Diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy is a type of mastopathy that has its own characteristics. Most often, the main symptom of this form of manifestation of the disease is tissue proliferation with a predominance of fibrosis.
In addition, one or more benign tumors appear in the breast. They come in different sizes and can be located in one breast or in both mammary glands.
The main symptoms of the disease are pain, the presence of lumps on palpation of the breast, specific discharge from the nipples, and swelling of the tissues. Often the disease changes the shape and size of the breast, which significantly affects the mental and emotional state of the woman.
Severe chest pain due to mastopathy worsens the patient’s quality of life, but in addition, lack of treatment can lead to quite serious complications that threaten the patient’s life. Therefore, under no circumstances should you hesitate to go to the doctor. And if any unpleasant symptoms occur, immediately undergo a full examination in a hospital.
…
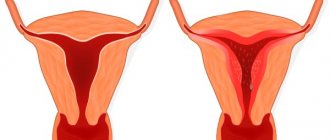
The structure of the mammary glands
The breast of an adult woman is a collection of connective, glandular and fatty tissues, conventionally divided into so-called “lobes”.
The mammary gland consists of about 16-20 lobes, and is an organ responsible for many processes in the female body, of course, the main one of which is breastfeeding.
As for the structure of the female breast, they consist of:
- chest;
- pectoral muscle;
- lobes of the mammary gland;
- areolas;
- mammary ducts;
- fatty tissue;
- skin.
There is no unambiguous treatment algorithm for diffuse mastopathy. Each case requires an individual approach. The advisability of using certain treatment methods can only be assessed by a mammologist.
If there is even the slightest suspicion of a possible malignant process in the mammary gland, the patient must be further examined. At the same time, an oncologist must necessarily participate in such additional examination.
In Russia, the traditions of self-diagnosis and self-medication are well developed, which is fundamentally contraindicated for any disease of the mammary gland - the cost of a mistake in self-treatment is too high. In this regard, we deliberately do not publish detailed information about treatment and limit ourselves only to general principles, otherwise this may lead to self-prescription of certain drugs.
1. Diet correction - it is necessary to exclude coffee, cocoa, chocolate, strong tea, and cola from the diet. It is recommended to widely eat seafood, fruits, and vegetables.
Traditional methods
Treatment with folk remedies is allowed only as an additional therapy to the main treatment.
Use:
- periwinkle . Fresh leaves of the plant are ground into a paste, mixed with honey and royal jelly, and taken a teaspoon three times a day;
- walnut partitions . The partitions of 25 nuts are filled with half a liter of alcohol. Infuse for 10 days, and then take 15 drops three times a day, diluting with water;
- herbal infusion . Juniper, yarrow, horsetail and corn silk are taken in equal parts, mixed, and a tablespoon of the mixture is poured with a glass of boiling water. Infuse and drink 50 grams three times a day;
- compress . Gauze is soaked in a solution of table salt and applied to the chest for 8 hours;
- cabbage compress. Apply butter and salt to a fresh cabbage leaf. The compress is applied to the chest and bandaged. It is better to leave the compress overnight;
- beet compress . Grate the raw beets, add a little 9% vinegar, apply to the chest and wrap with a warm scarf.
Causes of moderate fibroadenomatosis
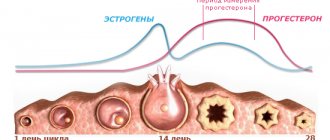
The main cause of the disease is hormonal disorders. Women with diffuse FCM have increased levels of estrogen in the blood. This occurs against the background of progesterone deficiency, which provokes the proliferation of gland tissue (connective tissue framework, alveolar epithelium). There is also an increased production of prolactin, a pregnancy hormone involved in lactation processes.
There are other provoking factors:
- injuries to the mammary glands due to prolonged wearing of uncomfortable underwear and compressive clothing, as well as blows;
- genetically determined predisposition, burdened heredity, the presence in the family branch of cases of breast cancer, mastopathy;
- treatment with hormonal drugs, use of hormonal contraceptives;
- diabetes mellitus, obesity;
- functional disorders of the endocrine system, thyroid diseases;
- sexual disorders, poor quality and irregular sex life;
- diseases of the reproductive system, diagnosed infertility, miscarriages, abortions, late pregnancy terminations.
It has also been established that diffuse FCM can occur during late pregnancy (after 35 years), short-term breastfeeding (less than 3 months) and complete refusal of breastfeeding. A woman’s lifestyle is also important: exposure to stress, drinking alcohol and smoking increase the risk of developing the disease.
The main cause of diffuse fibroadenomatosis of the mammary glands is hormonal disorders. As you know, the condition of the mammary gland is regulated by many hormones, the main ones of which are sex steroids (estrogens and progesterone) and prolactin. Luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones, corticosteroids, thyroxine and triiodothyronine, as well as insulin and some other bioactive substances also have an indirect effect.
· diseases of the genital area (ovarian cysts and tumors, polycystic ovary syndrome, chronic salpingoophoritis, uterine fibroids, endometriosis, etc.);
· unfavorable gynecological history (medical abortions, spontaneous miscarriages, early or late menarche, sexual infantilism, late childbirth, refusal to breastfeed or short-term lactation, lack of sexual activity, etc.);
· pathologies of the pituitary gland (adenomas, hemorrhages, brain injuries, infections of the nervous system - encephalitis, meningitis);
· diseases of the thyroid gland (thyroiditis of various etiologies, hypothyroidism, nodular, endemic, diffuse goiter, cancer);
· diseases of the adrenal glands;
· diabetes mellitus (especially type 2, in which there is abdominal obesity);
· liver diseases accompanied by its functional failure (chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis);
· obesity.
Disturbances in the hormonal sphere can be caused by an unfavorable environmental situation, poor diet, bad habits such as smoking and alcohol abuse, frequent overwork, and lack of adequate sleep and rest. More often than not, all these factors act together, aggravating the existing situation.
As mentioned earlier in this article, one of the main causes of mastopathy is hormonal imbalances in a woman’s body.
The work of the ovaries plays a huge role in this case. They produce most of the so-called female hormones.
They are mainly involved in the production of estrogen, androgen and progesterone. The slightest disruption in the production of these hormones affects the entire female body, and directly causes various diseases of the mammary glands, and mastopathy, as the most common breast disease in women.
In addition to this reason, it should be especially noted that mastopathy can occur as a result of failures in the normal functioning of the kidneys and adrenal glands, improper functioning of the liver, and improper functioning of the pituitary gland, which is responsible for the production of prolactin in women.
Many factors are to blame for the fact that over the past hundred years the number of women suffering from mastopathy has increased significantly:
- Increasingly older age of first-time mothers;
- Difficult childbirth;
- Increased number of abortions;
- Malfunctions of the ovaries;
- Refusal of breastfeeding or its sharp reduction, relative to the norms of feeding children in the past;
- The occurrence of lactostasis congestion;
- Excessive exposure to the sun's UV rays;
- Infectious diseases of the chest;
- Drinking alcohol and smoking;
- Use of hormonal contraception.
The most common type of fibrocystic mastopathy is its diffuse subtype. This form is characterized by an increase in the amount of glandular tissue and the formation of edema.
According to the symptoms and characteristic course of the disease, it is considered the simplest form of diffuse mastopathy:
- When the fibrous component predominates in mastopathy, a woman experiences swelling of the mammary glands, and the interlobular connective tissue septa increase and put pressure on all surrounding tissues of the chest, the lumens of the ducts narrow over time, and sometimes fuse completely.
- There is also a variant with a predominance of the cystic component. With this variant of the disease, cavities are formed in the mammary gland, clearly separated from other tissues, filled with liquid, varying in composition, and depending on the degree of the disease.
- The mixed form of mastopathy is characterized by both an increase in lobes and the proliferation of glandular tissue in the mammary gland. This form is the most difficult to treat and requires an individual approach when prescribing a treatment regimen for the disease.
The nodular form of fibrocystic disease is much less favorable.
In this case, in addition to the disorders described above that are characteristic of the diffuse form of mastopathy, the presence in the mammary gland of one or several nodes, which most often represent a fibroadenoma or adenoma, is added.
Fibroadenoma is a fairly common benign tumor, which affects mainly women of reproductive age, less often adolescents.
This neoplasm can have different sizes, from a pea in diameter to a tumor reaching up to 15 cm.
The situation is much worse with the nodular form of nodular fibrocystic mastopathy, represented by nodes with the proliferation of glandular tissue. Atypical hyperplasia is the medical name for nodes of this type. In cases of manifestation of nodes of this nature, mastopathy turns into oncology in every fifth woman
Mixed fibrocystic mastopathy is a combination of nodes, cysts and compactions. Most often occurs in women under 35 years of age. The early stage is very difficult to determine due to the absence of any discomfort in the area of the mammary glands, and can most often be determined only during an annual examination by a mammologist.
Over time, all formations begin to grow, which leads to compression of the nerve endings, pain, a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the chest area.
As the name of this form of mastopathy suggests, its main feature is that the disease occurs in both mammary glands.
A completely natural point is that with a bilateral course there can be the same different forms of the disease as with a unilateral course, but still more often women encounter bilateral mastopathy with a diffuse nature of mastopathy in the initial stage.
This is due to the fact that the form with the formation of nodes is characterized by the formation of single or multiple cysts or nodes in one breast.
The mechanism of development of mixed breast fibroadenoma is a change in the level of sex hormones, which provokes the influence of several factors:
- Severe, prolonged stress, accompanied by negative emotions.
- Heredity with changes in hormonal levels realized at the genetic level.
- Unfavorable gynecological history, which includes difficult childbirth, artificial termination of pregnancy, cesarean section, inflammatory diseases, complete lack of sexual activity.
- Early puberty in a girl.
- The climacteric period, during which there is an age-related decline in the functional activity of the gonads.
Late childbirth is a provoking factor for the occurrence of breast diseases - Negative environmental conditions, exposure to ultraviolet radiation, ionizing radiation, toxic compounds.
- Pregnancy and childbirth over 40 years of age.
- Decreased activity of the thyroid gland with a decrease in the level of the hormones thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
- Chronic somatic and endocrine pathologies, including diabetes mellitus, diseases of the heart, blood vessels, liver, kidneys.
Etiology
There are many reasons for the development of DFCM. The most common factor that provokes the occurrence of this pathology is an imbalance between estrogen, progesterone and prolactin. “Jumps” in the level of these hormones negatively affect the condition of the mammary gland tissue, which provokes the occurrence of pathological processes in them.
During menopause, the organs of the reproductive system become less active, therefore, the production of sex hormones decreases sharply. This entails a metabolic disorder in the cells of the mammary glands with their subsequent proliferation.
But an imbalance between sex hormones is not the only reason for the development of DFCM. There are many other factors that can lead to its occurrence. This:
- Hereditary predisposition to mastopathy and oncology.
- Mechanical damage to the mammary glands that occurs when wearing an incorrectly fitted bra, surgery, or a fall.
- Long-term use of oral contraceptives, drugs for ovarian stimulation before IVF, incorrectly selected hormonal therapy in the treatment of other diseases.
- Thyroid pathologies.
- Diseases characterized by impaired metabolism, for example, diabetes.
- Having excess body weight.
- Prolonged absence of sexual intercourse.
- Previous medical and surgical abortions, miscarriages.
- Infertility.
- Short lactation or its complete absence after childbirth.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the reproductive system.
- Smoking and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Sharp weight loss, adherence to mono-diet.
Before treatment, it is necessary to establish and, if possible, eliminate the factor that provoked the development of the disease. This will avoid complications and relapse of the pathology in the future.
What is it - moderate fibrocystic mastopathy?
There are three stages of mastopathy:
- initial;
- moderate;
- expressed.
At the initial stage, there are no tumors or cysts in the breast. Physically, the woman does not feel unwell or uncomfortable.
The moderate stage appears after the initial stage. Russian women rarely go to the doctor for a preventive examination, so FCM is most often detected at the second (moderate) stage.
At this stage, cysts or tumors have already formed in the breast, and there are also fibrous seals (overgrowth of connective tissue). Cysts and fibrosis, growing, put pressure on the milk ducts, which causes pain. Pain with moderate FCM is temporary. For example, pain may occur when pressing on the chest or in a certain position.
After pain occurs, a woman turns to a mammologist. The doctor conducts an examination. On palpation, compactions of an unknown nature are detected. Cysts and nodes have clear boundaries and are well felt upon palpation. Fibrosis is quite difficult to detect.
It can spread into the interlobular space or block the milk ducts. After the examination, the doctor will refer the patient for an ultrasound or x-ray. The pictures will tell you about the full picture of the disease. If necessary, the mammologist will refer the patient for additional examinations (puncture, biopsy) and tell her about the treatment regimen.
At a moderate stage, in addition to pain, lumps appear in the chest. Attentive women detect these lumps even before going to the doctor. If no fluid is released from the nipples, and the pain is not severe, then there is no inflammation. In this case, you should not postpone contacting a mammologist, but there is nothing to worry about.
It is at the moderate stage that mastopathy is most often detected. Typically, this form can be treated with medication. If the neoplasms are small, do not grow and do not cause discomfort, then it is enough to control their condition. If the tumors are large and constantly increasing in size, they need to be removed (surgically).
At a moderate stage of the disease, fluid may be released from the chest. It should be odorless, transparent or milky in color. If an unpleasant odor appears, you should immediately contact a mammologist. Most likely, inflammation of the cyst has appeared.
The pronounced form of FCM means that the tumors are visible to the naked eye. The shape of the breast is externally changed due to internal seals. The woman experiences severe constant pain.
What is moderate fibrocystic mastopathy?
This disease is a set of pathological changes in the mammary gland in the form of neoplasms, nodules and other benign changes.
However, despite its benign nature, experts consider fibrocystic disease to be a precancerous condition.
Fibrocystic mastopathy (FCM) occurs in 70% of cases. It is characterized by the appearance of compactions in the ducts and lobules of the breast, while cysts and adenomas are also found.
That is, both fibrous and cystic changes are observed. The mixed form is the easiest to detect: the outline of the breast has a pronounced asymmetrical appearance, there is noticeable pain, the breast is heavy and hot. An increase in body temperature is very likely.
There can be many reasons for the occurrence of FCM, the main ones include:
frequent abortions;
- heredity;
- abrupt cessation of breastfeeding;
- stress;
- hormonal diseases.
Cysts have clear outlines, can be felt as elastic seals, and the edges can be determined without ultrasound. Fibrous changes are revealed by palpation. Symptoms also include:
- soreness in the chest area.
- Discharge from the nipples (liquid, with an unpleasant odor, similar to pus).
- Breast asymmetry.
Diagnostics
Any signs of the disease are a reason to visit a doctor, since this disease must be treated. To clarify the diagnosis, patients should perform a number of actions:
- Consult a mammologist. (The doctor will ask questions regarding the time when the first symptoms of the disease were discovered, inquire about the patient’s complaints, collect an anamnesis (history) of the disease. Then the specialist will examine the mammary glands and palpate them.)
- Do an ultrasound of the mammary glands.
- Get a mammogram.
- If there are lumps or cysts, undergo a breast biopsy, and the resulting material will necessarily undergo cytological examination. Nipple discharge will be examined in the same way. (These studies are necessary to exclude the possibility of oncology.)
- Consult a gynecologist.
- Visit an endocrinologist.
- Donate blood for hormonal status, tumor markers, as well as do biochemistry and general analysis.
Classification
The diffuse form of the disease is divided into:
- adenosis – mastopathy with a predominance of the glandular component;
- fibrocystic – mastopathy with a predominance of the cystic component;
- fibroadenosis – mastopathy with a predominance of the fibrous component;
- sclerosing adenosis;
- mixed form.
In terms of localization, diffuse FCM can be unilateral or bilateral (affecting one or both mammary glands). According to the severity of clinical manifestations, moderate, minor and severe forms are distinguished.
Symptoms of mastopathy in women
The main symptom is the presence of a lump in the thickness of the mammary gland. The cystic node can be easily felt upon palpation. You can discover it yourself. Also, the mammary gland begins to swell and hurt. Having become heavy and painful, the gland causes discomfort. The pain can be aching, radiating to the armpit or shoulder blade. It can appear either constantly or periodically. With suppuration, chest pain intensifies.
With fibrocystic mastopathy, a light secretion may be released from the nipples. This is due to the development of a cystic cavity, inside of which there is serous fluid. Cysts can be single or multiple.
The lymph nodes in the armpits become enlarged. Mastopathy is characterized by engorgement of the glands, pain when raising the arms, and swelling of the breasts. These are the main signs of pathology. As photos and videos show, the affected mammary glands are subject to deformation. Focal pathology begins to predominate in their structure. Over time, it can develop into cancer.
Pregnancy and illness
With diffuse fibrocystic mastopathy of the mammary glands, pregnancy and a successful birth are possible. If conception occurs, it is important to inform your doctor. Mammography, examination of the milk ducts by injecting dyes, and other complex procedures are not recommended for pregnant women. It is recommended to be careful when treating with herbs.
Typically, expectant mothers are prescribed light maintenance therapy with hormonal correction. The doctor can prescribe safe herbal medicines that have a calming, decongestant and analgesic effect.
Breastfeeding is also allowed with diffuse FCM. Often it helps to correct the patient’s condition. Cysts may decrease in size or disappear altogether. The only thing is that it is important not to feed the baby for too long (no more than 12 months). Otherwise, the risk of tumors increases.
Many doctors consider pregnancy the best way to cure fibrocystic mastopathy, and even recommend that women become pregnant to recover from breast diseases.
The thing is that during pregnancy, a woman’s body releases a large amount of progesterone, which helps treat the disease and restore hormonal balance in the female body.
An important factor is also that while carrying a child, the female body receives a kind of impetus to renew cells and improve the functioning of all vital systems.
Statistical studies show that more than 80 percent of women after pregnancy are completely cured of mastopathy. Long-term lactation also promotes healing.
This is explained by the fact that during breastfeeding, the process of renewal of mammary gland tissue accelerates, and fibrosis and compactions resolve on their own.
After the birth of a child, a woman with a history of mastopathy must have a preventive consultation with the attending mammologist, since the risk of lactostasis and congestion in the diseased breast is very high, and can cause further development of the disease.
Treatment
If mastopathy is detected, therapy must be carried out without fail. And the sooner it starts, the lower the risk of serious complications. How to treat is determined only by the doctor, taking into account the results of the examination of the patient and her age category.
Conservative therapy for FCM is carried out only with a diffuse form of development of the pathology. Both hormonal and non-hormonal therapy can be used here. The latter implies the reception:
- Multivitamin complexes.
- Iodine-containing drugs (prescribed if a woman has thyroid pathologies).
- Sedatives, since any stress can lead to progression of the disease.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Herbal medicines and diuretics.
Conservative treatment for mastopathy also includes following a special diet that helps restore hormonal levels without the use of drugs. Nutrition for mastopathy completely excludes the following foods:
- bakery products;
- pasta;
- semolina;
- corn;
- White cabbage;
- confectionery;
- sauces (mayonnaise, ketchup, etc.);
- butter and margarine;
- pickles;
- smoked meats;
- semi-finished products;
- canned food;
- carbonated drinks;
- black tea and coffee.
The diet also completely excludes the consumption of fatty and fried foods. The main diet should be:
- legumes;
- fresh vegetables and fruits;
- nuts;
- seafood;
- lean meats and fish;
- dairy and fermented milk products.
And also a diet for mastopathy requires adherence to a regimen - meals should occur at the same time at least 5 times a day. In this case, a portion of food should not exceed 200 g.
We recommend reading: folk remedies for FCM
If non-hormonal therapy does not produce positive results, then treatment is carried out using hormonal drugs. In this case, the main emphasis is on the use of gestagens, androgens, inhibitors of prolactin production or antiestrogens. Drugs are prescribed on an individual basis after receiving the results of a hormone test.
If no positive dynamics are observed during hormonal therapy, the pathology is treated through surgery. During the operation, sectoral resection of the mammary gland or enucleation of the tumor can be performed.
Mastopathy is not a death sentence. If a woman promptly seeks help from a doctor, then she has a chance to get rid of this pathology without consequences, and without even resorting to surgery.
Echography
Echography is nothing more than a study of the mammary glands using ultrasound machines. Echography to detect mastopathy is carried out using modern sensors with increased resolution up to 10 MHz.
Conducting echography contributes to:
- Detecting and measuring the presence of cysts of even the smallest size in the breast. Also, a highly qualified specialist, using ultrasound machines, can identify the nature of the cystic formation: its benignity, or atypicality, which may indicate the malignancy of the neoplasm;
- Assessing the condition of the lymph nodes in the chest, armpits and tissues closest to the chest, to determine the spread of the disease in the body;
- Detection of adenomas, fibroadenomas and cancerous nodes in the mammary glands
- Detection of dilations in the milk ducts.
Carrying out echography helps not only to record and analyze examinations, but also allows you to monitor dynamic changes in the course of the disease. In addition, it is worth noting that echography is a harmless and informative examination.
Symptoms
Signs of mastopathy are individual in nature and they depend, first of all, on the form of the disease and the stage of its development. For example, if a woman develops fibrous mastopathy, she may notice small nodules on her breasts when palpating them, which have different sizes - from a few millimeters to 2 - 3 centimeters in diameter.
With the development of the glandular form of the disease, women experience symptoms such as pain and heaviness in the chest. Cystic mastopathy is considered an age-related disease and is detected mainly in women aged 40–45 years. This pathology manifests itself in the form of individual large formations, upon palpation of which severe discomfort is noted.
Regardless of the form of DFCM, all women experience swelling and swelling of the gland, which is always accompanied by severe pain. As the pathology develops, these symptoms intensify. And if at the initial stages of the onset of MFCM they bother a woman only at certain moments, for example, with a sudden change in body position or lifting weights, then after that they become permanent.
All this is complemented by signs of PMS syndrome. The woman becomes irritable, has frequent mood swings, sleep disturbances, etc. Headaches and weakness are also possible.
The main sign of the development of DFCM is discharge from the nipple, which has a mucous consistency and can be either yellowish or greenish.
Important! If, when pressing on the nipple, brown, red or black discharge is noted, you should immediately seek help from a doctor, as such a symptom indicates the development of oncology!
Disease prevention
Prevention measures:
- The main preventive measures for detecting and preventing the development of any type of mastopathy are regular visits to a mammologist.
- Women who have had or have relatives with various diseases of the mammary glands, or with oncology, need to visit a mammologist annually.
- Women, both those included and those not included in the risk group, in addition to consulting with a doctor, need to conduct regular self-examinations to check for lumps or changes in the symmetry of the mammary glands.
- It is worth remembering that the risk of mastopathy increases after forty years, due to hormonal age-related changes in the body and changes in general hormonal levels. Therefore, after a woman reaches this age, regardless of whether signs of the disease are detected or not, annual examinations to detect the presence of tumors in the breast are mandatory.
- To prevent the occurrence of mastopathy, a woman must monitor her hormonal levels and lead a healthy lifestyle. Thus, the risk of developing breast diseases is reduced if a woman takes various vitamin and mineral complexes containing iodine and all properly balanced microelements.
- It is impossible to imagine strong immunity of the body as a whole, without healthy, at least eight hours of sleep. To prevent the occurrence of mastopathy, you need to avoid stressful situations, and if stress cannot be avoided, then give the body the time necessary to restore the nervous system.
- It is important to know that, according to many experts, products containing cocoa butter provoke the occurrence of tumors in the breast. Therefore, limiting the consumption of chocolate and other products containing cocoa will reduce the risk of disease.
- Also, for preventive purposes, large amounts of direct sunlight should be avoided on the chest area.
- The correct choice of underwear plays an important role both in case of mastopathy and in preventing its occurrence. An incorrectly selected bra can cause deformation of the mammary glands, and also with various squeezing and selection of underwear that is not the right size, various kinds of deformations of tissues and ligaments can develop, which can cause the development of mastopathy or other breast diseases.
To prevent the development of mastopathy, you should adhere to a healthy lifestyle, stop smoking, and establish a proper and balanced diet. The menu should include more plant foods in the form of fruits, vegetables and various cereals, dairy products. It is also necessary to devote sufficient time to moderate physical activity.
In particular, frequent walks, cycling, swimming, skiing, and morning exercises are useful. If your job involves a sedentary lifestyle, you should take breaks whenever possible. Hormonal changes are often associated with stress. To increase stress resistance, you need adequate sleep of at least 7-8 hours a day.
At the first signs of mastopathy, you should contact a specialist for examination. All women, starting from 40 years of age, must undergo an annual mammogram or ultrasound examination of the mammary glands. Once a diagnosis of mastopathy has been established, you must strictly follow medical recommendations and regularly visit a doctor to monitor the dynamics of the disease.
Self-examination
Self-diagnosis is an integral measure for the prevention of moderate fibrous mastopathy and other pathologies of the mammary glands. Every woman who cares about her health should independently examine and palpate her breasts at least once a month. In this case, the symmetry of the mammary glands should be assessed, and attention should be paid to the appearance of any deformations or compactions in the breast structure.
When undergoing a course of hormone therapy, the drug is prescribed by a doctor in accordance with the test results
After diagnosis, the attending mammologist prescribes treatment. It mainly includes conservative therapeutic measures using various pharmacological groups of drugs:
- Hormonal drugs - oral contraceptives, including estrogens and progesterone, are usually used.
- Decongestant medications that reduce the feeling of heaviness and bloating.
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that reduce the severity of pain.
- Homeopathic remedies that have a complex effect. They are used only in combination with other drugs.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DVfHmXOByUg
Folk remedies, which include medicinal plants, are also used. You should not self-medicate, as this increases the likelihood of complications and negative health consequences.
Surgery for diffuse mastopathy is not prescribed. The pathological process is incurable. With the help of conservative therapy, it is possible to stop the progression of the disease. If treatment was started at the stage of fibrosis with replacement by connective tissue, irreversible residual effects remain in the breast. After cessation of therapy, re-exacerbation of the disease is possible.
Compliance with preventive measures reduces the risk of the disease and promotes a speedy recovery if it occurs. These include: giving up bad habits, avoiding stressful situations, choosing the right underwear, maintaining an active lifestyle, reducing salt consumption, timely treatment of diseases of the pelvic organs.
It is important to competently select hormonal contraceptives and regularly visit an oncologist and mammologist (at least once a year). Breastfeeding a child for more than 6 months reduces the risk of developing cancer by 2 times.
All women, including healthy ones, need to learn how to check their mammary glands on their own. This advice is especially relevant in the periclimacteric period (after the age of 45). This is done by visually examining the breast in the mirror and feeling it while lying down and standing. If any abnormal lump is detected, you should consult a doctor.
Despite the benign course, fibrocystic changes are a favorable background for the development of malignant diseases. With active proliferation (growth) of affected cells, the risk of cancer is 32%. With less activity of the pathological process, the risk decreases to 1%.
general information
DFCM is a complex disease in which the development of abnormal growth of gland tissue is observed. In this case, the following processes are noted - some cells begin to actively divide and grow, while others, on the contrary, regress, which causes an imbalance between the glandular and connective tissue components of the organ. This, in turn, entails a change in metabolism in the glands and the development of inflammatory processes, followed by the formation of small cysts inside the organ.
It is believed that all processes occurring during the development of mastopathy are benign in nature. However, it should be noted that their occurrence is an excellent soil for the formation of a malignant tumor. Therefore, this pathology is usually perceived as a precancerous condition.
The process of converting DFCM into oncology depends on several factors: the degree of proliferation of the affected tissues, cell activity and the treatment that the woman receives. Moreover, the earlier therapy begins, the lower the risk of developing cancer.
Important! In most cases, DFCM is found in women of reproductive age, since during this period there is increased activity of the mammary glands.
As a rule, at the initial stages of the development of this pathology, women do not go to doctors, since they perceive the unpleasant sensations arising in the chest as temporary discomfort. This is the biggest mistake, since DFCM tends to progress and can lead to serious consequences. That is why every woman should pay special attention to the condition of her breasts and, if primary signs of mastopathy appear, immediately seek medical help.
Preventive measures
To reduce the risk of developing mastopathy, you must:
- promptly identify diseases of the genitourinary and endocrine systems and treat them efficiently;
- monitor the stability of the menstrual cycle and, if necessary, adjust it;
- regularly check the condition of the thyroid gland;
- choose the right bra;
- have regular sex life;
- prevent abortions;
- breastfeed your baby for a long time;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- select contraceptives only together with a competent specialist;
- do not take hormonal medications unless absolutely necessary;
- protect the chest from injuries and bruises;
- Don't sunbathe topless.