Preparing for the test
The microflora of the genital organs consists of various microorganisms. To a greater extent it is represented by beneficial bacteria, to a lesser extent by opportunistic microbes and in small quantities by pathogenic bacteria.
A flora test is taken from all women who come to see a gynecologist. It allows timely detection of female diseases (for example, cervical erosion), various infectious and inflammatory processes, and sexually transmitted diseases.
The study is carried out in three cases - a preventive analysis, during a woman’s pregnancy, and also if the patient complains of unpleasant symptoms (vaginal discharge, itching, burning, hyperemia, pain, etc.).
Important: two days before the smear, you should refrain from using vaginal medications - suppositories, tablets, creams, etc. Their use can distort the reliability of the information received.
Features of preparation for a smear:
- Two weeks before the examination, you need to stop taking antibiotics and other synthetic drugs. Against the background of their use, inform the doctor so that when deciphering he takes into account their probable influence;
- Three days before the delivery of biological material, you cannot have sex;
- The night before, hygiene measures are carried out using soap or intimate gel. In the morning you can only wash yourself with warm running water, do not use soap;
- Immediately before visiting the doctor, you should not go to the toilet.
A few days before a gynecological smear, you should abandon the douching procedure, as the laboratory results obtained will be distorted.
During a gynecological examination, the doctor takes scrapings from three points. The medical procedure is painless, the woman feels slight discomfort. The biological material is applied to a glass slide and distributed evenly. Then it is sent to the laboratory.
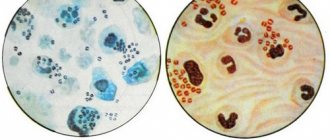
For microscopic examination, it is stained with a Gram stain, as a result, different cells become different colors, which helps to differentiate them. After washing off the paint, gram-positive microbes still remain colored because they have a thick membrane. Gram-negative are characterized by a thin membrane, so after washing off the paint changes its color. Based on this, the laboratory assistant fills out a medical form.
How is material collected for a smear?
During treatment, smears are constant companions of therapy; they are used to determine the effectiveness of the procedures performed and assess the general condition. A smear on the flora does not hurt, the woman experiences slight discomfort, as when examined with a gynecological speculum, but there is no pain and cannot be, since the material is collected using special devices.
Gynecological smears are collected for several areas of research: flora, sterility, cytology, latent infections.
A smear analysis for flora is done to assess the state of the microflora, find out the number of bacteria and the presence of pathogens among them. A good microflora smear will show the content of 95% beneficial lactobacilli in the material being tested. It is lactobacilli that are tasked with protecting the delicate vaginal environment, maintaining acidity levels and protecting against infections. When pregnancy occurs, the number of lactobacilli decreases, since natural protective functions are experiencing difficult times. During pregnancy, such tests are performed regularly.
A general flora smear can show the presence of a sexually transmitted infection. These include Trichomonas and Gardnerella.
If it is necessary to determine pathogens, a smear is taken for hidden infections, this method is called PCR. Even in healthy women, a certain amount of gardnerella and candida can be detected; at acceptable levels, they do not have any pathogenic effect. However, under unfavorable circumstances, a small environment can become active and develop into a disease. A woman’s immune system suffers during pregnancy, from systematic stress, emotional shock, and diseases associated with a disorder of the immune system.
Diagnosis of leukocyturia problems in women
Reasons for the appearance of cocobacillus in a smear in women
If elevated white blood cells are found in women, and scrapings were carried out from different points, then first of all a medical specialist must determine the cause of the pathological increase. Afterwards a certain treatment is prescribed.
In some pictures, elevated leukocytes are detected in a woman’s body, but there are no clinical manifestations or growth of opportunistic microflora. In addition, all laboratory tests show the absence of pathogens. This situation requires re-examination.
When there is an increase in white blood cells in the cervix, urethra and on the walls of the vagina, then expanded diagnostics are required. It includes additional tests:
- Examination of scrapings by bacterial culture;
- PCR is a method that helps diagnose sexually transmitted diseases;
- Ultrasound of the internal organs of the pelvis;
- Colposcopy – examination of the cervix;
- Visiting additional specialized specialists.
Bacterial culture involves isolating colonies of bacteria of a conditionally dangerous and dangerous type from scrapings. The specific type of microbe and its susceptibility to groups of antibacterial agents must be determined. The last study is necessary to prescribe the optimal antibiotic option.
PCR is a highly accurate method that can detect latent infections that do not give external symptoms. If they are not detected in time and therefore not treated, this can lead to infertility.
Ultrasound using a transvaginal sensor allows you to assess the condition of the walls of the uterus and its appendages. You can detect a focus of inflammation, a tumor neoplasm, compactions of various etiologies.
Worth knowing: colposcopy is the most informative method that allows you to examine the cervix through multiple magnification. At an early stage, it detects cancer, leukoplakia, dysplasia and other diseases that increase the number of leukocytes in the cervical canal.
Cocci detected in a smear in women: treatment
Quite often, cocci are found in the same standard smear of a gynecologist’s patient. This is a conditionally pathogenic microflora, and if they are contained in small, insignificant quantities, then there is no need to treat it. But if the cocci content is exceeded, further examination and therapy are required.
What cocci can be detected in a smear:
- Staphylococcus haemolyticus (staphylococci) - their active growth causes disorders of the genitourinary system; a swab from the throat and nose may also be required.
- Enterococci represent the intestinal microflora, and they speak of insufficient hygiene of the genital organs.
- Gonococci - bacteria cause salpingitis and cervititis, the inflammatory reaction occurs quite quickly.
Streptococcus, coccobacilli, diplococci can also be detected in the smear. In each case, subsequent more detailed research and therapy are required. Often after this it is necessary to treat not only women, but also men (since the infection is transmitted in this case classically - sexually).
If, for example, a staphylococcal infection is detected using smears, the patient needs to be examined in detail. Pathological lesions of the genital organs, hormonal disorders, and relapses of some chronic diseases can be detected. Often, regular use of tampons leads to the detection of cocci in a smear.
Whatever is found in the smears - streptobacilli, gonococci, Staphylococcus aureus, coagulase-negative staphylococcus, Staphylococcus aureus, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus intermedius warneri - you cannot self-medicate. Only a doctor can prescribe suppositories, tablets, and other medications. Otherwise, the result may not even be zero, but negative.
Deciphering a smear from the cervical canal
So, what should be the norm of leukocytes in a smear from the cervical canal? The doctor is deciphering the research. The norm of leukocytes in the cervix is no more than 30 per field of view.
Epithelial tissue covers the inner mucosa of the vagina and cervical canal. The canal must contain columnar epithelium, the norm of which is up to 15 in the field of view. An increase indicates the presence of an anomalous process.
The results of a cervical smear contain the following information:
The norm of leukocytes in a smear in women
- Key cells are normally absent;
- Gonococci, trichomonas, yeasts are not normally detected;
- Gram-positive lactobacilli are absent in the normal state (specifically in the cervical canal);
- Mucus – the amount should be moderate.
Ideally, a smear should be taken from 10 to 20 days of the menstrual cycle. The concentration of mucus during this period is normally moderate. Depending on the menstrual cycle, mucus can vary from scanty to abundant.
Smear and sterility
Taking a smear for flora and sterility is assessed in four groups. A healthy body will show the result of an acidic environment, a pH level of 4.0-4.5, a sufficient amount of lactobacilli, a low content of leukocytes and epithelium. A bad smear, and this is the third and fourth group, is an indication for further research. Usually the doctor sends a culture to the tank to find out the exact content of the flora. There is no need to be afraid of a bad smear; this does not always mean the presence of serious infections. The culture tank is prepared for about a week, after which the doctor will be able to make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
When taking a smear for flora in different laboratories, you may get different results, this is normal. It all depends on the methods used in a particular laboratory, the qualifications of specialists and the level of equipment.
The information received is deciphered by the attending physician. If necessary, he may refer you to another laboratory for repeat testing. When treating, you should always use the services of one research center so that the material is processed in the same way, then you can trace the changes with maximum accuracy.
Checking a smear for sterility allows you to assess the number of infectious cells, find out whether there are pathogens of sexually transmitted infections and what the patient’s hormonal background is.
A smear for hidden infections is carried out specifically to identify infectious agents. This cannot be done with a regular smear on the flora. PCR diagnostics is considered the most accurate; it identifies the type and type of bacterial environment. This is important for subsequent treatment, since in order to select a medicine, you need to know the exact name of the bacterium, otherwise the active substance in the drug will not work properly. PCR diagnosis helps determine the presence of gardnerellosis, chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, gonorrhea, and ureaplasmosis. In the initial stage, many diseases do not actively manifest themselves, and smear analysis makes it possible to detect them even before the onset of the active phase. This promotes rapid healing. The PCR technique is used to determine hepatitis and papilloma.
Why are leukocytes in the smear elevated?
The reasons for the increase in the content of leukocytes in a smear are due to disruptions in the reproductive system and failures in the functioning of other internal organs and systems. In the cervical canal, the norm of leukocytes is up to 30. If there is an increase, the following pathological conditions are suspected:
- Inflammatory processes in the cervix;
- A source of inflammation in the tubes or ovaries;
- Inflammation of the uterus (endometritis disease);
- Colpitis or vaginitis (vaginal damage);
- Urethritis (damage to the urethra);
- Tumors of a malignant nature (destruction of healthy tissue is always characterized by inflammation);
- Dysbacteriosis of both intestines and vagina;
- Venereal diseases.
Leukocytes, as gynecological practice shows, are concentrated in the focus of the inflammatory process. In turn, pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms lead to inflammation. A smear on the flora rarely reveals them, so it is necessary to undergo extensive diagnostics. A polymerase chain reaction is used to examine the blood, urine, and secretions from the woman’s genitals.
Note: PCR can detect pathogens of tuberculosis, granuloma inguinale, syphilis, HPV, gonorrhea, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, immunodeficiency, Candida fungi, etc.
In the presence of one or more provoking factors, growth and reproduction of opportunistic microflora is observed, which is accompanied by an increase in the content of leukocytes. The most common reasons include:
- Vaginal microtrauma due to intense sex;
- Decreased local or general immune status;
- Hormonal imbalance;
- Surgical interventions in the genital area;
- Allergic reactions to medications, etc.
A high concentration of leukocytes can be observed if the woman had sex before taking the test or had an intrauterine device installed.
Why is an increase in leukocytes dangerous?
Lack of adequate treatment and prolonged inflammatory process leads to the following consequences:
- Chronic diseases of the genital organs.
- Lesions of the urinary system and kidneys.
- Hormonal imbalance.
- Benign and malignant tumors of the reproductive organs.
- Ovarian dysfunction.
- Cervical erosion.
- Infertility.
- Miscarriages.
- Fading pregnancy.
- Mastopathy, fibroadenoma.
If the leukocyte count in the smear is below normal, then there is no cause for concern. The specified value of 15 units is the maximum allowed.
Norm of leukocytes in a smear
The white blood cell count is based on the point where the smear was taken. Normally, their number should not be large. In the urethra their content varies from zero to ten, in the vagina no more than 15, and in the cervical canal up to 30. If there are more of them, other diagnostic methods are needed to determine the cause of the pathological deviation.
Other indicators of flora analysis:
- Leptothrix is a bacteria that should not be detected. If they are present, this indicates urogenital candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, chlamydia or trichomoniasis.
- Key cells are missing in a healthy woman. Their detection indicates gardnerellosis and some other infections.
- A single presence of yeast-like fungi is allowed at any point in the scraping for a smear. Increased concentration – thrush.
- Lactobacilli should be contained in large quantities, but are absent in the cervical canal and urethra - this is the norm. At low levels, activity of opportunistic microflora is observed.
- The presence of mucus in moderate quantities at three points, and the absence in the urethra is the norm.
- In a normal smear, squamous epithelium is found 5-10. If there is 0 in the field of view, this is tissue atrophy; when there is a lot of it, this is an inflammatory process.
Let us note that while carrying a child, it is permissible to increase the number of leukocytes in a woman’s smear to 15-20. This is not a pathology, as it is associated with hormonal changes and a decrease in the immune status of a pregnant woman.
In conclusion: in the cervical canal, the norm for leukocytes is considered to be up to 30. If there are more of them, it is necessary to undergo additional studies. A high concentration is a signal of inflammatory processes and hidden infections that require adequate treatment.
Preparation and essence of the procedure
In order for the analysis results to be as reliable as possible, the woman must prepare for the study. She should refrain from sexual intercourse the day before the visit to the gynecologist, not use vaginal suppositories and pills, and not douche. Immediately before taking it, it is recommended not to urinate for 2-3 hours and wash the genitals with a weak soap solution.
The smear reflects the composition of the microflora of three anatomical areas: vagina, cervix, urethra. To collect biological material, only sterile instruments are used:
- bacteriological loop;
- gauze swab;
- putty knife.
The scrapings are placed on slides, which are dried, stained and examined under a microscope.
The number of leukocytes is determined primarily by simple counting. Normally, their content should be small, directly in the cervical canal from 0 to 30. During pregnancy, the physiological norm for the number of leukocytes is considered to be from 15 to 30.