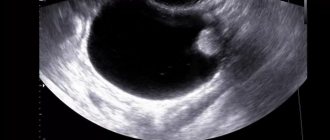
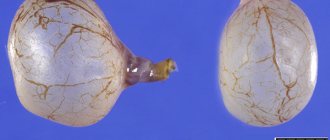
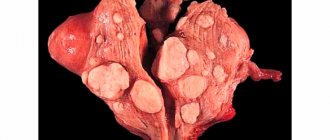
Ovarian cyst is a common disease that requires constant monitoring. It is a benign tumor-like neoplasm. In most cases it proceeds without complications. Occurs in 60 percent of women. Over time, the cyst becomes smaller or disappears. But, according to statistics, 8 percent of cases occur with a complication called torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst. Often occurs in children and young girls of reproductive age.
The main causes of neoplasms are a woman’s hormonal imbalance or inflammatory processes. Ovarian cysts are divided into five types:
- Paraovarian. The size reaches 10-18 centimeters in diameter. There is a clear liquid inside. It is difficult to detect a cyst; this often happens when it reaches a sufficiently large size.
- Follicular. The most common type, formed during ovulation. The size reaches 3-5 centimeters in diameter. The danger is as follows: reaching 8 centimeters, it can twist, disrupt blood supply, lead to rupture and other complications.
- Corpus luteum cyst. Formed after the period of ovulation. Reaches 5-8 centimeters in diameter. There are no symptoms. Treatment is necessary if the leg is torsed or ruptured.
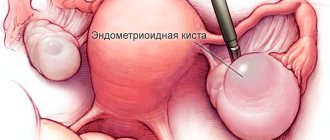
- Endometrioid cyst. The formation represents coagulated menstrual blood. The size reaches 20 centimeters. The influence is exerted by hormonal levels. The more stable it is, the slower the tumor growth occurs. Often diagnosed in women aged 20-40 years.
- Dermoid. Benign education. It can be congenital or caused by a hormonal disorder. Reaches 10 centimeters in diameter.
Causes of twisting
A cystic neoplasm is a tumor filled with fluid. In most cases it proceeds smoothly. Appears and completely disappears over several menstrual cycles. When the body is exposed to hormones, the cyst can enlarge, shift, or twist.
Torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst
Possible causes of torsion:
- Physical exercise. Any weight lifted by a woman can have negative consequences. The danger comes from both rearranging furniture in the apartment and regular exercise in the gym. Strength training puts a lot of stress on the body. A possible reaction is the development of serious complications.
- Sudden change in body position. Any sudden movement, such as a jump, can easily lead to twisting of the leg.
- Loose, weak stomach. Strong abdominal muscles have a beneficial effect on the functioning of internal organs and support them. Not only fitness trainers, but also doctors talk about this.
- Features of the anatomical structure of the body.
- Fast weight loss. The danger lies in the displacement of internal organs when burning fat.
- Pressure of the bladder on the ovary. It should always be emptied promptly. Otherwise, the pressure may cause twisting.
- During pregnancy, there is a high probability of developing neoplasms. Triggered by hormonal changes in the body. During pregnancy, the size of the uterus increases and pressure on neighboring organs increases. This can cause torsion of the ovarian cyst.
- The postpartum period is a dangerous time.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. With regular constipation, the pressure of feces on neighboring organs increases. This also applies to flatulence; gas formation has a similar effect.
- The cyst stalk is too long.
- The neoplasm is 6 centimeters in diameter or more.
- Hormonal disorders, disruptions.
- Bruises in the abdominal area often provoke the formation of tumors.
- Carelessness during intimacy.
Doctors note: small cysts are not dangerous; in most cases they resolve painlessly. Large ones are also not at risk - they are less mobile. Medium-sized cysts with an elongated stalk are more susceptible to twisting. Most often these are formations measuring 10 centimeters or more.
Treatment for torsion of the pedicle of an ovarian cyst
If the pedicle of an ovarian cyst is torsed, emergency surgery is necessary. Delay in surgical intervention can lead to peritonitis, bleeding, or fusion of the cyst with neighboring organs. The volume and method of surgery is determined by the nature of the cyst and the time that has passed since the torsion. If conditions exist (little time has passed, the appendages show signs of viability), laparoscopy is performed. During this operation, the pedicle is untwisted, the cyst is removed, and the ovary is restored.
If there are signs of peritonitis, then an open laparotomy is performed, which often ends with the removal of the cystic tumor along with the appendages. Indications for removal of appendages are irreversible necrotic processes in the ovary and tube, as well as suspicion of the malignant nature of the tumor. In this case, unwinding is not performed due to the risk of thromboembolism of important organs. After excision of the cystoma, an urgent histological examination is performed.
Symptoms
It is impossible to clearly determine the twisting of the cyst based on the symptoms. They are similar to complications of other serious gastroenterological, gynecological and urological diseases. If one or more signs appear, you should immediately call an ambulance. Even with a slight torsion, the symptom will be observed to a greater or lesser extent.
- Pain syndrome. Attacks of sharp cutting and nagging pain in the lower abdomen. In nine out of ten cases it radiates to the back or limbs.
- Weakness of the body is a characteristic sign of complications. Accompanied by a sudden desire to lie down. It is recommended to wait for doctors to arrive while lying on your side.
- Dizziness, and sometimes nausea, vomiting. The human body reacts to perceived pain in this way.
- A sharp increase in body temperature. Even at a temperature of 39 degrees and above, the patient's sweat is cold.
- Frequent heartbeat, breathing.
- Pale skin.
- Too tight abdominal wall. When this symptom is detected, it is easy to understand that serious inflammatory processes have begun in the body.
- Frequent, painful urination.
For torsion of an ovarian cyst, the characteristic behavior of a woman is the desire to lie down and pull her legs up to her stomach. In this position it is easier to endure pain. You should pay extreme attention to the symptoms. When torsion occurs slowly, then pain increases gradually. If the pain is not severe, this does not mean that there is no torsion. It may be incomplete. Once symptoms are detected, immediate assistance from specialists is required.
Symptoms of ovarian cyst torsion
If a functional or hemorrhagic cystic formation is small in size, then it does not manifest itself at all. A dysontogenetic cyst can grow to an impressive size, which provokes the appearance of aching pain in the lower abdomen and sometimes disruption of the cyclicity of menstrual flow.
incomplete torsion of the cyst complete torsion of the cyst
Since such symptoms accompany many other diseases of the reproductive system, a woman needs to undergo an ultrasound examination to detect a tumor. The pathology manifests itself as strongly as the torsion occurs sharply and quickly.
If the twisting of the cyst stalk is intense and rapid, then the woman will feel unwell almost instantly, but if it is weak and slow, then the symptoms will not be expressed. The main signs of ovarian tumor torsion include:
- severe attacks of pain in the lower abdomen, extending under the diaphragm to the limbs;
- weakness, lethargy, powerlessness, inability to stand for a long time;
- disruption of intestinal function, constipation, increased gas formation;
- nausea, vomiting, depending on the intensity of pain;
- tachycardia, accompanied by chills and cold sweat;
- increased heart rate up to 90 beats per minute;
- fast and shallow breathing, which helps to slightly reduce pain;
- paleness of the skin;
- tension in the muscles of the abdominal wall, pain in the abdomen when touched;
- high body temperature, indicating the onset of the inflammatory process;
- frequent urge to urinate, feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- bleeding from the genital tract;
- dry mouth, constant desire to quench thirst, dehydration.
Diagnostics
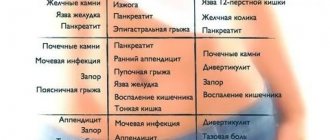
Ovarian cyst torsion is an acute gynecological disease. To establish a diagnosis, differential diagnosis is carried out. The method is based on a survey, excluding a number of diseases that do not match the majority of symptoms. After this, the diagnosis is reduced to a single disease.
Next, a number of necessary examinations are prescribed:
- A gynecological examination, during which the doctor excludes or confirms the development of visible pathologies, establishes the presence of displacement of internal organs. Palpation (palpation) is usually unpleasant, cutting pain when pressing on the inflamed area. The rest of the time the pain is constant and nagging.
- Taking a blood test. Based on its results, a specialist can determine the presence of inflammatory processes in the body.
- Ultrasound is the main diagnostic method. Thanks to it, the presence of a cystoma or tumor is clearly identified, and its size and degree of danger are determined.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy is used as a method for diagnosing a tumor. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, it is deleted.
Other research methods are prescribed based on detected pathologies or if the diagnosis is inaccurate. There are times when a patient needs urgent surgery.
Forms and types of torsion
The next important factor is how exactly the twisting occurred. This determines what actions doctors should take. And also how exactly to continue treating the patient.
There are two types of torsion:
- Complete – the cyst has twisted 360 degrees or more. Accompanied by sharp, intense pain that is difficult to endure.
- Incomplete - twisting less than 360 degrees. The blood supply does not stop completely. This form is accompanied by mild but increasing pain. If the twisting is incomplete, it may be difficult to diagnose the problem. It is recommended that if you identify signs, you should immediately consult a doctor.
There are two types of development of pathology:
- Slow - proceeds gradually, the venous vessels are compressed and the blood stagnates. This leads to an increased risk of rupture and hemorrhage in the organs. There is a risk of fusion of the cyst with the intestine.
- Acute – venous and arterial vessels are compressed. Necrosis of tumor tissue occurs, and infectious diseases of the intestines and other organs develop.
Doctors often use the term “acute abdomen.” The definition fits a number of serious diagnoses with similar symptoms. These include ectopic pregnancy, acute appendicitis and many others.
It is also important to know that the ICD-10 code for a twisted ovarian cyst is N83.5. In such cases, treatment is usually surgical.
Causes
It has not been fully established what exactly becomes the immediate cause of torsion. Several catalysts for this pathological process can be identified:
- sudden change in body position;
- lifting heavy objects;
- bladder fullness;
- weak abdominals;
- pregnancy and childbirth;
- disturbance of intestinal motility;
- increased pressure in the cyst;
- spread of cystic formation to the peritoneal area.
READ ALSO: What is ovarian apoplexy: methods of treating pathology with conservative and surgical methods
First aid
When a woman discovers one or more symptoms, immediate action must be taken. The first thing the patient should do is lie on her side with her legs pressed to her stomach. During inflammatory processes, it is prohibited to apply heat to the painful area. With such a serious complication, urgent medical attention is required.
You should call doctors immediately. It is prohibited to use antispasmodics or analgesics if there is a suspicion of twisting of the cyst. In this case, the likelihood of harm is high. And the risk of even greater complications increases.
Treatment
When diagnosing torsion of an ovarian cyst, surgical intervention is indispensable. Even a minor delay in treatment will lead to irreversible consequences in the form of infections or even death. Detection in the early stages will help save the ovary. When treatment is started too late, the infection also affects the fallopian tube and uterus. The ovary and all reproductive organs will have to be removed.
The operation is performed using a special device called a laparoscope. Thanks to equipment in the form of a camera and magnifying lenses, doctors are able to display a clear image of internal organs on screens. To perform the operation, 3-4 small incisions are made in the skin of the abdominal cavity. First of all, the internal organs are examined. Then they move on to studying the cyst. Before the removal operation begins, it is necessary to determine the degree of danger to the patient’s life. If necessary, the tumor is removed. The operation is performed under general anesthesia and lasts 30-60 minutes.
After the manipulation, it is advisable to start moving and walking within one day. Thanks to this approach, it is possible to avoid complications. If the patient’s condition worsens or complications begin, the clinic reserves the right to extend the hospital stay. Food should be ground to a mushy state before consumption. After 2-3 days, the patient is discharged from the hospital if she is recovering. After discharge, you must stay at home on sick leave for two weeks. After a month, if you feel well, you can return to normal life.
There is another method of tumor removal - laparotomy. This operation is more complicated, but allows the surgeon to get a greater view of the internal organs. It is carried out under anesthesia. It is carried out by longitudinally cutting the abdominal area. With this type of operation, the stem of the cyst is not untwisted, but cut off. After which the ovary is also removed.
The choice of method of operation and its complexity directly depend on the shape, type and stage of torsion, and size of the cyst. The sooner the operation is performed, the greater the chance that it will be easy and safe for the patient’s health.
Rules and methods of treatment
The pathological condition can only be treated surgically. And the sooner you start acting, the higher the chance of avoiding serious consequences. Any delay threatens the patient with cyst necrosis, peritonitis, and secondary infection.
READ ALSO: Tumor filled with mucin or mucinous cystadenoma of the ovary: what is dangerous and how to get rid of a benign tumor of the gonads
The volume and course of the operation depends on the size and type of formation, the degree of torsion, blood supply to the ovary and other factors. After the surgeon makes an incision, he first sends the material for histological examination. If the tumor is benign, the stem simply untwists. When the blood supply to the cyst is restored within 10-15 minutes, it is immediately excised. They try to preserve ovarian tissue as much as possible, especially in women of childbearing age. In case of complete disruption of blood circulation, the formation is removed along with the tissues of the organ. During a malignant process, not only the tumor is removed, but also the ovaries, appendages and uterus.
During the intervention, special instruments are used that make it possible to preserve the integrity of the capsule as much as possible and avoid its rupture. After the operation, a drainage is placed through which antibacterial solutions are injected to avoid infection of the wound. If complications occur, they may resort to repeat laparoscopy and adnexectomy.
Complications
Failure to see a doctor in a timely manner is a huge risk of even greater complications. These include cyst rupture. An extremely dangerous complication that causes internal bleeding into the organs. It can be assumed that harm will be caused by rupture of an exclusively malignant tumor, but this opinion is false. The rupture of any of the above tumors entails contamination with elements connecting to the cells of the organs.
Cyst rupture is not necessarily accompanied by severe pain. Patients note a feeling of fullness inside. Even if the rupture is relatively painless, urgent hospitalization and surgery are necessary in any case.
It is extremely rare for doctors to resort to a method such as vaginal oophorectomy or removal of the ovaries. Such cases include obesity in the abdominal area, heart or lung disease in severe or chronic forms.
Complications include the development of chronic aching pain in the abdominal area, the risk of ectopic pregnancy or infertility.
Prevention
To avoid dire consequences, you must adhere to several rules that will save lives:
- Visit your gynecologist regularly. This means not only an annual examination, but also an ultrasound of the pelvic organs. By following this rule, tumor detection occurs in the early stages.
- Observation of the cyst. Once a benign tumor is diagnosed, it should be monitored. Do not neglect visits to the doctor.
- Timely treatment. Any type of ovarian tumor can be eliminated exclusively by surgery. If you experience pain, nausea, or vomiting, you should immediately consult a doctor.
As with any other disease, timely detection and treatment will increase the chance of saving life and health. In most cases, doctors manage to preserve the reproductive organs. However, with late diagnosis, the chance is reduced.