What is follicular bulbitis?
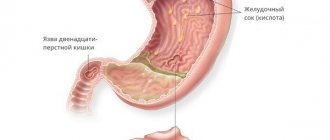
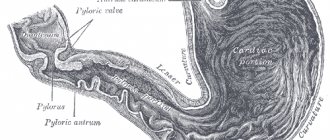
To understand the causes of follicular bulbitis, you need to know how the bulb (translated from Latin as bulb) - the initial part of the small intestine - is structured and how it functions. Anatomically, the bulbus - the initial section of the duodenum - has the appearance of a short swollen cylinder, truly reminiscent of an onion in shape.
The structure of the mucous membrane of the duodenum is characterized by special resistance to chemical irritants - it is an intermediate option, something between the structure of the gastric and intestinal mucosa, which have fundamental differences in function.
A feature of the structure of the bulb is the narrowing of its lumen at some distance from the entrance, straightening of the longitudinal folds when filled, and greater mobility (it is practically not secured by the ligamentous apparatus). This causes some temporary delay of part of the food bolus coming from the stomach.
The submucosa of the bulbus, like the entire duodenum (duodenum), is penetrated by numerous duodenal glands that produce alkaline mucus to neutralize gastric juice and protect the mucous membrane of the duodenum, and lymphatic capillaries. The excretory ability of duodenum has been poorly studied, since the secretion is difficult to isolate in its pure form, but its purpose is the chemical activation of digestive enzymes entering its lumen.
On one square millimeter of the surface of the mucous membrane of the bulbus there can be up to 100 stomata-exits of glandular elements, the so-called crypts - simply put, ducts through which intestinal secretions and mucus are released into the intestinal lumen, acting as a protective factor. A special structure of the intestinal wall is formed around each of the ducts, which, against the background of inflammation and swelling of the tissue, can become denser, blocking it. The mucous membrane is also densely intertwined with small nerve fibers and blood vessels.
A follicle is a formation in the form of a round, oval or pear-shaped vesicle with liquid contents. Its formation is caused by blockage of the gland - then the follicle is filled with accumulated alkaline secretion that does not receive release, or lymph, which can be supplemented with exudate - liquid secreted by inflamed tissues.
Diagnostic methods
The main diagnostic method used for suspected follicular bulbitis is fibrogastroduodenoscopy (FGDS). This method allows you to examine the mucous membrane of the duodenum and stomach, as well as select their contents for analysis. During diagnosis, additional studies may also be required:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- measuring the acidity of gastric juice with special devices.
After FGDS, a final diagnosis can be made. Ultrasound and other methods will be less informative, since they will not allow the doctor to visualize the intestinal mucosa from the side of its lumen.
Provoking factors
There are no specific causes of follicular bulbitis. Its etiology coincides with that which leads to any inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, and may have an indirect connection with disorders of the autonomic part of the central nervous system. The formation of follicles is an atypical, peculiar reaction of inflamed tissue, the result of complex biochemical reactions associated with dystrophic changes in its structure.
Follicular bulbitis occurs against the background of:
- long-term parasitic or bacterial infection, and above all Helicobacter pylori, but also occurs when the biliary or pancreatic tract is infected;
- smoking, dietary errors - systematic consumption of foods that stimulate acidity surges, long-term uncontrolled use of painkillers;
- gastritis or stomach ulcers;
- duodenal ulcers;
- intestinal lymphadenitis;
- neoplasms, including benign ones, in any part of the upper digestive tract (most likely the pylorus).
Note! Malignant formations localized in the mediastinum and inaccessible to the endoscopist can also become an indirect cause of follicular bulbitis. It is for this reason that in difficult cases, a fluoroscopic examination of the chest is performed.
Characteristic symptoms
The main symptom that indicates the development of inflammatory pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract is pain in the stomach and intestines. In this case, the pain will be localized in the epigastric region (projection of the stomach, upper abdominal wall).
Since diseases of the digestive system are often interrelated and appear in a complex, their symptoms may be similar. Patients with follicular bulbitis complain of characteristic changes:
- discomfort in the abdominal area, which intensifies after eating junk food;
- feeling of heaviness in the stomach, bloating, flatulence;
- indigestion, diarrhea or constipation;
- nausea, vomiting - may occur after eating or not be associated with food intake.
It is impossible to carry out a complete diagnosis without using special tools. The clinical picture of follicular bulbitis indicates inflammatory changes in the gastrointestinal tract, but cannot determine their location, cause and severity.
However, it is important to make an accurate diagnosis in time, otherwise the disease will progress. The follicles open up, and in their place erosions form that do not heal for a long time. The next stage of this disease, if treatment is not started, is a stomach and intestinal ulcer.
Symptoms of follicular bulbitis
The bulbus adjacent to the stomach is the receptacle of the food bolus and has a constant reflex connection with the stomach, therefore all imperfections of gastric digestion inevitably disrupt the physiological processes inside the duodenum.
The symptoms of follicular bulbitis are very individual and depend on the form of the disease. But bulbitis, unlike polyposis, is rarely asymptomatic and inevitably affects the level of secretion of bile and pancreatic juice, causing symptoms of both cholecystitis and pancreatitis.
As a rule, pain is localized at the site of projection of the inflammatory focus onto the abdominal wall and occurs 1.5-2 hours after eating.
Important! Night pain is an alarming symptom, a kind of red flag signaling a dangerous development of the condition.
Types of disease
There are several classifications of bulbite. According to the intensity of the inflammatory process, they are distinguished:
- Acute - develops against the background of severe inflammation, food poisoning or intestinal infection. Accompanied by nausea, vomiting, severe pain just above the navel, which intensifies with pressure. The temperature may rise, the patient may experience general malaise, headache and dizziness. The first thing to do in case of acute bulbitis is to refuse food for a day and consult a doctor. Depending on the cause of the disease, treatment is prescribed. In the following days, you should eat exclusively pureed food.
- Chronic occurs when acute bulbitis is not treated, mistaking it for ordinary poisoning. Another cause of chronic bulbitis is existing gastroduodenitis: in this case, the disease becomes chronic, bypassing the acute stage.
The classification of bulbitis according to the degree of damage to the mucous membrane is presented in the table.
| Name | Characteristics |
| Superficial mild or moderate bulbitis | Captures the topmost layer of mucous membrane. This is a mild form, in which, even with minimal treatment, complete recovery is possible without consequences, since the mucous membrane is regularly renewed. The disease often has no obvious symptoms. |
| Catarrhal | It affects deeper layers, often occurs acutely, and is accompanied by severe pain in the abdomen, especially in the upper part. The temperature rises, nausea and vomiting occur. The chronic form of catarrhal bulbitis is characterized by “hunger” pains that occur 2-3 hours after eating and at night. Based on its symptoms, it can easily be confused with a peptic ulcer, so a detailed diagnosis is required. Often catarrhal disease is of a bacterial nature (the chronic form occurs due to the presence of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach). In this case, the inflammatory process is moderate, and the patient is occasionally bothered by digestive disorders. Periods of remission can be long, exacerbations are caused by intestinal infections, consumption of fatty and fried foods, rough foods, and alcohol. The treatment is long-term. |
| Ulcerative, erosive | Ulcerative or erosive symptoms and manifestations are the same as peptic ulcers. In most cases, it is accompanied by increased acidity of gastric juice, which is thrown into the duodenum and irritates its walls. As a result, wounds form on it (superficial - erosions and deeper - ulcers). The acute form is accompanied by bleeding wounds, and vomiting with blood often occurs. Such a bulbitis is dangerous due to serious bleeding and the development of peptic ulcers. |
| Follicular (granular), or lymphoid hyperplasia of the duodenal bulb | The cause of the disease is an excessive reaction of lymphoid tissue to irritants, its proliferation. When diagnosed using a video gastroscope, you can notice a bumpy surface, the presence of numerous tubercles with a diameter of 2-4 mm on the mucous membrane. |
| Atrophic bulbitis | Appears after several years of the disease, when the blood supply and nutrition of the mucous membrane are impaired. As a result, it becomes thinner, becomes gray in color, and blood vessels are visible through it. |
| Hemorrhagic | Accompanied by the presence of areas of hemorrhage on the mucous membrane. Occurs when blood vessels are damaged as a result of inflammation. |
| Erythrematous | This form is characterized by the presence of oval red spots on the mucous membrane, which then transform into bleeding ulcers. Erythrematous bulbopathy occurs in the presence of infection or as a side effect of certain medications, as well as the use of toxic substances. |
| Hypertrophic | With prolonged inflammation, the walls of the bulb thicken and folds form on them. |
Another article on this topic: Why does my stomach growl after eating? Causes and treatment
According to the area covered, the bulbit is:
- Focal - occurs only in a separate area of the bulb, does not spread to the entire duodenum;
- Diffuse, which is characterized by the presence of several foci of inflammation.
Forms of follicular bulbitis
The formation of follicles indirectly indicates the long-term nature of the inflammation, which has not been subjected to adequate therapy.
The acute form of bulbitis necessarily indicates severe pain in the pit of the stomach or in the right hypochondrium, nausea and repeated vomiting. The acute form can be caused by food poisoning or certain medications, and can lead to rupture of the follicle, which carries the risk of bleeding or infection of the resulting wound.
In the chronic form of the disease and the small size of the follicles (up to 3 mm), nausea is episodic, and the pain is aching, not severe, and people endure it for years.
Diagnostics
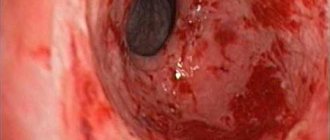
During an endoscopic examination, on a smooth, juicy pink mucosa, in addition to clearly defined vessels, multiple formations in the form of follicles, localized in the area of foci of inflammation, are usually visualized. Sometimes they have the appearance of a rash similar to acne.
Follicles must be differentiated from polyps, lipomas, fibroids and other formations in the initial stage. To do this, directly during endoscopy, a microscopic piece of tissue is taken and then its cytological examination is performed in order to identify - exclude (or confirm) - an oncological disease.
General information about the disease
When talking about gastric bulbitis, we mean an inflammatory process not in the organ itself, but in the initial part of the human small intestine, in the duodenal bulb. It is this section that receives the acidic contents of the stomach and is also a connecting link to the gallbladder duct. And here the active phase of intestinal digestion begins.
Bulbit is one of the types of duodenitis, an inflammatory process in the duodenal mucosa. In this respect, the disease is similar to papillitis and diverticulitis. Often bulbitis is accompanied by antral gastritis (inflammation of the gastric mucosa) and has symptoms similar to this pathology.
Follicular bulbitis in children
In children, the development of gastroduodenitis in general and bulbitis in particular never occurs out of the blue, and usually occurs in an acute form. It can be facilitated by stressful situations, which are often associated with very dangerous infectious diseases, and by taking certain medications. If the pain syndrome in a child lasts for several months, even once a week or even a month, it means that inflammatory changes have fully developed and a visit to the doctor has become a necessity. To make a diagnosis, the mother needs to decide:
- when the pain intensifies, has it become seasonal;
- how the pain is related to the time of day (an important diagnostic sign is morning, so-called “fasting” pain).
Note! Association with food is a characteristic sign of intestinal pain. They intensify precisely after, and not during, eating: while the food is in the stomach, enzymes secreted in parallel irritate the inflamed surface of the bulbus, which has not yet been filled with it.
The infectious agent cannot be discounted - after 5-6 years of age, acid formation increases in children, therefore, under certain circumstances, there is a possibility of developing bulbitis associated with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
In older children, starting from about 10 years old, alcohol and smoking are often additional irritating factors. In the therapy of bulbitis, the psycho-emotional background of the family and the friendly atmosphere around the child are extremely important.
Currently, the diagnosis of bulbitis does not involve an unambiguous endoscopic examination (unless there are special indications for this), which scares away children, and even more so, their parents. To determine the population, a urease breath test or a test of DNA residues in stool is promptly performed.
Treatment
This disease has several treatment methods - from a special diet for bulbitis to surgery. The basis of treatment for bulbitis is the elimination of the pathogen using anti-Helicobacter antibiotics, and if the structure of the mucous membrane is damaged, medications are prescribed that accelerate healing and increase the formation of mucus.
Surgical intervention is used only when the patient experiences bleeding and the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. This method of treating bulbitis will help reduce the effect of stomach acid on the duodenum by cutting certain nerves and stitching the ulcers. Only treatment of catarrhal bulbitis is sometimes carried out at home.
Great importance in the treatment of bulbitis is given to a special diet, which is based on avoiding the use of:
- fatty and salty foods;
- hot spices;
- products containing coarse fiber;
- coffee drinks;
- preserves and pickles.
The diet for bulbitis includes taking:
- only boiled foods, steamed and oven-cooked foods without the use of oil;
- first courses cooked in low-fat or vegetable broth;
- lean varieties of meat and fish;
- fruits and vegetables;
- fruit drinks and compotes;
- not solid food, i.e. ground or pureed.
It is very important to eat often, five times a day, but in small portions.
Treatment methods
Treatment methods for follicular bulbitis depend on the condition of the mucous membranes of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, the number and quality of follicles, the composition of the exudate, if any, the level of acidity, the age of the patient and a history of diseases. The treatment regimen for helminth infection undoubtedly differs from that which will be used for secondary duodenitis associated with cancer.
According to indications, follicles that are resistant to conservative treatment are removed using a minimally invasive method using an endoscopic probe. But in complicated cases, abdominal operations are also performed.
Drug therapy
Conservative treatment is aimed at relieving inflammation as the main cause of the follicular form of bulbitis, restoring normal tissue metabolism and relieving edema. According to indications, the following drugs are prescribed:
- antibacterial - to suppress Helicobacter pylori, which sharply reduces local immunity;
- antisecretory - so-called proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which correct acidity levels;
- so-called myotropic antispasmodics, or prokinetics (to eliminate functional disorders of the digestive tract);
- enveloping agents - to protect and accelerate epithelization of the mucosa.
The duration of treatment for uncomplicated inflammatory diseases of the duodenum is determined by the doctor - as a rule, they range from 4 to 6 weeks. Depending on the type of vegetative manifestations, sedatives are prescribed.
Traditional medicine recipes
The choice of the correct treatment in each specific situation belongs exclusively to the doctor after histological and a number of other examinations. Not a single herbal remedy can provide a comprehensive and integrated approach to traditional therapy, therefore folk remedies in the treatment of follicular bulbitis are assigned only a supporting role.
It is important to understand that taking herbal infusions against the background of persistent abdominal pain is a crime against one’s own body.
Therapeutic diet
Diet is an equal tool of therapy and depends on the form and stage of the disease. The main principle is to consume food that will not harm the mucous membrane dotted with follicles:
- does not contain coarse plant fibers, dyes and preservatives;
- having a viscous consistency and a temperature close to body temperature;
- does not cause acidity surges.
When organizing a dietary table, you need to understand what exactly is intended for consumption - how and under what conditions the food is prepared. It is necessary to avoid discomfort both from the quantity of food eaten - observe the measure, and from its quality - avoid canned, smoked and semi-finished products.
Bulbitis: how and how to treat it?
The duration of treatment depends on the cause and extent of the disease. Bulbitis, which arises as a consequence of food poisoning, can be cured in a couple of weeks with a diet and taking antibacterial drugs. It takes a long time to treat Helicobacter-associated pylori, which appears as a complication of gastritis and duodenitis, while therapy for the underlying disease is necessary.
Diet
Gastritis, bulbitis, duodenitis are diseases whose treatment begins with a strict diet.
Proper and rational gentle nutrition can speed up recovery. Acute bulbogastropathy requires daily fasting followed by consumption of processed pureed foods. The chronic form, especially with mild symptoms, does not require such radical restrictions: table No. 5 is recommended - the classic diet for most gastrointestinal diseases.
A strict diet is prescribed for a period of several weeks to six months to allow the mucous membrane to recover. Subatrophic bulbitis and other complex forms require a longer diet.
Even after complete recovery, the patient will have to adhere to certain dietary rules: eat often and in small portions, exclude spicy, sour, fried, fatty and alcoholic foods. This will help avoid recurrence of bulbitis and its transition to more complex and dangerous types.
Products during the treatment period should be light, meals – 5-6 times a day. You cannot fast for more than 3 hours (with the exception of night sleep). All food should be processed, especially vegetables and fruits. Flour, baked goods, and any types of bread must be excluded.
More precise dietary recommendations are formed by the attending physician, taking into account the patient’s condition and accompanying diagnoses. Liquid food, which is usually recommended for bulbitis, can provoke impaired intestinal motility if there are already disturbances in its functioning. In this case, the doctor will recommend products that stimulate peristalsis, but do not irritate the mucous membrane.
Drug treatment
In the acute form of the disease, intestinal antibacterial agents and droppers with saline are used. Sometimes before this a thorough lavage of the stomach and intestines is required if the cause of the bulbitis is food poisoning. Next, painkillers and antacids are used.
There is no single cure for bulbitis: in each case, specific therapy is prescribed. A mixed diagnosis requires an integrated approach, simultaneous treatment of all pathologies of the digestive system.
Another article on this topic: What are the causes of gastritis of the stomach in adults? Diagnosis and symptoms
Helicobacter-associated infection requires a special approach. Such patients are prescribed a minimum of 2, and for stable chronic conditions. forms - 3 types of antibiotics, plus antacids and H2-histamine receptor blockers (to reduce swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane).
Additionally, depending on the form of the disease, the following may be prescribed:
- anthelmintics;
- immunostimulating (indication – follicular bulbostasis);
- hormonal drugs (in the presence of Crohn's disease that affects the intestinal gastrointestinal tract);
- wound healing and enveloping (for the treatment of erosive bulbitis);
- sedatives if increased nervousness and stress have led to the onset or exacerbation of the disease.
Traditional methods
The use of herbal decoctions can relieve inflammation, normalize acidity, and stimulate the healing of the mucous membrane.
But it is advisable not to make do with them exclusively, but to supplement traditional treatment with folk remedies. Plantain juice stops bleeding and heals ulcers. It is used in combination with honey in the proportion of 45 ml of juice per 1 tsp. honey This is the daily dosage. Should be taken on an empty stomach, half an hour before meals, 3 times. Drink for 2 weeks, then take a 10-day break.
2 tablespoons of St. John's wort herb are poured into a glass of boiling water, infused, the portion is divided into 4 doses and drunk a day, half an hour before meals. This method is effective for catarrhal and superficial bulbitis. Instead of St. John's wort, you can use chamomile and yarrow.
In acute cases of the disease, you need to be careful with juices: they cause increased acid formation. But carrot juice is safe and even healthy. You need to drink freshly squeezed, 40 ml half an hour before meals three times a day.
Prognosis and prevention
To understand what can be the prevention of follicular bulbitis, you need to pay attention to the list of its causes. Their elimination is the main task for those individuals who are predisposed to the formation of foci of inflammation in the intestines or in whom they have been detected at least once. Therefore, putting aside the importance of adequate nutrition, it is necessary:
- be careful when choosing painkillers;
- know that any thermal procedures for pain are strictly prohibited;
- strictly follow the schedule of medical examinations drawn up by the doctor.
Regular use of PPIs is recommended for those who are at risk of developing bulbitis. Among the terrible complications of follicular bulbitis are a breakthrough of the intestinal wall, fraught with the development of peritonitis, the formation of multiple small ulcerations in the areas of ruptured follicles, scarring with irreversible loss of intestinal function in its large areas.
Strong immunity is a complex concept that consists of many components, and above all a healthy lifestyle - balanced nutrition, taking vitamins, observing a work and rest regime. They must be put at the service of their health.
Follicular bulbitis attracts the close attention of doctors because, with a high degree of probability, it can become a prerequisite for uncontrolled local growth of tissue during its regeneration. Therefore, medical support for the disease is a vital necessity.