Intestinal candidiasis is an infectious process of damage to the gastrointestinal tract, which is caused by the active reproduction of human fungal flora, against the backdrop of a weakening of the body’s protective functions. The disease manifests itself, depending on the course and form of the disease: increased flatulence, loose stools, abdominal pain, fungal sepsis, ulcerative kelitis. The diagnosis is made after an endoscopic examination, histological analysis and bacteriological culture of stool. Treatment takes place in three directions: prescribing antifungal agents (antimycotics), restoring intestinal microflora and strengthening weakened immunity.
What is intestinal candidiasis?
This disease, which is the most pressing problem of modern medicine, since determining the diagnosis and criteria for this disease is a little difficult for doctors and clinicians. The main reason for the development of this disease is the widespread distribution of the Candida fungus, including the body of a healthy person (up to 80% of the population are carriers of the Candida fungus in the intestines).
Invasive candidiasis infections of the intestines mainly occur in people with weakened immunity. Invasive candidiasis is an opportunistic infection, most often associated with an imbalance of immunity.
For a large number of specialists, it can be quite difficult to distinguish between non-invasive intestinal candidiasis (the main percentage of all cases of diseases of the digestive organs) and transient candidiasis (a temporary, passing condition). It is possible to distinguish between these two types only thanks to modern diagnostic equipment. To establish an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to: identify factors that increase the risk of developing the disease, endoscopic signs of the disease and a positive result of bacteriological culture. Antimycotics are not prescribed when Candida fungi are initially detected by culture.
Drug therapy
Drugs used for intestinal candidiasis belong to the following groups:
- Antimycotic agents to eliminate the causative agent of infection.
- Antibacterial - to eliminate secondary infections.
- Drugs for the symptomatic treatment of concomitant diseases.
- Probiotics used to restore intestinal microflora.
It should be noted that “Ketoconazole” and “Fluconazole” do not give positive results for intestinal candidiasis, since they are absorbed only by the upper intestines, as a result of which the required concentration of drugs does not reach the lumen of the colon, where the greatest accumulation of fungi is usually observed. By the way, in this case it is even possible to develop side effects in the form of toxic hepatitis.
For children and pregnant women, doctors often prescribe Pimafucin for intestinal candidiasis. This medicine does not cause adverse reactions and is considered an effective treatment for this pathology. It is taken one tablet four times a day for one week. Children are prescribed two tablets per day.
In parallel with the elimination of the infection, as already mentioned, therapy for concomitant diseases is carried out. For this purpose, antisecretory drugs, vitamins, H2 receptor blockers, and others may be prescribed.
Reasons for the development of candidiasis
Gastroenterologists distinguish two forms of intestinal candidiasis: invasive and non-invasive (invasion - attack, invasion).
In medical practice, the most common non-invasive form of intestinal candidiasis is: with dysbacteriosis and a mixed type of intestinal infection, Candida fungi begin to actively and uncontrollably multiply in the intestinal space, without penetrating into the mucous membrane. At the same time, toxic fermentation products are formed and characteristic fungal toxins are released, which has an irritating effect on the intestinal walls and provokes a further exacerbation of dysbiosis, the formation of fungal allergies and diseases of the immune system.
The mechanism of development of invasive candidiasis is somewhat different. Candida mushrooms, with a weakened immune system, closely attach to the mucous membrane of the large and small intestines, then penetrate into its thickness and transform into a thread-like form. With pronounced suppression of cellular immunity, the Candida fungus penetrates the blood and spreads throughout the body, causing visceral candidiasis (damage to the pancreas and liver). This form of candidiasis can develop as a result of severe neutropenia, with a decrease in the number of certain leukocytes.
Candida albicans is the most common form of candidiasis. These microorganisms are the most pathogenic species of fungi of the genus Candida, but are very sensitive to the action of antifungal drugs. Resistance appears only with extremely long-term use of antifungal drugs.
Hepatolienal candidiasis is a form of invasive candidiasis that occurs exclusively in hematological oncology patients; the only symptom of the disease is fever; the diagnosis is made only if the level of leukocytes increases.
Intestinal candidiasis can develop in the presence of just one of the following factors:
- Primary immunodeficiency (congenital or acquired in utero);
- Weak immunity during pregnancy, in old age, under severe stress;
- Oncology (after chemotherapy);
- After severe diseases of the endocrine system;
- After taking immunosuppressants, during organ transplantation;
- After treatment with antibacterial drugs and antibiotics;
- Severe lack of vitamins and protein in the diet;
- Allergic diseases;
- Chronic infections.
In medical practice, intestinal candidiasis is the most common of several factors listed above.
Diet
If you have intestinal candidiasis, you should adhere to a special diet. The diet involves consuming large amounts of food that has not been processed. These are, first of all, fresh vegetables. You should also give preference to protein foods in the form of boiled fish, skinless chicken, and unpolished rice. Lactic acid products such as kefir and yogurt are useful.
Your daily diet should include foods high in fiber. First of all, these are oat bran and oatmeal. You should drink filtered water.
It must be remembered that Candida loves sugar and reproduces well in a sweet environment. Therefore, you should exclude sugar, yeast, and fruits from the menu. The following products are contraindicated:
- dried fruits;
- bakery;
- chocolate;
- alcohol;
- smoked meats and marinades;
- potato;
- mature cheese;
- citrus fruits, sour fruits and tomatoes, which actually do not oxidize, but alkalize the environment where candida likes to multiply.
Subsequently, prohibited foods can be gradually included in the diet, for example, once a week.
Symptoms of the disease
Intestinal candidiasis can be divided into 3 clinical forms:
- Invasive diffuse form - fungal, pathological effect on the intestinal mucosa. Main diagnostic criteria: diarrhea, poor condition of the patient due to severe intoxication of the body, abdominal pain, high body temperature, mycosis (damage to the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, spleen, etc.), blood in the stool;
- The invasive focal form is a fungal infection of certain areas of the intestine. It appears most often with duodenal ulcer or ulcerative colitis. It is impossible to diagnose this form of fungal disease due to the lack of signs without the necessary examination methods;
- Non-invasive form - involves the rapid growth of Candida fungi in human organs, and can lead to the destruction of healthy microflora and the development of pathogenic ones.
Candidiasis manifests itself in a variety of clinical conditions, the most common being thrush. The main symptoms of thrush development: bloating, diarrhea, abdominal pain.
Symptoms when intestinal candidiasis (thrush in the intestines) spreads to the genitals in women:
- Curdled discharge, white in color with a slight unpleasant odor;
- Itching in the vagina, pain and discomfort during urination and sexual intercourse;
- Secondary infertility.
Symptoms in men:
- Curdled discharge, white in color with an unpleasant odor;
- Itching and burning of the genitals;
- Pain when urinating.
How to detect the disease in time?
First of all, monitor the condition of your own intestines. Every time you experience even the slightest discomfort in the intestinal area, try to understand why it appeared and what could be causing it. If pain appears for no apparent reason, you should immediately go to the hospital to conduct detailed tests and study various secretions.
Diagnosis of the disease
The lack of characteristic clinical signs makes it difficult to diagnose yeast in the intestines, as well as sensitive and specific methods for detecting Candida fungi in stool tests. In severe cases of the disease, a general blood test reveals a decrease in the number of red blood cells, lymphocytes and leukocytes. To choose the most effective method of examining the intestines, it is necessary to consult an endoscopist.
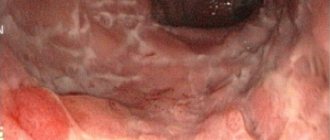
During endoscopy, nonspecific symptoms of mucosal lesions may be detected, therefore morphological examination of biopsy specimens and endoscopic biopsy play a decisive role in making a diagnosis.
The main difficulties in diagnostics are that yeast-like mycelia are not detected in all analyzes of the material, so quite often the results are false negative. When in fact, with the invasive diffuse form of intestinal candidiasis, symptoms of ulcerative and necrotic pathogenic effects on the mucous membrane are determined, and in the non-invasive form - catarrhal inflammation.
All patients must undergo a stool test for candidiasis dysbacteriosis and stool culture on nutrient media.
Basically, these tests determine mixed microflora, not only Candida fungi, but also staphylococci, E. coli, and Klebsiella. If more than 1 thousand fungal units per 1 gram are detected. pathological tissue, then carriage of fungal microflora is excluded. The most important task of microbiological research is to determine the type of pathogen and analyze the sensitivity of microorganisms to antimycotics (antifungals).
Diagnostic measures
After a person develops signs of intestinal candidiasis, he needs to go to a hospital for consultation. Highly specialized specialists may encounter difficulties in making a diagnosis, since the disease has a clinical picture with other pathologies. That is why this category of patients undergoes an extensive examination to identify intestinal or anal candidiasis, including both laboratory and hardware techniques:
- Patients are examined and interviewed.
- The attending physicians collect anamnesis.
- Feces are submitted for laboratory testing. A bacterial culture is performed, which allows you to determine the number of fungi and identify their sensitivity to specific types of medications.
- Blood is taken, in which a high concentration of immunoglobulins may be observed, indicating the active growth of colonies of pathogenic microflora.
- Urine for rent. D-arabinol is detected, indicating the progression of the pathology.
- Cytological and histological examination of fragments of mucous membranes in which pseudomycelium may be detected is carried out.
- Patients are shown radiography, fiberoscopy and colonoscopy (candidiasis of the anus is detected).
- An endoscopic examination of the intestinal sections is performed, during which the condition of the mucous membranes is assessed, ulcerative and erosive lesions are detected, with a whitish cheesy coating on the surface.
Treatment of intestinal candidiasis
Seeking advice from a specialist if you have intestinal candidiasis (candidiasis) helps to determine risk factors for the disease and determine the scope of necessary examinations. Since the disease does not have specific clinical signs, identifying this pathology is quite difficult. After laboratory tests of intestinal candidiasis, the choice of treatment method depends on the nature of the course, possible concomitant pathology and reaction to antimycotic drugs.
Treatment regimen for intestinal candidiasis:
- Treatment of the underlying disease, which led to decreased immunity and increased activity of fungal flora;
- Immunomodulation;
- Prescription of special antifungal agents.
Patients with an invasive diffuse form of intestinal candidiasis are referred for inpatient treatment, and special medications for invasive fungal diseases are prescribed - azole antimycotics - these are antifungal drugs - Fluconazole, which are well absorbed and tolerated by the body.
In the non-invasive form of the disease, non-resorptive polyene antimycotics are used to destroy fungal flora - they have an intense local effect and do not suppress the normal microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. Such drugs include tablets and rectal suppositories Pimafucin.
The disease manifests itself as a state of mixed microflora and intestinal dysbiosis, and in order to cure candidiasis dysbiosis, eubiotics (healthy microorganisms) must be prescribed. Digestive enzymes, analgesics, antispasmodics and sorbents are prescribed to treat the symptoms and manifestations of the disease.
Complications and consequences
With untimely therapy or its absence, as well as with self-treatment of the disease, it becomes chronic, in which the fungi penetrate deep into the tissues, destroying their structure. In the future, the pathology provokes the development of complications in the form of intestinal ulcers, the development of internal bleeding and sepsis. Such conditions are life-threatening as they can lead to death.
As a complication, prolonged diarrhea develops, which leads to dehydration. During pregnancy, pathology can cause fetal death or miscarriages.
Folk remedies
If we talk about treating a disease with folk remedies, they must be combined with medications, otherwise the treatment will be ineffective.
Iodine and baking soda, for topical treatment of thrush
Dissolve 1 tsp. iodine and 1 tsp. soda in 1 liter of boiled, cooled water. Use the resulting solution 2-3 times a day, taking baths or washing. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Herbs
Taking decoctions of sage, chamomile, oak bark, sage, oak bark, pomegranate peels, bird cherry, black currant leaves has a beneficial effect on the healing process and has regenerating, immunocorrective and anti-inflammatory properties.
Video: Candidiasis
Grandma's advice
Thrush has been known to people since ancient times, so traditional medicine has proposed ways to combat it, involving the use of natural ingredients. First of all, these are enveloping oils. They are recommended to be taken before meals. A diet containing large amounts of forest berries is recommended. These are blueberries, blueberries, honeysuckle. Cabbage of any variety and greens are useful. Every morning you should clean your tongue and mouth mucous membranes from white plaque. Rinsing with soda, a decoction of celandine, burdock, and sage are useful.
Traditional medicine methods can be an excellent addition to drug therapy
If you have intestinal candidiasis, you should eat fresh garlic; you can add it to carrot salad. Start with one clove per day, gradually increasing the amount to 10 pieces. After you have consumed garlic, you should not drink or eat for an hour. An infusion containing milk mushroom and garlic helps to overcome the symptoms of candidiasis. The proportions are as follows: for a glass of milk mushroom infusion, three cloves of garlic. You should drink it at night, keeping the mixture in your mouth. Horseradish should be added to dishes.
It is useful to eat oatmeal jelly and oatmeal. These dishes can be included in the diet daily or periodically. Add fresh vegetables, oils, and herbs to the jelly. To prepare jelly, pour oatmeal from a jar up to the shoulders. You need to fill them with cool water or kefir. Cover the neck with gauze and place the bottle in a warm place to allow fermentation to begin. After a few days, drain the liquid part and leave the bottle for another day.
After a day, drain the liquid again. Place the bottle with its contents in the refrigerator. Every morning, take a few spoons of the contents from the bottle, add half a liter of water and boil. After cooling, the jelly is ready. Remember that diet alone cannot rid you of the disease so that thrush goes away forever.
Folk remedies also do not always manage to cure completely. The immune system should be strengthened, for example, by hardening. Choose the methods that are right for you, based on your general health, age, and concomitant diseases.