During the period of bearing a child, a woman may face various difficulties. About half of all expectant mothers are concerned about the pubic symphysis. Unpleasant sensations can appear both at the very beginning of the term and closer to childbirth. This article will tell you what symphysis pubis dehiscence is during pregnancy. You will learn the characteristics of the pathology and how to diagnose it.
What it is
The pubic symphysis is the so-called area that connects the lateral bones of the woman’s pelvis. It is worth noting that this area is also present in the male body. The pubic symphysis is attached to the bones by ligaments. Their stretch usually does not exceed five millimeters.
The described area is located above the penis in men and on top of the clitoris in women. Outwardly, it resembles a trapezoid, inverted with the smaller base down. The symphysis, or symphysis pubis, has the structure of a cartilaginous disc. It can move freely under the influence of certain factors.
Prevention of symphysitis during pregnancy
It should be noted that symphysitis can develop not only during pregnancy. However, it is more often observed in expectant mothers. Due to the softening of the dense connective tissue that closes the bones, a divergence of the symphysis pubis occurs. If it is not very pronounced, there should be no cause for concern. In this case, only observation and limitation of loads is indicated. If there is severe divergence of the symphysis pubis, hospitalization is necessary.
There are several reasons why there is a distance between the pelvic bones. Among them:
- Heredity. Women whose mothers suffered symphysitis during pregnancy are more susceptible to this pathology.
- Insufficient consumption of foods containing calcium. As you know, this element strengthens bone tissue. During pregnancy, calcium becomes less, as the level of female sex hormones - estrogen - decreases.
- Vitamin D deficiency. This substance promotes the absorption of calcium, so it must be present in the body. The production of the vitamin is promoted by exposure to the sun.
- Kidney diseases. When urinary function is impaired, calcium in the body becomes less, which leads to softening of bone tissue.
Disjunction of the symphysis pubis during pregnancy is more often diagnosed in women with a history of multiple births. In this case, the body does not have time to restore strength. There is a long-term lack of estrogen, leading to “washing out” of calcium from the bones. Due to frequent childbirth, the weakness of the symphysis gradually increases. As a result, divergence of the pubic bones occurs.
Risk factors include pelvic injuries and physical inactivity. If the pubic bones have been damaged previously, then the likelihood of their divergence during pregnancy increases several times. Symphysitis is more often observed in women who lead a sedentary lifestyle. In this case, the ligaments and muscles of the pelvis do not stretch properly.
Bone separation and inflammation of the pubic symphysis in non-pregnant women can occur due to injury and physical stress. Risk factors include strenuous sports.
Disjunction of the pubic symphysis and its inflammation develops in 20% of pregnant women. In most cases, a mild degree of pathology is observed. Despite the fact that bone separation and symphysitis do not lead to serious consequences, the woman experiences discomfort. Painful sensations affect the emotional state of the pregnant woman. To avoid the development of symphysitis and divergence of the pubic bones, it is necessary to follow preventive measures. These include:
- Dieting. Nutrition during pregnancy should be balanced. Nutrients enter not only the body of the expectant mother, but also the child. It is recommended to consume foods containing sufficient amounts of protein, vitamins and minerals, in particular calcium and magnesium.
- Wearing a bandage. Fixation of the pelvic bones prevents the divergence of the symphysis.
- Gymnastics for pregnant women.
- Walks in the open air.
- Avoid physical activity and sudden movements.
- Swimming.
The appearance of pain in the area of the pubic symphysis is a reason to consult a doctor. To make sure that there is no discrepancy of the bones, it is enough to perform an ultrasound examination. This diagnostic method is safe for pregnant women.
In addition to the fact that the pelvis serves as a support for the female internal organs, it must also ensure the safe passage of the baby through the birth canal during childbirth. Normally, in patients, the symphysis pubis is dense and motionless, the pelvic bones are connected, and the joints do not change their position. For the baby to safely pass through the birth canal, the bones must move slightly apart.
In the body of a pregnant woman, there is an increased production of the hormone relaxin, the action of which is aimed at relaxing and softening connective tissue. The concentration of the hormone begins to increase from the 10th week, and decreases only 4–10 weeks after the birth of the child.
Thanks to the production of relaxin, the cartilage between the pubic bones and joints becomes loose and, as a result, stretches to the desired size. New gaps filled with fluid form in the joints, which increases their mobility, and the pelvic bones begin to “walk.” In addition, the bladder, slightly displaced by the enlarged uterus, puts pressure on the symphysis.
Prevention of symphysitis and other complications during pregnancy should begin at the planning stage.
A woman who plans to become a mother, safely carry and give birth to a healthy child, is recommended to:
- monitor your diet - eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals;
- do not neglect taking “women’s” vitamins;
- to walk alot;
- do yoga, aerobics, Pilates;
- pay great attention to strengthening the muscles of the back, abdomen and vagina (Kegel exercises);
- control weight gain;
- detect and treat diseases in a timely manner.
Unfortunately, it is impossible to prevent symphysiopathy 100%. Doctors still do not know the exact factors that provoke the disease in almost half of pregnant women. A woman with a baby under her heart should be very careful about her health. If her health worsens, she should immediately seek qualified medical help.
The structure of the pubic symphysis in men and women is practically no different. Essentially, this area is the place of articulation of the pelvic bones, which are present in humans regardless of gender differences. Fusion of bone structures is ensured by a cartilaginous disk of fibrous structure. There is liquid inside the cavity. The pubic symphysis is a low-moving joint. Doctors often diagnose inflammatory and degenerative processes.
The joint has a tight fixation provided by the ligamentous apparatus. In the male body, the penis is attached to this bone formation. In the normal position of the symphysis, its divergence can be up to 10 mm. However, for medical reasons, you should stick to 5 mm, and anything higher is already approaching a deviation.
Divergence of the pubic symphysis
Most often, in normal conditions, this area of the body does not bother men and women. However, during pregnancy, everything can change. Thus, about fifty percent of the fairer sex who are in an interesting position are faced with the fact that a severe sprain occurs. In this case, we are talking about the divergence of the pubic symphysis.
If there is a slight deviation from the norm, no correction is required. However, a strong increase in the clearance between the pubic symphysis and the pelvic bones leads to unpleasant symptoms. In especially severe cases, a woman is forced to seek help from doctors.
Causes of pubic bone problems
The pubic area in the female body quite often experiences shocks of a pathological nature. This provokes problematic conditions during labor and after the birth of the child.
The main causes of the pathological condition are:
- hereditary factor. Women are most susceptible to the development of symphysitis and rupture of the symphysis pubis if their mothers had a similar problem;
- hypocalcemia (a disturbance of the electrophysiological process caused by low levels of calcium in the body). During pregnancy, most of the calcium is used to build the bone structures of the fetus. Lack of calcium together with hormonal changes lead to the development of pathology;
- lack of vitamin D. The most characteristic symptom for pregnant women who bear a child in the autumn-winter period. The lack of ultraviolet radiation entering the body with sunlight is a provocateur of a weak pubic symphysis;
- diseases of the endocrine system. Endocrine disorders provoke excessive excretion of calcium with biological fluid, this contributes to increased softening of the pubic symphysis.
Particularly pronounced health problems arise when several of the listed factors are present, leading to problems with the symphysis pubis.
Diagnosis of pathology
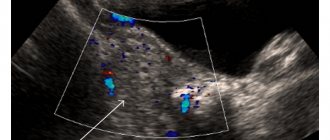
To determine the condition of a pregnant woman and the complexity of the situation, it is necessary to perform an ultrasound of the pubic symphysis. You can also examine the above-mentioned area using x-rays. However, during the period of bearing a baby, they try not to use this method. There are several stages of pathology.
- First degree of discrepancy. In this case, the symptoms are not clearly expressed. The clearance between the pelvic bones and the pubic symphysis is no more than nine millimeters. Often, expectant mothers have exactly this form of articulation divergence.
- Second stage. At this stage, the length of the ligaments stretches to two centimeters. At the same time, the woman already feels quite a lot of unpleasant symptoms. Doctors advise that it is with the second degree of discrepancy that you seek help.
- Third degree. When the bones move away from the pelvic base by more than two centimeters, we are talking about the third stage of the pathology. It is worth noting that the symptoms in this case become very pronounced. Sometimes a woman simply cannot move normally.
In addition to the information obtained through ultrasound or x-rays, the doctor must take into account the patient’s complaints. Sometimes it happens that the symptoms are very pronounced, while the discrepancy does not exceed one centimeter.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of symphysitis during pregnancy is somewhat complicated, due to the impossibility of using common methods, which include, for example, radiography. How exactly to determine symphysitis during pregnancy is decided by the doctor. As a rule, to make a primary diagnosis, it is necessary to study the clinical picture, the patient’s medical history, as well as a physical examination of the inflamed area.
Ultrasound
The only method for diagnosing symphysitis approved for use during pregnancy is ultrasound examination. Carrying out this procedure makes it possible to determine the presence of pathology, the area of localization of the inflamed area, as well as the size of the divergence of the bones of the symphysis pubis. Despite the relative safety of this method, it is still not recommended to use it too often.
X-ray of the pelvic bones
X-ray of the pelvic bones is a measure that is unacceptable for use during pregnancy. Carrying out such a procedure is allowed only if there are health reasons.
CT and MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are also not recommended during pregnancy. Exceptions are allowed only if there are vital indications. It should be noted that the above methods have maximum accuracy in making a diagnosis.
Symptoms of divergence of the symphysis pubis
Rupture of the pubic symphysis is always accompanied by unbearable pain. When such a complication develops, a person simply cannot move independently. However, among the symptoms of the onset of pathology (discrepancy), the following sensations can be identified:
- strong lumbago in the pubic area, radiating to the groin and lower part of the peritoneum (sometimes the lower back and upper thighs are involved in the process);
- inability to perform simple movements (climbing stairs, walking, getting out of bed, etc.);
- an audible sensation of a click when moving (intensifies when raising the leg up);
- premature abdominal prolapse;
- pain on palpation of the pubic area and during sexual intercourse.
As noted above, during pregnancy a woman may notice premature prolapse of the abdomen. This is explained by the fact that the bones move apart, and the baby begins to gradually move into the pelvic cavity.
Symptoms
Typically, early symptoms of symphysitis occur at the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy. A more complete picture of the pathology appears during the third trimester. Signs of symphysitis include:
- The appearance of tissue swelling in the area of the pubic symphysis.
- Heaviness in the lower abdomen.
- Pain that occurs when raising the leg straightened at the knee.
The main and especially unpleasant manifestation of symphysitis during pregnancy is pain. In the early stages of pathology, pain appears only when walking quickly or, for example, when lifting weights. As the weight of the fetus increases and pressure on the tissues of the joint increases, pain may appear even while maintaining a passive position.
Why is this happening
What can cause the pubic symphysis to diverge during pregnancy? Doctors talk about several reasons for the development of this condition. All of them can be divided into conditions that developed directly as a result of pregnancy, as well as pathologies that the expectant mother had previously.
The main reason for the discrepancy of the symphysis pubis is considered to be hormonal changes. Immediately after fertilization and implantation of the cell into the uterine cavity, active production of progesterone begins. This hormone is necessary for the normal development of the embryo. It has a relaxing effect on the uterus, preventing it from contracting. A similar effect is achieved in other organs and ligaments. Since the pubic symphysis is attached to the pelvic bones by ligaments, they can stretch.
Another reason for the development of pathology may be a lack of vitamins. The main deficient substance is calcium. A large amount of this component is necessary for the formation of the fetus. However, if the expectant mother does not eat properly or does not take vitamin complexes, the fetus begins to take calcium from her body. The bones, teeth, nails and hair are primarily affected.
Vitamin D deficiency may also play a large role. If a woman in an interesting situation receives the required amount of calcium, but there is not enough vitamin D in her body, then the substance is simply not absorbed. The consequence of this is poor condition of teeth, fragility of nails and bones, including the pubic symphysis.
The symphysis pubis: where it is located, how its discrepancy and rupture are treated
The largest bone in the human body is the pelvis. It consists of several smaller bones tightly fused together: the ilium, ischium and pubis. At the point of convergence of the pubic bones, the symphysis pubis is formed - the weakest point of the pelvic ring.
Anatomy of the pelvis, or what is the womb
The dense pelvic bones in combination with the sacrum form a complete structure - the pelvic ring. Its task is to unite the skeleton of the lower extremities with the spine. Nature assigns another important function to the pelvis: it serves as a container and support for internal organs.
This aspect takes on particular importance in women during pregnancy - the pelvis becomes a natural container for the pregnant uterus, which during this period almost completely displaces other organs (intestines, omentum).
All large muscles of the lower extremities, muscles of the anterior and lateral walls of the abdominal cavity are attached to the pelvic bones. Large nerves (sciatic, obturator) and vessels (femoral veins and arteries) pass through the openings in the pelvic bones.
Functions of the pelvis:
- Supportive - the entire weight of the upper half of the body is transferred to the pelvis through the spine.
- Motor - the muscles of the legs and back, which are responsible for movement, are attached to the pelvis.
- Balancing - the interaction through the pelvis between the legs and spine allows a person to maintain balance.
- Protective - protects large vessels and nerve trunks from damage.
- Hematopoietic - in the flat bones of the pelvis there is a significant mass of red bone marrow that produces blood cells.
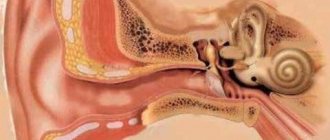
Where is the symphysis pubis located?
The human pelvic ring closes in front - that’s where it is located. Every person can feel it quite freely; difficulties may arise only in very plump people. If you place your hand 15-20 centimeters below the navel and press on the skin, you can feel the bones of the pubic symphysis underneath it.
The bladder is located directly behind the pubis in both men and women, so the location of the symphysis pubis can be determined by one more sign: when a person really wants to urinate, it is behind the pubis (behind the pubis) that the urge to urinate is felt.
Articulation pubis: norm and pathology
Normally, the pubic bones are connected to each other by a special type of interosseous joint - the symphysis. The peculiarity of this structure is that it is a cartilaginous plate between two bones. This plate has a small longitudinal cavity, which allows for slight displacement of the bones relative to each other.
Read also…. Plexitis - symptoms, causes and treatment of the disease
Condition of the symphysis pubis during pregnancy
The ability of the pubic bones to shift plays an important role in the biomechanism of childbirth: when a child passes through the birth canal, the bones of the pubis move slightly apart. This allows, in most cases, to avoid serious injury to both the mother and the newborn baby. Normally, before childbirth, there is even some softening of the cartilage of the pubic symphysis, which further facilitates the birth process.
Causes of pubic bone problems
The area of the symphysis pubis in women is very susceptible to various pathological processes, which sometimes leads to problems during and after childbirth. All reasons can be grouped into several categories:
- Heredity - it has been clearly proven that the risk of symphysitis and rupture of the symphysis pubis in primiparous women is several times higher if their mothers also suffered from this problem.
- Hypocalcemia - in pregnant women, a relatively large percentage of dietary calcium is used to build the fetal skeleton. This fact, as well as hormonal changes, as a result of which the absorption of calcium by a woman’s joints deteriorates, leads to weakness of the pubic symphysis.
- Vitamin D deficiency - this cause is especially noticeable in women who are pregnant in the autumn-winter period, when due to lack of sunlight their own vitamin is not produced.
- Endocrine disorders - diseases of the endocrine system can cause excessive calcium excretion in the urine, which leads to softening of the pubic symphysis.
It is especially difficult for those women who have a combination of several causes at the same time.
Divergence and rupture of the symphysis pubis
The most common pathology of the musculoskeletal system in women giving birth is represented by discrepancy of the pubic bones. This is a very unpleasant phenomenon, the symptoms of which are:
- Pain in the pubic area, increasing when the hip is moved to the side. The pain syndrome can be insignificant, resembling the already mentioned urge to urinate, or it can be quite intense, forcing the woman not to move. The pain can “shoot” along the inner thigh.
- Change in gait - due to unpleasant sensations, a woman is forced to walk with a mincing “duck” gait.
- Limitation of leg mobility - it is impossible to lift your leg while lying on your back.
- “Snap” symptom - when you turn your torso or move your leg sharply, a click is felt in the pubic area.
Degrees of divergence of the pubic bones
The ligaments of the pubic symphysis are very plastic and have a good margin of safety. The severity of the condition in case of discrepancy can only be assessed by measuring the distance to which the pubic bones have moved away from each other. Based on this criterion, the following degrees of divergence of the symphysis pubis are distinguished:
- The first is that the width of the diastasis (the space between the bones) is in the range from 0.5 to 1 cm. The symptoms are mild, most often no treatment is required - the bones will subsequently restore their original configuration.
- The second is that the pubic bones diverge by 1-2 cm, which is accompanied by severe pain and can complicate childbirth and the postpartum period.
- The third, or direct rupture of the pubis, is a discrepancy exceeding 2 cm and can be determined by palpation.
Read also…. Cervical plexitis - description of the clinical picture of the disease
With the second and third degrees of divergence of the symphysis pubis, a pregnant woman should be in a hospital in order to be able to receive qualified medical care at any time.
Inflammation of the symphysis pubis
Another unpleasant phenomenon that significantly complicates the life of a pregnant woman is symphysitis. This is an inflammation of the symphysis, which may be accompanied by a discrepancy, or may occur without it. Symptoms of symphysitis are the same: pain in the pubis, changes in gait.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of symphysitis can be made only on the basis of a woman’s typical complaints. To confirm it and to identify discrepancies with the determination of the degree, it is necessary to conduct some instrumental studies.
The most accessible diagnostic method is ultrasound of the symphysis pubis. In non-pregnant women, the most informative diagnostic method will be an x-ray of the symphysis pubis after childbirth.
An ultrasound of the symphysis pubis should be done to determine whether a woman needs hospitalization or whether she can be treated at home.
Possible complications
With a discrepancy of 1-2 degrees of the symphysis pubis, in most cases there are no consequences for the woman. At grade 3 there is a risk of severe complications:
- bladder rupture;
- damage to the urethra;
- clitoral trauma;
- fracture of the pubic bones;
- hemorrhage in the fracture area.
Some women may develop arthrosis of the symphysis pubis. It usually occurs in women with many children, in whom each pregnancy proceeded with symptoms of symphysitis.
All these phenomena occur as a result of pathological displacement of the pubic bones. To prevent complications from occurring, it is necessary to promptly identify the pathology and begin preventive and therapeutic measures.
Treatment methods
This pathology is treated conservatively, that is, no operations are performed. The exception is a complicated rupture of the symphysis pubis due to damage to neighboring organs.
The goal of treatment is to stabilize the frontal bones, allowing the symphysis to fuse. Treatment is always long-term - at least 1-2 months even in simple cases, and in severe cases it can last six months.
Treatment of discrepancy and rupture of the pubic symphysis
Therapeutic measures are as follows:
- Limitation of physical activity - for 1-2 weeks the patient is not recommended to move at all if the symphysis is ruptured.
- Positional treatment - the patient can be placed in an orthopedic hammock, which helps move the frontal bones.
- Tight bandaging of the pelvis or wearing a special symphyseal bandage.
- Physiotherapy: electrophoresis with local anesthetics reduces pain.
- Taking vitamin complexes with a high calcium content speeds up the healing process.
In pregnant women, treating discrepancies with medications is very difficult - they can have an adverse effect on the child, so therapy is limited to the above methods. Women who have given birth can take painkillers to relieve pain, but only after consultation with an obstetrician and orthopedist.
Exercises to relieve pain
You can reduce the pain of symphysitis with the help of some exercises from the arsenal of physical therapy. They will not be able to completely remove the pain syndrome, but they will significantly alleviate the general condition.
Cat pose. The patient should get on her knees and elbows, after which she should arch her back as much as possible (like an angry cat). In this case, you should strain your abdominal and pelvic muscles as much as possible.
The exercise is repeated 5-10 times, after which you can rest. 5-7 approaches are performed per day.
This exercise is suitable for early pregnant women who have already given birth; in the later stages it is difficult to implement.
Kegel exercise - the task is to tense the pelvic floor muscles. It is necessary to simulate interruption of the urine stream during urination. The exercise is relatively simple and can be performed at any time.
Prevention of symphysitis
All women should be concerned about prevention, but this applies to a greater extent to the risk group, when there are all the reasons for the occurrence of symphysitis and rupture of the symphysis pubis.
No doctor can guarantee a pregnant woman that she will not have symphysitis. You can reduce the likelihood of this pathology by following simple recommendations:
- Adequate nutrition throughout the entire period of bearing a child. The diet should be enriched with proteins and calcium.
- Taking vitamin complexes and microelements according to indications.
- Regular ultrasound examinations to assess the expected weight of the child.
- Timely treatment of any concomitant diseases.
- Preventing excess weight gain.
If, despite all the preventive measures, pain in the pubic area still appears, then you should not delay it - you should immediately consult a doctor for advice. Early initiation of treatment significantly improves the prognosis and reduces the likelihood of complications.
Source: https://proinfospine.ru/lonnoe-sochlenenie-gde-nahoditsya-kak-lechitsya-ego-rashozhdenie-i-razryv.html
Corrective measures
How to treat pubic symphysis during pregnancy? In most cases, the woman is not prescribed any medications. However, if there is severe pain, there is a need to take painkillers. These include Paracetamol. It is the safest during this period. Also in the second trimester, Nurofen or ibuprofen-based products can be used. However, such drugs can only be used on the recommendation of a specialist and after diagnosis.
In case of first-degree pathology, the expectant mother is advised to be careful when moving. When getting out of bed or chair, do not make sudden actions. When climbing stairs, first place one foot on the step, then move the other there. Try to use elevators and walk less.
In particularly severe situations (with the second or third stage of the pathology), a woman may be prescribed bed rest. It is recommended to maintain this state until childbirth. At the same time, medications that relieve inflammation and relieve pain may be indicated.
Why does the pubic bone hurt during pregnancy?
Very often you can hear complaints from pregnant women about pain in the bones of the pelvis, pubis and lower extremities. In most cases, pain and discomfort are observed late in pregnancy, being harbingers of impending birth. Pain in the bones and pelvis is caused by physiological changes associated with muscle strain due to a significant increase in the size of the uterus and fetus.
In addition, very often bones ache during pregnancy due to a disorder of phosphorus-calcium metabolism, in which a softening of the bone skeleton occurs in the body of the expectant mother. Also, pain and aches in the bones are affected by a lack of vitamin D. In this case, the expectant mother is prescribed complexes of vitamins and preparations containing calcium. It is worth noting that the drugs must be prescribed by a gynecologist, and calcium is not prescribed to pregnant women after 34 weeks.
At the end of pregnancy, a woman may suffer suffering and discomfort from pain in the pubis due to the divergence of the pubic symphysis - a process in which the pelvic bones rapidly diverge during pregnancy, preparing the exit of the fetus through the birth canal. The expectant mother feels pain in the middle of the pubis, and a change in gait may be observed, which resembles a “duck” gait, fatigue increases, and weakness in the legs and muscles is felt. During this period, it is important to undergo an ultrasound examination and consultation with a gynecologist.
Pain in the pelvic region is considered a normal physiological symptom associated with bearing a child. Changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy lead to softening of the ligaments and muscles surrounding the pelvic bones. In this case, pregnant women feel pain not only in the pelvic area, but also in the womb, lower back, which radiates to the tailbone or perineum.
- Excessive load on the pelvic bones. As the fetus grows, the load on the back muscles and pelvis increases, so in order to slightly reduce the load, you need to pay attention to posture, regularly wear a prenatal bandage and perform special exercises for expectant mothers that help strengthen and train muscles and ligaments. Exercises in the pool will be useful. It is not recommended to lift weights and try to reduce physical activity.
- Chronic diseases of the musculoskeletal system. If before pregnancy you were bothered by diseases of the back or spine, then during pregnancy the disease may remind you of itself with pain in the pelvis. Women suffering from osteochondrosis, curvature of the spine, may experience severe pain in the bones of pregnancy.
- Symphysitis. One of the most serious causes of unbearable pelvic pain in expectant mothers is symphysitis. This is a complication in which ligaments diverge and excessive softening of the symphysis pubis occurs, the bones of the pubic arch diverge and become mobile.
The expectant mother experiences pain in the pelvis and pubic bone. The pain especially intensifies and brings unbearable pain when walking up the stairs, with sudden movements, changes in gait occur, as the disease progresses, it is difficult for a woman to raise her legs from a lying position, she is physically unable to do this. If you observe this symptom, you should urgently consult a doctor, undergo an ultrasound and find out how much the space between the bones has diverged in order to determine the severity of the disease.
Symphysitis causes a lot of inconvenience and torment for a woman, but the main danger for a pregnant woman suffering from symphysitis is a possible rupture of the symphysis during natural delivery. The consequence of a rupture is a long rehabilitation period, the inability to live a full life, since you will have to spend at least two weeks in bed rest and undergo a course of therapeutic exercises.
Sometimes pregnant women experience pain in their pelvic bones at the beginning of pregnancy. Such pain is intermittent and not intense, and does not cause discomfort. Under the influence of hormones, physiological changes occur in the body, leading to nagging pain in the pelvic area and above the womb. The discomfort is also caused by a lack of magnesium and calcium in the body.
Early toxicosis, which is accompanied by nausea and severe vomiting, can lead to a deficiency of vital microelements. A woman may experience heaviness in her legs, cramps at night, pain in the pelvic bones during pregnancy, and pain in the perineum. By replenishing the body with the microelements it lacks, painful sensations and pain are significantly reduced, and relief comes.
Pain in the pubic bone is usually observed shortly before childbirth. The body is intensively preparing for the upcoming event, the uterus with the fetus gradually descends into the pelvis. This natural process is associated with the appearance of severe pain in the perineum and pubic bone, as the load on them increases many times. If a pregnant woman experiences pain in the pubis and perineum before 37 weeks, this may indicate the possibility of premature birth.
At week 37, many pregnant women suffer from severe pain in the bones between the legs; this pain can appear for the following reasons:
- Descent of the fetus into the pelvis. The fetal head puts pressure on the pelvic bones during pregnancy, causing discomfort in the bones between the legs.
- The pelvic bones diverge during pregnancy. This process is accompanied by severe shooting pain in the legs and perineum.
- Poor nutrition. Constipation can lead to painful sensations in the intestines, which radiate unpleasantly to the perineum.
- Compression of the sciatic nerve by the fetus. If the sciatic nerve is compressed, it will be difficult for a pregnant woman to stand or lie in a certain position. As soon as the child takes a different position, the pain will subside.
- Varicose veins in the perineal area. If varicose veins are observed in the perineal area, then the expectant mother will feel painful sensations radiating to the perineum.
- Loosening of ligaments associated with the production of pregnancy hormones.
Unpleasant sensations in the hip joint can be of two types:
- Acute – occur spontaneously, characterized by severe pain that shoots and impedes movement.
- Chronic – appear periodically, have a relatively low intensity, and are directly related to the presence of chronic inflammatory and degenerative processes in the pelvis.
If we consider the etiology of the origin of pain, they can be divided into two subgroups:
- Pathological – caused by the presence of pathological and degenerative processes in bone tissue, as well as nearby organs.
- Non-pathological - arise as a result of exposure to external factors not related to disease.
The first group can include diseases such as:
- arthritis;
- arthrosis;
- neoplasms;
- tendon inflammation;
- hip injuries;
- the presence of inflammatory processes in connective tissue.
These diseases gradually destroy the hip joint, depriving a person of the ability to move painlessly.
Non-pathological causes may be due to factors such as:
- being overweight;
- strong physical activity;
- sedentary work;
- improper poor nutrition;
- sedentary lifestyle, devoid of any physical activity.
Arthritis
The disease is determined by the presence of an inflammatory process in the hip joint, in which the cartilage tissue is destroyed and the bones in the joint compress each other. Depending on what exactly triggered the inflammation, arthritis can be divided into types such as:
- Infectious – occurs against the background of active reproduction of an infection, which remains untreated for a long time and becomes chronic.
- Parasitic – inflammation is caused by parasites and their metabolic products (toxins).
- Post-traumatic – occurs against the background of an injury, during which an infection was introduced.
- Viral – develops in the presence of viruses in the blood, as well as in weakened immunity.
- Allergic – occurs when there is an acute reaction of the body to any irritant.
- Psoriatic – the root cause is psoriasis, which significantly weakens the immune system.
Type of pain The pain is sharp, sharp, shooting and restricting movement. It is painful for a person to walk, squat, and increased loads in the form of jumping or lifting weights are generally impossible. Localization The pain increases in the groin area, after which it spreads to the thigh, radiating to the knee and lower back. Diagnostics
Initially, a surgeon or traumatologist examines the patient, assessing such important indicators as:
- Nature, intensity and duration of pain.
- Presence of lameness and pain in the groin when walking.
- Compare the length of the limbs.
Laboratory tests of urine and blood help to identify the cause of the pathology, indicating the presence of an inflammatory process, as well as its causative agent.
If there is a suspicion of an infectious nature of arthritis, a puncture of the synovial fluid of the joint is performed, which is examined and the type of pathogen is identified, which will allow further selection of appropriate treatment.
The following hardware diagnostic methods are capable of assessing the condition of the joint and making a final diagnosis:
- Radiography.
- MRI and CT
- Ultrasound of the hip joint.
- Contrast arthrography.
Tuberculin diagnostics is performed only when there are prerequisites and suspicions for the presence of tuberculosis, which could serve as an impetus for the development of arthrosis. Treatment
Using a bandage and corset
In the second half of pregnancy and before childbirth, doctors recommend wearing a bandage or a special corset. Such manipulations will help relieve pain and support the body of the uterus. It is worth noting that such products should be used only after consulting a specialist. Supportive devices should be properly sized and worn only when lying down.
Doctors recommend wearing the selected accessories for several days after childbirth. It is at these moments that the pathology reverses. Supportive and tightening accessories will help improve the condition of the new mother.
Where is the symphysis pubis in women and what is it?
The pelvic bone is the largest in the human skeleton.
The hip joint is made up of several smaller bones that fit tightly together. These bones have the following names: ilium, ischium and pubis.
Where the pubic bones meet is the symphysis pubis, which is considered the weakest point of the pelvic ring.
To understand what state of the symphysis pubis is normal, and when we can talk about pathology, it is necessary to study in detail the anatomical structure and possible reasons for deviations from standard indicators.
Anatomy
The pelvic ring is the final structure of the pelvis, formed from bone tissue and the sacrum. Its task is to unite and fix the bones of the lower extremities and spine into a single whole.
An additional function of the pelvis is to contain internal organs, maintain balance and support the skeleton.
This function is of particular importance during pregnancy, when there is an embryo in the woman’s womb that needs constant growth and nutrition.
At this time, the uterus almost completely displaces other organs from the pelvic area. The bones of the lower extremities of the skeleton, the muscles of the anterior and lateral walls of the peritoneum are attached to the pelvic bone structures.
In this case, the symphysis pubis is at the epicenter of the overlapping structures.
The openings in the pelvic bones are dotted with large nerve fibers (sciatic and obturator nerves) and vessels (femoral, venous, arterial).
The main functions of the pelvis are:
- Support (the pelvic region takes on the entire load of the upper half of the body);
- Ability to move (bone and muscle tissues of the lower extremities and back are attached to the hip joint, which allows movement);
- Balancing function (direct contact of the pelvis with the legs and spine makes it possible to maintain balance);
- Protection from mechanical damage (large bone preserves blood vessels and nerve fibers in normal condition);
- The ability to form blood (the flat bones of the pelvis contain a significant amount of bone marrow, which subsequently forms the cellular structures of the blood).
Divergence of the symphysis pubis
Norm and pathology
In normal condition, the pubic bone tissues are connected to each other by a special form of interosseous components - the symphysis.
A characteristic feature of this connective tissue is that it is essentially a plate located between two bones.
In its structure there is a small longitudinal cavity, which contributes to a slight displacement of bone tissue relative to each other.
Symphysis dysfunction is the most common pathology. Most often this is recorded in the second half of pregnancy. The norm during pregnancy often fluctuates, which can cause a lot of disagreement about a woman’s health.
Delivery
When pathology develops, classical delivery is usually performed. At the same time, do not forget to inform the obstetricians about your condition. Doctors must take this into account during the process.
When it comes to the second or third stage of divergence, a caesarean section may be chosen. If the ligaments are sprained and there is a distance of more than two centimeters between the pelvic bones and the area of the pubic symphysis, a planned caesarean section is performed. Otherwise, the ligaments may rupture and emergency surgery will be required.
Treatment of symphysitis
After diagnosis, the doctor will tell you how symphysitis can be treated. There is no specific prescription, but pregnant patients are often prescribed vitamins - calcium supplements. Any physical activity and heavy lifting are contraindicated. In addition, in later stages you will need to wear a pelvic band to support the sides of the abdomen and reduce pain.
Bandage
To hold the bones in the required position and reduce the distance between them, a bandage is used in late pregnancy. This is a bandage made of hard material, which must be selected individually, based on the condition and your own feelings. During pregnancy, such a bandage is worn while lying down, slowly and tightly, but so that the arm passes through.
Exercises
Let's consider popular recommendations for symphysitis, which can significantly relieve the pain caused by symphysitis or divergence of the pelvic bones during pregnancy:
- do not cross your legs;
- in a standing position, distribute your weight evenly on both legs;
- do not sit or lie on too hard surfaces - this is an important rule during pregnancy that is best remembered;
- change your body position more often - do not sit, do not stand, do not lie for a long time;
- if you are lying down, first turn your upper torso on its side, and then your pelvis to relieve pain in the aching part of the body;
- strictly control weight during symphysitis;
- Eat foods with calcium: fermented milk, fish, nuts;
- provide yourself with walks - under the rays of the sun, the skin produces vitamin D, which is necessary for the absorption of calcium during pregnancy, try to avoid drafts;
- sleep on an orthopedic mattress.
There is also a set of specific exercises for expectant mothers in the early and late stages of pregnancy:
- Lying on your back, bend your knees and pull your legs towards your buttocks. Slowly spread your knees and bring them back. Repeat 6-10 times.
- The position is the same, but move your feet slightly away from your buttocks. Slowly lift your pelvis up and lower it back down. In the 3rd trimester, simply lift your pelvis off the floor. Raise 6-10 times.
- Get on your knees, relax your back. The back, pelvis, neck and head should be at the same level. Arch your back upward, while lowering your neck and head down. Tighten your abdominal and thigh muscles. Repeat 3 times.
Pregnancy is the most anticipated event in the life of any woman. The changes occurring in the body are not always favorable for the mother and the child. Often accompanied by discomfort and discomfort.
Pain in the pelvic area is a common problem in the early stages and before childbirth. The causes and nature of pain in the pelvic bones arise for various reasons.
We will try to answer the question why the pelvic bones hurt during pregnancy.
Causes of pain
To understand why problems of this nature begin, you need to find out the reasons for their occurrence.
The main cause of pelvic pain during pregnancy is insufficient calcium in the body. To check, it is recommended to consult a doctor and then do a blood test. Next, you can assess the calcium status for a given period.
If its deficiency is confirmed, vitamins for expectant mothers with a high calcium content or independent medications are prescribed. In addition to using medications, it is recommended to enrich your diet with vitamin D. Another reason why the pelvis hurts during pregnancy is increased stress.
During this period, weight increases significantly.
Discomfort in the hip joint causes imbalance. The growing belly shifts the center of gravity forward, loading the lower back. This body position is unusual, which causes discomfort.
Pelvic pain during pregnancy occurs when the hormone relaxin is actively produced. The substance produced during pregnancy weakens tissue connections, resulting in increased pelvic mobility.
In most cases, diseases worsen due to increased loads, with poorly developed lower back muscles, and bending. Inflammatory processes that took place before pregnancy cause the formation of adhesions, which is why problems with conception often arise. During pregnancy, they cause pain in the pelvic area, as the enlarging uterus pulls on these adhesions.
Symphis dehiscence
It was said above that pain in the pelvic bones during pregnancy occurs due to a lack of calcium, leading to the occurrence of a pathology - the symphysis (pubic symphysis or pubis). Gaining mobility during pregnancy, the joint stretches. Symphysis is a condition where the joint is severely stretched, which leads to its hypermobility.
Causes of occurrence There are several causes of symphysis:
- Calcium deficiency in the body, excess of the hormone relaxin, hormonal imbalances.
- Features of heredity.
- Disturbances in the musculoskeletal system.
- Rapid weight gain, increased stress, poor diet, disrupted sleep patterns.
Symptoms of symphysis
- Pain in the pubic area that occurs when walking or climbing stairs.
- The pain begins to bother you in a quiet position or while turning in bed.
- Swelling appears in the pubic area.
How to cure? This disease is not treated, it goes away immediately after childbirth. You can make your pregnancy easier with a few simple tips.
First: it is necessary to wear a bandage that supports the hips and pelvis, preventing the joints from stretching.
Second: doctors advise not to sit or walk in one position for an hour. Third: add foods containing large amounts of calcium to your daily meals. There are particularly severe cases of symphysis development that require hospital treatment. Includes a course of physiotherapy, anti-inflammatory drugs, painkillers.
Symphysis is a common problem, affecting up to 50% of pregnant women.
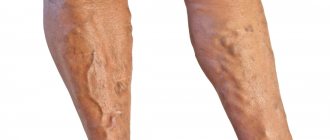
Discomfort during pregnancy is caused by varicose veins of the small pelvis. The pathological process proceeds almost unnoticed. Occurs when the growing uterus blocks the flow of blood through the main vessels. Varicose veins of the small pelvis are dangerous during a cesarean section; bleeding may occur.
Causes of occurrence Varicose veins can occur for the following reasons:
- Heredity, meaning weak vascular walls.
- Venous insufficiency.
- During pregnancy, there is an increase in blood volume in the body, which leads to stagnation and backflow of venous blood.
- Growth of the uterus and compression of other organs by it.
- Abortions or pregnancy failures that occurred before conception.
- Lifting and carrying heavy objects.
- Smoking.
Symptoms of varicose veins
- Heaviness in the pelvic area.
- Swelling of the labia.
- Prominent veins on the buttocks.
- Unpleasant sensations in the vaginal area during or after sexual intercourse.
- Drawing pain in the lower abdomen.
- When the disease spreads to the bladder, pain occurs when urinating.
Methods for diagnosing varicose veins and treatment
- Ultrasound of the pelvis, examination of the bladder, uterus and ovaries.
- Doppler sonography is used to identify the characteristics of blood circulation in the uterus and placenta.
- Transuterine venography - detection of places where blood clots form.
- Laparoscopy is used when it is necessary to exclude related diseases.
Under the supervision of a doctor, the following drugs are prescribed: venoruton, detralex, ginkor-fort. Exercises recommended for varicose veins Moderate walking for 1 minute, bending forward;
- Breathing in a lying position with your hands on your stomach for 1 minute;
- Arching your back upward, supporting yourself on your elbows and knees;
- Walk with a high hip awareness for 1 minute.
There are a number of folk remedies to combat varicose veins: horse chestnut, dandelion root, kombucha.
Tinctures made from these ingredients normalize venous tone.
A pregnant woman's body is actively preparing for future birth.
A week before giving birth, you lose your appetite. I no longer want to eat fatty and high-calorie foods. Anxiety and unreasonable anxiety appear.
During labor, the baby's head begins to actively press on the mother's pelvis, gradually beginning to enter its small part. Contractions and fetal pressure cause the pelvic bones to move apart.
The increase in diameter occurs on average by 1-3 centimeters.
It happens that during childbirth the pelvic bones diverge too much. This occurs as a result of strong stretching of the symphysis and low calcium content in the body. In this case, the following symptoms are observed:
- Pelvic bones hurt after childbirth for more than 2 months.
- Difficulty climbing stairs.
- Pain is felt when turning while sleeping.
Other causes of pelvic pain after childbirth:
- The pelvic bones and tailbone, displaced during childbirth, cause severe pain. The displacement process itself is painless, but sometimes bone restoration takes longer than usual, accompanied by pain.
- Softening of tissue occurs with the active production of a calming hormone. There is a strong load on the pelvis, as the tissues cannot perform their functions.
- Trauma during childbirth. Dislocation or fracture of the pelvic bones may occur. Since the woman is under anesthesia, it is almost impossible to detect the injury immediately. Failure to diagnose injuries in a timely manner leads to improper fusion of bones. As soon as you suspect an injury of any severity, you should immediately consult a doctor.
A pelvic brace is prescribed, loads are reduced, and it is recommended to sleep on an orthopedic mattress. For severe pain, painkillers are prescribed, but if a woman is breastfeeding, it is better to refrain from taking such drugs. Typically, such pain goes away in 2 to 6 months. Be sure to watch the video below
Prevention
Of course, it is usually difficult to avoid pelvic pain during pregnancy. But you need to try to prevent these negative factors or reduce their influence. Prevention should begin before conception.
Ordinary uncomplicated symphysitis does not require special medical treatment. It goes away on its own a few months after birth; less often, clinical symptoms of softening of the symphysis persist throughout the first year after the baby is born. But it is imperative to treat a rupture of the symphysis pubis if it occurs. Without proper and timely therapy, a woman can remain disabled for life. The rupture is treated exclusively with surgery and long-term (several months) fixation. The operation is aimed at reconstructing the damaged ligaments.
For symphysitis during pregnancy, therapy is aimed primarily at relieving pain and preventing rupture of the pubic ligaments. The treatment regimen may include painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs - antispasmodics, such as No-shpa, Baralgin, Paracetamol. They are allowed to be taken only in doses approved by the doctor and only in cases where the woman has to spend a long time in an upright position. Uncontrolled and frequent use of painkillers can cause drug addiction.
Regardless of the degree of illness, the pregnant woman is prescribed relative rest. The pubic symphysis should not experience heavy loads. With a mild degree of symphysitis, it may be recommended to reduce the usual loads; for grades 2 and 3, bed rest is often prescribed. Expectant mothers with suspected symphysitis or a confirmed illness are not recommended to walk up and down stairs, sit for long periods of time, stand in one position, or walk for long periods of time.
A woman is recommended to take multivitamins, complexes created specifically for expectant mothers with a high calcium content, or calcium supplements in addition to the vitamins she takes. Unauthorizedly starting to take calcium in any form means endangering the baby, because an excess of this mineral in the body of the expectant mother can harm the baby, especially in the third trimester of pregnancy. It is not recommended to take calcium at all for several weeks before giving birth.
If symphysitis is diagnosed, more careful weight monitoring will be required. Excessive weight gain increases the load on the weakened symphysis pubis, and the risk of rupture increases proportionally. A woman is recommended to have a universal diet for pregnant women, proper drinking regimen, and fasting days. Starting from 6-7 months of pregnancy, a woman can wear a prenatal bandage corset; it will support the growing belly and reduce the load on the womb. You can purchase a bandage at any pharmacy or orthopedic salon.
After childbirth, you will need another bandage, the wearing of which is designed to reduce the distance between the pelvic bones. It can also be purchased at an orthopedic salon. In some cases, a woman after childbirth is recommended to walk with the support of a cane or crutches.