The ankle joint is the connection between the talus bone of the foot and the bones of the lower leg. The joint provides dorsal and plantar extension - flexion of the foot and its lateral movements. Normal functioning of the ankle joint is the key to normal motor activity. But he experiences the impact of the mass of the human body. If a person suffers from excess weight, then the load on the ankle joint increases, it may become “overloaded” and, as a result, deformation of the joint occurs and deforming arthrosis occurs.
The cause of arthrosis is not only overload, but also the presence of herniated discs or pinched nerves. Disturbances in the functioning of the spine lead to unfavorable changes in the lower leg and foot.
Arthrosis can also develop as a result of injury - this is traumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint. It occurs especially often when the injury is ignored, not treated at all, or not treated.
The heaviest load is located in the ankle joint.
Other causes of the disease are known:
- metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, gout, etc.), which causes the deposition of salts and other elements that lead to inflammation of the tissues around the joint and its destruction;
- arthritis and other inflammatory processes that occur in the tissues of the body.
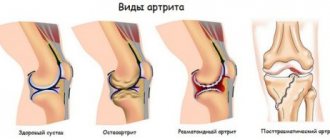
Arthrosis of the ankle joint - symptoms and treatment regimen
Ankle arthritis is an inflammatory disease that occurs against the background of other systemic diseases of the body. Infection with infectious pathologies can provoke the problem. Penetration of the pathogen into the joint cavity occurs by hematogenous or lymphatic route.
Rheumatoid arthritis of the ankle occurs equally in patients of any age. Various reasons can provoke the development of pathology, but most often the disease begins after injury.
If treatment for ankle arthritis is not started promptly, the patient may lose mobility forever. Irreversible consequences arise. The cartilage tissue is destroyed, joint movement is impaired and disability occurs.
Arthritis of the ankle - external manifestations of pathology
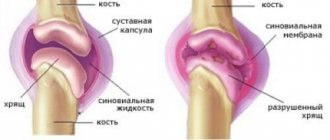
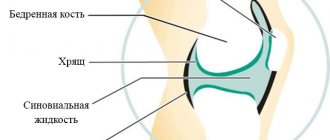
The ankle consists of 4 bones: the tibia and fibula of the leg, the calcaneus and the talus of the foot. The abundance of ligaments, as well as the peculiarity of the structure of the joint, provides the possibility of movement along several axes, including rotating ones.
Between the bony processes there is cartilage tissue, which ensures painless movements and shock absorption. All components of the joint are enclosed in a synovial bursa, which contains synovial fluid. The latter ensures mobility of the articular surfaces relative to each other, shock absorption and nutrition of cartilage and bone tissue.
The ankle joint bears a colossal load due to the weight of the entire body. Restriction of his mobility makes it impossible to walk. A large load leads to extreme sensitivity of the joint components to any pathological influences and the rapid development of the inflammatory process, that is, the development of arthritis.
Regarding life, arthritis has a favorable prognosis, only in exceptional cases putting it at risk. Thus, rheumatoid arthritis when the heart valves are damaged can lead to heart failure and death.
However, in a fairly large proportion of cases, arthritis is a disabling pathology, especially if left untreated.
Arthrosis of the ankle joint is a pathology of inflammatory-destructive nature, which not only brings significant discomfort to the patient, but can cause him to lose the ability to fully move. The progression of pathology gradually leads to disability of the patient, and therefore the problem of arthrosis does not lose its relevance.
In most cases, older people, mainly women, are prone to developing ankle arthrosis, the symptoms and treatment of which will be described below, due to the hormonal characteristics inherent in the female body. However, in some cases, arthrosis can develop in fairly young patients.
Arthrosis of the ankle joint: causes of pathology
In most cases, arthrosis of the ankle joint is the result of a combination of several factors. Among the most significant are:
- natural age-related changes in the body - during the aging process, the trophism of tissues gradually decreases, blood circulation in them slows down, the layer of cartilage covering the articular surfaces becomes thinner, decay processes increase in the cartilage cells, bone tissue also becomes more fragile due to a decrease in the content of organic components in it and disorders of calcium metabolism - thus, over time, the articular surfaces become exposed, bone growths appear on them, and arthrosis develops;
- hormonal imbalances, hormonal characteristics - the level of female sex hormones is directly related to the process of calcium metabolism in the body, which affects the condition of both bone and cartilage tissue. In addition, all metabolic processes in the body are interconnected in one way or another, so hormonal fluctuations, even at first glance not related to the joints, can also affect their condition;
- joint injuries - both acute and chronic; post-traumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint is a common complication of foot injuries;
- excessive physical stress on the ankle due to professional activities or sports, dancing;
- excess body weight: even a few extra pounds create additional stress on the feet, which leads to gradual degradation of cartilage tissue;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes that cause uneven distribution of the load on the foot;
- the patient’s dietary habits can also serve as a provoking factor for arthrosis;
- some somatic diseases;
- introduction of infection into the joint when it is injured or from other infectious foci in the body (teeth affected by caries, kidneys, tonsils);
- hereditary predisposition to arthrosis.
Arthrosis of the ankle: symptoms
Symptoms of arthrosis, as a rule, are quite characteristic. The first symptom that usually attracts the patient’s attention is pain in the joint. At the beginning of the disease, it occurs after a load on the joint and goes away on its own after rest. With the progression of the pathological process in the cartilage, the pain becomes constant and occurs at rest.
An early manifestation of ankle arthrosis is stiffness in the affected joint. It creates a feeling of stiffness in the foot, which makes it difficult to walk. However, after 10-15 minutes of walking around the house or doing simple exercises for the feet, the stiffness disappears on its own.
A characteristic sign of arthrosis is a crunching, clicking sound in the joint when moving in it. It is a consequence of the appearance of bone growths on the articular surfaces, which interfere with the normal sliding of the parts of the joint relative to each other.
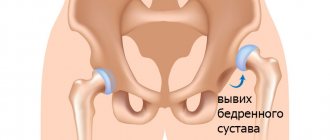
Immobility of the affected joint gradually increases, and therefore atrophy of muscles and tendons can develop. The consequence of this can be various displacements of the articular surfaces, joint subluxations.
With intense inflammation in the joint, inflammatory changes can be noticeable to the naked eye: swelling of the skin and tissue in the area of the affected joint, increased skin temperature, and redness. General manifestations of inflammatory intoxication may also occur: weakness, nausea, fever.
Degrees of arthrosis of the ankle joint
Arthrosis of the ankle of the 1st degree corresponds to the very first manifestations of the disease and minimal changes in the tissues. As a rule, at this stage the symptoms are insignificant; most patients do not pay attention to the signs of the disease at all, considering them to be a consequence of joint overload. At this stage, the main concerns are morning stiffness and moderate pain after physical work, which goes away on its own. The range of motion in the ankle is the same. On x-ray, changes at this stage are usually minor.
Arthrosis of the ankle of the 2nd degree corresponds to the stage of the height of the pathological process. At this stage, cartilaginous tissue is destroyed, and bone outgrowths - osteophytes - appear in its place. Clinically, this is manifested by constant pain in the joint, which is disturbing both during movement and at rest, crunching when moving, and decreased mobility of the joint.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mxbmf9Xo4dA
Arthrosis of the 3rd degree of the ankle corresponds to an advanced stage of the pathology, when pain becomes constant and mobility in the joint practically disappears. The foot loses flexibility and shock-absorbing properties, walking becomes difficult, grade 3 arthrosis of the ankle joint actually leads to disability.
Deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint
Deforming arthrosis of the ankle is a pathological process that leads to significant changes in the shape of the articular surfaces. In most cases, it is a consequence of chronic excessive load on the joint. The progression of the pathological process quickly leads to deformation of the joint and loss of mobility.
Treatment of ankle arthrosis
The treatment program is determined by the doctor after examining the patient and making an accurate diagnosis. Among the diagnostic measures, in addition to questioning and examining the patient, there are laboratory tests, as well as instrumental techniques (fluoroscopy, tomography, ultrasound examination of the joint).
First of all, you should take into account: the earlier treatment measures are started, the more effective they are. That is, the best solution would be to visit a doctor, undergo an examination and begin therapy literally from the first symptoms of arthrosis - when irreversible destruction in the tissues of the joint and deformation of the bones that form it have not yet developed.
Treatment of osteoarthritis begins with conservative therapy. It is aimed at relieving inflammation and relieving pain, for which non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers are usually used. At the same time, one should remember the possible side effects of such drugs - NSAIDs have an ulcerogenic effect on the digestive system, which is why their long-term, unsystematic use can lead to inflammatory pathologies of the stomach and duodenum. Drugs in this group are taken only as prescribed by a doctor.
Taking chondroprotectors, for example, the drug Dona, has worked well for arthrosis. The active ingredient of the product is crystalline glucosamine sulfate, it is a natural component of healthy cartilage. Without glucosamine, natural metabolic processes in cartilage tissue are impossible, since only in its presence is it possible to produce the structural basis of cartilage, proteoglycan proteins.
Taking a chondroprotector allows you to stimulate metabolic processes in cartilage tissue, eliminate inflammation in it, and slow down the destruction of cartilage. However, to obtain a sufficient effect from treatment, it is necessary to start taking chondroprotectors as early as possible, and also take them for a course of at least three months.
Treatment of leg swelling
In order not to aggravate circulatory disorders due to swelling of the legs, it is necessary to use a complex of microelements.
For example, when consuming manganese, the state of blood clotting improves; when consuming cobalt, the severity of swelling is significantly reduced. It is important that the body receives enough iodine. To treat swelling of the legs, medications in the form of gels and ointments are successfully used. Their purpose is for external use, and they effectively help eliminate both swelling and heaviness in the legs and pain. The most famous drugs are troxevasin, venorutin and lyoton.
My legs are swollen, what should I do?
If your legs swell, what should you do? Use special ointments such as Essaven gel, Troxevasin, Lyoton, Venitan and heparin ointment. These ointments contain heparin and rutin. They help strengthen the capillary system. Ointments based on horse chestnut work well.
1.
Change shoes throughout the day and avoid wearing high platform shoes;
2.
If your feet are swollen, it is not recommended to wear the same shoes for more than two days;
3.
Try to rest your feet, massage and stroke them;
4.
Using special therapeutic stockings or tights that prevent the appearance of edema;
5.
To avoid swelling of the legs, you should try to consume less water and salt. Do not drink carbonated drinks and water;
6.
My legs are swollen, what should I do? Every day, try to do a foot massage and special baths to eliminate swelling;
7.
At home, lie down on the floor and raise your legs, resting them directly against the wall for about fifteen minutes. After this, vigorously massage your legs, starting from the feet and ending with the knees;
8.
While sleeping, use a cushion by placing your feet on it; use herbal baths of sage, eucalyptus, mint;
9.
If all the recommendations do not help and swelling of the legs becomes a constant phenomenon, and there is also an increase in temperature and hardness in the legs, then you should definitely consult a doctor;
10.
Do simple exercises. For example, walking on your toes for several minutes, squeezing and unclenching your toes, and so on.
Folk remedies for swelling of the legs
1.
A decoction of flax seeds for the treatment of swelling of the legs: four tablespoons of tea seeds and one liter of water are boiled for ten to fifteen minutes. After this, the pan is closed and placed in a warm place for just one hour. To make the taste more pleasant, add fruit or lemon juice. Drink hot every two hours, up to eight times a day, one-half glass. The duration of treatment is three weeks.
2.
In order to eliminate various swelling on the legs, parsley root and greens help very well. The parsley is thoroughly washed and passed through a meat grinder. A glass of the finished mass is placed in an enamel or glass container and poured with boiling water (two glasses). Then it is infused in a warm place for about nine hours. After this, the infusion is thoroughly filtered and lemon juice is added. Take one third of a glass for several days. Then - for three days and again continues for several days in a row.
3.
To treat swelling of the legs, Kalanchoe leaves (fresh) are broken and placed in a half-liter jar and filled with vodka. Infuses for two weeks. After which you can use it as a foot rub before bed.
4.
My legs are swollen, what should I do? Use a patch made from olive oil, wax, and water.
5.
The use of woodlice herb baths (the decoction is made very strong) to treat swelling of the legs.
Pathogenesis
Normally, the articular surfaces are smooth, elastic, slide smoothly relative to each other during movements and provide effective shock absorption under load. As a result of mechanical damage (trauma) or metabolic disorders, cartilage loses its smoothness, becomes rough and inelastic. Cartilage “rubs” during movements and injures each other, which leads to worsening pathological changes.
Due to insufficient depreciation, excess load is transferred to the underlying bone structure, and degenerative-dystrophic disorders also develop in it: the bone is deformed and grows along the edges of the articular area. Due to secondary trauma and disruption of the normal biomechanics of the joint, not only the cartilage and bone suffer, but also the surrounding tissues.
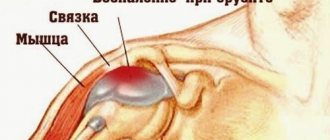
The joint capsule and synovial membrane thicken, and foci of fibrous degeneration form in the ligaments and periarticular muscles. The ability of the joint to participate in movements and withstand loads decreases. Instability occurs and pain progresses. In severe cases, the articular surfaces are destroyed, the supporting function of the limb is impaired, and movements become impossible.
Forecast
The prognosis for ankle arthritis is complex. Degenerative-dystrophic disorders cannot be “reversed” and articular cartilage restored to its previous state, but the pathological process can be slowed down, and with some effort, progression can be reduced to a minimum. This will require early intervention from doctors. Competent prescriptions will allow you to extend the “service life” of the ankle joint.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
2, total, today
( 60 votes, average: 4.40 out of 5)
Elbow bursitis: causes and signs, how to treat
Dislocated finger on the hand: symptoms of dislocation, what to do if it is dislocated
Related Posts
Reasons for the development of the disease
The ankle joint takes on a lot of load when moving. This joint is strong, but no less susceptible than others to the development of degenerative pathologies, such as arthrosis. The disease is characterized by deformation and destruction of cartilaginous structures, after which adjacent soft and bone tissues are affected. The course of the disease is chronic, accompanied by periods of remission and exacerbation.
In high-heeled shoes, the load on the joints is distributed unevenly.
Arthrosis of the ankle can occur on its own, without the influence of predisposing factors. In this case, the primary form is diagnosed. Deformation in secondary arthrosis is a consequence of the progression of other disorders of various etiologies in the body. In this case, the reasons may be:
- injury, dislocation, bruise and fracture of the ankle, foot or ankle;
- chronic ankle damage, for example, when a person constantly wears uncomfortable shoes;
- increased load on the lower limbs in obesity;
- complications after joint surgery;
- progression of systemic diseases such as diabetes, gout, rheumatoid arthritis;
- osteochondrosis and curvature of the spine;
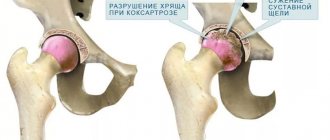
- coxarthrosis of the knee joint;
- specific infectious diseases - tuberculosis, gonorrhea, syphilis;
- genetic predisposition;
- unfavorable environmental conditions.
The causes of ankle arthritis are varied. Most often, the following factors contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- The presence of systemic pathologies;
- Metabolic disorders;
- Injuries received;
- Penetration of infection;
- Excess body weight, which causes the joint to be constantly overloaded;
- Hormonal imbalances;
- Irregularities in the functioning of the immune system;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Work associated with constant stress on the ankle;
- Having bad habits;
- Tendency to allergic reactions.
An infectious disease that triggers the development of arthritis can be present in the body for many years and not cause problems. However, if a pathological pathogen enters the joint cavity through the blood or lymph flow, an inflammatory process may begin.
People at risk of developing ankle arthritis are those who are exposed to the following factors:
- Frequent hypothermia;
- Menopause (menopause) in women;
- Excess weight;
- Wearing uncomfortable and unstable shoes;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- Flat feet.
The presence of several factors increases the risk of developing joint pathology. It is important to protect the ankle from injury and carry out timely treatment of any infectious diseases.
Causes of ankle arthritis
Mechanism of development and causes of pathology
Have you been trying to heal your JOINTS for many years?
Head of the Institute for the Treatment of Joints: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure your joints by taking the product every day for 147 rubles ...
Read more "
The disease begins with the fact that less synovial fluid is produced in the ankle joint, and the cartilage is less nourished and lubricated. At the same time, the joint gap becomes narrower, and the bones can grow together completely. Once crusarthrosis has begun, it is practically impossible to reverse it. However, treatment is necessary to slow its progression.
Arthrosis of the ankle joint is a degenerative inflammatory process. The pathology affects not only hard tissues, but also muscles, tendons, blood vessels, and nerves.
So, crusarthrosis of the ankle joint occurs due to the following reasons:
- Changes in joints and ligaments associated with age. That is, most often this disease is observed in people who have crossed the 60-year mark. If the patient did not have any health problems, the disease develops much more slowly. However, disability does not always appear.
- Severe obesity (grade 2-4). Excessive body weight negatively affects the ankle joints of the legs, so they wear out much faster. If the patient has been obese since childhood, then arthrosis of the ankle joint can appear as early as 20 years of age.
- High load on the ankle joint, which occurs as a result of sports training and hard work.
- Fractures of the ankle joint.
- Congenital foot deformity, as well as acquired flat feet.
- Genetic predisposition. People who have close relatives with the same pathology are at risk of developing arthrosis.
- Constantly wearing shoes with flat soles or stiletto heels.
- Uneven load on the joint due to improper resistance of the articular surfaces.
As for the mechanism of development of arthrosis, it is simple. With constant compression of the cartilage tissue, as well as due to changes in the chemical properties of the synovial fluid, the structure of the hard tissues is disrupted. That is, microscopic cracks appear in the cartilage, they become much thinner.
When small particles of cartilage break off, they can further injure the bone surfaces. This condition provokes an increase in the sensitivity of receptors in the joint, pain and other symptoms appear.
Main symptoms
Symptoms of ankle arthritis depend on the type of pathology and stage of development. In the acute course of the disease, the following symptoms occur:
- Sudden onset of illness;
- Rapid increase in painful symptoms;
- The occurrence of swelling;
- Redness of the skin around the joint;
- Increase in local temperature.
In chronic arthritis, the following symptoms occur:
- The joint becomes less mobile;
- The patient begins to suffer from pain;
- Pain increases at night;
- In the morning there is severe stiffness in movement.
In chronic forms of the pathology, there is no swelling or redness around the joint. Arthritis of the ankle joint can progress quickly. There are cases where complete destruction of cartilage tissue occurred within two years after the onset of the disease. With timely drug treatment, destructive processes slow down.
Regardless of the type of foot disease, the main symptoms of arthritis include the following:
- Pain;
- Edema;
- Limited movement;
- General weakness;
- Lethargy;
- Deterioration in health.
We invite you to read: X-ray of hip joints in children with dysplasia: norms of angles, description of the procedure
Arthritis of the ankle joint in children is characterized by similar symptoms. Children tolerate them less well and may express severe anxiety. If proper treatment is not carried out at an early age, the disease will end in disability.
Symptoms of ankle arthritis
Initially, rapid fatigue and mild pain in the ankle joint are detected after a significant load. Subsequently, the pain syndrome becomes more intense, its nature and time of occurrence change. Distinctive features of pain with arthrosis are:
- Starting pain. Appear after a state of rest, and then gradually disappear with movement.
- Dependence on load. There is increased pain during exercise (standing, walking) and rapid fatigue of the joint.
- Night pain. Usually appear in the morning.
The condition changes in waves, during exacerbations the symptoms are more pronounced, in the remission phase they first disappear, then become less intense. There is a gradual progression of symptoms over several years or decades. Along with pain, the following manifestations are determined:
- When moving, crunching, squeaking or clicking noises may occur.
- During an exacerbation, the periarticular area sometimes swells and turns red.
- Due to instability of the joint, the patient often twists his leg, causing sprains and tears in the ligaments.
- Stiffness and limitation of movements are noted.
Degenerative pathology occurs in 3 stages, at each of which the symptoms become more pronounced. Arthrosis of the 1st degree of the ankle joint is characterized by thinning of the cartilage fibers of the right or left joint, the patient is concerned about:
- increased fatigue after physical activity;
- stiffness of movement, especially in the morning after waking up;
- periodic pain in the lower leg, disappearing after rest and reduction of load.
If grade 2 arthrosis of the ankle joint begins to develop, the pathological process involves bone structures, on which the load has increased due to thinning of the cartilage. Bone growths-osteophytes form in the cavity of the joint space, which are clearly visible on x-rays. Due to injury to soft tissues, inflammation develops and the following symptoms appear:
- exacerbation of pain syndrome;
- restriction of joint functioning;
- crunching and clicking when moving;
- worsening of symptoms when the weather changes.
The last stages of the disease completely destroy the joint.
Deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint of the 3rd degree is characterized by thinning of the bone structures, due to which the limb is deformed and completely loses its functionality. The pathological process involves muscle fibers that become inflamed due to constant spasm necessary to keep the joint in the correct position. The last degree of arthrosis causes the following symptoms:
- unbearable pain that the usual painkillers cannot remove;
- narrowing of the joint space;
- complete or partial impairment of limb mobility;
- local temperature increase;
- crunching and clicking sounds while walking.
To cope with arthrosis, it is important to make a correct diagnosis as early as possible.
Here are the main symptoms that suggest that ankle arthrosis is developing:
- Constant pain during physical activity, as well as immediately after it.
- Stiffness of movements.
- Crunching sound when walking. Sometimes it seems that something clicks during movements.
- Swelling that occurs under the ankles.
- Due to the fact that a person begins to take care of the affected leg, weakness of the joints and ligaments occurs.
- Temporary stiffness of the joints during careless movements.
- At stage 2 arthrosis, joint deformation may begin.
The cause may be injury, overexertion, improper functioning of metabolic processes, inflammation, etc. Most often, the disease begins to manifest itself without any reason. The first sign is pain with any movement of the joints.
| First degree | Even with X-ray examination, no changes in the joints are still noticeable. However, slight morning stiffness is still present, although it passes quickly. Treatment needs to start now. |
| Second degree | Here the mobility of the limb is limited, a crunching sound is heard in the joint when moving, and there is slight swelling. X-rays already show a slight decrease in the interarticular space. The talus trochlea becomes flat. A person may experience lameness, and morning stiffness lasts longer. |
| Third degree | Crusarthrosis in this case manifests itself very clearly, and the deformation of the joints is clearly visible. At the same time, muscle atrophy is strong, there is a significant limitation of movements. The ankle joint almost always requires a state of rest, although even in this case there is pain. |
| Fourth degree | There is almost no joint space here, and mobility is greatly impaired. In the picture you can see strong growths of osteophytes. Treatment in this case can only be surgical. |
As you can see, ankle arthrosis develops gradually, so the patient has a chance to start treatment on time, which will slow down its progression.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of arthrosis vary depending on its type. In many cases, the affected joint will be painful and inflamed. Typically, pain develops gradually over time, although sudden onset is also possible.
Main symptoms
- Pain when moving.
- The appearance of sharp pain during physical activity.
- Pain when pressing on a joint.
- Swelling, increased body temperature and redness of soft tissues.
- Increased pain and swelling in the morning.
- Difficulty moving when walking.
Patient complaints may vary depending on the type and location of arthrosis. In general, patients with ankle arthritis will experience pain, stiffness, and soft tissue swelling.
Symptoms often worsen with exercise. It is important to determine the exact nature, location, duration and progression of symptoms in order to correctly diagnose the type of arthrosis and the nature of damage to joint tissues and bone.
Localization of the area of maximum discomfort can contribute to successful differentiation of the disease.
In the case of ankle arthrosis, pain is often felt in front of the joint. With subtalar arthritis, it is localized on the lateral side of the ankle.
Classification of arthritis
Periarthritis is a form of arthritis in which damage affects not only the joint itself, but also the periarticular tissues.
The cause of the gouty form of the disease is a metabolic disorder. Uric acid is deposited, which leads to inflammation and painful attacks.
Reactive arthritis occurs due to previous pathologies. The disease is a complication of another disease.
With arthrosis-arthritis, not only inflammatory processes occur in the joint. The cartilage that provides mobility to the joint is destroyed and in most cases cannot be restored.
Rheumatoid arthritis of the ankle has a systemic course. Complications can affect internal organs, and the patient’s well-being depends on the level of the immune system.
Purulent forms of arthritis do not occur often. They are characterized by the accumulation of purulent exudate directly in the joint cavity.
The acute course of the disease is characterized by a short duration of the disease with pronounced symptoms. Usually the stage of acute arthritis ends after 2 months.
They speak of a chronic course if the disease lasts more than 2 months. Periods of remission alternate with periods of exacerbation. For some time there may be no symptoms at all.
Acute and chronic forms of pathology
Physiotherapeutic procedures and massage
Physiotherapeutic procedures and massage are a mandatory element in the complex treatment of arthrosis. Quite often you can come across such a statement, despite the fact that in medical practice there is no consensus regarding the effectiveness of these treatment methods. However, magnetic therapy and electrophoresis with glucocorticoid paraffin enhance the effect of medications and are excellent for eliminating swelling and relieving inflammation in the foot. Magnetic therapy and electrophoresis are used in the remission phase of arthrosis processes. The positive effect obtained from these types of physiotherapeutic procedures can and should be consolidated during the period of spa treatment.
Massage is very beneficial for joints.
Another, no less effective method of treating arthrosis is massage, not only of the injured joint, but also of the foot, hip, and lower leg. Why is that? Strengthening the muscles of the lower leg and foot is the key to strengthening the entire ligamentous apparatus of the ankle joint. The massage is carried out in an upward direction, that is, first the massage movements are carried out on the toes, then on the foot itself, ankle joint, lower leg and thigh. Each massage session lasts 15-20 minutes. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. It is recommended to repeat the course 2-3 times.
Stages of the disease
The diagnosis of arthritis is made based on complaints and examination by the attending physician. However, a number of studies are being conducted to identify the causes of the disease.
- X-ray diagnostics. An X-ray picture can not only confirm the diagnosis, but also clarify the extent of the lesion. The image shows a narrowing of the joint space, thinning of the cartilage, destruction of bone tissue, the formation of pathological growths and salt deposition.
- An ultrasound of the joint allows you to assess the condition of the soft tissues, the amount of joint fluid and confirm or refute the presence of inflammation.
- Arthroscopy is an invasive procedure that can be performed both for the purpose of diagnosing the disease and treating it. An endoscope is inserted into the joint cavity through a small incision, allowing one to assess the condition of the joint from the inside and perform the necessary surgical procedures.
- Arthrography is an x-ray examination using a contrast agent injected into the joint cavity. The difference in contrast accumulation allows one to determine inflammation and other damage to joint components.
- MRI is the most accurate diagnostic method, allowing a thorough examination of the joint and adjacent tissues.
- A laboratory test, including a general and biochemical blood test, which allows you to determine the level of specific antibodies: C-reactive protein and some enzymes. This test can often pinpoint the cause of arthritis and establish a diagnosis.
We suggest you read: Recovery after a torn ankle ligament
Arthrosis is an inflammatory process that develops in articular cartilage. It causes pain in people and destroys joints. If the disease is started or treated incorrectly, it can lead to irreversible changes and even disability.
There are many joints in the musculoskeletal system that can be affected. Particularly common is arthrosis of the hip joints (coxarthrosis), as well as crusarthrosis or defarthrosis affecting the ankle.
Deforming arthrosis affects the lower extremities. It is the ankle joint that is the most mobile and performs the most important functions when walking. It carries the entire weight of the body, ensures its transfer from heel to toe, as well as the roll of the foot.
Arthrosis of the left or right ankle is characterized by several stages, which are usually distinguished by X-ray images.
Regarding arthrosis of the ankle joint of the 1st degree, it is possible to make a correct diagnosis only thanks to X-rays. There is almost no pain during this period, and if it does appear, it is mild. Often the patient attributes the pain to general weakness or a slight sprain. Swelling, which goes away quite quickly in the first stage of arthrosis, is attributed to problems with blood circulation or impaired kidney function.
Arthrosis of the ankle joint on x-ray
At the second stage of arthrosis, the cartilage tissue of the lower leg begins to gradually deteriorate. Bone tissue grows along the edges of deformed ankle joints. At this time, the joint space is already narrowed, which leads to regular and quite severe pain. Swelling at this time becomes permanent. In the morning it is difficult to get up on your leg, and there is a feeling of stiffness.
During the third and fourth degrees of arthrosis of the ankle joint, cartilage and bone tissue are destroyed. Because of this, the functioning of muscles and ligaments deteriorates, and the ankle joints become deformed. Pain also occurs at rest, and the patient’s ability to work decreases.
Causes
Main causes of the disease:
- Increased stress on the ankle.
- Obesity.
- Uneven distribution of loads when walking.
- Injuries: sprains, fractures, bruises.
- Old age (loss of elasticity and gradual degradation of joint tissues).
- Salt deposits.
- Difficult working conditions.
- Chronic diseases.
- Inflammatory processes.
- Heredity.
Prevention
Preventive measures include reducing the level of injuries, especially in winter, during periods of ice. If you are obese, it is necessary to take measures to reduce body weight to reduce the load on the joint. You should maintain a regime of moderate physical activity, avoid overloads and microtraumas, and promptly treat diseases that can trigger the development of arthrosis of the ankle joint.
It is impossible to completely cure arthrosis of the ankle joint. But if you strictly follow your doctor’s recommendations and monitor your health, you will be able to prolong the remission stage and avoid dangerous complications. Preventive procedures are simple: it is important to lead an active lifestyle, eat right, drink enough fluids, give up bad habits, and in case of exacerbation of symptoms, do not self-medicate, but promptly seek qualified medical help.
To protect yourself from arthrosis of the ankle joint, you should follow some rules and recommendations:
- proper nutrition;
- daily gymnastics for the ankle and knee joints;
- avoid hypothermia;
- reduce physical activity;
- choose the right shoes;
- control weight;
- visit a doctor periodically.
As for choosing the right shoes, it is important that when you walk in them, there is no pressure on your big toe; all your toes should serve as support.
{SOURCE}
Non-drug treatment
His methods are especially important for the treatment of post-traumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint, since the changes occurring in it differ from the classic manifestations of arthrosis and can be eliminated without the use of many medications.
Lifestyle change
An ankle affected by arthrosis is extremely vulnerable to injury, so the patient should choose only those types of activities and levels of stress that reduce the risk of injury to a minimum.
It is very important to use special insoles: they allow you to relieve the affected joint by cushioning the movements of the foot. They can be purchased at a pharmacy or orthopedic salon.
It is very important to use special insoles for shoes
Correction of the diet helps to enhance the effect of treatment. A diet for osteoarthritis includes the following:
- a large amount of fiber, as well as vitamin C and B vitamins found in vegetables, fruits and grains;
- the presence of phosphorus, which is found in sea fish;
- a sufficient amount of calcium, which is rich in dairy products;
- required amount of clean water.
Massage
Massage of the ankle joint for arthrosis has an additional role, but in practice the effect of its use exceeds expectations.
To relax tense muscles and improve local blood circulation, it is necessary to use gentle techniques:
- kneading;
- trituration;
- vibration;
- stroking.
Ankle massage for arthrosis
Massage courses are conducted by a specialist, but the patient can always perform massage movements at home on their own, since they are quite simple, and the area of influence - the ankle joint - is easily accessible. Massage can be performed using topical products or essential oils that have a relaxing effect, such as peppermint, pine needle, lavender or juniper essential oil.
Physiotherapy
For the treatment of arthrosis, methods are used that make it possible to more effectively achieve the goals of drug treatment.
- Electrophoresis. Drugs whose action is aimed at combating inflammation and pain are quickly and fully delivered to the joint due to thermal effects.
- Ultrasound methods. The special properties of ultrasound make it possible to perform micromassage and improve blood circulation in the damaged joint.
- Treatment with magnetic fields. The method helps eliminate inflammation, restore tissues and improve their nutrition.
- Radiation treatment. Physiotherapy is used only if there is no desired effect from using the methods listed above.
Physiotherapeutic methods can relieve pain
Physiotherapy for ankle arthrosis can be used during periods of exacerbations and remissions.
Important! Physiotherapy is prohibited for patients with contraindications, for example, with benign and malignant tumors.
What happens in the joint
If your leg hurts in the joint area, it can be difficult to understand what causes this phenomenon. It is worth considering the processes occurring inside the joint depending on the stage of development of the pathology. There are 4 stages in total:
- Collagen fibers grow inside. The process is stimulated by autoimmune disorders or age-related changes;
- Due to increasing pressure, tissue destruction accelerates. Rapid cell division promotes the formation of nodules;
- Osteophytes appear and friction between bones increases. Exudate accumulates, the joint begins to deform;
- The cartilage tissue is completely destroyed. The fusion of fibers and then bones begins. The patient becomes disabled.
It is impossible to accurately determine ankle arthritis and its stage with the naked eye. A number of diagnostic procedures are required.
Surgery
In case of large destruction of cartilage and deformation of bone tissue, conservative treatment may not give the expected effect, while ankle arthrosis can be cured surgically:
- Arthrodesis with preservation of the remnants of cartilage and artificial “closure” of the joint, that is, immobilization due to the removal of the ankle joint and fusion of the bones with each other. The work of the ankle is taken over by other joints and provides some mobility of the foot in relation to the lower leg.
The radiograph shows an arthrodesed ankle joint.
- Arthroplasty with joint preservation. Arthroscopy relieves the patient of pain by removing destroyed fragments of cartilage, bone spurs and other elements. The effect after surgery lasts for several years.
The photo shows an approach (incision) to the joint to remove destroyed elements of bone and cartilage tissue
- Endoprosthetics with complete replacement of a joint with a prosthesis made of metal, ceramics or plastic at 3-4 stages of the disease. The operation completely restores the mobility of the leg and ankle.
The photo on the left shows an endoprosthesis
Principles of treatment
It is impossible to cure ankle arthritis once and for all, either at home or in a hospital setting. All treatment methods are aimed at stopping the progression of the pathology and preserving your own cartilage tissue as much as possible.
Treatment of ankle arthritis with drugs includes the use of the following groups of drugs:
- Antibiotics – for infection and purulent forms of pathology;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - for severe pain and swelling, both ointments and tablets are used;
- Hormonal drugs for very pronounced pain syndrome;
- Vitamins for general strengthening of the body;
- Analgesics;
- Chondroprotectors for maintaining cartilage tissue.
Medicines for the treatment of ankle arthritis
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B45A1vlSjcQ
The ankle joint is constantly exposed to high loads. Therefore, just taking medications is not enough to improve your well-being. In addition to drug treatment, the following methods are used:
- Diet;
- Physical training;
- Massage;
- Physiotherapy;
- Folk methods.
In order for the medications used to be as effective as possible, it is important to follow a diet. Spices, smoked foods, fatty and fried foods should be excluded from the diet. You need to eat less salt and ensure adequate drinking regimen. You should avoid any foods that activate immune activity.
Physical education may include the following activities:
- Walking on your heels;
- Walking in socks;
- Rolling from heels to toes and vice versa;
- Jumping at low heights with tension in the calf muscles.
At first, it is better to conduct training with a medical professional. After improvements occur, classes continue at home.
It is better to massage daily. The goal of treatment is to improve blood circulation in the affected joint. You need to press gently so as not to cause pain.
Physiotherapy includes the following procedures:
- Warming up;
- Hydromassage;
- Ultrasound;
- Cryotherapy;
- Healing mud.
These treatments are used for both adults and children. It is important to choose shoes that will be stable and will not contribute to frequent dislocations.
Treatment of ankle arthritis with folk remedies is carried out along with drug therapy. Baths made from freshly cut spruce branches have a good effect. You can apply heated dry flax seeds - an excellent alternative to hospital warming.
Massage, exercise therapy and physiotherapy for ankle arthritis
Fast-acting drugs
Quick-acting medications are used to relieve pain in the ankle joint. In contrast, slow-acting drugs are used to prevent the progression of the disease.
Medicines that reduce pain in arthrosis deformans belong to the class of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, for example: ibuprofen, diclofenac, naproxen, aceclofenac, acetaminophen, nimesudide and other drugs. All of them relieve pain well, thereby easing the patient’s condition. But these remedies also have some disadvantages. Thus, non-steroidal drugs have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa, and it is possible that gastritis may develop due to them. In some cases, with long-term use of drugs, an ulcer may develop that is difficult to treat.
Thus, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can only be taken in short courses as prescribed by the attending physician. This recommendation should be followed by all people suffering from the disease, but especially the elderly and those who have diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
How is the disease diagnosed?
A rheumatologist who conducts an initial examination, palpation, and collects the necessary information will help diagnose arthrosis of the ankle joint. You can find out the final diagnosis using such instrumental diagnostic methods as:
- Radiography. The pictures will show a narrowing of the joint space, and the doctor will also notice a bone growth-osteophyte that has grown along the edges.
- CT or MRI. Prescribed when osteoarthritis develops in the later stages, and it is necessary to assess the degree of destruction of soft articular structures.
Treatment methods
Arthrosis of the ankle joint, like other localizations, requires complex, long-term and course treatment.
- Unloading the ankle joint during a period of severe exacerbation (walking with a cane on the side of the healthy limb), using a bandage;
- Elimination of shock loads (jumping, running), vibration, heavy lifting, long periods of standing;
- Body weight control;
- To give up smoking;
- Wearing a semi-rigid orthosis with concomitant joint instability;
- Physiotherapy (UHF, SMT, laser therapy, magnetic therapy);
- Drug therapy:
- NSAIDs externally, orally, by injection;
- glucocorticoids (kenalog, diprospan) together with anesthetics (lidocaine, novocaine) intra-articularly and periarticularly to relieve inflammation;
- vascular agents;
- muscle relaxants to eliminate spasm of muscle tissue;
- chondroprotectors - drugs administered intra-articularly (Alflutop) are more effective. If it is not possible to receive intra-articular injections, intramuscular administration (Alflutop, Chondroguard), or oral administration (Arthra, Structum) is indicated;
- hyaluronic acid preparations (Synvisc, Gilgan, Fermatron) to restore the quality of synovial fluid.
- Orthopedic insoles, wearing comfortable shoes with small heels;
- Gymnastics to strengthen the muscular-ligamentous apparatus. The suggested exercises should be performed daily:
- lying or sitting, bend and straighten your toes 10 times;
- lying or sitting, pull your feet towards you and away from you 10 times;
- turn your feet out and in 10 times;
- make circular movements with your feet clockwise and counterclockwise 10 times;
- sitting on a chair, place your feet on the floor with your toes and heels together, alternately move your legs forward and backward, repeat 15–20 times.
- Swimming, water aerobics;
- In the 3rd stage of arthrosis and the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment, endoprosthetics of the ankle joint or removal of the destroyed cartilage covering and joint capsule with its closure using a rod structure or an Ilizarov apparatus (arthrodesis) is indicated.
Treatment: general characteristics
Treatment objectives:
- Reducing pain -
- Removal of local inflammation -
- Regeneration of cartilage tissue -
- Restoration of motor activity -
- Improved metabolism.
All existing treatment methods can be classified as either conservative or surgical. Thus, conservative treatment is: 1) medications - 2) physiotherapeutic procedures - 3) physical therapy - 4) massage. Operative: 1) surgical intervention. Traditional medicine can also be used in the treatment of ankle arthrosis.
Symptoms
At the very beginning of the disease, a person may not feel any discomfort other than mild pain after physical activity. When the patient does not move, there are no signs of pain. The following phenomena may also be observed:
- crunching sound when moving (especially when twisting);
- fast fatiguability;
- muscle stiffness.
The progression of initially smoothed out unpleasant moments is characteristic of later stages of the disease. The pain haunts a person even at night, when the legs are resting and do not experience any stress. Gradually, the movements become less “amplitude”; sometimes complete immobility of the joint can be observed. Bandaging and the use of orthoses help for the normal functioning of the joint. Increase in size, swelling, externally noticeable changes in shape are characteristic symptoms for this type of disease. In addition to the crunching sound when walking, you can also hear other extraneous sounds - for example, clicking.
When the disease is in an advanced form, a person cannot begin to move until the diseased joint develops. The pain practically does not go away. Only painkillers help get rid of it.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is indicated for various types of arthrosis: post-traumatic, deforming arthrosis of the ankle joint. But it is especially significant in post-traumatic. Most ankle injuries result in it, but especially those that require immobilization with splints, plaster casts, and the Ilizarov apparatus. The main task of exercise therapy in this case is to restore lost muscle tone and restore motor activity. Initially, the load on the ankle joint during exercise therapy is minimal. Exercises are performed lying on your back: circular movements in the foot, adduction and abduction of the foot. Next, exercises are performed that are performed in a sitting position, without lifting the heels from the floor, for example, foot rolls and movements are performed. The most appropriate set of movements is developed by a physical therapy specialist.
Every person wants to be healthy for as long as possible. But, unfortunately, life is designed in such a way that over time all human organs wear out, and especially often the structures of the musculoskeletal system. It is they who bear the main load, because... Man is an upright creature. Joint degeneration is one of the pressing problems of older people. Arthrosis of the ankle joint occurs after overcoming the forty-year mark in ten cases out of a hundred.
Symptoms of the disease
The main symptoms of arthrosis include:
- pain that intensifies with exercise;
- crunching in joints, clicks, creaking;
- “starting pain,” that is, occurring at the beginning of movement after a long or short state of rest;
- limited mobility or stiffness during movements;
- curvature of the tibia axis (it can take on an X- or O-shape);
- frequent subluxations;
- atrophy of the muscles that are adjacent to the injured ones;
- swelling of the joints;
- feet may be hot.
Discomfort with this disease Post-traumatic arthrosis of the ankle joint is also characterized by rapid fatigue and pain during physical activity.