinning of cartilage and bone resorption. If there are unfavorable factors at an early age, then the pathology develops in adulthood.
What affects the appearance of the disease:
- Previous injuries and bruises. Not in all situations, injury to ligaments or tendons leads to bone growths of osteophytes, but can become a trigger for the emergence of a destructive and pathological process. Usually, after injuries suffered in youth, spondylosis occurs at an older age.
- Physical effort associated with professional sports. Athletes who lift weights are most susceptible to spinal disorders, including spondylosis.
- Incorrect posture. Due to the misalignment in the spine, improper distribution of weight throughout the body occurs, which is why some muscle groups are heavily overloaded, while others are underloaded. As a result, over time, trophic tissue disorders occur, the quality of restoration decreases, and a degenerative complication appears—spondylosis.
- Age-related degenerative changes. After 40–50, the elasticity of connective tissues gradually decreases, and the strength of bone tissue decreases. If microtraumas and damage occur, they are replaced by osteophytes, which subsequently grow greatly.
- Hormonal disorders. During the period of female menopause, there is a persistent lack of estrogen, which causes bone tissue to become weak. When men enter andropause and testosterone levels become low, similar changes occur that negatively affect bone strength.
- Hereditary factor. It has been proven that if close relatives have spondylosis, the likelihood of the disease occurring in children is increased.
- The presence of congenital anomalies of the spine. If a patient has an anomaly of tropism in the lower back, then in the future there is a risk of spondylosis.
- Infectious lesions. With chronically reduced immunity, constant colds occur. If the disease is not completely cured, it can cause complications in the joints and bones. As a result, without timely use of antibiotics, the patient develops spondylosis.
- Metabolic disorders. In the presence of metabolic syndrome, the risk of pathology is increased.
- Obesity. With increased body weight, increased pressure occurs on ligaments, muscles and joints, which leads to overload of the spine. The problem is especially relevant if the muscular corset of an obese person is not developed. Persistent pain and impaired mobility occur.
- Presence of systemic autoimmune diseases. Such pathologies contribute to the appearance of spondylosis - diabetes mellitus, uncompensated hypothyroidism, atherosclerosis, pathologies of the adrenal glands.
- Oncological diseases. The presence of a tumor process has a destructive effect on the condition of the patient’s body, including the spine.
According to doctors, the most predisposing disease on the path to spondylosis is osteochondrosis. This pathology is also associated with degenerative and dystrophic disorders in the structure of intervertebral discs. As a result, softening of the bone structure and cartilage tissue occurs, which subsequently leads to serious complications, including lumbar spondylosis.
Degrees of the disease
An interesting feature of the course of spondylosis is that the intensity of symptoms often does not correspond to the changes that have occurred in the discs and ligaments. Some patients complain of limited movement even at the initial stage of the disease. And others do not experience significant pain with severe growth of bone tissue. Therefore, spondyloses are classified depending on radiographic signs.
| Degree of spondylosis deformans | Characteristic signs of the course of the disease |
| First | The anterior portions of the discs begin to slowly deteriorate. Due to any increased load, the nucleus pulposus moves beyond the annulus fibrosus. The longitudinal ligament cannot withstand the load and is completely or partially torn off from the bone base. A hematoma forms in this area, and nearby a bone growth (osteophyte) |
| Second | With repeated microtraumas, other ligaments are damaged and more and more osteophytes are formed. They constantly irritate the fibers of the anterior longitudinal ligaments. The first signs of limited mobility appear |
| Third | Osteophytes slowly but steadily increase in size. They become so large that they connect with each other |
Spondylosis manifests itself by the appearance of growths. They usually affect the fourth or fifth vertebra on one or both sides, deforming and destroying it.
Spondylosis of the lumbar spine occurs as a complication of osteochondrosis. In cases where the patient does not receive full treatment, the cartilage tissue begins to undergo significant destructive changes. Intervertebral discs lose their shape, lose their basic functions, and become deformed. Such processes affect bone tissue, joints, blood vessels and nerve endings.
Spondylosis manifests itself by the appearance of growths. They usually affect the fourth or fifth vertebra on one or both sides, deforming and destroying it. Gradually, the fibrous ring is drawn into the development of the disease, in which cracks appear.
As a result, the muscular-ligamentous apparatus suffers, exfoliating from its base under the influence of osteophytes. They themselves continue to grow, leading to the final destruction of surrounding structures.
Therefore, the answer to the question of what spondylosis is is that it is a pathology that occurs due to a number of reasons. Most often it develops due to:
- age-related changes;
- injuries;
- obesity;
- metabolic disorders;
- hereditary predisposition;
- physical inactivity;
- posture disorders;
- unbalanced diet.
Endocrine diseases contribute significantly to the progression of lumbar spondylosis. Chronic internal pathologies, diseases of the spinal column and joints can also provoke its development.
The reasons for its onset can also be excessive physical activity, prolonged weightlifting, or working in an uncomfortable position.
The effect of vibration and elevated temperature on the spine also has an adverse effect. Therefore, treatment of this disease should be preceded by a thorough study of its symptoms, the general condition of the patient and the internal processes in his body.
Classification and signs of spondylosis
To finally establish a diagnosis, you need to rely on the international classification of diseases. The lesion can affect any of the five vertebrae of the lumbosacral segment:
- L1-L2 – spondylosis of the first and second lumbar vertebrae.
- L2-L3 – detection of pathology between the second and third lumbar vertebrae.
- Level L4 – L5.
- L5-S1 – lesion of the lumbosacral region.
The last option is the most common. The disease occurs in the presence of unfavorable factors and includes vivid symptoms.
Stages of the disease include:
- The development of the disease at the initial stage practically does not manifest itself in any way. In rare cases, when there is a heavy load on the spine, moderate pain occurs in the lumbar region. At the initial stage of development of spondylosis, deformations are insignificant. It is possible to determine pathology at the initial stage of development by chance. If you conduct a diagnostic study, you can notice on the pictures of the spine the beginning of the growth of bone growths on the affected areas of the discs.
- At the second degree, the pain becomes significant, and stiffness is felt in the morning. The pain intensifies when standing and bending forward, so prolonged static load should be avoided. Signs of spondylosis intensify. Pain changes course. Severe discomfort occurs, characterized by a long duration.
- At the last stage, the occurrence of pain does not depend on provoking factors. There is numbness, paresthesia of the limbs, loss of sensation in the legs. The patient cannot perform usual actions, motor skills are almost completely impaired, because the osteophytes have grown greatly, which is why mobility is severely limited. Surgical removal of the pathology is required.
Common symptoms of spondylosis that indicate the disease include:
- Pain syndrome is aching and pulsating at the level of development of the lesion. There is no irradiation to other parts of the spine or internal organs. Usually the discomfort is chilling in the morning and intensifies with bending over and physical activity. Warming up the muscles slightly and temporarily alleviates the condition.
- Impaired mobility. The patient cannot bend his back or bend all the way. When turning the body, there is a clear restriction of movement to the sides.
- Lameness is a sign of compression of the sciatic nerve fibers. First, lameness occurs during physical activity, and later - in a calm state.
- Loss of sensation in the lower extremities is a symptom associated with pinched nerve root.
In a third of cases, the disease is asymptomatic, but less often only lameness is observed. With such scant symptomatic signs, the pathology is already determined at a late stage, when the patient becomes really ill. In the later stages, stiffness in the spine appears due to the proliferation of osteophytes.
Depending on the severity of symptoms, several stages are observed:
- At the initial stage of spondylosis, signs of the disease are absent or mild.
- At the second stage of development of the pathology, partial restriction of mobility occurs. Sometimes numbness of the limbs is observed.
- The third stage is terminal. The patient has chronic back pain and movements are constrained. The patient is assigned a disability.
The sooner unfavorable symptoms occur, the sooner you need to seek help from a specialist. At the initial stages of the disease, it is still possible to cope with discomfort with the help of conservative therapy.
Diagnostics
Determining the diagnosis begins with an appointment with a doctor. An initial survey of the patient is carried out, the symptoms and possible causes of the disease are clarified. The patient’s lifestyle, diet, work and rest regime are clarified. The next step is a physical examination. The specialist determines the degree of damage to the spine through visual examination and palpation.
After this, the following types of examination are prescribed:
blood, urine and stool tests;
- panoramic radiography;
- magnetic resonance and/or computed tomography.
To obtain a complete clinical picture, the patient is scheduled for consultations with specialized specialists. This allows you to identify and get rid of a number of ailments that weaken the body. After a comprehensive examination and establishment of an accurate diagnosis, the doctor determines how and with what to treat spondylosis.
Diagnosis of spondylosis of the lumbar spine
If a patient has characteristic complaints, he should make an appointment with an orthopedic traumatologist. The specialist conducts a visual examination of the patient’s back and listens carefully to complaints. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies:
- Radiography. X-rays can show adverse pathological changes that can lead to spondylosis. Example - instability of the spine, non-closure of the arches or spinous processes, anomalies of tropism are clearly visible.
- MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging can look for adverse soft tissue changes, including inflammation, trauma, and the presence of spondylosis. This is one of the most reliable methods for studying spinal tissue.
- CT is an improved version of radiography. Suitable for those patients who cannot undergo magnetic resonance imaging. This type of examination distinguishes hard tissue well and will easily detect osteophytes and imbalance of the spine.
- Lab tests. Some blood tests can reveal inflammatory markers that indicate a rheumatoid course of the disease. The patient submits UBC, ESR, C-peptide, and rheumatic tests.
Based on the results of the examination, a diagnosis is made, after which a treatment regimen is prescribed.
Consider a spondylosis clinic
Damage to the cervical spine with spondylosis most often occurs in patients 40-50 years old who spend a lot of time at their desk in the wrong position and without breaks. A so-called “cervical migraine” occurs - severe pain that can radiate to the arm or shoulder blade area. Such a function as turning the head suffers greatly.
There is stiffness, tension in the neck muscles, hearing and vision impairment can also be observed precisely because of spondylosis. Compression of the carotid arteries leads to changes in blood pressure. When feeling the neck, the patient notes severe pain, which significantly interferes with the examination. It becomes impossible to tilt your head back.
The thoracic region is rarely affected by spondylosis; occasionally the lower part of this segment is affected. Symptoms include pain in the projection of pathological changes, which radiates to the chest. The back muscles become tense and sore, which causes significant discomfort and can limit deep breaths.
The lumbar region is affected by spondylosis quite often. Again, those who spend a long time at the computer or papers, and also endure intense loads, suffer. Most often, changes affect the fourth and fifth vertebrae. Osteophytes of the vertebrae affect the nerve endings, which causes severe back pain. Sometimes the sensory and motor function of the nerves that innervate the lower extremities decreases. The legs go numb, become “wobbly”, and the gait is disturbed. There is also discomfort in the lower back, tension in the back muscles.
Treatment of lumbar spondylosis
The treatment regimen depends on the stage of the disease. At the initial stages, conservative therapy is indicated, aimed at improving the patient’s well-being. During an exacerbation, medications are prescribed to relieve pain and improve joint function. If large osteophytes are discovered, and there is no improvement from conservative treatment, then the problem is solved using a radical method - the growths that impair the mobility of the spine are excised.
Drug treatment of spinal spondylosis
Conventionally, drugs can be divided into two types - supportive and symptomatic. In the first case, medications are prescribed in combination with conservative treatment when bone tissue support is needed. These medications are ineffective in the acute period, since they do not affect inflammatory mediators and pain. Symptomatic treatment is aimed at normalizing the patient’s well-being in a short period.
During a painful attack, what medications are prescribed to alleviate the patient’s condition:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. NSAIDs are the first line of choice, as they can easily relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the damaged area of the back. The drugs act quickly. Within a few hours after administering the injection or taking the pill, the patient feels significant relief. The duration of administration depends on the severity of the situation and should not exceed 2–5 days for non-selective NSAIDs and 3 weeks for selective medications. Examples of non-selective drugs are Ketorol, Diclofenac, Nalgesin. Priority is given to the use of selective NSAIDs, which have a lower frequency of side effects - Movalis, Nimesil, Lornoxicam.
- Corticosteroids. These are systemic hormonal agents aimed at suppressing inflammation in soft tissues and reducing the immune effect. The use of these drugs is relevant in two cases - the ineffectiveness of NSAIDs and the presence of rheumatological diseases. If painkillers do not give the desired effect, then corticosteroids are used in the form of intra-articular injections. The procedure is called injection blockade. Under the control of an ultrasound sensor, a long-acting glucocorticosteroid is injected into the affected area. Usually one blockade is enough for the patient to feel long-term relief. An example of a product is Diprospan. Intermittent corticosteroids may also be prescribed if rheumatologic disease worsens. Tablet forms of the drug are suitable, including Prednisolone, Dexamethasone.
- Muscle relaxants. These drugs relax muscles and eliminate pain associated with excessive spasticity. In many diseases of the spine, muscle imbalance is observed, which consists in the fact that some muscles are in reduced tone, while others are in increased tone. Muscle spasms must be eliminated for the pain to go away. Muscle relaxants are effective when taken as a course. The duration of therapy is selected individually. Examples of medications are Baclofen, Sirdalud, Mydocalm.
- Neurotropic B vitamins. If a patient has pinched nerve roots due to the proliferation of osteophytes, then it is necessary to use B vitamins in large doses. Thiamine, pyridoxine and cyanocobalamin can eliminate pain when taken in a course, as part of a complex drug treatment. For several weeks, the patient is prescribed an injection form of release, and then switches to tablets. The duration of therapy is selected individually. Examples of drugs are Neurorubin, Milgamma, Neuromax.
These medications help with pain caused by a sudden flare-up. When the discomfort has subsided, the patient can be prescribed supportive medications:
- Chondroprotectors. With long-term course use, these substances nourish cartilage tissue and reduce the risk of accelerated destruction. Typically, glucosamine and chondroitin are used as active agents. These components are not able to stop the degenerative processes occurring in the joints, but with regular use of chondroprotectors, deterioration of the condition is prevented. Examples of medications are Dona, Chondrogard, Mukosat.
- Calcium in combination with D3. The strength of cartilage is interrelated with the strength of bone tissue. The main building material for bones is calcium. When there is a lack of calcium, bone tissue is resorbed, which causes a tendency to fractures and the formation of kidney stones. In order for calcium to be absorbed, you need to take additional vitamin D3. Without this component, taking calcium tablets is ineffective. With combined treatment, calcium is fixed in the bones, which significantly reduces the risk of fractures and degenerative processes in the spine.
Homeopathy or traditional recipes are used less often. This last point must be considered with caution. Traditional medicine does not have a strong evidence base, so in the absence of drug therapy, self-medication can be harmful.
Conservative treatment methods for spinal spondylosis
In the period after an exacerbation, most doctors prescribe comprehensive supportive procedures aimed at restoring the patient’s well-being. These recommendations are relevant for people with an unadvanced stage of the disease, which can last for many years if the progression of the pathology is actively counteracted with the help of auxiliary procedures.
Which sets of interventions are more effective during the rehabilitation period:
- Physiotherapy. Special exercises help maintain posture and strengthen the muscle corset, which is an important step towards improving well-being. The job of a physical therapy instructor is to show the correct technique for performing exercises. Classes are aimed at developing flexibility, improving blood circulation and strengthening weak muscle groups. Over time, the patient will learn to perform the complexes correctly at home. For the first few months, it is advisable to train under the supervision of a specialist.
- Physiotherapy. Using hardware in combination with medications, pain in any part of the spine is relieved. The recommended procedure is electrophoresis. Using a special hardware device of a certain frequency, they begin to direct radiation to the affected area of the spinal canal, after first applying the medicine to the skin. Usually B vitamins, ascorbic acid, dimexide or heparin are used. As a result, warming occurs and blood flow in the vessels improves, which leads to the complete elimination of chronic pain.
- Massage. This type of conservative treatment often helps with severe muscle pain associated with spasm. Since such deterioration often occurs in degenerative diseases of the spine, massages are an indispensable procedure. The action of the hands causes a temporary improvement in blood flow, causing tight muscles to relax. You need to do the procedure for several days in a row to feel relief. It is recommended to carry out the procedure in a series of 10 sessions several times a year.
Wearing a bandage for spinal diseases
Special support corsets can improve the patient’s well-being if he has chronic back pain. The essence of the bandage is simple - the device partially relieves the load from the affected area of the spine, and if the pain is really associated with muscle weakness, an elastic corset can help for a while. You cannot wear a bandage for days, otherwise muscle atrophy will occur and subsequently the patient will harm himself even more.
Before going to bed, the elastic belt must be removed. It is recommended to wear a bandage during prolonged static loads, if you need to stand or sit for a long time. The duration of wearing should not exceed 2-3 hours without a break, after which you need to remove the belt. In the interval between wearings, it is useful to do general strengthening exercises.
It is not recommended to choose a bandage yourself. If the attending physician believes that such support is necessary, he will provide the name of the model and manufacturer. Then the patient selects bandages according to size in the medical products salon. Elastic corsets are measured in a horizontal position. It is necessary to ensure that the device does not press anywhere and sits comfortably on the buyer.
Surgery to remove osteophytes
In advanced cases, when osteophytes have reached large sizes, surgical intervention is recommended. Removing spinous growths will alleviate the patient’s condition and relieve pain. Such operations return patients to normal life, so they should not be postponed if doctors insist on a radical solution to the problem.
The essence of surgery is to remove overgrown bone tissue. At the second stage of treatment, osteosynthesis is performed, which is necessary to connect the intervertebral discs. It is important to understand that surgical treatment does not protect against relapse, so it is necessary to identify the cause of the disease. This will help avoid recurrent disease in the future.
Causes
It is difficult to single out any one reason responsible for damage to the spinal column. This happens differently for each person. The problem of spondylosis has a multifactorial nature - the following points take part in the development of the disease:
- Excessive and prolonged load.
- Prolonged uncomfortable positions.
- Poor posture.
- Inactivity.
- Overweight.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Age characteristics.
Needless to say, many of these aspects are present in modern life in one way or another. For an increase in the level of comfort, one often has to pay too high a price when faced with the “diseases of civilization.” But this is only true in the absence of proper prevention and the desire to preserve one’s own health. Your doctor will tell you how to protect yourself from the risk of spinal damage and minimize the strength of problematic factors.
The appearance of spondylosis is due to common reasons, which many simply do not pay attention to. But the prolonged existence of risk factors will invariably lead to pathology.
Prevention of spinal spondylosis
There are no special measures aimed at preventing the onset of the disease. General recommendations aimed at preventing the occurrence of complications from the spine can be applied in practice, which include:
- Maintaining correct posture. When sitting or standing incorrectly, an uneven distribution of the load on the spine occurs, which negatively affects muscle tone. As a result, the spine is bent, which provokes scoliosis.
- Wearing orthopedic shoes. The absence of high heels takes the strain off the legs and lower back.
- Refusal to lift weights.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, quitting smoking and alcohol.
- Maintaining an active lifestyle. Recommended exercises are swimming, moderate jogging or brisk walking.
Prevention
To prevent spondylosis of the thoracic spine, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
— lead a healthy and active lifestyle;
- - maintain correct posture;
- — sleep on an orthopedic mattress and an anatomically correct pillow;
- — it is necessary to observe safety precautions and avoid mechanical damage to the spine and chest.
- - undergo a scheduled medical examination in a timely manner.
Spondylosis of the thoracic spine is a serious disease that requires timely contact with a qualified specialist for diagnosis and conservative treatment. Do not allow complications to arise, take care of yourself and your health.