Clinical picture
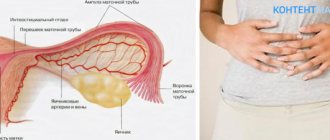
Salpingitis can be acute, subacute and chronic. Usually the disease begins acutely, accompanied by severe pain, fever, and severe symptoms of intoxication. The infection can penetrate the fallopian tubes either ascending or hematogenously. Sometimes the disease occurs as a result of an inflammatory process in the abdominal cavity (appendicitis).
Damage to the mucous membrane causes purulent inflammation, and this can lead to further spread of the infectious process into the urinary system and abdominal cavity. The tube becomes swollen, hyperemic, and the formation of connective tissue fibers increases in it, so even with the treatment of salpingitis, adhesions may form in the tube itself or in the abdominal cavity.
In case of complications, the fallopian tube is removed, and in case of a bilateral process, which more often occurs against the background of a specific infection, removal of both tubes leads to infertility. Since salpingitis is often accompanied by inflammation of the ovaries, this sharply reduces a woman’s ability to have children, even when using modern methods such as in vitro fertilization. Therefore, it is important to use preventive measures and treat the disease in a timely manner.
Salpingitis and oophoritis: what is it?
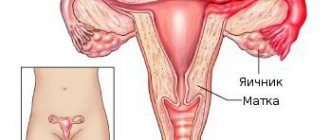
The history of the diseases salpingitis, which in translation means (salpingos “tube”) and oophoritis (oophoron “ovary”) goes back to the Middle Ages, when the fallopian tubes were first discovered and described. These are one of the few gynecological ailments that are common to humans and animals with similar anatomy.
In women, salpingitis and oophoritis appear after various bacteria and cocci begin to enter the tubes, and a little later, into the ovaries. You need to understand that cocci, like E. coli, leak out of the uterus in an ascending way, and mycobacterium tuberculosis is spread precisely by the blood that passes through the lungs and other organs.
In the event that acute inflammation develops, the entire epithelial cover of the tubes is disrupted, so microorganisms uncharacteristic for them leak inside, which leads to soldering with the ovaries into one integral formation. The disease is accompanied by recurring painful sensations in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar region, accompanied by spasms before defecation, leading to the failure of menstruation or its cessation.
Often women turn to the Internet for help, read forums, look at Wikipedia, trying to determine a diagnosis. The consequences of self-medication with folk remedies and pills that helped the neighbor are catastrophic. Lack of competent prescriptions can lead to hydrosalpinx, purulent complications, and, as a result, the inability to get pregnant.
Salpingitis and oophoritis can develop into a chronic form of inflammation of the appendages - Adnexitis or Salpingoophoritis, in which their symptoms appear and the necessary treatment is carried out: this.
Causes
The causes of salpingitis are specific and nonspecific infections. Of the specific lesions, gonorrheal and chlamydial salpingitis are often observed, and sometimes an inflammatory process occurs against the background of tuberculosis.
Nonspecific inflammation can be associated with opportunistic microorganisms that normally live in the human intestine, on the skin and mucous membranes. Their aggressiveness is due to decreased immunity, damage to barrier functions, hypothermia and other factors.
Thus, the causes of salpingitis are as follows:
- surgical gynecological interventions, curettage, intrapartum infection;
- infectious diseases of the genitourinary tract;
- decreased general immunity;
- hypothermia;
- infectious chronic diseases (tuberculosis);
- pathologies of development and diseases of the genital organs (prolapse of the uterus);
- overwork, stress, depression;
- bad habits;
- eating disorders;
- hormonal disorders.
Symptoms of acute salpingitis
Most often, they are clearly expressed and do not present any difficulties for diagnosis. True, upon a superficial examination they can be confused with manifestations of acute poisoning or the same appendicitis, so when talking with a doctor, try to remember everything that bothers you in one way or another.
- An unprovoked increase in temperature to 37.5–39 degrees, accompanied by weakness, chills, malaise and increased heartbeat. By the way, it is believed that each “additional” degree increases the heart rate (heart rate) by 7–10 beats per minute.
- Severe pain in the groin area.
- Obvious signs of damage to the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system. The reason for this “promiscuity” of salpingitis is that the development of the inflammatory process leads to enlargement and swelling of the fallopian tubes, which because of this begin to put pressure on the surrounding tissues, and the resulting pain begins to radiate to the rectum and tailbone.
- Abnormal vaginal discharge (purulent, foamy, or even bloody, depending on the type of pathogen).
Symptoms
Symptoms of salpingitis can be pronounced in acute cases, and almost absent in chronic cases. Patients with salpingitis note:
- pain that can occur suddenly, be strong, sharp;
- pain and burning when urinating;
- discharge is mucous or purulent, dirty white;
- pain during sex;
- discomfort;
- symptoms of intoxication (fever with chills, weakness, myalgia, lack of appetite);
- symptoms of irritation of the peritoneum and intestines (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bloating).
With subacute salpingitis, the symptoms are mild, most often discomfort in the genital area is determined, the temperature can be low-grade, while with acute salpingitis it rises to 38-40 degrees Celsius.
Symptoms of right-sided salpingitis
Due to some features of the anatomical structure of a woman, it can be easily confused with ovarian apoplexy or appendicitis, and the existing signs of the disease are associated with damage to muscle tissue, swelling and the formation of adhesions. In other words, it is almost impossible to determine the presence of right-sided salpingitis based only on external manifestations.
Complications
Complications of salpingitis occur in both acute and chronic cases. In the acute form, purulent complications are more common, such as:
- pelvioperitonitis;
- pyosalpinx;
- diffuse peritonitis;
- cystitis;
- urethritis;
- salpingo-oophoritis;
- sepsis.
The chronic course of the disease leads to infertility, adhesions in the abdominal cavity, and the formation of infiltrates in the pelvis. The adhesive process can cause disorders of the digestive system (constipation, acute intestinal obstruction).
Consequences
- The infection spreads to neighboring pelvic organs: ovaries, peritoneum, uterus.
- Adhesive process in the pelvis. Adhesions form both in the fallopian tubes and between neighboring organs - the uterus, bladder, and large intestine. Obstruction leads to chronic pain. May be complicated by infertility.
- Melting of abscesses and phlegmons formed between the tubes and ovaries. Peritonitis is possible.
- Ectopic pregnancies, miscarriages, disruption of intrauterine development of the child.
- Menstrual cycle disorder, discomfort during sexual intercourse.
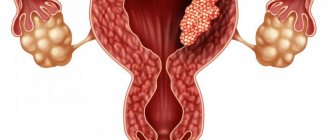
- Malignant neoplasm. Chronic inflammation is dangerous for the development of cancer cells. If a patient with diagnosed salpingitis loses weight, weakness and fatigue appear, the development of an oncological process can be suspected.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of salpingitis can present certain difficulties in its chronic course. In addition to collecting anamnesis, the doctor examines the patient, during which it is sometimes possible to palpate a dense, painful cord between the uterus and ovary. Laboratory tests are also prescribed to determine the general condition of the patient (intoxication), as well as examinations to identify the causative agent of the disease. This can be a smear from the vagina or urethra, PCR, ELISA.
Puncture of the posterior vaginal fornix helps determine the presence of inflammatory, purulent exudate in the pouch of Douglas. Instrumental research methods are also used:
- ultrasonography;
- hysterosalpingography;
- diagnostic laparoscopy;
- X-ray examination;
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
Diagnosis of salpingitis
Diagnostics consists of detecting immobile, painful tumors of varying consistency. For the correct diagnosis of salpingitis, determining the probable infectious diseases of a woman is of utmost importance. So, for example, salpingitis diagnosed in a young girl is most likely of tuberculosis origin, and salpingitis in a married nulliparous woman signals a gonorrheal infection. The presence of infection is determined by laboratory tests of uterine secretions.
Pain syndrome during salpingitis is often confused with an attack of appendicitis due to the similarity of the nature of the pain. However, salpingitis gives pain located in the deeper parts of the pelvis. The disease is often diagnosed in combination with an ectopic pregnancy. Confirmed diagnosis Salpingitis is a disease unfavorable in terms of cure. Most often, the disease has the ability to remind itself throughout the entire period of functioning of the female reproductive system. In medical practice, cases of death of patients from peritonitis caused by an advanced form of acute salpingitis have been described. Curing the disease in order to completely functionally restore the patency of the fallopian tubes to achieve the pregnancy desired by the patient occurs in very rare cases.
Treatment
Treatment of salpingitis should begin as early as possible; both conservative and surgical methods are used. In the acute phase of the disease it is required:
- bed rest;
- cold on the stomach;
- antibiotic therapy;
- diet therapy;
- vitamin therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- balneotherapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- paraffin therapy;
- electrical stimulation;
- immunomodulators.
In severe cases, they resort to drainage and lavage of the posterior vaginal vault and infusion therapy. In case of complications, surgical treatment is indicated. Surgery for salpingitis can be performed by laparoscopy or laparotomy. Typically, the affected tube is removed and the abdominal cavity is drained.
Treatment of salpingitis
Treatment of salpingitis is prescribed by a gynecologist based on diagnostic data, the cause of infection and the stage of inflammation.
The acute form of the disease requires hospitalization with constant monitoring of the patient and ensuring rest, as well as the use (in the first days) of ice on the stomach, painkillers, antibiotics, calcium chloride and sulfonamides.
If the disease was detected at a subacute stage, then physiotherapeutic treatment of salpingitis (quartz, for example) is indicated.
Chronic salpingitis requires all types of balneotherapy and physiotherapy. In case of relapses, the use of antibiotics and sulfonamides is not indicated, since the exacerbation is not due to the activation of autoinfection or reinfection.
If conservative treatment of salpingitis is ineffective, surgical intervention is resorted to. In this case, the patient goes through several stages:
- Preoperative preparatory;
- An operation during which purulent exudate is evacuated and the lesion site is sanitized;
- Comprehensive postoperative rehabilitation.
At the first stage, it is necessary to relieve acute symptoms of inflammation, suppress the aggression of pathogenic microorganisms and correct metabolic disorders. It is very important to select antibacterial drugs and products that will restore the affected microflora.
Surgical intervention occurs in one of the following ways:
- laparoscopy;
- puncture of the uterorectal recess through the posterior vaginal fornix;
- sanitation and transvaginal aspiration and lavage drainage of the pelvis;
- adhesiolysis.
With timely treatment of the disease, the prognosis is positive.
Prevention
Prevention of salpingitis includes measures to prevent infection and general strengthening methods, it is necessary:
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- avoid promiscuous relationships;
- use barrier contraception (condom);
- carry out full treatment after surgical and gynecological interventions;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- eliminate bad habits;
- increase the overall immunity of the body;
- exercise;
- establish proper nutrition;
- don't get too cold.
An important role in prevention is played by sexual education of adolescents, informing them about the danger of diseases such as salpingitis, leading to infertility.
Symptoms of purulent salpingitis
- Acute pain localized in the lower abdomen (left and right groin areas), which migrates over time to the lower back and rectum.
- “Cold” effects, which, as you understand, have nothing to do with acute respiratory infections or acute respiratory viral infections (slight increase in temperature, chills).
- Purulent vaginal discharge.
- Author: Evgenia
Hello, dear readers of our site! My name is Evgenia. I write articles for this site with the hope that my knowledge and experience will help people. I grew up in a family of doctors. I met my husband while a student at a state medical institute, so medical issues are discussed in our family to this day. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(1 vote, average: 5 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
When to go to the gynecologist: main reasons
Postpartum depression: basic treatment techniques