Loss of consciousness is a syndrome widely encountered in clinical practice. Up to 40% of people lose consciousness at least once in their lives. At the same time, doctors distinguish between the concepts of fainting (syncope, syncope) and impaired consciousness. Diagnosis and treatment of the causes of syncope are primarily carried out by cardiologists; patients with disorders of consciousness (epilepsy, strokes, comas) are examined and treated by neurologists.
At the Institute of Clinical Cardiology named after. A.L. Myasnikov National Medical Research Center of Cardiology examines and treats patients with fainting in the laboratory of syncope, created on the basis of the Department of Clinical Electrophysiology and X-ray Surgical Methods for the Treatment of Heart Rhythm Disorders. Specialists have accumulated unique experience working with such patients, and have developed algorithms for their diagnosis and treatment. In 2011, a Russian Federation Patent was received for an original method of determining the cause of fainting of various origins. Every year, the Institute examines up to 300 patients with attacks of loss of consciousness of various origins.
Patent of the Russian Federation for the invention “Method for determining the cause of fainting of various origins”, 2011
The unit meets all modern requirements for centers for examining patients with attacks of loss of consciousness. Special questionnaires have been developed for interviewing patients, which make it possible with a high degree of probability to suspect the cause of loss of consciousness already at the stage of the initial examination. Directly, the employees of the Department carry out all the necessary examination methods (ECG, Holter monitoring of ECG, telemetric monitoring of ECG, echocardiography, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, non-invasive topical diagnosis of arrhythmias, standard and modified stress tests, transesophageal electrophysiological study, vagal and orthostatic tests, etc.). On the basis of the Department, in a cath lab, complex invasive examination methods are performed: intracardiac electrophysiological examination (experience since 1977), as well as implantation of monitors for long-term ECG recording. If necessary, it is possible to use other examination methods available in the arsenal of the National Medical Research Center of Cardiology, including angiographic studies (coronary angiography, angiography of the brachiocephalic arteries, etc.), magnetic resonance and computed tomography, consultations with a neurologist, EEG recording, etc.
The laboratory’s specialists are leaders in the country in terms of experience in conducting long-term passive orthostatic tests (performed at the Institute since 1990), the “gold standard” in diagnosing the causes of syncope. A special protocol for testing on a bicycle ergometer has also been developed and introduced into clinical practice in order to determine the causes of fainting.
Room for orthostatic and stress tests
After determining the cause of loss of consciousness, an individual treatment plan is developed. The complexity of the treatment methods used depends on the identified disorders. For patients with orthostatic fainting, educational materials and recommendations for modifying lifestyle and nutrition have been developed, “training” (specific physical exercises to prevent the development of fainting) is used, indications for drug therapy and non-drug treatment methods are determined. Patients with cardiac arrhythmias undergo radiofrequency and cryoablation of arrhythmia sources. When diagnosing cardiac conduction disorders that act as causes of fainting, implantation of pacemakers is performed. In a special category of patients with serious heart disease and a high risk of developing malignant arrhythmias, implantation of cardioverter-defibrillators and resynchronization devices is performed.
X-ray operating room of the Department of Clinical Electrophysiology
Unique long-term experience in managing patients with attacks of loss of consciousness, developed proprietary diagnostic and treatment methods, make it possible to establish the cause of fainting and select effective therapy in more than 95% of cases, which surpasses many world centers in effectiveness.
Causes of syncope:
The immediate cause of fainting is a decrease in blood flow to the brain due to a decrease in blood pressure. This can be caused by various conditions, such as cardiac rhythm or conduction disturbances, heart defects and tumors, the consequences of a previous myocardial infarction or inflammation of the heart muscle (heart failure), in which there is a decrease in blood output from the heart. Such patients require examination in a specialized cardiology department.
Often the cause of syncope is a reflex decrease in blood pressure in response to medical procedures (blood sampling, a visit to the dentist), pain, emotional arousal, severe coughing, straining during urination or defecation. But most often, fainting of this type is caused by staying in a stuffy room, standing for a long time (in transport, in a queue), or abruptly stopping physical activity (quickly climbing stairs, finishing an intense workout, stopping after running). Due to the mechanism of development of this type of syncope, they are called vasovagal (neurogenic, neuroreflex). In such cases, a full examination may not reveal any heart disease, and to confirm the cause of loss of consciousness, a long-term passive orthostatic test, a special type of exercise test, and so-called vagal tests are used. In older people, a common cause of fainting is orthostatic hypotension - a decrease in blood pressure when standing up. In some cases, these symptoms can appear at a young age, and can also be so severe that the patient loses the ability to remain in an upright position for a long time. It must be remembered that the appearance of such symptoms can be a sign of a number of neurological diseases and requires mandatory consultation with both a cardiologist and a neurologist. Fainting that occurs as orthostatic hypotension can also develop with varicose veins of the lower extremities, with blood loss, in pregnant women, etc.
Syncope is less common in the presence of carotid sinus syndrome. In such patients, loss of consciousness can occur during any manipulation or pressure in the neck area - shaving, tying a scarf, wearing clothes with a tight collar. This is due to the increased sensitivity of receptors located in the area of the carotid arteries (vessels supplying the brain). Fainting is often the result of uncontrolled use of medications or incorrectly selected dosages and frequency of administration. This is especially true for the use of nitrates, diuretics, antiarrhythmics, and blood pressure lowering agents. The prescription of drugs must be carried out by a doctor and be justified. If you suspect a connection between syncope and the drug therapy you are taking, you should consult your doctor to change your medication regimen.
Clinical picture:
Before loss of consciousness, the patient may experience warning signs of fainting: palpitations, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, lightheadedness, nausea, flashing “spots” before the eyes, sweating or, conversely, coldness of the extremities. Most often, these symptoms occur in an upright position of the body, but can also be observed while sitting and even lying down. In some cases, loss of consciousness develops suddenly, when the patient does not even have time to understand what happened. This type of fainting is the most dangerous in terms of the risk of injury from a fall. In the unconscious period, pallor of the skin and loss of muscle tone are noted. The patient does not answer questions. “Bending” of the body, twitching of the limbs and even convulsions may be observed, which in itself is not a criterion for diagnosing epilepsy. Blood pressure levels are low or even undetectable. When trying to determine the pulse, there may be a significant decrease in its frequency up to a pause in the heart, or the pulse may be so fast that it is difficult to count.
A distinctive feature of syncope is its short duration (fainting rarely lasts more than 5 minutes) and complete reversibility (after the return of consciousness, the patient remembers everything, recognizes those around him, and answers questions). The skin may remain pale and moist. Patients often experience weakness and general poor health. Blood pressure and heart rate depend on the cause of fainting and may be normal, low or high.
Diagnosis of the causes of loss of consciousness:
If syncope occurs, you should consult a doctor to find the cause of fainting. It is important to provide a detailed description of the circumstances of the loss of consciousness - under what conditions it happened, what the patient experienced before and after syncope. Eyewitness accounts of fainting are also valuable. The more information the doctor receives, the more accurately he will be able to select the necessary examination methods. Their number and degree of complexity depend on the suspected cause of syncope. The doctor may limit himself to taking blood tests, taking an electrocardiogram and conducting an echocardiogram, or may expand the examination using long-term electrocardiogram monitoring, conducting a transesophageal or intracardiac electrophysiological study, a long-term passive orthostatic test, exercise tests, tomographic studies, etc. The correct thing to do is to consult a doctor for the first time and develop an examination plan for the fastest and most accurate diagnosis of the cause of fainting.
Treatment of syncope:
Treatment for syncope can be divided into immediate care at the time of loss of consciousness and treatment of the identified cause of fainting.
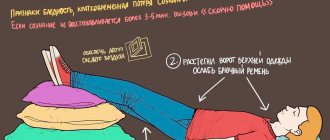
It is important for the patient to recognize the warning signs of loss of consciousness in order to take timely measures aimed at preventing injury as a result of a fall. If warning signs appear (nausea, dizziness, palpitations, etc.), you should immediately sit down or (better) lie down, preferably with your feet elevated (headboard, bag, folded clothes). Also, if the cause of fainting has not been established or there is a suspicion of the development of life-threatening conditions, it is necessary to call an ambulance team. The use of medications, unless previously discussed with a specialist, can be dangerous and aggravate the course of fainting. If you witness the development of fainting, place the victim on his back, turning his head to the side and, if possible, elevate his legs. Make sure the patient's airway is clear. If there are convulsions, you should not forcibly hold the patient’s head or limbs; it is enough to protect them from injury (for example, put something soft under the head). It is important to try to determine the pulse - its presence and characteristics (frequent or rare, regular or irregular) may be important later in determining the cause of syncope.
The success of treating fainting directly depends on the accuracy of identifying the cause that caused it. Reflex fainting often does not require drug treatment, but such patients need to undergo a special training stage, during which patients learn to apply measures to subsequently avoid recurrence of loss of consciousness, receive recommendations for changing lifestyle, level of physical activity, etc. Patients with cardiac causes of syncope require specialized treatment - antiarrhythmic therapy or surgical treatment of arrhythmias, implantation of a pacemaker in patients with cardiac conduction disorders, removal of obstructions to blood flow in the presence of heart disease, drug or invasive treatment of heart failure. For patients with orthostatic hypotension, recommendations and treatment regimens have also been developed depending on the presence of chronic diseases and signs of diseases of the nervous system. During the visit, a detailed analysis of the drug therapy that the patient takes constantly or occasionally is carried out to eliminate or minimize the effect of drugs on the frequency of fainting.
It must be remembered that loss of consciousness is a reason to contact a specialist to establish the cause of syncope, determine the prognosis for life and develop an optimal treatment regimen for the identified disease.
Hypoglycemia
This condition develops when blood sugar levels drop.
Manifestations of hypoglycemia:
- restlessness, agitation and increased aggressiveness, anxiety, fear;
- increased sweating;
- muscle hypertonicity and tremor;
- tachycardia and arrhythmia;
- headache, dizziness;
- dilated pupils, visual impairment;
- increased blood pressure;
- pale skin;
- loss of coordination, disorientation;
- breathing and circulatory disorders.
What causes people to faint during hypoglycemia? This condition can contribute to fainting in people susceptible to it or even cause coma.
State of shock
What causes people to faint when in shock? Shock develops under the influence of a super-strong irritant, leading to disruption of all vital functions. The causes of loss of consciousness due to shock are a serious condition of the body, which is accompanied by severe pain, major blood loss, extensive burns, or a combination of these factors.
Manifestations of shock:
- inhibition of body functions after a short period of excitement;
- indifference and lethargy;
- skin is cold, pale, bluish or gray;
- perspiration;
- breathing is rapid, but shallow;
- weak pulse, acceleration of its frequency;
- vomit;
- pupil dilation.
Over the centuries, epilepsy has had many names: “divine”, “demonic”, “lunar”, “bad”, “black infirmity”, “shaking”, “sorrowful suffering”, “punishment of Christ” and others. Worldwide, about 50 million people suffer from this disease, according to data from the World Health Organization (WHO).
“Epilepsy is a chronic brain disorder that affects people all over the world. The disease is characterized by recurrent seizures. These seizures occur as brief, involuntary convulsions in one part of the body (partial seizures) or throughout the body (generalized seizures) and are sometimes accompanied by loss of consciousness and loss of bowel or bladder control,” according to a WHO advisory on the subject. disease.
Interestingly, up to 10% of people in the world have ever experienced such a seizure. However, according to doctors, the only case does not mean anything. The disease is diagnosed if attacks recur. Even though epilepsy is one of the oldest recognized conditions in the world, there are still a lot of rumors surrounding it.
“In many countries around the world, people with epilepsy and their families may be subject to stigma and discrimination,” WHO experts confirm.
AiF.ru spoke with Tatyana Batysheva, chief freelance specialist of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation for child rehabilitation, president of the National Association of Experts on Cerebral Palsy and Related Diseases, member of the Presidium of the All-Russian Society of Neurologists, to dispel the 10 most common myths about epilepsy.
By the way, a new series of educational events for patients and their relatives “Attention - epilepsy!”, organized by the Russian Anti-Epileptic League (RPEL) and the Non-Profit Partnership “Association of Epileptologists and Patients”, has started in Russia. The main goal of the project is to improve the health and quality of life of patients suffering from epilepsy, as well as help them adapt to society. In total, more than 400 schools will be held in Russia in 2020. Events for adults and children will be held separately. This is due to the fact that different age groups differ from each other in the characteristics of the course of the disease and the social problems that they have to face.
Seizures (convulsive syndrome) - causes, treatment, first aid, types, medications and pills
Statistics show that seizures happen to every person at least once.
You should worry if such a phenomenon goes into the system. The concept of convulsive syndrome is defined as a pathological condition characterized by unaccountable contractions of the muscular system. In this case, cramps can appear in one specific place or spread to an entire muscle group.
There are many reasons for this disease. There are specific medications for each case.
The main thing is to make the correct diagnosis. And only a qualified doctor can prescribe adequate treatment.
Kinds
There are several types of seizures:
- tonic-clonic convulsions;
- myoclonic contractions;
- partial seizures.
Tonic-clonic seizures are manifested by loss of consciousness:
| Tonic spasms occur first | At the same time, the pupils dilate, the eyes roll up and all the muscles tense. |
| Then comes the phase of clonic convulsions | There is an alternating alternation of muscle contractions and relaxations. |
| Sleep or coma occurs | The attack may be accompanied by the appearance of bloody foam as a result of biting the tongue and profuse salivation. |
Children and adolescents may experience myoclonic contractions. The process involves the entire muscle or only a certain group of muscles. For example, the muscles of the fingers or face. Many seizures can cause a child to fall, resulting in injury.
Convulsions of clonic origin without loss of consciousness are called partial. The process can involve the muscles of the face, feet and other parts of the body.
Many people confuse calf muscle spasms during sleep with cramps. This phenomenon is called myoclonus. Often accompanied by contractions of the thigh muscles.
Myoclonic states occur as a result of calcium deficiency, as well as due to the influence of low temperatures.
During sports training, painful contractions occur due to insufficient warm-up, loss of fluid and excessive increase in loads.
Causes
The following causes of seizures in different age groups of the population can be identified:
- the occurrence of various neuroinfectious diseases, for example, meningitis or encephalitis;
- deviations in the development of brain activity;
- hypoxia;
- lack of calcium, glucose and magnesium in the blood;
- the occurrence of gestosis during pregnancy;
- severe intoxication;
- severe forms of dehydration;
- complex diseases of the nervous system;
- high fever and respiratory infectious diseases;
- birth injuries in newborns;
- pathologies of metabolic processes;
- epilepsy;
- various brain tumors;
- traumatic brain injuries.
Even bright light and loud noise can trigger seizures. Hereditary factors also play an important role.
If your hands cramp
Most often, hand cramps appear in people who work a lot at the computer.
Reductions can be caused by the following reasons:
- state of stress;
- poor blood supply to the upper extremities;
- excessive sports activities;
- hypothermia;
- lack of calcium;
- various poisonings.
Coffee lovers should remember that this drink contributes to a significant leaching of calcium from the body, which can also cause cramps.
The following manipulations can help with this problem:
| Gymnastic exercises | In this case, you need to actively move your fingers, as well as clench and unclench your fists. |
| It's worth doing self-massage | Use your healthy hand to stretch your hand. |
To prevent such conditions, you need to follow simple rules:
- Consume foods rich in potassium and calcium.
- Avoid extreme cooling.
- Warm baths with the addition of essential oils have a beneficial effect.
Diseases and consequences
The manifestations of convulsive syndrome are due to the diseases that caused them.
| Tonic-clonic convulsions | May be the result of traumatic brain injury. |
| Febrile spasms | Appear in children with very elevated body temperature. |
| Cramps in the legs above the knee or in the arms | Appear at night. Their cause is considered to be a lack of magnesium, as well as problems with the spinal column. |
In some cases, seizures can even cause death. This is due to associated complications. For example, cardiac arrest, spinal fracture, arrhythmia or various injuries.
Normal muscle spasms are not dangerous.
Convulsive phenomena occur as a result of disorders of the central nervous system, which can occur due to neurological and infectious diseases, toxic processes, disorders of water-salt metabolism or hysteria.
Seizures occur in the following diseases:
| Epilepsy | This is a brain disease that is characterized by periodic seizures. At the beginning of the attack, various hallucinations may occur, and then a seizure occurs. First, the tonic phase occurs, and then the clonic phase:
Frequent seizures lead to the death of brain cells, and personality changes may also occur. It is worth remembering that during such attacks the patient should be protected from bruises, and it is also not recommended to insert plastic or metal objects into the mouth to prevent bites. |
| For tetanus | An exotoxin is produced that affects the medulla oblongata and spinal cord. This disease occurs from infection in a wound. The disease has the following manifestations:
|
| A brain tumor | In the initial stage it is accompanied by convulsive spasms. |
| Rabies | A person can become infected after being bitten by a sick animal.The following consequences appear:
|
| Tetany occurs when calcium levels are low | This condition is accompanied by muscle and nervous excitability. Partial convulsions occur. |
| Chronic alcoholism | It is characterized by increased excitability of the nervous system. In this case, generalized convulsions appear. |
| Eclampsia | It is the last stage of late toxicosis. Contractions of the facial muscles appear first, followed by clonic contractions. |
| Hysterical attack | Occurs as a result of emotional shock. Patients may squirm in an arc. Clonic convulsions develop. After the attack, sleep does not occur. |
What to do if you have seizures
Treatment of seizures occurs in two stages. First, the attack is stopped, and then treatment is given to the underlying cause.
Drug treatment should be carried out only as prescribed by a doctor. Medicines are often prescribed in the presence of a generalized or partial epileptic seizure.
Medicines for stopping an attack of epileptic convulsions
| Group of drugs | Indications | Medicine |
| Gamma amino acid acid and its derivatives. | Rehabilitation after brain injuries and strokes, severe forms of psychosis, seizures. | Sodium hydroxybutyrate by injection. |
| Benzodiazepines. | Generalized and partial convulsions. | Diazepam injections. |
| Anticonvulsant microelements. | Arrhythmia, convulsions in pregnant women and poisoning. | Magnesium sulfate in the form of injections. |
Medications to eliminate the causes of seizures
| Medication group | Purpose | Medicine |
| Barbiturates. | Partial and generalized convulsions. | Phenobarbital sodium. |
| Valproic acid derivatives. | Seizures of varying strength. | Sodium valproate in the form of syrup. |
| Benzodiazepines. | Partial and generalized contractions. | Phenazepam tablets. |
| Neuroleptics. | Complex forms of psychosis. | Aminazine injections. |
| Fibrinolytics. | For ischemic stroke. | Urokinase in the form of injections. |
| Cardiac glycosides. | For heart failure. | Digoxin tablets. |
| Iron supplements. | Convulsive syndrome caused by anemia. | Sorbifer tablets. |
In preventive measures, to avoid the recurrence of seizures, you need to follow the correct work and rest schedule, eat well and avoid excessive physical exertion.
Magnesium and potassium
With a deficiency of magnesium and potassium, muscle contractions may occur. You may also experience tingling and crawling sensations.
A deficiency of these microelements can occur in the following cases:
- if you take laxatives or diuretics for a long time;
- when dehydrated;
- during fasting;
- as a result of poisoning or alcohol abuse;
- with diabetes mellitus.
In order to compensate for magnesium deficiency, the drug Magne B6 is prescribed. You also need to eat foods rich in beneficial microelements. For example, watermelons, milk, oranges, bananas, buckwheat and bran.
First aid
Before providing assistance, it is necessary to find out the exact cause of the seizure syndrome.
| For partial seizures in adults | The person must be seated in a chair to prevent falling. |
| During a generalized attack | An ambulance should be called. Before her arrival, the patient must be placed on his side and his head protected from blows. |
| If the cause of convulsions is not epilepsy | Then it is necessary to give the limbs an elevated state. Massage will help relieve local cramps. |
The sequence of actions when providing assistance is as follows:
- The patient should be seated or laid down.
- Then grab your toes and bend your foot towards your knee. First bend halfway and release. Then bend as much as possible and hold it until the attack stops.
- Perform a muscle massage.
- Ensure complete rest.
After a binge
Convulsive syndrome often occurs after heavy drinking.
There are several reasons for this:
| Drinking alcohol | Leads to dehydration of the body and leaching of magnesium and potassium |
| Hangover syndrome | It affects the nervous system, which leads to changes in the human psyche. |
The last stage of seizures in alcoholism is called alcoholic epilepsy. It is accompanied by severe pain in the limbs, salivation and breathing problems.
You need to pay attention to the systematic occurrence of seizures and promptly seek medical help.
Methods for preventing complications:
- you should start leading a healthy lifestyle;
- you need to monitor the water balance in the body;
- avoid serious physical activity;
- take essential microelements.
If you take care of your health, many problems can be avoided.
Febrile convulsions with fever in a child
It is possible to say that febrile seizures have begun when convulsive or convulsive seizures form. They must be accompanied by a high body temperature (more than 38 degrees) and occur in children who have not previously experienced seizures of this type, up to 6 years of age. It is imperative to differentiate this…
Cramps during pregnancy
The problem of cramps can appear from the first weeks of pregnancy and continue both before the birth of the child and during breastfeeding. To avoid cramping in the future, it is important to determine the cause of the muscle strain and take preventive actions that can help manage and avoid the spasm...
Description of seizures in children
Convulsive syndrome in children develops when a focus of pathological excitation appears in the brain and is accompanied by the sudden appearance of partial or generalized seizures of a clonic, tonic or mixed (tonic-clonic) nature. This pathological condition can develop with…
Description of leg cramps
Cramps are a state of constant contraction of a muscle that does not respond to involuntary relaxation. It leads to a pronounced painful reaction, which is associated with a deficiency of oxygen and nutrients. The muscle also produces a lot of waste products, which irritate the nerves and lead to pain. By…
Source: https://nerv.hvatit-bolet.ru/sudorogi/
Myth 6. Antiepileptic drugs have many side effects and are dangerous to take.
Antiepileptic drugs are used to prevent various seizures. They are often used to treat bipolar disorders.
“Indeed, drugs for the treatment of epilepsy are quite serious, but seizures are much more dangerous. In addition, patients tolerate modern medications more easily. The drugs do not affect mental functions and are not addictive. The dose is slowly increased from minimal to effective in order to reduce the likelihood of unwanted reactions,” the expert explained.
Myth 9. Only brightly flickering light can provoke an attack
Flickering light is not the only environmental irritant that can trigger an epileptic attack. Moreover, most of the factors that provoke seizures and other manifestations of the disease can be controlled by a person independently.
“In addition to brightly flickering light, attack provocateurs can be stress and anxiety, alcohol abuse and hangover, drug use, certain medications such as antidepressants, antipsychotics, anxiolytics, fatigue, lack of sleep, a long break between meals, leading to a decrease in glucose levels in the blood, rise in body temperature, menstruation,” Batysheva listed the factors.
Causes of fainting and seizures
Causes of fainting with convulsions, signs of convulsive loss of consciousness in epilepsy
Convulsive fainting is one of the most common pathological conditions. As a rule, it occurs due to a sharp decrease in blood supply to the brain. The approximate duration of loss of consciousness varies from 5-10 seconds to a quarter of an hour. At the same time, a person’s prolonged stay in this state can be life-threatening.
Convulsive syncope in children
A person can lose consciousness at any age. Convulsive fainting occurs in children from 7 months. The predisposition to the occurrence of such a condition in childhood depends directly on the degree of development of the nervous system. However, this is not the only factor that can lead to this form of loss of consciousness; they also highlight:
- a sharp increase temperature ;
- traumatic brain and birth injuries.
At the age of 7 months to 2 years, a similar phenomenon can occur as a reaction of the body to fear, acute pain or strong negative emotions. Since it is at this age that the nervous system is formed and is characterized by increased excitability.
Frequently, convulsive fainting occurs in adolescence due to rapid body growth, problems with blood vessels occur, as a consequence of the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia and frequent loss of consciousness.
This type of fainting is very common in childhood, which is why it is so important to strengthen the immune and nervous system of the child’s body.
Pregnancy and loss of consciousness with seizures
During pregnancy, women often experience dizziness and various types of ailments. However, if convulsive fainting occurs in this case, this is evidence of the occurrence of serious complications.
In some cases, such loss of consciousness ends in a state close to comatose. In addition, the risk of premature birth increases sharply, creating a danger to the health and life of the child.
In case of convulsive loss of consciousness, a woman needs to consult a specialist, since frequent repetitions of this condition can lead to death.
Features
In some cases, convulsive syncope is confused with an epileptic seizure. However, both conditions have their own characteristic features:
- Before losing consciousness, a person feels dizziness and weakness throughout the body, and tinnitus. A minor epileptic seizure begins abruptly and asymptomatically.
- When fainting, the convulsions are clonic in nature, in which the muscles relax, contract variably and extremely quickly. In the case of epilepsy, they are tonic-clonic in nature. The muscles become stiff for a period of 3 to 10 minutes, after which clonic contractions occur.
- An epileptic seizure may not stop for 30 minutes . With convulsive fainting, consciousness returns to the person after a few seconds, less often after a few minutes.
- Loss of consciousness extremely rarely occurs in a supine position; epilepsy often begins even when a person is sleeping.
According to theory, it is almost impossible to confuse convulsive fainting and an epileptic attack, but in practice it is extremely difficult to distinguish between these conditions.
Convulsive fainting is a common pathological condition, which in most cases is associated with disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, insufficient blood circulation to the brain and prolonged stressful situations. To avoid such situations, it is important to monitor your body and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Source: https://nevralgia.ru/obmoroki/s-sudorogami-prichiny/