Tumors in the internal organs of a benign nature form unnoticed by patients and often remain asymptomatic for a long time. The first signs appear when the changed tissue grows, the growth is compressed, and it degenerates into cancer. Endometrial polyps, including glandular fibrous ones, are often found in women. The disease requires adequate treatment, otherwise the risk of complications will increase.
General characteristics of the pathology
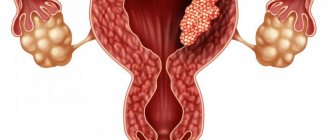
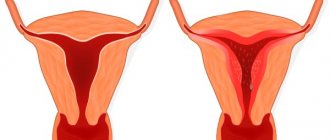
A glandular-fibrous endometrial polyp is a tumor-like formation that forms on the uterine mucosa and consists of glandular cells and connective tissue. The disease is not dangerous, but if there is no treatment and the symptoms are ignored, it leads to consequences. It can occur at any age, but more often women during menopause encounter pathologies.
The growths are small in size (but can grow greatly). It is a smooth pink substance. Has stroma and body. Situated on a thin stem or on a wide base. The second type is more prone to malignancy. The stalk has many blood vessels that supply it for growth. Polyps with a glandular-fibrous structure can be single or multiple.
Glandular cystic endometrial polyp
This type of neoplasm is small in size. These are single or multiple growths with the formation of cysts. The shape of the formations is oblong, cone-shaped and irregular. The surface is flat, smooth, sometimes cystic growths with a thin wall and transparent contents are visible above it. The shade of the growths is pale yellow, light pink, grayish pink. It happens that the top of the growth has a bluish-purple or dark purple hue. A capillary network of blood vessels is visible on the surface of the formation.
Causes
The main reason for the formation of formations in the organs of the female reproductive system is an imbalance of hormones. The likelihood of polyps, including those with a mixed fibrous and glandular structure, increases with excessive estrogen concentration and progesterone deficiency. Because of this, focal changes occur in the mucosa.
The disease may be caused by:
- Chronic infections and inflammation of the appendages and uterus. They are accompanied by impaired blood circulation in the endometrium, which creates a favorable environment for tumor growth.
- Genetic predisposition. A woman whose relatives (grandmother, mother) suffered from pathology are at risk.
- Having excess weight, obesity.
- Long-term use of hormones, use of an intrauterine device.
- Artificial termination of pregnancy.
- Injury to mucous membranes.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
Polyposis can also be provoked by hypertension, diabetes, decreased immunity, frequent stress, and metabolic disorders.
Causes and predisposing factors
Polyps are formed from the epithelium of the cervical canal. Questions regarding the origin of polyps of the cervical canal of the cervix remain poorly understood. According to statistics, they are most often diagnosed in women after they reach 40 years of age. Experts in this field are unanimous in the opinion that the main role in the likelihood of polyps in this part of the genital organ is played by changes in hormonal levels and age-related changes that occur in the female body during menopause.
Immune disorders in combination with a stress factor are important. Mechanical trauma to the cervix contributes to the occurrence of such formations. This can happen during childbirth or diagnostic curettage, artificial surgical termination of pregnancy.
The appearance of the disease in question can be provoked by the following pathologies of the female reproductive organs:
- ovarian cyst;
- uterine fibroids;
- erosion and pseudo-erosion of the neck;
- endometriosis;
- endometrial polyps;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- atrophic colpitis.
There is also a dependence of the occurrence of such growths on sexually transmitted infections and vaginal microflora. Women with STIs are more likely to have cervical polyps.
Classification
The uterine cavity is lined with two types of tissues, which, according to histology, correspond to the types of polyps: functional and basal. The first is considered hormone-dependent, cyclically replaced. The second does not depend on hormones. This is the basis during menstruation. Based on this, glandular fibrous polyps are basal and functional.
Functional type
The appearance of a growth is provoked by the action of hormones. Due to the lack of progesterone and excess estrogen, fertile soil is created for the formation of a polyp. The tumor grows directly from the endometrium.
When fertilization does not occur during active ovulation, the cells of the functional layer of the endometrium are released along with menstrual blood. If there is insufficient exfoliation, the remnants of the endometrium form the basis for a future tumor. In this way, a polyp is gradually formed. With each cycle, the growth changes along with the functional layer.
Glandular fibrous formations of this type do not reach large sizes, but they quickly spread and are often localized in groups. The pathology is very rarely accompanied by any manifestations. Fibrous tumors of the functional type are often detected during ultrasound.
Basal type
The growths from the cells of the basal layer are located on a thin stalk. A characteristic feature of a polyp is the presence of blood vessels. Consists of glandular tissue and muscle fibers. Fibrous tumors of this type are distinguished by a mature structure and a variety of morphological variants. Localized unevenly, chaotically.
Pathology often occurs against the background of stable mucosa in healthy women. Often diagnosed during menopause.
It is distinguished by the non-functionality of epithelial cells and the absence of hormonal dependence on menstruation. There are polyps:
Even more interesting:
Ulcers due to thrush in women
Pits on fingernails reasons photo
- Indifferent. Characterized by an increase in the number of neutral cells.
- Proliferative. Accompanied by endometrial hyperplasia. They often become inflamed.
- Hyperplastic. They are characterized by the proliferation of internal cells and the formation of a “substratum” of the basal stroma.
Kinds
In medicine, depending on what tissue the growth consists of, three types of endometrial polyps are distinguished. Each of them has certain characteristics.
Fibrous
The neoplasm begins to form from fibrous connective tissue. In addition, the composition may include glandular inclusions or collagen fibers.
Polyps have their own vessels, the walls of which are thickened. The growths are often single and can reach significant sizes.
Glandular fibrous
Diagnosed in rare cases and mainly in women of reproductive age who have a stable menstrual cycle.
The growths are formed from glandular tissue and have a variety of lengths and shapes. A feature of this type of polyps is their orientation in different directions. Stromal structures predominate.
New growths are much denser at the base and may consist of fibrous tissue. The walls of the vessels, which intertwine with each other in the form of balls, are thickened and located in different areas.
The glandular fibrous polyp of the endometrium is most susceptible to the spread of the inflammatory process.
Adenomatous
A growth of this type is extremely rarely detected during a gynecological examination and is accompanied by focal adenomatosis.
A distinctive feature is the distribution of glandular tissue over the entire surface of the neoplasm.
Also, during diagnostics, the presence of layers of morphological structures is established. The formations are small in size and irregular in shape, characterized by focal fibrosis of the storm.
Endometrial polyps of this type are distinguished by their heterogeneous structure and the presence of mitoses. In addition, at the base of the growth there are vascular tangles.
The adenomatous type is dangerous for the female body, as it can mutate into a malignant neoplasm.
Symptoms
Manifestations of fibroglandular endometrial polyp do not always occur. Often the course of the disease is hidden. Only when the growth increases in size, is squeezed or is injured, signs may appear. The intensity of symptoms depends on the diameter and location of the tumor. The pathology is accompanied by:
- menstrual disorder;
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- pain during intimacy;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- early termination of pregnancy;
- mucous secretions.
The occurrence of severe pain that radiates to the legs and back may indicate the transformation of the polyp into cancer. Malignancy of cells along with ingrowth into the mucous membranes signals that the formation is metastasizing.
Drug therapy
The standard treatment after polyp removal is medication. The doctor prescribes the following groups of drugs to the patient.
Hormonal agents
Based on the test results, medications are prescribed aimed at suppressing the active formation of estrogen and the production of progesterone. Taking hormones is permissible only after the scar on the uterus has healed.
Painkillers
Prescribed at the initial stage of the recovery process to eliminate pain.
Antispasmodics
On this topic
- Female reproductive system
Differences between cytology and colposcopy
- Natalya Gennadievna Butsyk
- December 6, 2020
Medicines are prescribed after removal of an endometrial polyp to relieve spasms and tingling in the lower abdomen. The drugs also relieve muscle tension and prevent the accumulation of blood in the uterine cavity.
Sedatives and tranquilizers
In the postoperative period, increased irritability often occurs, which requires taking appropriate medications to eliminate.
Possible complications
If alarming signs of the disease appear, you must go to the hospital, undergo examination and therapy. Even the slightest delay in treatment (especially with a severe clinical course), refusal to undergo surgery or take medications is fraught with:
- Degeneration of a benign fibrous growth into cancer. With endometrial atypia, a threat to the patient’s health arises.
- Deterioration in the quality of intimate life. With an enlarged formation, a woman experiences pain during and after sexual intercourse. There is a loss of interest in sex (the girl is trying to avoid discomfort).
- Inability to conceive a baby. Due to the strong enlargement, glandular fibrous polyps cover the cervix. Against the background of changes in the endometrium, the egg will not be able to attach to the mucosa.
- Miscarriage. The tissue deformed by the fibrous tumor is not able to support the growing baby. The pathology is accompanied by bleeding, which leads to detachment of the child's place.
- Menstrual cycle disorders. Due to hormonal imbalance, menstruation fails. They become irregular and are accompanied by severe pain. Bleeding with fibrous growth is profuse.
- Anemia. Due to blood loss, a woman experiences malaise and a decrease in the body’s protective properties.
How does polyposis manifest?
Polyps may not manifest themselves for a long time. The most commonly observed signs of the disease are:
- spotting bloody discharge from the genital tract;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- discomfort after sexual intercourse;
- polymenorrhea;
- leucorrhoea;
- infertility.
Polymenorrhea (menorrhagia) is a condition in which the volume of blood loss during menstruation exceeds the norm. A healthy woman loses no more than 100-150 ml of blood during menstruation per month. Menorrhagia is most often observed in young girls. At an older age, bleeding or spotting with blood appears, which is not associated with menstruation. During the postmenopausal period, discharge may be one-time. Symptoms may be subtle, making diagnosis difficult.
Pain with polyps can be cramping. They are felt in the lower abdomen above the pubis. The pain syndrome may intensify during sexual intercourse. A typical sign of polyposis is leucorrhoea. They represent pathological discharge. They can be observed in women with large polyps.
A serious complication of polyposis is the inability to get pregnant. Pregnancy may not occur immediately or may not occur at all. Even young girls can develop infertility.
Diagnostics
When symptoms of a fibrous polyp appear, you need to consult a doctor. Pathology, if you delay its treatment, leads to unpleasant complications. To prescribe the correct therapy, it is necessary to differentiate polyposis from other diseases. During diagnosis, the doctor, in addition to collecting complaints and anamnesis, and also examining in a chair, prescribes:
- Ultrasound. A safe method that allows timely detection of any changes in the membrane (thickening, expansion). Additionally, you can study the condition of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
- Hysterosonography. A more accurate ultrasound examination technique involves injecting a saline solution into the uterus.
- Colposcopy. Thanks to imaging, any abnormalities in the endometrium are detected.
- Metrography. The growth can be seen under the influence of x-rays.
- Hysteroscopy. The most informative method. The procedure is often carried out in combination with curettage. To study the polyp, a biopsy is performed.
- Laboratory tests - smear for flora, bacteriological culture from the cervical canal, tests for sexually transmitted infections.
- Blood test to determine hormone concentrations.
Treatment methods
Treatment of pathology can be conservative or radical. Often, a glandular fibrous polyp is treated in a comprehensive manner, first the growth is removed, and then medications are prescribed to restore the body and heal tissue, and also prevent relapse.
Medication
If the polyp is small and does not cause pain or other symptoms, surgery is not required. If there is a hormonal imbalance, steroids are prescribed.
There are cases when excision of a polyp is contraindicated. One of these is childhood. Pathology can occur even in a 10-year-old girl, for whom surgery is undesirable.
For women under 35, the use of oral contraceptives is indicated. The scheme and duration of the course is determined by the doctor.
Table - Drug therapy for fibrous polyps
Drugs
Effect/properties
When no positive dynamics are visible after drug therapy, surgery is prescribed.
Surgical
If fibrous polyps are large, multiple and accompanied by severe symptoms, they are removed. The most harmless and effective methods of excision of growth:
- Hysteroscopy. Low-traumatic method. The operation is performed using light anesthesia on the third day after menstruation. The duration of the intervention is on average 30 minutes. It consists of inserting a hysteroscope through the dilated cervix (to examine the cavity, determine the size and number of formations). Then the tumor is cut off with a surgical loop or forceps and the remains are scraped out.
- Laparoscopy. This method is preferred if there is a high risk of cancer. It involves removing the polyp along with the uterus. The procedure is performed using general anesthesia. During the operation, several incisions are made in the abdomen through which a device with a camera is inserted. After examining the organ, it is excised.
- Laser treatment. Removal of glandular fibrous polyps with a laser beam is a non-traumatic method. After the operation, no scars remain, and reproductive function is still preserved.
For rapid tissue healing and restoration of the body after the intervention, the use of antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa), antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Sumamed), gestagens (Marvelon, Triquilar), and vitamins is prescribed.
After excision of a polyp, you cannot take a bath, visit a bathhouse, sauna, have sex, or swim in ponds.
Why is endometrial glandular fibrous polyp dangerous and how to treat the disease?
Tumors in the internal organs of a benign nature form unnoticed by patients and often remain asymptomatic for a long time.
The first signs appear when the changed tissue grows, the growth is compressed, and it degenerates into cancer. Endometrial polyps, including glandular fibrous ones, are often found in women.
The disease requires adequate treatment, otherwise the risk of complications will increase.
General characteristics of the pathology
A glandular-fibrous endometrial polyp is a tumor-like formation that forms on the uterine mucosa and consists of glandular cells and connective tissue. The disease is not dangerous, but if there is no treatment and the symptoms are ignored, it leads to consequences. It can occur at any age, but more often women during menopause encounter pathologies.
The growths are small in size (but can grow greatly). It is a smooth pink substance. Has stroma and body. Situated on a thin stem or on a wide base. The second type is more prone to malignancy. The stalk has many blood vessels that supply it for growth. Polyps with a glandular-fibrous structure can be single or multiple.
Causes
The reason for the formation of formations in the organs of the female reproductive system is an imbalance of hormones. The likelihood of polyps, including those with a mixed fibrous and glandular structure, increases with excessive estrogen concentration and progesterone deficiency. Because of this, focal changes occur in the mucosa.
The disease may be caused by:
- Chronic infections and inflammation of the appendages and uterus. They are accompanied by impaired blood circulation in the endometrium, which creates a favorable environment for tumor growth.
- Genetic predisposition. A woman whose relatives (grandmother, mother) suffered from pathology are at risk.
- Having excess weight, obesity.
- Long-term use of hormones, use of an intrauterine device.
- Artificial termination of pregnancy.
- Injury to mucous membranes.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
Polyposis can also be provoked by hypertension, diabetes, decreased immunity, frequent stress, and metabolic disorders.
Classification
The uterine cavity is lined with two types of tissues, which, according to histology, correspond to the types of polyps: functional and basal. The first is considered hormone-dependent, cyclically replaced. The second does not depend on hormones. This is the basis during menstruation. Based on this, glandular fibrous polyps are basal and functional.
Functional type
The appearance of a growth is provoked by the action of hormones. Due to the lack of progesterone and excess estrogen, fertile soil is created for the formation of a polyp. The tumor grows directly from the endometrium.
When fertilization does not occur during active ovulation, the cells of the functional layer of the endometrium are released along with menstrual blood. If there is insufficient exfoliation, the remnants of the endometrium form the basis for a future tumor. In this way, a polyp is gradually formed. With each cycle, the growth changes along with the functional layer.
Glandular fibrous formations of this type do not reach large sizes, but they quickly spread and are often localized in groups. The pathology is very rarely accompanied by any manifestations. Fibrous tumors of the functional type are often detected during ultrasound.
Basal type
The growths from the cells of the basal layer are located on a thin stalk. A characteristic feature of a polyp is the presence of blood vessels. Consists of glandular tissue and muscle fibers. Fibrous tumors of this type are distinguished by a mature structure and a variety of morphological variants. Localized unevenly, chaotically.
Pathology often occurs against the background of stable mucosa in healthy women. Often diagnosed during menopause.
It is distinguished by the non-functionality of epithelial cells and the absence of hormonal dependence on menstruation. There are polyps:
- Indifferent. Characterized by an increase in the number of neutral cells.
- Proliferative. Accompanied by endometrial hyperplasia. They often become inflamed.
- Hyperplastic. They are characterized by the proliferation of internal cells and the formation of a “substratum” of the basal stroma.
Symptoms
Manifestations of fibroglandular endometrial polyp do not always occur. Often the course of the disease is hidden. Only when the growth increases in size, is squeezed or is injured, signs may appear. The intensity of symptoms depends on the diameter and location of the tumor. The pathology is accompanied by:
- menstrual disorder;
- heavy bleeding during menstruation;
- pain during intimacy;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen;
- early termination of pregnancy;
- mucous secretions.
The occurrence of severe pain that radiates to the legs and back may indicate the transformation of the polyp into cancer. Malignancy of cells along with ingrowth into the mucous membranes signals that the formation is metastasizing.
Possible complications
If alarming signs of the disease appear, you must go to the hospital, undergo examination and therapy. Even the slightest delay in treatment (especially with a severe clinical course), refusal to undergo surgery or take medications is fraught with:
- Degeneration of a benign fibrous growth into cancer. With endometrial atypia, a threat to the patient’s health arises.
- Deterioration in the quality of intimate life. With an enlarged formation, a woman experiences pain during and after sexual intercourse. There is a loss of interest in sex (the girl is trying to avoid discomfort).
- Inability to conceive a baby. Due to the strong enlargement, glandular fibrous polyps cover the cervix. Against the background of changes in the endometrium, the egg will not be able to attach to the mucosa.
- Miscarriage. The tissue deformed by the fibrous tumor is not able to support the growing baby. The pathology is accompanied by bleeding, which leads to detachment of the child's place.
- Menstrual cycle disorders. Due to hormonal imbalance, menstruation fails. They become irregular and are accompanied by severe pain. Bleeding with fibrous growth is profuse.
- Anemia. Due to blood loss, a woman experiences malaise and a decrease in the body’s protective properties.
Glandular fibrous formations that follow a functional type can grow. Multiple growths are more difficult to treat.
Treatment methods
Treatment of pathology can be conservative or radical. Often, a glandular fibrous polyp is treated in a comprehensive manner, first the growth is removed, and then medications are prescribed to restore the body and heal tissue, and also prevent relapse.
Medication
If the polyp is small and does not cause pain or other symptoms, surgery is not required. If there is a hormonal imbalance, steroids are prescribed.
There are cases when excision of a polyp is contraindicated. One of these is childhood. Pathology can occur even in a 10-year-old girl, for whom surgery is undesirable.
For women under 35, the use of oral contraceptives is indicated. The scheme and duration of the course is determined by the doctor.
Table - Drug therapy for fibrous polyps
| Drugs | Effect/properties |
Gestagens:
| They stabilize hormonal levels and stop tumor growth. Often, under the influence of gestagens, formations resolve |
| Antibiotics: | Destroy pathogenic microflora |
Painkillers:
| Eliminate discomfort |
When no positive dynamics are visible after drug therapy, surgery is prescribed.
Surgical
If fibrous polyps are large, multiple and accompanied by severe symptoms, they are removed. The most harmless and effective methods of excision of growth:
- Hysteroscopy. Low-traumatic method. The operation is performed using light anesthesia on the third day after menstruation. The duration of the intervention is on average 30 minutes. It consists of inserting a hysteroscope through the dilated cervix (to examine the cavity, determine the size and number of formations). Then the tumor is cut off with a surgical loop or forceps and the remains are scraped out.
- Laparoscopy. This method is preferred if there is a high risk of cancer. It involves removing the polyp along with the uterus. The procedure is performed using general anesthesia. During the operation, several incisions are made in the abdomen through which a device with a camera is inserted. After examining the organ, it is excised.
- Laser treatment. Removal of glandular fibrous polyps with a laser beam is a non-traumatic method. After the operation, no scars remain, and reproductive function is still preserved.
For rapid tissue healing and restoration of the body after the intervention, the use of antispasmodics (Papaverine, No-shpa), antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Sumamed), gestagens (Marvelon, Triquilar), and vitamins is prescribed.
After excision of a polyp, you cannot take a bath, visit a bathhouse, sauna, have sex, or swim in ponds.
Features of pathology during menopause
Changes in hormonal levels during menopause can provoke the appearance of fibrous polyps in the uterus. Small growths are treated with hormones, and in case of severe growth, with surgical methods.
During menopause, it is not easy to identify pathology. One of the manifestations is disruptions in the menstrual cycle, which, in principle, are normal during the onset of menopause.
Glandular fibrous polyp and pregnancy
Growths in the uterus interfere with conception, but even with their presence, fertilization is possible. However, education left unattended by a doctor can lead to the inability to get pregnant in the future. This is one of the reasons why doctors advise removing the tumor as soon as it is discovered. Fibrous growths are dangerous during pregnancy, as they increase the likelihood of miscarriage.
Prevention
After removal, polyps may appear again. Reducing the risk of relapse helps:
- treatment of concomitant diseases;
- regular examinations by a gynecologist;
- leading an active, healthy life;
- rejection of bad habits;
- exclusion of casual sex.
conclusions
Glandular fibrous tumor in the endometrium is an unpleasant disease that every girl can face. With adequate therapy, the prognosis is favorable - women's health is preserved. Ignoring the manifestations of pathology or refusing treatment is fraught with complications, including infertility and cancer.
Source: https://ginekologius.ru/zhelezisto-fibroznyi-polip-jendometrija
Features of pathology during menopause
Changes in hormonal levels during menopause can provoke the appearance of fibrous polyps in the uterus. Small growths are treated with hormones, and in case of severe growth, with surgical methods.
During menopause, it is not easy to identify pathology. One of the manifestations is disruptions in the menstrual cycle, which, in principle, are normal during the onset of menopause.
Causes
There is still no consensus on why glandular fibrous polyps suddenly appear on the lining of the uterus. Even modern examination methods are not able to shed light on this process. Scientists are left to speculate and put forward theories.
- First of all, the main reason for the formation of polyps is inflammation of the uterine mucosa.
- The next reason for the formation of a benign tumor is treatment with hormones over a long period of time. For example, a glandular polyp of the endometrium of the basal type, its hyperplastic version is a consequence of taking hormones.
- The presence in the body of a gene that causes endometrial growth. This gene leads specifically to the formation of polyps in the uterus.
- Hormonal imbalances, which are expressed in an excess of estrogen.
- Another reason is a change in the sensitivity of receptors to steroid hormones.
- Among the reasons for the growth of polyps, doctors cite long-term use of the drug Tamoxifen, which is necessarily prescribed for breast cancer.
At the same time, through observations it was noticed that metabolic problems do not in any way affect the growth of polyps. According to scientists, all other reasons that can be found in the scientific literature are questionable or related to those indicated in the main list.
conclusions
Glandular fibrous tumor in the endometrium is an unpleasant disease that every girl can face. With adequate therapy, the prognosis is favorable - women's health is preserved. Ignoring the manifestations of pathology or refusing treatment is fraught with complications, including infertility and cancer.
Gynecological diseases in women are quite common nowadays, including benign formations. Among them, the most frequently diagnosed are polyps - tumor-like growths from red to purple, predominantly localized in the cervical canal. Can be either single or multiple. According to statistics, among all women who come to see a specialist, 20% are diagnosed with polyps. In the vast majority of cases, the disease requires removal, since it has a fairly high chance of malignant transformation.
Endometrial polyp - types
There are several types of polyp - depending on the histological structure, treatment is prescribed:
- Endometrial fibrous polyp - consists mainly of fibrous tissue and a minimal amount of glandular tissue. It develops mainly in older women (after 35 years).
- Glandular (functional) endometrial polyp - consists mainly of endometrial glands and a small amount of loose connective tissue. It most often develops in young women under 35 years of age.
- Fibrous-glandular polyp of the endometrium - contains both glandular and fibrous tissue in large quantities, can appear at any age.
- Adenomatous polyp of the endometrium of the uterus is the most complex type of hyperplasia, the only one that can become malignant. Develops at older ages and often requires removal along with the uterus.
Glandular fibrous polyp of the cervical canal
This type of polyp is a mixed type neoplasm that contains epithelial cells, connective tissue and can reach 2.5 centimeters in size. It has the most pronounced symptoms, in contrast to fibrous and glandular polyps. Most often, such a formation is diagnosed in women who have given birth, but it also occurs in pregnant women. This can be caused by:
- diabetes;
- obesity;
- consequences after abortion;
- disruption of the adrenal glands;
- decreased immunity;
- use of an intrauterine device;
- diseases of the uterus accompanied by inflammation.
Glandular fibrous polyp of the endometrium: what is it, features of treatment after removal
- An endometrial polyp is a local benign hyperplastic process of the endometrium.
- Benign hyperplastic processes in the endometrium
- Read more about what “endometrial hyperplasia” is.
Unlike the glandular fibrous or fibrous polyp, the glandular polyp develops mainly due to proliferation of the basal endometrium, i.e. the glandular component in it significantly predominates over the stromal one.
Unlike adenomatous ones, there are no atypical changes in the cells of a glandular polyp.
Iron polyps usually grow up to 0.3-3 cm. But there are also large ones, up to 6 cm or more. They fill the entire uterine cavity. Sometimes they move in and out of the cervix.
Then they treat a bruised finger at home
Macro of drugs. Intrauterine polyps
Functional type endometrial glandular polyp
These polyps are the product of pathological proliferation of the glands of the functional layer of the endometrium. The connective tissue component of such polyps resembles the stroma of the adjacent mucous membrane.
Iron polyps of functional or, as they are called, type 1 occur during reproductive age. Most authors classify them as polypoid forms of endometrial hyperplasia and call them pseudopolyps.
Two types of endometrial glandular polyps
The tissues of functional glandular polyps respond to the action of sex hormones, just like the surrounding endometrium
Iron polyps of the 1st type develop mainly against the background of diffuse endometrial hyperplasia and are more often susceptible to malignant formations.
Basal type glandular polyp
Maternal iron polyps, basal or type 2, are true uterine polyps.
They are lined with non-functioning, especially curved basal glands. Stroma elements carry fibrous and muscle fragments.
The tissues of true glandular polyps of the endometrium do not respond to the action of sex hormones.
Unlike functional polyps, the proliferative growth of true glandular polyps is not limited by hormonal or other known stimuli. The reason for this growth, as well as the reliable cause of any tumor process, remains unclear.
Endometrial polyp type 2 - a true glandular polyp of the uterine body is a benign tumor of the basal endometrial layer. What do endometrial glandular polyps look like? Genuine glandular polyps most often grow in the area of the corners of the tube and the base of the tube, less often - on the anterior inner surface of the uterus.
At first they resemble flat, wide hills and beards. As they grow, they “retract” the muscular elements of the myometrium, grow into additional vessels, form a narrow base stalk and resemble elongated, finger-shaped “mushrooms”.
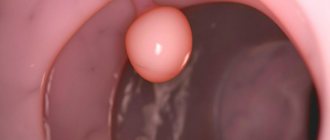
polyps
The vessels of glandular polyps are thickened, sclerotic, and twisted into spheres. The surface of the polyp is pale pink, smooth, sometimes with purple blood spots (traces of vascular destruction). The body on a skin section is spongy, porous, interspersed with deformed, chaotically located glands.
Symptoms of endocervical polyps
Most polyps, especially small ones, are characterized by an insidious course. They are discovered during an examination by a gynecologist by chance when visiting for another disease. Education does not make itself felt in any way until it reaches impressive dimensions, or undergoes secondary changes. They occur due to:
- injuries;
- infections;
- inflammation.
However, not all symptoms that appear during this period indicate a polyp. For example, menstrual irregularities occur due to concomitant pathological changes. A developed endocervical polyp manifests itself as:
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen;
- spotting outside of menstruation;
- painful sexual intercourse;
- mucopurulent vaginal discharge;
- copious mucus discharge.
Not all of these symptoms will appear at the same time; it all depends on the structure of the neoplasm, its size, content, and also on the period of development. A polyp discovered during pregnancy can trigger spontaneous premature birth due to reflex irritation of the cervix.
Causes of cervical canal polyp
The reason for the appearance of benign formations in the uterine canal has not been clearly established to date. Most of the facts associated with the occurrence of a polyp are considered to be provoking factors leading to the inflammatory process. In this sense, the following may be relevant:
- canal injury;
- structural changes in the surface of the endometrium;
- genital infections;
- violation of vaginal microflora;
- incorrect functioning of the ovaries;
- nonspecific infections (vaginitis, cervicitis, etc.);
- various physiological processes.
As you can see, the causes of cervical canal polyps cover a fairly large area of women's health. In addition to them, there are risk factors that predispose to the development of the disease:
- violation of fat metabolism;
- endocrine diseases;
- complicated childbirth.
In most cases, diagnosing endocervix polyps in patients also reveals diseases such as true erosion or pseudo-erosion, ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, atrophic colpitis, etc. This means that a favorable background is created for the neoplasm over a long period of time, about which the woman can even don't suspect until you visit a doctor.
Polypous formations in the uterine cavity and cervical canal are an area of research in modern gynecology and oncology. The main danger of polyps lies in the risk of their degeneration into adenomatous lesions with subsequent malignancy. If pathological growths appear, their planned removal is recommended. Despite the fact that not all polyps become malignant, clinicians recommend starting early prevention of malignancy of tumor cells.
Why is endometrial glandular fibrous polyp dangerous and how to treat it?
A glandular fibrous polyp is a benign neoplasm that forms on the lining of the uterus and consists of glandular and connective cells. This neoplasm must be cured, otherwise the risk of malignant degeneration is increased.
Causes and symptoms
A glandular fibrous polyp is a benign formation that is localized in the uterine cavity
With a glandular-fibrous polyp, the formation has glandular epithelium and overgrown areas of the uterine mucosa. This formation is often diagnosed in older people and can be observed in adulthood.
This polyp has a pink or burgundy color and a varied shape. The formation is attached to the tissue using a stalk, which is equipped with blood vessels.
The processes occurring in the endometrium depend on the concentration of hormones in the female body. The main reason for the development of pathology is hormonal imbalance. The risk of polyp formation increases with a lack of progesterone and excess estrogen. Against this background, focal changes appear in the endometrium. Over the course of several menstrual cycles, the polyp increases in size.
The following factors also contribute to the development of polyps:
- Inflammatory processes in the genital organs.
- Infectious diseases.
- Abortion and trauma.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Thyroid diseases.
- Hypertension.
The development of a glandular fibrous polyp can be influenced by hereditary predisposition, use of certain medications, and prolonged wearing of an intrauterine device.
In addition, if at the time of birth placenta clots remain inside, then later they are replaced by connective tissue, from which a polyp is subsequently formed.
Tamoxifen blocks receptors responsible for sensitivity to sex hormones, so the formation of a polyp in some women is associated with the use of this particular drug. When a polyp forms at the initial stage, there are no clinical manifestations and appear later.
The following symptoms are characteristic of a glandular polyp:
- Pain during menstruation.
- Bloody discharge outside of menstruation and after menopause.
- Pain during intercourse.
- Menstrual irregularities.
- Bleeding after sexual intercourse.
Symptoms increase as the polyp increases in size. If you experience these symptoms, you should definitely consult a doctor to avoid serious consequences.
Why is a polyp dangerous?
Polyp can cause endometrial cancer
Pathological formation in the uterus is dangerous due to possible complications:
- Often a woman fails to conceive a child during her reproductive years. Large polyps block the entrance to the cervix, which causes infertility.
- A woman may complain of irregularities in the menstrual cycle and loss of large amounts of blood during menstruation. This causes anemia.
- A woman may refuse sexual activity due to pain caused by large polyps.
- A glandular fibrous polyp poses a great danger if it degenerates into a malignant tumor.
- If a woman becomes pregnant with a polyp, it can lead to placental abruption. If the polyp is injured as the fetus grows, bleeding may occur. Often, polyps resolve on their own during pregnancy.
Diagnostics
Pathology can be diagnosed using ultrasound
If the symptoms listed above cause discomfort to a woman, it is important to consult a gynecologist. During the examination, the doctor may detect some formation on the cervix, but polyps in the endometrium are difficult to determine by palpation and using a gynecological speculum. The gynecologist will take a Pap smear and prescribe additional examination.
For a more accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination. For this purpose, instrumental methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics is one of the most common and informative research methods. During a pelvic ultrasound, dilation and thickening of the endometrium can be detected. This method is not always informative for some reasons. It is impossible to determine the structure of the polyp and differentiate the neoplasm from fibroids or adenomyosis. Polyps of the glandular structure are similar in structure to the endometrium, so such polyps are difficult to visualize.
- Hysteroscopy. With the help of hysteroscopy, endometrial polyps can be accurately identified. It is also possible to remove it during the procedure. If necessary, a biopsy of the cervix is performed, which will exclude degeneration into a malignant neoplasm.
- Metrography. This is an additional technique that allows you to see a tumor under the influence of X-rays.
Read: Interstitial uterine fibroids: treatment, prognosis and complications
Methods of treating the disease
Most often, treatment consists of removing the polyp.
Treatment of glandular fibrous formation can be carried out in two ways: medication and surgery.
If the polyp is small, then drug treatment is indicated:
- Oral contraceptives are usually prescribed, such as Regulon, Yarina, Zhanin, etc. These drugs are taken according to a specific regimen for a long period. Typically, such drugs are prescribed to women under 35 years of age. Persons over 35 years of age are prescribed gestagens in the form of Norkolut, Duphaston, etc.
- If a woman is diagnosed with an inflammatory process, then antibacterial drugs are used. During menopause, it is recommended to take Zoladex, Diferelin, etc.
- Symptomatic therapy involves the use of painkillers: Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, etc.
If drug treatment does not bring positive results, then surgical resection is performed. During hysteroscopy, the doctor examines the surface of the uterine cavity in detail. This will reveal abnormalities in the structure of the uterus.
When performing hysteroscopy, a polyp is removed using a coagulating loop, and if they are multiple, they are scraped out.
To avoid re-formation of polyps and possible complications after manipulation, cauterization is done at the site of formation. Subsequently, the material is sent for histological examination. After the procedure, bloody discharge and spasmodic pain may appear. After a few days, the woman should have an ultrasound to assess the quality of the hysteroscopy.
More information about endometrial polyps can be found in the video:
You can remove a polyp using a laser. This manipulation will not leave scars on the uterus and will not affect reproductive function. After removal of the polyp, hormonal therapy is indicated. During treatment, a woman must maintain sexual rest, carefully maintain hygiene,
Since bleeding is observed after the operation, the woman should not take hot baths, go to the sauna, take aspirin, acetylsalicylic acid, or lift heavy things. In addition, douching is prohibited.
Prognosis and complications
Timely and correct treatment – a favorable prognosis!
To avoid the formation of polyps in the uterine cavity, you must monitor your health and adhere to the following recommendations:
- Treat infectious and inflammatory diseases.
- For preventive purposes, visit a gynecologist 2 times a year.
- Avoid possible trauma to the uterus (abortion, curettage, etc.).
- Avoid casual sex.
- Prevent unwanted pregnancy.
- In addition, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat properly and nutritiously, monitor your weight, and move more.
To avoid complications, you should promptly consult a doctor if you have any symptoms. It is important to remember that polyps can form again, even with successful timely treatment. Frequent relapses increase the likelihood of developing a malignant tumor.
These simple recommendations will help prevent the development of diseases of the female reproductive system, including polyps. The prognosis after surgery is favorable. If curettage was performed, then an unsuccessful operation may contribute to the development of complications.
It is possible to develop an inflammatory process in the uterus, perforation of the uterus, and the formation of a hematometer.
After removing the glandular fibrous polyp and completing a course of hormonal therapy, you can prepare on your own or with the help of IVF. It is recommended to plan pregnancy no earlier than a month after hysteroscopy.
If pregnancy occurs, it proceeds without complications. However, it should be remembered that during pregnancy, women are prone to the appearance of new growths. They do not pose any danger to the fetus if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations.
Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
Source: https://DiagnozLab.com/analysis/cancer/zhelezisto-fibroznyj-polip.html
Glandular polyp as a pathology
A glandular growth in the lumens of the cervical canal is a pathological neoplasm, the structural content of which is glands and other connective tissue components. The predominance of glands in the morphological structure of the polyp body is also reflected in the name of the type of polypous focus.
The stroma or base of the polyp consists of the mucous tissue of the cervical canal. Glandular polyps are usually long-pedunculated and have a small mushroom-shaped or spherical body, no more than 1.5 cm.
The localization of polypous foci is diverse:
- lumen of the cervical canal,
- base of the cervix,
- exit into the vaginal cavity.
The extreme location of polyps increases the risk of strangulation, permanent trauma, and internal bleeding. The structure of polyps is soft, elastic, and prone to severe trauma.
Glandular growths of the mucous membrane are a common gynecological situation that occurs in women of reproductive age from 25 to 35 years. Mostly, these are localized single growths of the mucous membrane, but multiple types are also found. There can be up to 10 such growths in one lumen.
Note ! The extreme location of polyps increases the risk of strangulation, permanent trauma, and internal bleeding.
Features of glandular-fibrous growth
When highlighting the characteristics of a fibroglandular polyp, it is important to note the morphological combination of pathological proliferation of the mucous membranes of the cervical canal:
- Fibrous tissue . Fibrosis is a special reaction of the mucous membranes to various inflammations, chronic diseases, surgical or diagnostic procedures. Fibrous tissue is characterized by compaction, scarring, and loss of any functional features. When fibrotic changes occur, the functionality of an organ or tissue decreases.
- Glandular structures . The glands can be non-functional or secreting, secreting droplets of water and other enzymes.
The morphological structure of these tissues is usually a combination of glandular and fibrous tissue in equal proportions. The size of such polyps can vary from 0.5 mm to 3 cm. Typically, fibroglandular growths have a wide base and a flat body, rising above the surface of the mucous membranes.
All types of tumor-like growths are formed against the background of damage to the mucous membranes and epithelial tissue, and therefore are predominantly secondary in nature.
Important ! The danger of a glandular fibrous polyp lies in the high risk of cell malignancy and transformation into adenomatosis with subsequent formation of a cancerous tumor.
Glandular polyp of the endometrium: causes of formation, treatment, complications
Endometrial iron polyp is one of the most common pathologies besides glandular fibrosis. This type of neoplasm is typical for women of reproductive age and occurs on average in 30-40% of all cases.
Attention! Photos with shocking content. Click on the link to view.
Endometrial polyp is a common pathology in women of reproductive and menopausal age and is a kind of glandular-cystic or atypical endometrial hyperplasia. It takes the form of increased formation (growth) and may consist of adenomatous (glandular) cells and connective tissue cells.
You might be interested in: Papilloma on the lip: diagnosis and removal methods, who to contact?
Clinically, the neoplasm can remain undetected for a long time without causing symptoms. This is very dangerous because, as you know, a malignant tumor occurs - a benign polyp is born in a malignant form.
What is an endometrial polyp?
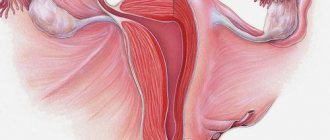
Uterine lining
The endometrium is one of the three linings of the uterus. The outer membrane is called the perimeter (or serum membrane). The middle, largest lining of the uterus is the myometrium, which consists of smooth muscle cells (myocytes).
The lining of the uterus consists of three layers
The inner lining is the endometrium. It is represented by two layers of cells: basal and functional. The cells of the basal layer have a small number of receptors for hormonal substances, which makes them practically unaffected by hormonal effects. The stratum basale is the basis of the functional layer above.
The most superficial layer is the functional layer, the cells of which react most sensitively to hormonal changes in the female body. During menstruation, it is shed along with menstrual blood and after the end of menstruation it is completely restored by the basal layer.
How does growth occur?
A polyp is formed only from the endometrium of the uterus as a result of hyperplastic processes. Due to intensive growth, the endometrium grows and forms a nodular neoplasm consisting of legs and body.
When growth begins, vessels begin to sprout to provide blood supply. Thus, its dimensions can vary from a few millimeters to 5-6 centimeters or more.
Types of polyps
Since the endometrium consists of several types of cells, neoplasms are formed with a predominance of one of them. Polyps are distinguished:
- adenomatous (glandular): a process with a predominance of glandular cells;
- fibrous: formation is formed by connective tissue cells;
- glandular-fibrous: the composition consists of connective tissue cells and gland cells.
Features of a glandular polyp
- The iron endometrial polyp is represented more by glandular cells and less by stromal cells.
- Depending on the layer from which it is formed, two types are distinguished:
- The functional node is very sensitive to all hormonal changes, so its shape and structure can change throughout the menstrual cycle if the endometrium is healthy.
- Based on histological type, pseudopolyps are divided into the following types:
- proliferative;
- hyperplastic;
- secretory.
Iron tumors are extremely rare and are considered the most dangerous because they are prone to malignant transformation, especially in postmenopausal women, against the background of neuroendocrine and metabolic disorders.
The risk of degeneration into a malignant form increases in proportion to size. For a size of 1.5 cm, the probability of transformation is 2%, for 1.5-2 cm - 2-10%, and for a size of more than 2 cm - a malignant tumor occurs in more than 10% of cases.
The number of polyps in the uterus may also indirectly indicate the risk of transformation. Thus, single neoplasias are rarely malignant (1-2%), multiple ones are more common (20%), diffuse (familial) neoplasias are very common (80-100%).
Reasons for the development of pathology
The reasons for the formation of functional and basal polyps are somewhat different.
The development of functional and basal endometrial polyps has various causes
Functional form
Since the functional layer is most susceptible to hormonal changes, the formation of the functional type is enhanced against the background of hormonal disorders, namely hyperestrogenation.
The causes of dishormonal conditions can be
- frequent stress;
- obesity, high blood pressure;
- diabetes, thyroid disease and other neuroendocrine disorders;
- hyperestrogenia due to insufficient treatment with estrogen-containing drugs;
- injuries and inflammatory processes of the uterine mucosa (endometritis);
- some other gynecological diseases.
Basal form
The basal layer is practically not subject to hormonal effects, so dishormonal conditions do not play a key role in the development of the basal endometrial polyp.
Injuries to this layer and some other pathologies are a common cause:
- abortion;
- fractional diagnostic scraping;
- prolonged presence of an intrauterine device in the uterine cavity, its incorrect installation;
- performing a biopsy of the internal walls of the uterus without high-quality sterilization of instruments, its inaccurate execution;
- diseases of the immune system: allergies, autoimmune diseases, especially with the participation of the vascular wall, immunodeficiency states;
- inflammatory processes in the uterus caused by sexually transmitted infections and some other pathogenic microorganisms;
- complicated obstetric history (miscarriages, abortions, complicated childbirth)
- 9 uterine fibroids
- 7 regular checkups a woman should undergo
- 7 signs of fat deficiency in your diet
Symptoms
The onset of the tumor will almost always go unnoticed, since during this time the woman will not experience any symptoms and will not be able to be visualized by ultrasound methods.
One of the symptoms of the pathology is drawing pain in the lower abdomen
Above a certain size, a polyp can cause the following symptoms:
- acute pain before and during menstruation;
- the occurrence of bleeding long before menstruation (intermenstrual bleeding). A woman may notice bleeding in her underwear every day of her menstrual cycle:
- delayed menstruation followed by large amounts of menstrual blood;
- pain in the lower abdomen of a traction nature;
- dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse);
- bleeding after sexual intercourse, physical activity, stress;
- lack of a regular menstrual cycle.
Bleeding from the genital tract is observed in women during menopause. At this age, this is an excellent sign, often indicating cancer processes in the gynecological area.
Diagnostics
If at least one of the symptoms occurs, you should immediately consult a gynecologist. Based on symptoms, medical history, results of bimanual gynecological examination and speculum examination, the doctor may suspect this pathology.
Laboratory research methods
To make a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a hormonal background study: Determine the amount of estrogens, progesterones, follicle-stimulating, luteinizing hormones, thyroid hormones, adrenal hormones and others. Samples of material are taken on different days of the cycle.
In addition, oncomarkers can be tested, especially in menopausal and postmenopausal women.
Instrumental research methods
Instrumental research methods are mandatory; they allow you to visualize the tumor, perform a biopsy, and then examine the tissue for benignity or malignancy.
Pathology is often detected using ultrasound
The following types of instrumental examination are used:
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs (ultrasound). The method allows you to assess the condition of the uterine mucosa, the presence of hyperplastic processes and neoplasms in it;
- endoscopic examination using a hysteroscope (hysteroscopy). A hysteroscope is a special optical device that is inserted into the uterine cavity and allows a detailed examination of the endometrium.
During hysteroscopy, a targeted biopsy of the tumor can be performed for subsequent cytological and histological examination.
Another possibility is fractional diagnostic scraping. Tissue fragments isolated during the procedure are also sent to the laboratory to assess the composition of cells and tissues.
Cytological and histological examination is necessary to assess the degree of cell differentiation, the presence or absence of cellular malignancy and determine further patient tactics.
Therapy
Iron polyps are most often treated surgically.
During the operation, the gynecologist inserts a hysteroscope into the uterine cavity. After the growth has become noticeable in the field against the background of pathologically unchanged endometrium, it is removed mechanically or laser ablation, electrocoagulation, etc. The gynecologist is able to determine the degree of cell differentiation.
Polyp removal is usually performed during hysteroscopy
If during the diagnostic phase a fractional diagnostic scrap was made and the polyp has proven its functionality, then no further surgical intervention is required.
You may be interested in: Treatment of polyps in the gallbladder with folk remedies
Extirpation of the uterus and appendages is recommended in postmenopausal women, especially with frequent relapses and multiple polyps, as these factors significantly increase the risk of developing malignant neoplasms.
Treatment of endometrial glandular polyp after removal
This is an important stage in therapy. It is used to restore hormonal levels:
- Progestins (preparations containing progesterone): Micronor, Levonorgestrel, Duphaston, Utrozhestan;
- Estrogen Progestin or combined oral contraceptives: Yarina, Janine, Diana 35.
For treatment, progesterone-containing drugs are prescribed, in particular, native;
The regimen and duration of therapy are determined by the gynecologist individually for each patient.
If the results of a cytological examination of the material taken during a biopsy indicate a malignant tumor and there are signs of cancer, then the treatment is different from the usual and should be carried out by a gynecologist.
Complications
Promptly and properly untreated glandular polyps can cause the following complications:
- infertility, miscarriage, placental abruption, fetal hypoxia during pregnancy;
- metrorrhagia (uterine bleeding) with the development of anemia;
- addition of infection or trauma to the blood supply with the development of necrosis;
- malignant tumor, adenomatous transformation.
For early detection of hyperplastic processes in the uterine mucosa and other gynecological pathologies, it is necessary to visit a gynecologist regularly (at least once a year) to try to eliminate risk factors and treat gynecological diseases in a timely manner.
Video
We invite you to watch a video on the topic of the article.
Predisposing factors
The mechanisms of formation of polypous foci are determined by exogenous and endogenous factors. The risk of cancer is based on heredity and a burdened gynecological history.
There are several common causes of the formation of polypous neoplasms:
- hormonal disorders;
- natural childbirth;
- artificial termination of pregnancy;
- regular gynecological manipulations;
- constant stress;
- mental disorders, psycho-emotional instability;
- age-related changes and irregularities in the cyclicity of menstruation;
- chronic inflammatory processes;
- venereal diseases.
It is reliably impossible to determine the true cause of the pathological proliferation of mucous membranes, just as it is impossible to assess the degree of influence of any factor. Typically, several negative factors contribute to the formation of a polyp.
Diagnostic directions
The traditional diagnosis of a cervical canal polyp consists of a routine examination of the vaginal cavity and cervical pharynx using gynecological speculum.
The final diagnosis is made based on the woman’s complaints, her clinical history, age and some physical criteria, as well as after the following diagnostic methods:
- ultrasound examination (intravaginal and superficial);
- cervicoscopy (endoscopic research method);
- colposcopy (examination of the vagina and walls of the cervical canal using a colposcope);
- diagnostic curettage (hysteroscopy);
- biopsy (find out what the result of a cervical polyp biopsy can show here).
All these methods fully reflect the condition of the internal os of the genital organs. Additionally, blood, stool, and urine tests are prescribed to determine concomitant diseases. An effective method for examining polyps is hysteroscopic examination and biopsy.
Histology after taking a biopsy allows:
- Reliably assess the nature of the pathological growth;
- Determine the degree of oncogenic risks;
- Develop further tactics for patient management.
Clinical manifestations
Unfortunately, the main danger of polyposis structures in the cervical canal lies in the asymptomatic course of polyposis in the early stages of the development of pathology. Moreover, the smaller the polyp, the less its clinical manifestations.
Typically, polyps are diagnosed accidentally during a routine examination of a woman or for other complaints.
As the polyp grows, the following symptoms may appear::
- Atypical spotting;
- Intermenstrual bleeding;
- Severe pain in the lower abdomen;
- Painful menstruation (especially if this has not previously been noted);
- Pain after sexual intercourse;
- Impossibility of conceiving a child.
Note ! Internal bleeding can be reflected in the form of bloody or brownish discharge and provoke the development of iron deficiency anemia. If alarming symptoms appear, you should definitely consult a specialist.
Treatment of fibroglandular polyp of the endocervix
Treatment of fibroglandular lesions involves its mandatory removal. The operation is planned. Before treatment, a course of drug therapy is carried out, especially in the presence of inflammatory processes.
Indications for surgical removal are:
- Large growths of the mucous membrane (can cause blockage of the cervical lumen and interfere with pregnancy);
- Woman’s age over 35 years (risks of multiple polyps and polyposis);
- Ineffectiveness of drug treatment, including hormone replacement therapy;
- Infertility of a woman caused by pathological tissue proliferation;
- Risks of malignancy.
Considering the planned nature of the removal, the woman has the opportunity to carefully prepare, and the doctor has the opportunity to formulate the correct removal tactics and choice of method.
Main types of surgery
The following manipulations are effective against polyps::
- Laser coagulation . The method involves removing the polyp by excision of the stalk and evaporation of the pathological tissue under the influence of a laser beam. During the operation, simultaneous soldering of the vessels occurs, which prevents the development of bleeding. The disadvantage of this method is the presence of heavy smoke during surgery and the inability to remove large or multiple polyps.
- Polypectomy . Removal of a pathological growth by excision or twisting from the walls of the cervix. The method is effective for polyps up to 2.5-3 cm. After removal, the wound surface of the bed is cauterized with electrodes or a laser.
- Diathermoexcision . Loop removal, which involves placing a loop on the growth and excision it, followed by cauterization with electric current. It is used for severe dysplasia of the walls of the cervical lumen, as well as for the risk of adhesions and erosive lesions.
- Cryodestruction . The method involves freezing the stalk or body of the polyp using liquid nitrogen. After freezing, the polyp is removed. The main advantage is low trauma and rapid recovery. After manipulation there is no risk of scar tissue formation.
- Radio wave coagulation . Removal is carried out using special equipment - the Surgitron apparatus. It is characterized by minimally invasiveness, low trauma and speed of execution.
- Resection . Abdominal surgery, which involves removing part of the uterine cavity or the entire organ. A radical decision is made when the tumor becomes malignant in order to avoid metastasis to other parts of the pelvic organs.
The type of intervention is selected based on the size and symptomatic picture of the polyposis lesion, as well as on the basis of the characteristics of the woman’s medical history.
Possible complications
Despite the small volume of most removal methods, the risk of complications still remains. The main complication of the operation is the emergence of new lesions. In almost 12% of all clinical cases, relapse occurs.
Other complications are considered:
- Formation of adhesions and scar tissue;
- Infectious lesion;
- Malignancy of an incompletely removed polyp;
- Bleeding when the canal walls are damaged;
- Allergic reactions, severe swelling;
- Hematometra is severe internal bleeding followed by stagnation of blood in the uterine cavity.
Correct behavior of the patient after surgery and following all medical instructions is the key to successful post-operative recovery without complications.
All about the endometrial glandular polyp: symptoms, causes, treatment
A uterine polyp made of iron is a growth in the uterine cavity that does not damage the body itself. In the early stages of development, it does not manifest itself and does not bother the woman in any way. However, if it is not detected in a timely manner and the pathology is not eliminated, this can lead to various complications.
When an endometrial polyp expands, its presence manifests itself in bleeding between menstrual cycles, inability to become pregnant, abdominal pain and even the birth of cancer.
Characteristics of glandular polyp
Such neoplasias have a basal and functional type.
An iron polyp of the basal endometrial type is a nodular formation growing from the basal layer of the uterus. It does not respond to hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle, is small in size and is attached to the walls of the uterus by a polyp bone equipped with a network of blood vessels.
Functional type neoplasia grows from the functional lining of the uterus and is dependent on hormonal changes throughout the month.
The functional layer selections are divided:
- into proliferation. The cells of this formation are susceptible to inflammation;
- - secretory. Serious exudate collects in the canals of their glands. Such cavities form a cyst. Mucus is constantly released from such polyps;
- - hyperplastic. They occur against the background of endometrial hyperplasia. They ä
It is possible to understand which polyps have affected the inner uterus only after a histological examination.
Identify glandular and glandular cystic growths. The former consist mainly of endometrial glands, while their dense stalk consists of fibrous tissue. The latter are small and have a glandular body with mucous sacs.
Features of symptoms
If a woman experiences one or more of the following symptoms, she should consult a gynecologist to rule out the possibility of pathology. And if a benign mass is found, it must be removed immediately.
Most often, women complain about glandular polyps:
- with extensive and painful menstruation;
- pain in the lower abdomen during and after sexual intercourse;
- secretion of blood ointments from the vagina after sexual intercourse;
- menstrual irregularities in which menstruation does not occur, followed by unexpected bleeding.
Often, the lack of ovulation in women of reproductive age with this pathology is due to hormonal imbalance. Pregnancy may occur, but there is no guarantee that it will not be terminated spontaneously.
These symptoms are typical for overgrown polyps. Small young tumors can be detected using ultrasound, after a diagnostic scrape, or by a gynecologist, who must be consulted at least once a year for preventive purposes.
Causes
Iron endometrial polyps are found in women of various age groups who have and have not given birth, have a stable sex life and have sexual intercourse from time to time. However, there are common causes for polyps:
- hormonal imbalance in the body caused by excess estrogen or lack of progesterone.
- Endometrial deformation due to infection.
- Mellitus diabetes mellitus.
- Heredity.
- High pressure.
- Abnormal growth of the endometrial lining.
- Metabolic disorder.
- Adipose.
- Weakened immune system.
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Endometrial injury due to abortion, childbirth with complications, unsuccessful scraping.
- Inflammation of the endometrium.
- Long-term use of an intrauterine device as a contraceptive.
Long-term use of tamoxifen is often associated with the appearance of polyps. Endometrial tumors are common in women with limited function or polycystic ovaries.
During pregnancy
Often a polyp of the iron uterus prevents pregnancy. This is due to the fact that it is difficult for a fertilized egg to implant into the abnormally changed lining of the uterus.
Even if this happens, there is a risk of miscarriage, stopping the baby's development, or premature birth.
Therefore, it is very important to get tested before planning a future pregnancy so that your life is not at risk.
It also happens that the formation and development of a polyp occurs after pregnancy. In this case, if the tumor does not grow and does not have a negative impact on the health and development of the baby’s expectant mother, they try not to touch it and remove it only after childbirth.
But there are times when it is necessary to get rid of growth during pregnancy:
- The polyps bleed and help the infection reach the fetus.
- Benign growth increases rapidly.
- The tumor grows in the fallopian canal.
Fertilization is controlled by hormonal or antibacterial therapy. When identifying inflammatory processes, antibiotics are used.
And only if drastic measures are necessary, surgery to remove the growth is performed. This is done if there is severe pain or heavy bleeding.
In most cases, the glandular polyp is removed by a hysteroscopic procedure. After the operation, the woman is under observation in the hospital. She will be given medications to stop the bleeding and prevent it from becoming infected in the affected area.
Difference from the glandular-fibrous type
These adenomas have a similar appearance. Their main difference is the predominance of glandular tissue in one and much less in the other. But there are other distinctive features:
- Iron polyps form mainly in the genitals of women of reproductive age, while iron-containing polyps form in mature and even older women of the weaker sex.
- The iron type consists primarily of glands and stromal cells of the lining of the uterus, while glandular fibrosis tissues are predominantly fibrotic and have little epithelium.
- Iron polyps constantly secrete mucus due to the large volume of the glands. They respond better to drug treatment and exhibit more severe symptoms as they grow taller.
- Pathologies such as glandular fibrosis occur more often with chronic infections of the uterine mucosa. After removal of this form of growth, antibacterial therapy is prescribed to prevent relapses.
Diagnostics
Modern medicine has a large arsenal of tools for identifying this type of pathology:
- Ultrasound can be used to quickly and painlessly search for new growths in the female genital organs. Ultrasound can also be used to determine how well the entire sexual system is working together.
- Polyp hysteroscopy allows you to carefully examine the inner surface of the uterus using a photo or video camera on a probe. This is a more accurate method of studying pathology than ultrasound.
- A blood test shows the estrogen-progesterone ratio taking into account the menstrual cycle, since polyps often arise due to hormonal deficiency.
- A gynecological examination can reveal neoplasia near the cervix.
- To determine the growth trend toward cancer development, a histological examination of the removed tumor is performed. The doctor will then prescribe appropriate post-operative treatment.
You might be interested in: Enema before colonoscopy
This is how an ultrasound doctor or gynecologist detects a formation during palpation or visual examination. And histology helps to determine the nature of the pathology and choose treatment appropriate to the diagnosis.
Therapy depends on the type of adenoma, the woman’s age and the characteristics of the body, such as the presence of chronic diseases. Therefore, self-medication in this situation is dangerous to health, and in some cases even life-threatening.
Treatment of endometrial polyp
To combat the formation of fibers or glands, two main methods are used:
- Hormonal therapy.
- Surgical destruction of tumors.
Hormone therapy is used in the following cases:
- the woman has not yet given birth;
- contraindicated surgery;
- pregnancy is planned in the near future.
This therapy may take about six months. Although glandular polyps respond well to hormonal treatment, a healthy endometrium may not always be achieved.
The most effective treatment for uterine neoplasia is polypectomy. During this manipulation, all tumors are removed from the genitals. For this purpose, laser, hysteroresection or hysteroscopy is used. And after this procedure they prescribe medications.
Medication
The main goal of treating polyps with tablets and injections is to suppress the growth of tumors and eliminate associated symptoms. It is used for this purpose:
- Taking hormonal oral contraceptives;
- GnRH agonists. They are prescribed to women over 35 years of age and postmenopausal women;
- progestin; progestin. For example, Rutestan or Duphaston for polyps. They are taken in the second half of the menstrual cycle. Polyps dissolve in the body thanks to balanced hormones.
Drugs are also prescribed after surgical removal of polyps.
Surgical intervention
Polyps are removed using minimally invasive surgery. Hysteroscopy is most often used for this purpose. This method does not damage other organs and tissues. Once the glandular growth is destroyed, the woman can recover easily, and subsequent treatment leads to good results.
This manipulation is performed under general anesthesia so that the woman does not feel pain or other unpleasant sensations. After removing the endometrium from the surface, the endometrium along with the stalk is scraped off with a curette and then disinfected with liquid nitrogen or current. This is done to avoid complications.
The work does not take more than half an hour. The removed pathology is then sent to histology for examination to rule out the presence of cancer or precancerous lesions.
The woman then undergoes hormonal therapy, which lasts from 3 to 6 months. She then undergoes an ultrasound examination to determine the effectiveness of the treatment.
Complications when a glandular polyp occurs
As soon as this pathology is detected, therapy should be started immediately. Otherwise, the woman is expected:
- Heavy and painful bleeding not associated with menstruation. This leads to anemia, health problems and a significant decrease in immunity.
- Discharge of blood, discomfort in the lower abdomen during and after intimacy.
- uterine cancer. This is not a common occurrence, but it is still possible. Therefore, it is very important to send it to histology after surgery to remove the polyp.
- Incorrect cycle. It is observed as a consequence of hormonal imbalance associated with the formation of glands.
Most women with polyposis tumors cannot become pregnant. And in the presence of such a pathology, conception can lead to infection of the fetus by bleeding, placental abruption, spontaneous abortion or premature birth.
Therefore, when planning a pregnancy, it is very important to undergo a medical examination in order to prevent any pathology before conception. And even without planning a child, a gynecologist should consult with him at least once a year for prevention. Treatment of a disease detected at an early stage of development brings less hassle and anxiety.