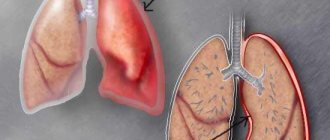
Pulmonary edema occurs when the normal level of interstitial fluid in the lungs is exceeded. This condition is a serious complication of many heart diseases. Swelling can also be triggered by a severe allergic reaction, injury, as well as poisoning by various chemicals. In this case, the patient’s condition sharply worsens, the functioning of the heart and respiratory organs is noticeably impaired. The patient urgently needs the help of a doctor, otherwise the consequences will be very sad. The algorithm for providing emergency care for pulmonary edema includes various measures, but all of them are aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition.
Mechanism of edema development
Pulmonary edema occurs when fluid accumulates in the tissues instead of air. Due to this, the blood circulation of the respiratory organs is disrupted, oxygen enters the cells in insufficient quantities, which ultimately leads to disruption of the functioning of the lungs and the entire body as a whole.
Doctors identify only two main mechanisms that can lead to swelling of the respiratory organ:
- Exceeding the level of intercellular fluid due to increased pressure in the blood vessels of the respiratory organ. This type of edema is called hydrostatic.
- Excess of intercellular fluid volume due to excessive filtration of plasma at absolutely stable pressure. This type of edema is called membrane edema.
Regardless of the pathogenesis of edema, the patient’s condition is extremely serious and requires immediate medical attention.
Treatment of pulmonary edema
In a hospital setting, therapy is continued.
- Oxygen therapy - inhalation of oxygen with ethyl alcohol to extinguish foam in the lungs
- Narcotic analgesics (painkillers) and antipsychotics (drugs to reduce psychomotor agitation): reduce hydrostatic pressure in the pulmonary vessels and reduce venous blood flow. Drugs: morphine, fentanyl
- Diuretics - reduce the volume of circulating blood, cause dehydration of the lungs: furosemide
- Cardiac glycosides (provide a cardiotonic effect): strophanthin, corglycone
- Other drugs for the treatment of pulmonary edema depending on the blood pressure level (see above)
- Relief and prevention of bronchospasm: aminophylline, aminophylline
- Glucocorticosteroids, surfactant therapy: used for non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
- For infectious diseases (pneumonia, sepsis) - broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Important to know: cardiac glycosides are mainly prescribed to patients with moderate congestive heart failure; Glucocorticosteroids are contraindicated for cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Causes
Membrane and hydrostatic edema have different causes. Therefore they are divided into groups.
Causes of hydrostatic pulmonary edema
The causes of such edema are various pathologies of the heart and respiratory system:
- Heart defects at the stage of decompensation. Most often observed with mitral valve insufficiency and stenosis;
- Blockage of large and small vessels of the lungs;
- Deterioration of contractile functions of the heart. Most often, edema develops with left ventricular infarction and severe myocardial damage;
- Pneumothorax;
- Severe respiratory failure. This can happen with bronchial asthma, aspiration, or blockage of the airways by foreign objects.
Persistent arrhythmia can also cause hydrostatic edema. In this case, blood circulation in the heart is disrupted.
Causes of membranous pulmonary edema
Membrane edema occurs in diseases of a general nature, which include:
- Non-inflammatory pathologies - respiratory syndrome, aspiration, prolonged inhalation of certain chemical components;
- Inflammatory pathologies – pneumonia and sepsis.
First aid for pulmonary edema caused by various reasons is practically the same. The main task is to normalize the functioning of the heart and respiratory system.
Severe complications of pulmonary edema are suffocation and cardiogenic shock.
Specifics of occurrence
Edema in the lungs does not occur as an independent disease. Most often it is provoked by heart disease and acts as the second phase of acute left ventricular failure. The first phase, cardiac asthma, is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the lung tissues. After this edematous fluid passes into the alveoli, pulmonary edema occurs.
There are 2 types of acute pulmonary failure:
1 type is associated with various heart diseases, and 2 occurs due to increased permeability of the alveolar membranes.
In addition, a mixed form is isolated, caused by neurogenic conditions.
This division is due to the reasons that cause this emergency condition:
- Toxic effects in bacterial infections;
- Overdose of drugs or drugs, sepsis;
- Heart failure diseases;
- Pathologies of the lungs and bronchi;
- Predisposition to blood clots;
- Chest injuries;
- Kidney and liver failure;
- Circulatory disorders.
In addition, there are a number of factors that contribute to the manifestation of an attack:
- Stress and mental tension;
- Strong physical activity;
- Abuse of alcohol and nicotine;
- Sudden changes in weather conditions;
- Pregnancy;
- Premenstrual condition;
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
The disease occurs in two stages. At the first stage, the blood plasma is steamed into the lung tissue, and then, at stage 2, it penetrates into the alveoli. At this moment, alveolar edema occurs.
Most often, pulmonary edema is diagnosed in people after 40 years of age; in children it occurs much less frequently, most often with failure of the left ventricle of the heart.
Clinical picture
It is not difficult to determine this condition if you know the main signs of manifestation. The speed of development determines fulminant, acute, subacute and prolonged edema.
Swelling can be triggered by active physical exercise, intense stress, or a sudden change in body position. In some cases, so-called precursors appear before this condition. This may include progressive shortness of breath, rapid breathing, regular coughing and moist rales in the lungs.
The first symptom of edema will be chest pain and a feeling of squeezing. After this, motor activity increases and shortness of breath increases. It is difficult for the patient not only to inhale, but also to exhale. A person lacks oxygen, his heartbeat is too rapid, and cold and sticky sweat appears on his skin. The skin becomes bluish. At the very beginning, the cough is dry, then it gradually turns into a wet one. In the end, the sputum becomes foamy and pinkish. In particularly severe cases, foam may be released from the nasal passages.
A striking symptom of changes in the lungs is loud and bubbling breathing, it is frequent and intermittent . The patient is very frightened. Consciousness may be confused. As the symptoms progress, the pressure drops significantly and the pulse is difficult to palpate.
It is very difficult for the patient to breathe, he takes a forced sitting position, this makes breathing much easier for him. Even an inexperienced person can notice the blueness of a patient’s lips. In some cases, moist rales can be heard even without a stethoscope.
In the fulminant form, all dangerous symptoms develop very quickly, literally in a matter of minutes. Due to the sudden development, it is very difficult to save a patient with this form.
With a protracted form of the pathology, symptoms increase gradually and the prognosis is much better than with a rapid and acute form.
Urgent Care
Emergency care for pulmonary edema is provided in several successive stages. The person providing assistance must act decisively, but very carefully. It is necessary to adhere to the following algorithm of actions:
- The patient is given a semi-sitting position; in this position of the body it is much easier to breathe. This is considered the optimal body position for pulmonary edema;
- If necessary, mucus is removed from the upper respiratory tract. If a person is conscious, he can blow his nose; if the patient is unconscious, then they resort to suctioning out the mucus with a rubber syringe;
- Inhalation of alcohol vapor is performed. It is necessary to take 70% medical alcohol;
- Venous tourniquets are applied to the limbs;
- According to the doctor's indications, Lasix solution is administered intravenously if the medication has no effect. Then after 20 minutes a higher dose is administered;
- Eufillin and Prednisolone are administered.
Emergency care also includes the administration of nicotinic and ascorbic acid, as well as sodium bicarbonate solution.
If a person has symptoms of pulmonary edema, they can be given a nitroglycerin tablet as first aid. But such actions must be agreed with a doctor.
Nurse tactics
If there is a nurse near the patient, then the emergency tactics will be as follows:
- The doctor is promptly notified;
- The patient is seated comfortably, pillows are placed under his back, and his legs should hang down;
- If a person is very nervous, the nurse should calm him down;
- All compressive clothing is removed from the patient. These could be belts, ties, things with tight elastic bands and a bra;
- If a person becomes ill in the house, then it is necessary to open the windows to provide fresh air.;
- Before the doctor arrives, it is necessary to regularly monitor the patient’s condition. To do this, measure your pulse and blood pressure. It is better to write down the data so that you can show it to the doctor later;
- The patient is placed under the tongue with a nitroglycerin tablet to improve myocardial nutrition;
- A few minutes after taking nitroglycerin, the patient’s blood pressure is measured; if the systolic reading is high, then another tablet is given;
- To relieve the pulmonary circulation, it is necessary to apply tourniquets to all limbs or only to the legs;
When applying tourniquets, care must be taken to ensure that they do not compress the arteries. The tourniquets are applied for no more than 15 minutes and removed from the limbs gradually.
- If pulmonary edema is observed while the patient is in the hospital, he is immediately provided with inhalation of clean and humidified oxygen;
- Treatment tactics are determined by the attending physician.
It is worth knowing that the first symptoms of pulmonary edema most often appear at night, so on-duty nurses need to be vigilant. The lives of patients depend on the attentiveness of these health workers.
You need to start providing first aid for pulmonary edema as early as possible. With timely treatment, the prognosis is very good. It takes a couple of weeks for the patient to fully recover. If the dangerous condition was not noticed in a timely manner and first aid was not provided, everything could end very sadly. Pulmonary edema often leads to the death of patients.
Is it possible to use traditional medicine recipes?
When symptoms of pulmonary edema appear, urgent professional help is needed to avoid dangerous consequences. Accordingly, traditional medicine recipes at this stage do not apply to alternative treatment. Even the most popular decoction or tincture cannot replace pharmaceutical drugs. But if the victim’s condition is successfully stabilized, herbal components can be used as additional methods. They allow you to cope with some residual symptoms - cough or sputum production. A preliminary consultation with a doctor is necessary. The most popular recipes are:
- An expectorant decoction is prepared from anise seeds in the amount of three small spoons and a glass of natural liquid honey. After mixing the ingredients, you need to boil them for another 15 minutes, then add ½ small spoon of soda to the mixture.
- If cardiogenic pulmonary edema has been diagnosed, marshmallow roots can be used to eliminate phlegm. The decoction is prepared as follows: two large spoons of crushed dried raw materials are poured with boiling water in a volume of 300 ml. Place the container on low heat, bring to a boil and leave for 10 minutes, infuse the product for 60 minutes. The filtered liquid is taken up to 5 times a day before meals. A single dose is one large spoon.
- You can use flax seed. To prepare the decoction, pour four large spoons of the ingredient into a liter of water, bring to a boil, remove the product from the stove and leave in a warm place. Then it is filtered and drunk up to six times a day with an interval of 2-2.5 hours. The volume of each serving is ½ cup.
- Another recognized remedy is a decoction of cyanosis roots . A large spoonful of the crushed component is poured with 500 ml of water, the container is placed in a water bath, and left for 37-40 minutes. After filtration, give the victim 50-70 ml of drink at a time after meals. During the day you need to take the product four times.
- Parsley seeds are also used. The decoction is prepared by brewing four small spoons of the crushed ingredient in a glass of boiling water. Then the product is put on fire and boiled for 20 minutes. Afterwards, the broth is infused until cooled and filtered. It must be taken four times a day after meals. The volume of each serving is one large spoon.
It should be noted that even with proper treatment, the prognosis after pulmonary edema is rarely favorable. To ensure survival throughout the year, constant supervision by specialists is required.