TRICHOPHYTIA
(
trichophytia
; Greek thrix, trichos hair + phyton plant; synonym:
herpes tonsurans, dermatomycosis trichophytica, tinea tonsurans, tinea trichophytica, ringworm
) is a fungal skin disease of humans and animals caused by anthropophilic and zoophilic trichophytons. When the disease occurs, the skin (see) and its appendages are affected - hair (see), less often - nails (see) and extremely rarely - the musculoskeletal system and internal organs.
Trichophytosis is distributed throughout the globe. In addition to humans, the disease is observed in cattle and small livestock, as well as in wild animals. There are anthroponotic and zoonotic (zoonotic) Trichophytosis.
Superficial trichophytosis
The incubation period of the disease is 7 days. Depending on the location of the fungal infection, superficial trichophytosis of the scalp and smooth skin are distinguished.
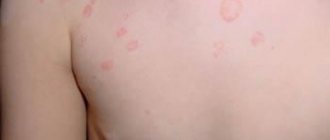
Superficial trichophytosis of the scalp most often occurs in children. Rarely, the disease affects newborns and adults. A person with ringworm may have single or multiple lesions with unclear boundaries and irregular outlines. They can reach 2 cm in diameter, but are located isolated from each other. The skin around the lesion is usually red, slightly swollen and covered with white pityriasis scales.
Swelling and redness with dermatomycosis can be aggravated by blisters, crusts and pustules. Hair located within the lesions loses its shine, color and elasticity. Trichophytosis can cause their thinning, as the hairs break off at a level of 3-4 mm from the surface of the skin. Hair can break off at the very root, leaving black spots on the head, which in this case can be covered with plaque. Sometimes the affected area may only peel off.
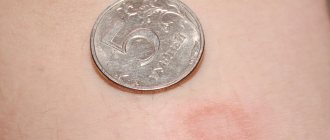
Superficial trichophytosis of smooth skin can occur in isolation or be combined with damage to the scalp. As a rule, this form of trichophytosis is localized in open areas of the skin - the torso, forearms, neck and face. This dermatomycosis occurs in people of different ages. The disease begins with the appearance of one or several swollen red-pink spots with sharp boundaries and rounded outlines that protrude slightly above the level of healthy surrounding skin. Over time, the inflammation weakens, and the source of infection takes on the appearance of a ring. Itching may be absent or mild.
Inguinal trichophytosis
When the groin area is affected by fungi, an inflammatory process forms on the genitals and on the inner thighs. Usually all this is accompanied by unpleasant painful sensations due to rashes and peeling, resulting in injury to the skin. In most cases, inguinal trichophytosis affects men. And it is transmitted through the personal belongings of a sick person or through direct contact with him.
Treatment of the disease
Treatment of trichophytosis in humans is carried out with medications, which are prescribed by a doctor depending on the form and severity of the disease. If the fungal infection has affected only the smooth surface of the human epidermis, then treating the inflamed areas with the following means is quite sufficient:
- ordinary iodine;
- salicylic ointment;
- Sulfuric ointment;
- ichthyol ointment;
- Clotrimazole;
- Isoconazole;
- Triderm;
- Mikozolon et al.
But if the disease has spread greatly and many inflamed lesions have appeared on the surface of the skin, then more serious treatment is required using complex antifungal therapy. The most effective antifungal drug is griseofulvin, which must be taken every day until a special laboratory test shows a negative result for fungi. But even after this, the drug is not canceled; it must be taken for some more time, which is determined by the attending physician, to consolidate the result.
Griseofulvin is also used for the treatment of infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis, affecting both the scalp and the epidermis on the body. During treatment, all affected hair should be shaved off. And it is recommended to apply lotions with ichthyol or a solution of silver nitrate to the inflamed areas. As for nails affected by fungus, it is better to remove them surgically.
Crusts that appear on the scalp should be lubricated with salicylic ointment, which is applied in a thick layer. Then, the softened elements are removed, and the affected surface is treated with furatsilin or potassium permanganate.
Typically, treatment of trichophytosis continues for quite a long time, often reaching several months. In no case should you stop therapy until you receive a test result indicating complete recovery from the infection.
You should not self-medicate or take medications without consulting a dermatovenerologist, since many antifungal medications in tablets have a negative effect on the liver. Therefore, it is very important to be under the supervision of a doctor throughout the entire course of treatment.
After completion of therapy, experts recommend taking vitamin complexes, particularly if a chronic form of trichophytosis is observed. For example, Alphabet, Vitrum or Centrum.
Treatment of children occurs in the same way as adults. But not all medications used to treat adult patients are suitable for children. Terbinafine is considered the best medicine for children, as it is less toxic compared to other medicines.
Chronic trichophytosis
The disease most often occurs in adolescents and adult women. This is due to the fact that in boys who contracted dermatomycosis in childhood, spontaneous self-healing occurs during puberty, and in girls it develops into a chronic disease.
This type of disease has rather mild clinical manifestations. In most cases, ringworm is discovered by examining the “epidemiological chain” to identify the carrier of the fungus within the family. The lesion spreads to the scalp, smooth skin, and nails. Quite often, trichophytosis is localized in the back of the head and manifests itself as slight pityriasis-like peeling.
Chronic trichophytosis of smooth skin is most often localized on the buttocks (tinea inguinalis), legs, elbows, forearms, and less often on the trunk or face. In rare cases, the process may become widespread. The lesions have the appearance of vaguely defined pinkish-bluish spots with a flaky surface. There are no pustules, vesicles or marginal ridge. A person with infected palms or soles may experience redness, increased skin patterns, and peeling. In places, deep furrows or cracks may form due to thickening of the stratum corneum.
Against the background of chronic trichophytosis, lesions of the nail plates may occur. The disease begins with the appearance of whitish-gray spots on them, which gradually increase in size. Then the nail becomes dirty gray with a yellowish tint, and its entire surface becomes lumpy. Next, the nails become deformed, thicken and crumble quite easily.
Surface form
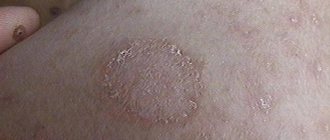
In the superficial form of trichophytosis, the foci of the disease are located mainly on the head and on open areas of the skin of the body. Nails are rarely affected. Initially, with this form, foci of ringworm appear as single pink-red spots of a round shape, covered with grayish scales. Over time, the number of such foci increases. Abscesses, small blisters and crusts may appear on them, which then dry out, forming marginal ridges in the form of a ring.
On the affected areas of the head, the hair thins, becomes brittle and dull. The skin at the roots becomes covered with a grayish coating or begins to peel off. Itching in the superficial form of trichophytosis is either completely absent or mild. This type of dermatomycosis occurs in men and women at any age.
Infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis
The incubation period of the disease ranges from 2 weeks to 2 months. The disease begins with several pale pink, round, scaly spots outlined by clear boundaries. The resulting marginal ridge consists of small bubbles and plaques that shrink into crusts. In the future, the inflammation worsens, which leads to a significant increase in the size of the spots and their merging with each other.
Over time, trichophytosis affects the scalp, as well as the facial area - above the upper lip and chin. The patient may complain of swelling, redness, and the appearance of sharply demarcated hemispherical nodes of a bluish-red color, the surface of which is covered with ulcerations. The hair in these places partially falls out and is easily removed.
With infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis, lymph nodes may enlarge.
Some patients experienced general malaise, a significant increase in general body temperature and headaches.
Deep form of the disease
With deep or infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis, lesions also occur in the hairy area and smooth skin. And in men, the disease often appears in the mustache or beard area.
Deep trichophytosis is more severe and painful than superficial trichophytosis. Here, the foci of inflammation are covered with ulcers, from under which pus oozes profusely, and the wounds, as a rule, have clear outlines and are bright red in color. Hair in this area falls out easily. A distinctive feature of this form of the disease is that pus is released from absolutely every hair follicle. The second name for deep trichophytosis of the scalp is follicular abscess.
With infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis, which manifests itself on the scalp, the following symptoms occur, which are uncharacteristic of other forms of the disease:
- severe pain when pressing on the affected area of the human scalp;
- general malaise, weakness;
- increase in temperature level;
- migraine;
- The lymph nodes increase in size and become painful to the touch.
Infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis extremely rarely goes away without the appearance of purulent ulcers, and after recovery, deep scars remain at the site of the infected areas.
Deep ringworm on smooth skin is characterized by the presence of an inflamed lesion, which has fairly clear boundaries, significantly different from healthy areas of the skin. This formation gradually increases, but after a certain amount of time, the focus of trichophytosis goes away on its own, leaving behind a spot or scar on the surface of the epithelium.
Many experts call infiltrative-suppurative trichophytosis zoophilic, since it affects not only people, but also animals. Pets in most cases become the main carriers of the disease in question. If a person becomes infected with trichophytosis from an animal, then the most severe course of the disease may occur.
The consequence of infection with trichophytons, which results in deep follicular trichophytosis, often results in allergic reactions of the body.
Diagnosis of trichophytosis
Ringworm in humans is confirmed by the presence of characteristic rashes and certain symptoms. If there is no effect of antifungal therapy or if there are complications, the doctor may prescribe the following laboratory tests:
- Analysis of clinical material (hair, nails or skin flakes);
- Wood's lamp examination (examination using ultraviolet light);
- Blood test (to identify fungal microorganisms);
- Biopsy (in rare cases).
Inguinal ringworm
Fungal skin diseases are common diseases, which, along with trichophytosis, include dermatomycosis inguinal. It mainly affects the groin area, sometimes spreading to the inner thighs and buttocks. Inguinal dermatomycosis is most often observed in residents of regions with warm climates and high air humidity. Men are especially susceptible to it.
Inguinal ringworm is a contagious disease and can be transmitted through direct contact with a patient, hygiene products or shared objects. Signs of the disease:
- severe itching and burning in the groin area, sometimes accompanied by severe pain;
- the appearance of a bright red or brown ring-shaped rash in the affected areas;
- peeling and cracking of the skin in the affected areas;
- redness of the affected skin and the appearance of small blisters.
Treatment of ringworm
Depending on the pathogen and severity of trichophytosis, treatment can be carried out both on an outpatient basis and in a hospital setting.
Treatment for ringworm should only begin after consultation with a specialist.
For mild trichophytosis, local treatment of the lesions with antifungal ointments is recommended. The duration of treatment for ringworm is from 7 to 14 days. Oral antifungal drugs are prescribed only for severe forms of trichophytosis.
For inguinal dermatomycosis, external treatment of lesions on the skin and oral antifungal medications are recommended. Patients with inguinal dermatomycosis must strictly observe the rules of daily personal hygiene.
Traditional medicine and trichophytosis
Trichophytosis can be cured with medication, but folk remedies can be used as an additional method of therapy. However, before turning to alternative medicine, you should consult your doctor.
- For various skin diseases, tar is widely used, which has anti-inflammatory, drying and antiparasitic effects. To effectively eliminate foci of ringworm, you need to mix tar and butter, and apply the resulting mass to the sore spots.
- Everyone knows about the beneficial properties of garlic, which is considered a natural antibiotic. For trichophytosis, it is necessary to lubricate the inflamed areas with garlic juice or apply it in grated form.
- There are various herbal preparations from which you can prepare an infusion and take it orally. For example, calendula flowers, St. John's wort, horsetail, toadflax, calamus, string, all these herbs are taken in equal proportions. Pour boiling water over a small amount of the mixture and leave for several hours.
- Against trichophytosis, dark, seedless raisins are used, which contain substances that have a detrimental effect on trichophytons. To do this, place well-washed raisins in hot water for several hours and then grind them with a blender. The resulting mass should be applied to sore spots.
- Against fungal infections on the scalp, you should rub an infusion of chamomile petals into it.
- You can prepare your own propolis ointment, which is also effective against this disease.
Medical certificate
Trichophytosis is a dermatological disease of a fungal nature. It affects the hair, skin and nails. Initial signs of infection appear within the first week. With timely treatment, the disease goes away without a trace. Otherwise, a progressive pathological process can lead to disruption of the integrity of the skin and permanent baldness.
Trichophytosis in humans comes in several types: superficial, infiltrative-suppurative (deep), chronic. Each form of the disease is characterized by a specific clinical picture. They will be discussed in more detail below.
Diagnostic methods
Trichophytosis in humans is a dermatological disease. Therefore, if you suspect an illness, you should contact a dermatologist for help. There is also another specialist working in this area - a mycologist.
Diagnosis of a fungal infection is quite simple. First, the doctor performs a physical examination, sometimes supplemented by a Wood's lamp examination. It is necessary for differentiation from microsporia, which gives a green glow in the light of this device.
The next stage of diagnosis is microscopic and cultural examination of scrapings from the affected areas. This approach allows you to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. During the procedure, the doctor scrapes off flakes of skin or fragments of hair with a scalpel, and then examines them under a microscope and sows them into Sabouraud's nutrient medium.
In practice, microscopic and cultural examinations are not always prescribed. An urgent need arises only when it is necessary to determine the type of pathogen and its sensitivity to antifungal drugs. Inexpensive but effective remedies against trichophytosis will be mentioned below.
Differences from microsporia
Quite often, trichophytosis is confused with microsporia.
But these diseases are characterized by the presence of certain distinctive features. Trichophytosis is popularly called lichen. During the pathological process, hair breaks off. This is why it feels like the hair has been cut. Trichophytosis and microsporia are fungal diseases. The distinctive features between them are fungi, which cause a pathological process . Ringworm occurs due to exposure to trichophyton fungi, and microsporia occurs due to microsporum. Since these diseases are characterized by almost the same symptoms, they are both called ringworm.
Trichophytosis and microsporia are quite difficult to distinguish. That is why, to determine ringworm, the patient is recommended to undergo appropriate laboratory tests.
Prevention of lichen
Prevention of ringworm involves timely identification of the disease in a child or adult and immediate isolation from others for the period of treatment. The personal belongings of the infected person must be thoroughly disinfected. Relatives and close people who have had contact with the infected person in the last 1-2 weeks should also be examined for microsporia infection.
Important! If there are pets in the patient's home, they are the first to be examined. Everyone's beloved pets are very susceptible to this disease.
The disease in animals can be determined by the presence of bald areas on the face, ears, and paws.
Transmission routes
The main carriers of fungi are considered to be street animals, as well as young and middle-aged children. In the first case, the disease will be more severe. The thing is that ringworm can also be caused by other fungi. However, trichophytons are the most common causative agents of the disease.
The fungus tends to persist on household items. Therefore, the main route of transmission of the disease is through household contact. It is not at all necessary to have direct contact with an animal or an infected person. Trichophyton spores easily spread through the air and quickly “take root” in the body.
On the other hand, after direct or indirect contact a person does not always get sick. If the fungus simply gets on the skin, it will be destroyed by the immune system. For infection to occur, predisposing factors must be present. These include traumatic damage to the skin, prolonged exposure to high humidity and a decrease in the body's defenses.
Treatment
To treat ringworm of the superficial form and the chronic form of trichophytosis, antifungal ointments Mycospora, Lamisil, clotrimazole, exoderil, 10–20% sulfur ointment, 10% sulfur-tar ointment, 10% sulfur-salicylic ointment are used. The affected areas are initially wiped with 2–5% tincture of iodine, and after a few hours are treated with ointment.
In the presence of multiple foci, significant inflammation and significant damage to the scalp, treatment of trichophytosis requires the use of combined hormonal drugs. In this case, systemic therapy is required, in which the hair on the head is shaved and fluffy hair on the body is removed using epilation.
One of the main treatments for ringworm is griseofulvin in tablets and ointments. In the chronic form, treatment of the scalp involves detachment of the stratum corneum in the affected area. To do this, apply a bandage with milk-salicylic ointment to the lesion for 2 days. Then it is removed and replaced with a compress with 2–5% salicylic ointment. After 2 days, remove the compress and use a blunt scalpel and tweezers to clean the stratum corneum with black spots. The procedure is carried out 2-3 times.
In the treatment of trichophytosis of the infiltrative-suppurative type, 2-3% salicylic ointment, absorbable ointments and disinfectant solutions are used to remove crusts.
Treatment of inguinal ringworm is similar to that of ringworm. But, unlike it, inguinal dermatomycosis does not require complex therapy. Treatment involves careful hygiene of the affected area, keeping it clean and dry, and treating it with topical antifungal medications. These can be creams, ointments, aerosols, which are applied to washed and well-dried skin in the affected areas.
Trichophytosis reviews
Pavel, 35 years old, Perm
Hello. I want to share my experience in treating this unpleasant scourge. We have a son. This year he went to first grade, but the school could be covered with a copper basin due to the fact that in the summer he contracted lichen in the village. Trichophytosis was on the arms and head. What he touched there, cats, dogs or goats, we never found out. Having discovered the first symptoms, we began to treat with improvised means. The wife and her mother flatly refused to use any pills and creams, arguing that they were terribly expensive and it was unclear what they were made of... For the first five days of the little one, they smeared them with birch tar. I am skeptical about such methods, but the result amazed me. After just a week, all the spots and bald spots are almost gone. Then the mother-in-law made a decoction of burdock, moistened the tampons and applied it to the sore spot. So another 5 or 6 days. Let me remind you: no pharmaceuticals. As a result, in a little more than two weeks the little one was completely relieved of ringworm, and he went to school normally. I wish you all health and goodness!!
Ira, 35 years old, Astana
My grandmother made a special tincture from celandine against ringworm (trichophytosis). After sunset, when the plant was ready to rest, the grandmother picked off the leaves and flowers, placed them in a dark container (or a bottle), poured a little diluted alcohol and left for 10-14 days, shaking the contents periodically. Afterwards, I filtered the tincture and applied the resulting solution to the areas affected by ringworm. 10 days of daily procedures and any fungus disappeared. Like this. I hope our old recipe helped))
Tatyana Aleksandrovna Pukhova
Dermatologist , 14 years of experience.
Generalist specialist. Engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the skin, nails, scalp, as well as sexually transmitted diseases.
Education: 2006 Diploma in General Medicine, Perm State Medical University
Advanced training courses: 2011 “Pillings of superficial-medium impact” 2013 “Plasmolifting in cosmetology and trichology” 2014 “Dermatovenereology”, South Ural State Medical University
Main causes of the disease
The causative agent of trichophytosis in any form is microscopic fungi of the genus Trichophyton. Their spores remain active for a long time and are easily transmitted from an infected person or animal. Depending on the source, the disease is divided by dermatologists into two types:
- Anthropophilic: characterized by receiving the pathogen from an infected person. The basis is direct tactile contact or the use of personal belongings with particles of the epidermis and hair residues.
- Zoophilic: transmitted from an animal that has lichen. Owners of domestic cats and free-ranging dogs may also encounter this problem. You can even get sick by coming into contact with fur or scales invisible to the eye.
The main factors that indirectly affect susceptibility to mycosis are weak human immunity, some chronic diseases or microcracks in the skin.