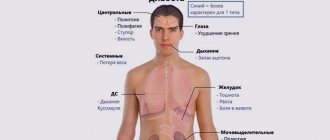
Retinopathy
If type 2 diabetes is advanced, retinal pathology may begin. Almost every patient, regardless of age, can lose vision.
More and more new vessels, swelling and aneurysms appear. This occurs due to pinpoint hemorrhage in the optic organ. In this situation, there is a high probability of retinal detachment.
Diabetic retinopathy occurs in people with type 2 diabetes (both men and women). Two decades after the onset of the disease, retinopathy affects 100 percent of patients.
The condition of the retina will directly depend on the degree of advanced disease.
Consequences of type 2 diabetes in women
In women, type 2 diabetes mellitus can have the following consequences:
- lesions of small, medium and large blood vessels;
- dehydration of the skin;
- the occurrence of alopecia areata;
- thrombocytopenia;
- anemia.
Atherosclerotic blockages of the arteries occur. Due to this pathology, blood can no longer circulate at full strength to all systems and organs. As a result, their usual work rhythm is significantly deteriorated. A severe form of this pathology is the occurrence of ischemic stroke.
At the age of 47, I was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. In a few weeks I gained almost 15 kg. Constant fatigue, drowsiness, feeling of weakness, vision began to fade.
When I turned 55, I was already steadily injecting myself with insulin, everything was very bad. The disease continued to develop, periodic attacks began, and the ambulance literally brought me back from the other world. I always thought that this time would be the last.
Everything changed when my daughter gave me an article to read on the Internet. You can’t imagine how grateful I am to her for this. This article helped me completely get rid of diabetes, a supposedly incurable disease. Over the last 2 years I have started to move more; in the spring and summer I go to the dacha every day, grow tomatoes and sell them at the market. My aunts are surprised how I manage to do everything, where so much strength and energy comes from, they still can’t believe that I’m 66 years old.
Who wants to live a long, energetic life and forget about this terrible disease forever, take 5 minutes and read this article.
Due to diabetes, women's kidneys stop working normally, removing all unnecessary substances. A condition of diabetic nephropathy appears.
The consequences of type 2 diabetes in women include damage to the retina of both eyes. The person gradually becomes blind.
The appearance of diabetic neuropathy leads to changes in nerve endings, which contributes to the appearance of infectious and ulcerative diseases of the lower leg and foot.
The body's susceptibility to pathogenic microorganisms, which rapidly develop during periods of epidemics, increases. They affect the urinary tract of diabetic patients. Hair becomes sparse. There is tooth decay, periodontal disease occurs, and hearing loss occurs. The carbohydrate and fat balance undergoes changes. Therefore, in many cases, women experience a pathological state of hepatosis.
To all of the above consequences of diabetes mellitus in women is added a state of excessive irritability, an outburst of attacks of anger, and hysterics. Therefore, in order to at least slightly reduce the negative impact of the consequences, it is necessary to strictly adhere to all the recommendations of the attending physician.
Nephropathy
If the process of damage to the renal glomeruli and tubules begins, then in this case we can talk about the beginning of the development of nephropathy. Metabolic disorders cause quite serious pathologies of renal tissue. We are talking about arteries and small arterioles.
The prevalence of this complication of type 2 diabetes reaches 75 percent of the total number of patients. Diabetic nephropathy can occur for a long time without any noticeable symptoms.
At later stages, renal failure may occur, and in a chronic form. If the case is too advanced, you may even need permanent dialysis or a kidney transplant. In case of nephropathy, an older or middle-aged patient will receive a disability group.
Useful video
How to protect yourself from dangerous pathological processes? Watch the video.
A diabetic should:
- Control glycemic levels, maintaining them at an optimal level;
- Follow a diet;
- Monitor and adjust blood pressure;
- Do not smoke, do not abuse alcohol ;
- Exercise regularly;
- Be examined by doctors annually.
A person diagnosed with T2DM can sometimes get rid of the disease completely by following a diet and doing exercise.
If you cannot cope with the disease, you need to prevent the development of severe complications and avoid exacerbations.
To do this, it is enough to keep the blood sugar level at an acceptable level, avoiding its sharp fluctuations. Your doctor will tell you how to do this.
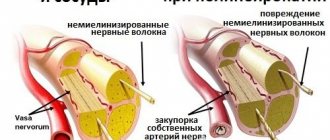
Angiopathy
Angiopathy is a rather serious complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus. With this disease the following is observed:
- damage to blood vessels;
- thinning of capillary walls, their fragility and fragility.
Medicine distinguishes 2 types of such damage: microangiopathy and macroangiopathy.
With microangiopathy, the vessels of the kidneys and eyes are affected. Over time, problems begin in the functioning of the kidneys.
With macroangiopathy, the vessels of the lower extremities and heart are affected. The disease usually occurs in four stages. First, atherosclerosis of the arteries occurs, which can only be diagnosed with the help of instrumental examination. Next, pain begins in the lower leg and thigh when walking.
At the third stage of development of the disease, pain in the legs intensifies, especially if the patient assumes a horizontal position. If you change your position, it becomes much easier for the patient.
At the last stage of the disease, ulcers appear and gangrene begins to develop. In the absence of medical care, there is a high probability of death.
Causes of complications in diabetes
If you do not monitor your health and do not detect the presence of the disease in time, the consequences of diabetes can lead not only to disability, but even to death. The more pronounced the symptoms, the more severe the patient’s condition and the likelihood that complications will soon arise.
They were divided into two types:
- Early or acute.
- Late or chronic.
Any complications always arise as a result of the fact that a diabetic does not adhere to the instructions of the attending doctor.
At the same time he:
- violates the dietary regime;
- ignores the maintenance of sugar levels in the blood and does not control it;
- does not lead a healthy life without observing even the simplest rules;
- does not want to get rid of bad habits and even begins to abuse them;
- leads sedentary daily life activities.
Diabetic foot
This disease is caused by damage to the nerves and blood vessels of the legs due to type 2 diabetes. There is a disturbance in tissue nutrition and blood circulation through the vessels. At the very beginning of the disease, the patient may feel tingling or burning on the surface of the lower extremities.
The patient will be constantly haunted by:
- weakness;
- pain in the legs;
- numbness of the limbs;
- decreased pain threshold.
If an infection occurs, the pathogenic microflora will spread very quickly, affecting other organs of the diabetic. According to the severity of the damage, 3 stages of diabetic foot can be distinguished:
- diabetic polyneuropathy of the lower extremities (damage to nerve endings occurs);
- ischemic (impaired nutrition of vascular tissues);
- mixed (with a high risk of gangrene of the feet).
The risk group includes those people who have had diabetes for more than 10 years. To exclude such a complication of the disease, it is important to pay special attention to your shoes, preventing the formation of calluses and cracks on the feet. This is especially true for men with a difficult work schedule.
Prevention of complications
As already noted, the first and second types of the disease are most often diagnosed. There are also specific types of the disease, such as Modi and Lada diabetes. They are difficult to diagnose and are often confused with the first two types.
Regardless of the type of illness, the patient must take all necessary preventive measures to help prevent the development of acute and chronic complications.
New information: First aid for diabetic coma: algorithm of actions
First of all, you need to constantly monitor your blood sugar levels. This should be done not once a week or day, but much more often, several times every day. For example, immediately after waking up, before and after breakfast, during lunch, after physical activity, etc.
Only timely detection of a sugar surge will allow it to be immediately reduced, and accordingly, the likelihood of developing complications will be reduced to zero.
Basic rules for diabetics:
- Strict adherence to dietary nutrition (calculating calories, dividing carbohydrates into several meals, choosing foods with a low glycemic index).
- Regular visits to the doctor, preventive examination for possible complications.
- Constant physical activity (slow running, brisk walking, swimming, cycling, going to the gym).
- Complete abstinence from drinking alcoholic beverages.
- Timely treatment of existing concomitant diseases.
To live a full and normal life, a diabetic must always keep his “finger on the pulse” - this is the only way to minimize possible complications in the present and future.
What do you think about this? What measures are you taking to prevent chronic complications?
Cataract
This consequence of type 2 diabetes can cause vision loss. High glucose levels have a detrimental effect on the lens and intraocular fluid.
The lens itself begins to absorb moisture and swells, which leads to a change in its refractive ability.
Impaired circulation, as well as nutritional deficiencies, can cause clouding of the lens. It is typical that cataracts affect both eyes at once.
Important! This disease can occur in those who suffer from diabetes for a long time. If vision loss or a significant decrease occurs at an early age, then the patient will be given a disability group.
general information
Before considering the consequences of a sugar disease, it is necessary to consider the pathology in more detail. Glucose (in everyday life it is called sugar) is the main source of nutrition for the human body.
This substance can only be obtained by consuming food. During food processing, glucose is released, binds to insulin at the cellular level, and is then transformed into energy, which allows the body to function normally and fully.
When the functionality of the pancreas is impaired, it leads to a decrease in insulin production in the human body. Since glucose cannot be absorbed on its own, that is, without a hormone, there is an accumulation of sugar in the blood.
Most often in medical practice, type 1 and type 2 sugar diseases occur. The second type of disease develops after 40 years of age and progresses relatively slowly. At the same time, even before the diagnosis is made, the patient experiences complications.
Type 1 diabetes occurs in young adults, teenagers and young children. Despite the fact that medical practice has not established the exact causes of the development of pathology, it is often associated with genetic predisposition.
New information: First aid for diabetes: how to help children and adults with types 1 and 2 diabetes?
The disease itself does not threaten the patient’s life in any way. However, a chronic hyperglycemic state (persistent increase in blood sugar) disrupts the functionality of internal organs and systems, leading to numerous malfunctions in the body.
There are acute complications that result from excessive increases in blood sugar, as well as chronic consequences that arise from constantly high glucose.
Encephalopathy
Diabetic encephalopathy must be understood as brain damage. It may be caused by:
- circulatory disorders;
- oxygen starvation;
- mass death of nerve cells in the brain.
Diabetic encephalopathy can manifest itself as severe pain in the head, decreased quality of vision and asthenic syndrome.
This pathology can be detected in more than 90 percent of patients with diabetes. In the first stages of the disease there are practically no symptoms. Further, the symptoms of the disease will be similar to the course of impaired brain activity in older people.
As encephalopathy develops, the following will be noted:
- increased anxiety;
- increased fatigue;
- decreased ability to concentrate;
- increased insomnia;
- increased headaches.
Pain in the head can be called squeezing and makes it impossible to concentrate. The patient is unable to walk without unsteadiness, dizziness and loss of coordination overtake him.
The picture of the disease includes adynamia, lethargy, and disturbance of consciousness.
Myocardial infarction in a diabetic
OUR READERS RECOMMEND!
Our readers successfully use DiabeNot to treat joints. Seeing how popular this product is, we decided to bring it to your attention.
Myocardial infarction in diabetes mellitus is a severe complication that can lead to the death of the patient. These two mutually aggravating diseases require intensive treatment, strict adherence to all doctor’s instructions and lifelong prevention.
How does a heart attack develop?
What is a heart attack? This is nothing more than the death of the myocardium after an acute cessation of blood circulation in a certain part of it. A heart attack is preceded by long-term developing atherosclerotic changes in various vessels, including myocardial vessels. The mortality rate from heart attack in our time remains quite high and amounts to approximately 15-20%.
Atherosclerosis is the deposition of fat in the vascular wall, which over time leads to a complete closure of the artery lumen, and blood cannot move further. There is also the possibility of a piece of fatty plaque forming on the vessel tearing off with the subsequent development of thrombosis. These mechanisms lead to the occurrence of a heart attack. In this case, a heart attack does not necessarily occur in the heart muscle. This could be an infarction of the brain, intestines, or spleen. If the process of stopping blood flow occurs in the heart, then we talk about myocardial infarction.
Several factors will lead to the rapid development of atherosclerosis. Namely:
- excess body weight;
- male gender;
- arterial hypertension;
- smoking;
- lipid metabolism disorder;
- diabetes;
- kidney damage;
- hereditary predisposition.
Heart attack in diabetes
If a diabetic has a myocardial infarction, then one should expect a severe course, the consequences will also be serious. As a result of studying such conditions, it was revealed that a heart attack in diabetes mellitus develops at an earlier age than what happens in coronary heart disease without diabetes. This is facilitated by some features of the course of diabetes.
- The severity of the disease is determined by the fact that with excess glucose in the blood, its toxic effect develops, leading to damage to the inner wall of blood vessels. And this leads to increased deposition of cholesterol plaques in damaged areas.
- Obesity. Poor nutrition over a long period of time leads to serious illnesses.
- Arterial hypertension is a constant companion to type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. This factor affects the damage to large vessels.
- In diabetes mellitus, the composition of the blood changes towards increasing viscosity. This factor greatly accelerates the onset of myocardial infarction.
- Myocardial infarction has been observed in close relatives, even those who do not have diabetes.
- Violation of lipid and cholesterol metabolism. Nutrition plays a key role.
An experienced diabetic usually develops the so-called diabetic heart. This means that its walls become flabby, and cardiac dysfunction gradually develops.
Mortality from heart attack in diabetes mellitus increases significantly due to disruption of metabolic and recovery processes in the body.
Symptoms and features
In people without carbohydrate metabolism disorders and in diabetics, the symptoms of myocardial infarction can differ significantly. Often it all depends on the length of the disease: the longer the duration of diabetes, the less pronounced the symptoms of a heart attack, which often complicates diagnosis.
The main symptom characteristic of acute myocardial circulatory disorders - chest pain - is leveled out in diabetes mellitus or may be completely absent. This is due to the fact that the nervous tissue is affected by high levels of sugar, and this leads to a decrease in pain sensitivity. Because of this factor, the mortality rate is significantly increased.
This is very dangerous, because the patient may not pay attention to minor pain on the left side, and the deterioration of the condition may be regarded as a jump in sugar levels.
What symptoms may bother a diabetic if he has a heart attack? The patient may experience the following conditions:
- pain, feeling of compression behind the sternum;
- the left cutting hand has lost strength, pain is felt in it;
- On the left side of the lower jaw there may be pain and obsessive discomfort;
- severe deterioration in health, weakness;
- there is a feeling of interruption in the work of the heart;
- shortness of breath occurs;
- weakness and dizziness develop.
Since all recovery processes are impaired in diabetes mellitus, the development of large-focal myocardial infarction occurs much more often than in people who do not have diabetes. The consequences of such a heart attack are much more severe.
A diabetic person has a higher risk that a myocardial infarction will occur again.
Treatment
In order for the treatment of myocardial infarction to be successful and undesirable consequences not to develop, it is necessary first of all to normalize blood sugar. Only with sufficient control of glucose levels can positive results be achieved.
Surgical treatment is recognized as the most effective method of restoring blood flow after a heart attack. This is especially true for diabetes mellitus, since the risk of complications and mortality in such patients is much higher. They resort to angioplasty and stenting of blood vessels. This is more effective than treatment only with drugs that dissolve blood clots.
If it is impossible to provide emergency surgical care, treatment of myocardial infarction is reduced to thrombolytic therapy. Statins, aspirin derivatives, and, if necessary, drugs to lower blood pressure and cardiac glycosides are also prescribed.
Nutrition
After a heart attack with diabetes, you must adhere to the standard table No. 9. It is this food that fully meets the requirements of the diet for coronary heart disease. In addition, by constantly adhering to this diet, you can forget about heart problems for a long time. Diet principles:
- nutrition must be complete;
- it is necessary to abstain from fast carbohydrates;
- animal fats should be excluded;
- food must follow a strict regime;
- constant monitoring of glucose levels;
- control cholesterol levels.
Nutrition is the starting point that can influence the course of the disease, reduce the risk of complications after a heart attack, or, conversely, increase it if the diet is not followed. Mortality after a heart attack largely depends on nutrition.
Prevention
Preventive measures will help slow down the progression of coronary heart disease. If you have diabetes, the first point in prevention is constant monitoring and correction of blood sugar levels. To avoid such serious consequences as a heart attack, it is also necessary:
- bring your diet back to normal, namely, switch to table No. 9;
- move more, walk, walk;
- quit smoking;
- treat arterial hypertension;
- drink enough fluid;
- control and regulate cholesterol and glucose levels;
- promptly treat concomitant diseases.
Treatment of myocardial infarction in diabetes mellitus should be carried out strictly in accordance with the doctor's instructions. Self-discipline and adequate treatment will help you avoid complications after a heart attack.