Venereology
2761
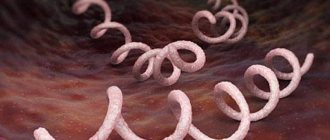
Syphilis is a venereal disease, its causative agent is Treponema pallidum. As a rule, this pathogen lives in the lesion - on the skin, in blood vessels, in nerve fibers. Every 33 hours, the pathogen multiplies by division. Most often, the pathogen enters through the mucous membrane and open wounds. Routes of infection can be sexual or domestic. Syphilis is one of the most complex diseases; it is characterized by a chronic nature with periods of exacerbations. In order to determine the presence of the disease in time, you need to know how it manifests itself, so let’s look at the symptoms of syphilis in women.
Warning signs
The first signs indicating infection may begin to bother you 21-28 days after infection. Primary symptoms include:
- A chancre on the genitals, in the mouth, or near the anus;
- Nodules and purulent rashes on the skin;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Deep rashes on internal organs.
Syphilis occurs in 3 periods, each of which is accompanied by its own symptoms:
- Primary;
- Secondary;
- Tertiary.
Preventive therapy
During treatment, sexual contact is strictly prohibited and it is highly advisable to limit any physical contact. To prevent household infection of people living in the same house as a sick person, it is important to maintain personal hygiene. A strictly individual towel, bath accessories, dishes, and bed linen are required. In some cases, the doctor recommends preventative treatment.
All sexual partners of the patient must be examined within 6 months (12 in the case of secondary syphilis).
An important issue is emergency prevention of syphilis. If there is a possibility that you could become infected with syphilis during accidental sexual intercourse, you must thoroughly treat the external genitalia with a disinfectant solution (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine). Women are advised to douche with this solution, men - injection into the urethra. Such methods do not provide complete protection against infection, but they reduce their likelihood. But even after this you should contact a venereologist for consultation. Your doctor will recommend additional preventive therapy that is appropriate for your case.
To prevent re-infection, all sexual partners should undergo examination, and if necessary, treatment
Symptoms of the primary period
At this time, the formation of chancre is typical. The location of this hard growth mainly depends on the type of sexual contact in which the infection occurred. It mainly forms on the labia, as well as on the pubis, but can appear in the mouth, abdomen, and anal area.
Often girls do not notice this primary symptom, since the formation appears in the rectum or inside the vagina.
Also, syphilis on the labia may be overlooked due to its painlessness.
The size of the chancre can be insignificant - from 1 millimeter, to quite impressive - 2 centimeters. This primary syphilide is an ulcer. Its shape is most often round, but on the mucous membranes it may look like a crack. Depending on their size, chancres are called dwarf and giant.
14 days after the appearance of chancre, syphilis in girls is manifested by enlargement of the lymph nodes that are located next to the formation. In addition to chancre, the following manifestations are also observed:
- Swelling of the genitals;
- Headache;
- Deterioration in general health;
- Increased irritability;
- Excitability;
- Body temperature is about 38 degrees;
- Joint pain;
- Feeling of aching bones;
- Syphilis discharge becomes thick, pus-like, itchy, and has an unpleasant odor.
This stage lasts for 6-9 days. After this time, numerous rashes begin to appear, which indicates the transition of the disease to the secondary period.
What is latent syphilis
The concept of disease is known to almost everyone, which cannot be said about its hidden form.
What is latent syphilis? This is an infection in which there are no external symptoms of the pathogen and internal lesions. But when the tests are taken, the research result turns out to be positive. The causative agent of the virus is Treponema pallidum. A history of latent syphilis, according to researchers, is associated with frequent and large-scale use of antibiotics by the world’s population. This is the main reason for the infection to pass into a latent asymptomatic form.
Symptoms of the secondary period
About 200 days after the formation of a chancre due to syphilis, women develop a rash all over their body. The rash affects not only the skin, but also bones and internal organs.
Roseola rash
In the secondary period, the most common symptom is a small, spotty rash. These rashes are very profuse and disordered. The color of the rashes is bright, and the shape is symmetrical. If the rash is not treated, it goes away on its own after 2 months, but a hidden secondary stage of the disease occurs in the body.
With a hidden course, the area of the rash becomes significantly smaller and it turns pale. Syphilitic rashes mainly form on areas of the body exposed to mechanical stress, for example, on the elbows, in the folds under the mammary glands, between the buttocks, and under the knees.
Papular syphilide
Along with roseola rash, papular syphilide often appears, manifested by dark red nodules, dense structure, and regular shape. The size of such rashes is similar to lentil grains, but smaller ones and, conversely, large formations the size of a coin can occur.
At first, these nodules are located abundantly, and with relapses they are larger, but few in number. Papular syphilide is usually localized on the feet and palms, on the chest, on the head along the hair, on the genitals, near the anus. During this period, the woman is bothered by weeping papules in the intimate area.
Baldness
Signs of syphilis in women can be supplemented in the secondary period by another very unpleasant manifestation - female pattern baldness. Hair can fall out all over the body, but mainly on the head. Often, syphilitic leukoderma appears on the back, chest and neck, looking like light round spots.
Infection during pregnancy
Detection of the virus during pregnancy is considered dangerous specifically for the health of the fetus.
Since in this case genetic deformities, miscarriage and even pathologies are possible, which can cause artificial termination of pregnancy. The disease is diagnosed by donating blood for RPGA and ELISA. This usually happens by accident during routine tests. Medical therapy is mandatory. If the treatment gives a positive result before the 20th week of pregnancy, the patient is allowed to give birth independently. If not, then a commission is assembled to schedule a birth by caesarean section. Therapy during pregnancy is of a general nature for the treatment of patients with syphilis.
Symptoms of the tertiary period
Today, the percentage of women with tertiary syphilis is extremely small, but such patients still exist.
As a rule, the tertiary phase occurs with a significant decrease in immunity. The main signs in the tertiary phase are gummas and tubercles on the skin.
Tuberous syphilide
Such formations are dense in structure, copper-red in color with a blue tint. The tubercles do not have a clear boundary. They are located asymmetrically. The shape of the tubercles is hemispherical or flat. Their size is comparable to a cherry pit. The tubercles are grouped, but they do not merge with each other. However, sometimes tubercular syphilide transforms into creeping syphilide, in which the rashes merge together.
Gummous syphilide
Gummas are formed under the skin, they are located in the fat layer. At first, gummas are not associated with the skin, they are painless. As the tertiary period progresses, the gummas become immobile and fuse with the skin. Their size increases and they reach the size of a walnut. Over time, the node opens, and a hole forms in its central part, from which a viscous liquid emerges.
As the disease progresses, the bumps and gummas become ulcers. When the ulcers heal, deep, star-shaped marks remain in their place. Such scars lead to severe modification of organs and tissues. For example, gummous syphilides that appear in the nose can cause complete destruction of cartilage. If gummas form in the internal organs, then their work is disrupted, in which case the death of the patient is possible.
Additional treatments for syphilis
When treating syphilis, to enhance the effect of traditional methods, non-standard methods of therapy are used, which increase the body’s ability to resist infection, force it to accumulate internal protective resources to fight the disease, and stimulate the immune system. These include:
- Oxygen therapy . The essence of this method of treating syphilis is that, along with injections of penicillin drugs, oxygen is injected under the patient’s skin. This element stimulates metabolic processes in affected tissues, normalizes redox reactions in cells, and increases the body's energy reserves. The course of oxygen therapy for syphilis is 10 - 15 sessions.
- Pyrotherapy . This is a method of artificially increasing the patient’s body temperature, which improves the formation of specific antibodies by the immune system, stimulates the production of gastric enzymes, activates the blood supply to pathologically altered tissues, and enhances the ability of phagocytes to capture and destroy Treponema pallidum.
- Vitamin therapy . When treating syphilis, vitamin complexes are used, which include B vitamins, ascorbic acid, etc.
- Irradiation with a mercury-quartz lamp . The use of this unconventional method helps reduce the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes, restores the body's strength, and puts the nervous system in order.
- Spa therapy . In the treatment of secondary and tertiary syphilis, when the internal organs and bone tissue of the patient are affected, he is prescribed sulfide, carbon dioxide, radon and iodine-bromine baths.
Alternative methods of treating syphilis increase the effectiveness of traditional drug therapy, but are not its substitutes. Therefore, at the first suspicion of the development of syphilis or typical symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor in order to prevent the disease from developing into a form that is difficult to treat.
Syphilis and pregnancy
Syphilis is extremely dangerous, and for pregnant women it is doubly dangerous, since there is a high risk that the child will suffer. Syphilis symptoms in women are often detected during this period, since the woman is regularly tested, but the infection could have occurred much earlier.
It is worth noting that syphilis is not an indication for abortion. A woman can undergo treatment while carrying a child. If it is not carried out, the child also has a chance of being born healthy, but it does not exceed 10%. The drugs prescribed to a pregnant woman with syphilis are not harmless, but they increase the chance that the child will be born without severe pathologies.
Many women are concerned that it is not safe to become pregnant after suffering from syphilis; this question is difficult to answer, since it all depends on the form of the disease and the presence of complications. If a woman has treated syphilis in the early stages, then she can safely become a mother.
Syphilis in women, stage 4
Without treatment, the disease progresses and goes through 4 stages: primary, secondary, latent and tertiary. It can be acquired or congenital (transmission route is in utero from an infected mother).
Syphilis manifests itself in a variety of ways and can mimic many other infections and immunological processes in later stages. That is why he earned the nickname “the great impostor.”
The causative agent of the disease, Treponema pallidum (treponema pallidum), can hardly survive outside the body. Transmission of the microbe requires direct contact with the carrier of the infection; the microorganism is exclusively a human pathogen.
Treponema does not withstand drying or exposure to disinfectants. Therefore, household transmission (for example, by sharing toilets) is practically impossible. Unprotected sex is a major risk factor for infection.
Syphilis remains common in many developing countries and in parts of North America, Asia and Europe, especially in the eastern part. Most new cases occur in women aged 20-29 years.
www.emedicine.medscape.com
Treatment of the disease
This is a serious disease that can seriously harm your health, so treatment must be immediate. The method of treatment depends on how the disease manifests itself, that is, on the stage.
Most of the drugs prescribed for syphilis are Penicillin. Treponema pallidum is sensitive to this group of drugs.
Primary syphilis begins to be treated with daily injections of Penicillin, followed by injections of Bicillin-3. Intramuscular injections are administered in 2 stages into the buttocks. The skin should be kept dry from the alcohol as it can destroy the penicillin. In addition to injections, the woman is prescribed antihistamines. Injections are given for 16 days.
Treatment of the secondary period is accompanied by a longer course of Penicillin injections. The number of injections is almost doubled. In addition to Penicillin, the patient is prescribed Doxycycline and Ceftriaxone during this period.
When treating the tertiary period, that is, the advanced stage of syphilis, injections are given with Penicillin and Biyonquinol.
Home remedies to treat syphilis
Traditional methods for the prevention of syphilis
Treatment of syphilis at home can be supplemented with traditional medicine. Healing compounds that include red wine and garlic are especially effective. To prepare a medicinal drink for the treatment of syphilis you will need:
- strawberry jam - 200 ml;
- cold water - 100 ml;
- wine - 400 ml;
- apple juice - 400 ml;
- garlic - 1 large head.
First, mix the jam with water and bring the mixture to a boil, then pour red wine and juice into it. Stir all ingredients, remove from heat and cool. Next, add crushed garlic to the liquid and leave for at least 3 hours. Then strain and drink 100-200 ml every day. As an alternative, you can use a drink that contains:
- red wine - 200 ml;
- lemon or cranberry juice - 100 ml;
- garlic - 1 large head.
To prepare a medicine for the treatment of syphilis, you first need to heat the wine, and then pour the juice into it and heat it again. Add chopped garlic to the cooled mixture, infuse the mixture, strain it and take it before bed every day. Another recipe for a drink with wine and garlic, which gives no less lasting results:
- red wine - 0.5 l;
- coffee powder - 0.5 cups;
- honey - 0.5 l;
- garlic - 1 piece;
- ground cinnamon - 0.5 tsp.
To prepare a healing liquid, add honey and cinnamon to the heated wine. Heat the liquid again and pour instant coffee into it, stir and add crushed garlic. Remove from heat and let the mixture sit for 30 minutes. Take 0.5 cups daily before bed.
Recipes for garlic treatment
The following healing mixture helps to support the body in the fight against syphilis:
- Antonov apples - 2 pcs;
- hawthorn berries - 1 cup;
- rose hips - 1 cup;
- garlic - 1 pc.
Mix pre-grated apples with hawthorn, rose hips and chopped garlic in a small container. Then pour 2 liters of boiling water over the mixture and leave for 2 hours. Strain the infusion and take 0.5 cups after meals.
When treating syphilis at home, you can use infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs:
- Hops. You need to take 2 tbsp. l. chopped hop cones and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for 2 hours and strain. Drink throughout the day, evenly dividing into 3 parts.
- Field yarutki. You should take 2 tbsp. l. herbs, pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave the liquid for 4 hours. Then strain and take 1 tsp. 5 times during the day.
- Sandy sedge. You need to peel and rinse the root of the herb, and then grind it in a meat grinder. Next, take 20 g of the mass and pour boiling water in a volume of 0.5 liters. Boil the liquid over low heat until it reduces by half. Then leave for 2 hours and then strain. Drink 50 ml. 4 times during the day.
- Burdock. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. finely chopped burdock root, pour 1 cup of boiling water and keep on fire for another 20 minutes. Take 1 tbsp of strained liquid. l. 4 times a day.
The use of the listed remedies at home can only be considered as additional, and not primary, methods of treating syphilis. They are not medicines that directly affect the causative agent of the disease - Treponema pallidum, as antibiotics do, but serve as means to strengthen the immune system and vitality of the body. Therefore, they can only be used in combination with medications prescribed by the attending physician.
Complications of the disease
Syphilis has a destructive effect on the body; it disrupts the functioning of many organs. Therefore, you need to know what syphilis looks like in women in order to cure it in time and prevent complications, which can be quite sad. If you start syphilis, you can get the following problems:
- Partial or complete loss of vision;
- Meningitis;
- Bone damage;
- Violation of the structure of the joints;
- Paralysis;
- Disability;
- Fatal outcome.
Syphilis can cause infection of all family members; in order not to risk health and life, it is necessary to treat any disease at the initial stage.
Rash in the fair sex
During the primary phase, one, painless node (papule) usually appears, which quickly collapses and becomes denser. The edge and base of the ulcer have a cartilaginous consistency to the touch.
Although classic chancre is not painful, it can cause discomfort if it becomes contaminated with bacteria or is located in the anal canal. Non-genital chancres occur most often over the neck, usually affecting the lips or oral cavity.
Secondary syphilis manifests itself differently in women, but usually involves a localized or diffuse mucous rash. Exanthema can be spotty, nodular or mixed.
Initial lesions are usually bilateral and symmetrical, pale red to pink in color (in fair-skinned individuals) or pigmented (in dark-skinned individuals).
The rash is separate, round, consists of uniformly colored spots with a diameter of 5-10 mm, distributed over the torso and limbs. After a few days or weeks, red nodular formations measuring 3-10 millimeters appear. The lesions become necrotic (purulent) and often spread to the palms and soles.
10-15% of patients with secondary syphilis develop painless superficial mucosal erosions on the palate, pharynx, larynx, vulva, or anal canal and rectum.
These spots are round, silver-gray defects with a red areola (edge). They are a reservoir of treponemes and a source of infection.
www.emedicine.medscape.com
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of syphilis consists of an external examination of the patient and laboratory tests. During the examination, primary or secondary syphilides are identified.
To identify methods of infection and determine the possibility of spreading the infection, anamnesis is taken. Using laboratory tests, it is possible to determine the presence of treponemes in the body and the presence of antibodies.
Unfortunately, many people are ashamed to go to the doctor and delay precious time for treatment. Today it is possible to test for syphilis at home. This test can be purchased online or at a regular pharmacy.
Classification of secondary syphilis
Fresh secondary syphilis - develops after primary syphilis and is manifested by an abundant disseminated small polymorphic rash, the presence of a hard chancre in the resolution stage and polyadenitis. Duration 2-4 months.
Latent secondary syphilis is characterized by the disappearance of clinical symptoms and is detected only by positive results of serological tests. Lasts up to 3 months or more.
Recurrent secondary syphilis - there is an alternation of relapses of syphilis with hidden periods. During relapses, the rash appears again. However, unlike fresh secondary syphilis, it is less abundant, larger and located in groups, forming arcs, rings, garlands and semi-rings.